Cell-Based Sensors for the Detection of EGF and EGF-Stimulated Ca2+ Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Microscopic Imaging Apparatus
2.2. Plasmid Construction
2.3. Live Cell Imaging for EGF and Ca2+ Sensing
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
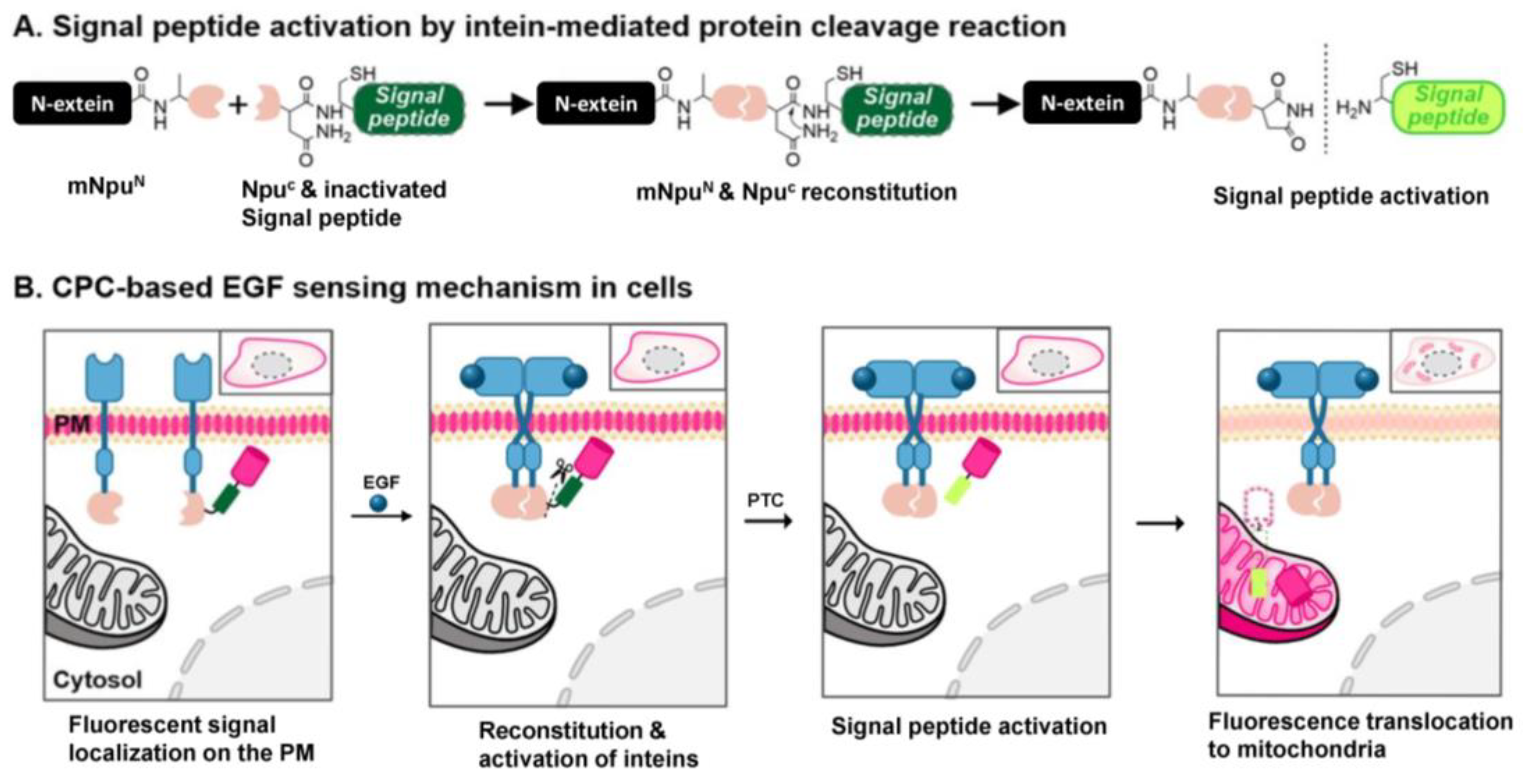
3.1. The Design and Construction of Sensor Proteins for Detecting Ligand-Induced EGFR Dimerization
3.2. Generation and Evaluation of the EGF-Detecting Sensor Cells
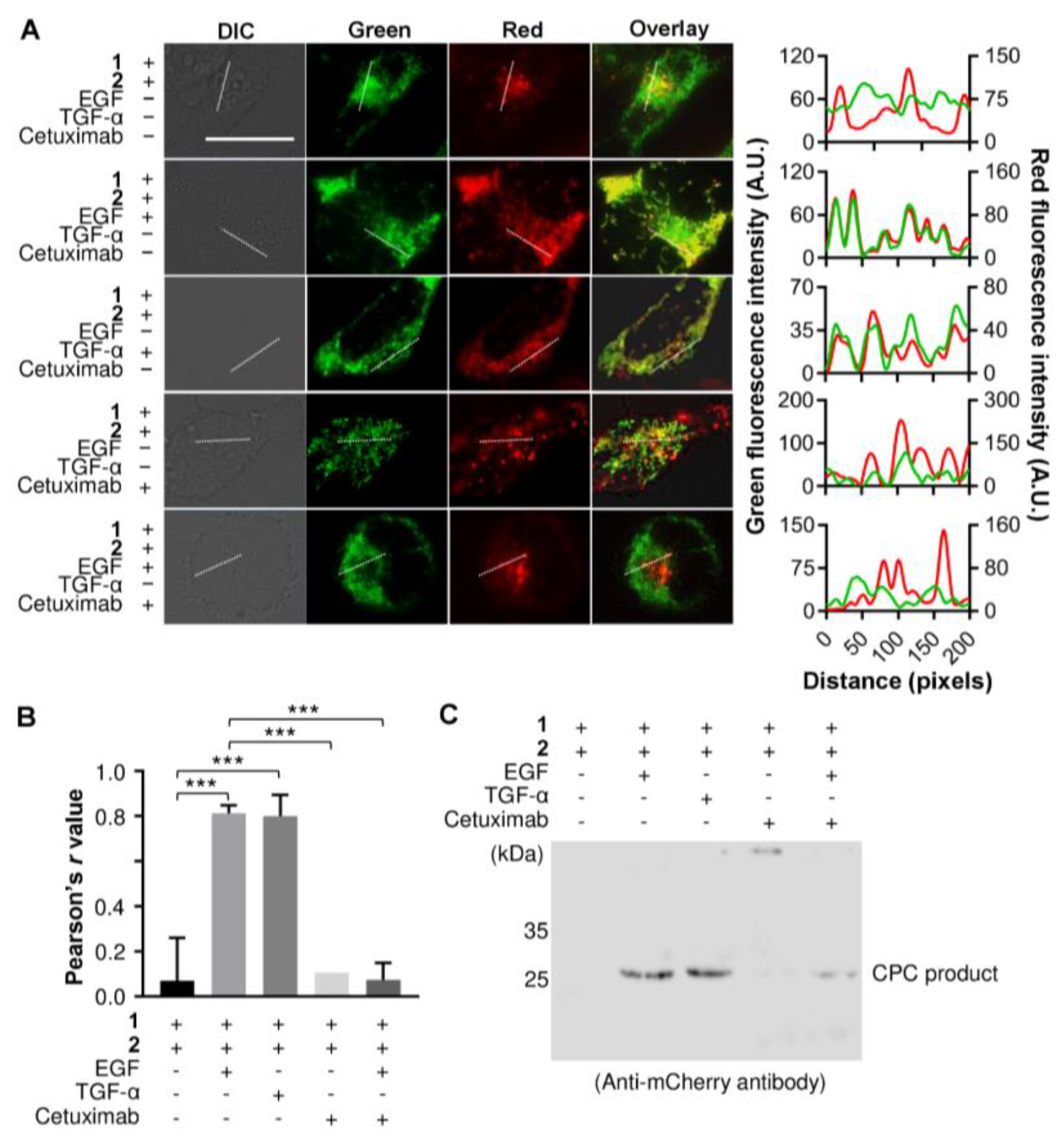
3.3. Detecting an Agonist and Antagonist of EGFR Using the Genetically Encoded EGF Sensor Cells
3.4. Monitoring Ca2+ Signaling Induced by EGF Stimuli
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jura, N.; Zhang, X.; Endres, N.F.; Seeliger, M.A.; Schindler, T.; Kuriyan, J. Catalytic control in the EGF receptor and its connection to general kinase regulatory mechanisms. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor cell proliferation signaling pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higashiyama, S.; Iwabuki, H.; Morimoto, C.; Hieda, M.; Inoue, H.; Matsushita, N. Membrane-anchored growth factors, the epidermal growth factor family: Beyond receptor ligands. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.; Hung, M. Nuclear EGFR signalling network in cancers: Linking EGFR pathway to cell cycle progression, nitric oxide pathway and patient survival. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Hajjo, R.; Sweidan, K. Review on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) structure, signaling pathways, interactions, and recent updates of EGFR inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Hiroki, K.; Yamashita, Y. The role of epidermal growth factor receptor in cancer metastasis and microenvironment. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 546318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tokunaga, A.; Onda, M.; Okuda, T.; Teramoto, T.; Fujita, I.; Mizutani, T.; Kiyama, T.; Yoshiyuki, T.; Nishi, K.; Matsukura, N. Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor (EGF), EGF receptor, and c-erbB-2 in human gastric cancer. Cancer 1995, 75, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Brown, B.P.; Kim, S.; Ferguson, D.; Pavlick, D.C.; Jayakumaran, G.; Benayed, R.; Gallant, J.N.; Zhang, Y.K.; Yan, Y.; et al. Structure–function analysis of oncogenic EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication reveals insights into activation and a potential approach for therapeutic targeting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, H.K.; Ku, M.; Yang, J. Beyond EGFR inhibition: Multilateral combat strategies to stop the progression of head and neck cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uribe, M.L.; Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. EGFR in cancer: Signaling mechanisms, drugs, and acquired resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Avanzato, D.; Lanzetti, L. Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seshacharyulu, P.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Haridas, D.; Jain, M.; Ganti, A.K.; Batra, S.K. Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karimzadeh, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N. Bio-assay: The best alternative for conventional methods in detection of epidermal growth factor. Int. J. Bio. Macromol. 2019, 133, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.T.; Lin, W.C.; Chang, K.C.; Huang, J.Y.; Yen, K.C.; Young, I.C.; Sun, Y.J.; Lin, F.H. Quantitative analysis of ligand-EGFR interactions: A platform for screening targeting molecules. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiroshima, M.; Saeki, Y.; Okada-Hatakeyama, M.; Sako, Y. Dynamically varying interactions between heregulin and ErbB proteins detected by single-molecule analysis in living cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13984–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawashima, N.; Nakayama, K.; Itoh, K.; Itoh, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Biju, V. Reversible dimerization of EGFR revealed by single-molecule fluorescence imaging using quantum dots. Eur. J. Chem. 2010, 16, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.E.; Roberts, S.K.; Needham, S.R.; Tynan, C.J.; Rolfe, D.J.; Winn, M.D.; Clarke, D.T.; Barraclough, R.; Martin-Fernandez, M.L. Single-molecule imaging and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy show different structures for high-and low-affinity epidermal growth factor receptors in A431 cells. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 803–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teramura, Y.; Ichinose, J.; Takagi, H.; Nishida, K.; Yanagida, T.; Sako, Y. Single-molecule analysis of epidermal growth factor binding on the surface of living cells. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4215–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.; Yan, F.; Yu, J.; Chan, H.L.; Yang, M. The application of organic electrochemical transistors in cell-based biosensors. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3655–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Xu, G.; Qin, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Cell-based biosensors and its application in biomedicine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, C.; Cai, H.; Hu, N.; Zhou, J.; Wang, P. Cell-based biosensors and their application in biomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 6423–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojo, H.; Igawa, K.; Ohba, S.; Yano, F.; Nakajima, K.; Komiyama, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Lichtler, A.C.; Woo, J.-T.; Yonezawa, T. Development of high-throughput screening system for osteogenic drugs using a cell-based sensor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 376, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Kim, S.; Lee, E.; Ryu, J.; Lee, M.; Kwon, Y. Genetically Encoded Sensor Cells for the Screening of Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) Effectors in Herbal Extracts. Biosensors 2021, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daringer, N.M.; Dudek, R.M.; Schwarz, K.A.; Leonard, J.N. Modular extracellular sensor architecture for engineering mammalian cell-based devices. ACS Synth. Biol. 2014, 3, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuno, H.; Sakurai, T.; Namiki, S.; Mitsuhashi, H.; Kanzaki, R. Novel cell-based odorant sensor elements based on insect odorant receptors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiseh, M.; Veiseh, O.; Martin, M.C.; Bertozzi, C.; Zhang, M. Single-cell-based sensors and synchrotron FTIR spectroscopy: A hybrid system towards bacterial detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, K.E.; Kim, Y.; Huh, W.K.; Park, H.O. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) analysis: Advances and recent applications for genome-wide interaction studies. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 2039–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senarisoy, M.; Barette, C.; Lacroix, F.; De Bonis, S.; Stelter, M.; Hans, F.; Kleman, J.P.; Fauvarque, M.O.; Timmins, J. Forster Resonance Energy Transfer Based Biosensor for Targeting the hNTH1–YB1 Interface as a Potential Anticancer Drug Target. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frommer, W.B.; Davidson, M.W.; Campbell, R.E. Genetically encoded biosensors based on engineered fluorescent proteins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellón-Echeverría, I.; Carralot, J.P.; Del Rosario, A.A.; Kueng, S.; Mauser, H.; Schmid, G.; Thoma, R.; Berger, I. MultiBacMam Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) tool-kit identifies new small-molecule inhibitors of the CDK5-p25 protein-protein interaction (PPI). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Nakata, E.; Hamachi, I. Recent progress in strategies for the creation of protein-based fluorescent biosensors. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 2560–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.E.; Cui, Z.; Wang, D. Sensing of biomolecular interactions using fluorescence complementing systems in living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerppola, T.K. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) analysis as a probe of protein interactions in living cells. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2008, 37, 465–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerppola, T.K. Design and implementation of bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays for the visualization of protein interactions in living cells. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zadran, S.; Standley, S.; Wong, K.; Otiniano, E.; Amighi, A.; Baudry, M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based biosensors: Visualizing cellular dynamics and bioenergetics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piston, D.W.; Kremers, G.J. Fluorescent protein FRET: The good, the bad and the ugly. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Taylor, S.S.; Tsien, R.Y. Genetically encoded reporters of protein kinase A activity reveal impact of substrate tethering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14997–15002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leavesley, S.J.; Rich, T.C. Overcoming limitations of FRET measurements. Cytom. J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2016, 89, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, H.; Lee, E.; Kim, D.; Lee, M.; Ryu, J.; Kang, C.; Kim, S.; Kwon, Y. Cell-based biosensors based on intein-mediated protein engineering for detection of biologically active signaling molecules. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9779–9786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Jeon, H.; Ryu, J.; Kang, C.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Kwon, Y. Genetically encoded biosensors for the detection of rapamycin: Toward the screening of agonists and antagonists. Analyst 2020, 145, 5571–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Lee, E.; Kang, C.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Lee, D.; Kwon, Y. Rapid screening of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) effectors using cortisol-detecting sensor cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Shrestha, K.L.; Kwon, S.; Park, S.; Kim, J.; Kwon, Y. Intein-Mediated Protein Engineering for Cell-Based Biosensors. Biosensors 2022, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.; Jung, D.; Jung, Y.J.; Jeoung, E.; Kwon, Y. Site-specific and effective immobilization of proteins by Npu DnaE split-intein mediated protein trans-splicing reaction. BioChip J. 2013, 7, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Sato, K.; Min, K.; Shigenaga, A.; Jung, J.; Otaka, A.; Kwon, Y. Photo-triggered fluorescent labelling of recombinant proteins in live cells. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9670–9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Lee, M.; Jang, W.; Kwon, Y. Intein-mediated Protein Engineering for Biosensor Fabrication. BioChip J. 2016, 10, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, G. Signals guiding proteins to their correct locations in mitochondria. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 165, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeepLoc-2.0. Available online: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?DeepLoc-2.0 (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Bitler, B.G.; Goverdhan, A.; Schroeder, J.A. MUC1 regulates nuclear localization and function of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.H.; Wu, C.C.; Huang, K.Y.; Chuang, W.Y.; Hsueh, C.; Li, H.J.; Chen, C.Y. Profiling of subcellular EGFR interactome reveals hnRNP A3 modulates nuclear EGFR localization. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Electrochemical immunosensor for detection of epidermal growth factor reaching lower detection limit: Toward oxidized glutathione as a more efficient blocking reagent for the antibody functionalized silver nanoparticles and antigen interaction. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8047–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Seo, C.; Ji, M.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.D.; Jeong, D.H.; Lee, W.; Paik, M.J. Monitoring of Epidermal Growth Factor Degradation Products by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2018, 39, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayego-Mateos, S.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.; Morgado-Pascual, J.L.; Valentijn, F.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Goldschmeding, R.; Ruiz-Ortega, M. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and its ligands in kidney inflammation and damage. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 8739473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yogev, O.; Pines, O. Dual targeting of mitochondrial proteins: Mechanism, regulation and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedl, J.; Knopp, M.R.; Groh, C.; Paz, E.; Gould, S.B.; Herrmann, J.M.; Boos, F. More than just a ticket canceller: The mitochondrial processing peptidase tailors complex precursor proteins at internal cleavage sites. Mol. Biol. Cell 2020, 31, 2657–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loza, J.; Carpio, L.; Lawless, G.; Marzec, N.; Dziak, R. Role of extracellular calcium influx in EGF-induced osteoblastic cell proliferation. Bone 1995, 16, S341–S347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, E.; Shrestha, K.L.; Kang, S.; Ramakrishnan, N.; Kwon, Y. Cell-Based Sensors for the Detection of EGF and EGF-Stimulated Ca2+ Signaling. Biosensors 2023, 13, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030383
Lee E, Shrestha KL, Kang S, Ramakrishnan N, Kwon Y. Cell-Based Sensors for the Detection of EGF and EGF-Stimulated Ca2+ Signaling. Biosensors. 2023; 13(3):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030383
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Euiyeon, Keshab Lal Shrestha, Seonhye Kang, Neethu Ramakrishnan, and Youngeun Kwon. 2023. "Cell-Based Sensors for the Detection of EGF and EGF-Stimulated Ca2+ Signaling" Biosensors 13, no. 3: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030383
APA StyleLee, E., Shrestha, K. L., Kang, S., Ramakrishnan, N., & Kwon, Y. (2023). Cell-Based Sensors for the Detection of EGF and EGF-Stimulated Ca2+ Signaling. Biosensors, 13(3), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030383




