MICaFVi: A Novel Magnetic Immuno-Capture Flow Virometry Nano-Based Diagnostic Tool for Detection of Coronaviruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3. Flow Cytometry Analysis and Gating Strategy
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Synthesis of Spike-Protein-Functionalized Virus-Mimicking Silica Particles (VM-SPs)
2.6. Synthesis of Anti-Spike Antibody-Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles (AS-MNPs)
3. The Results and Discussion
3.1. MICaFVi Basic Principle
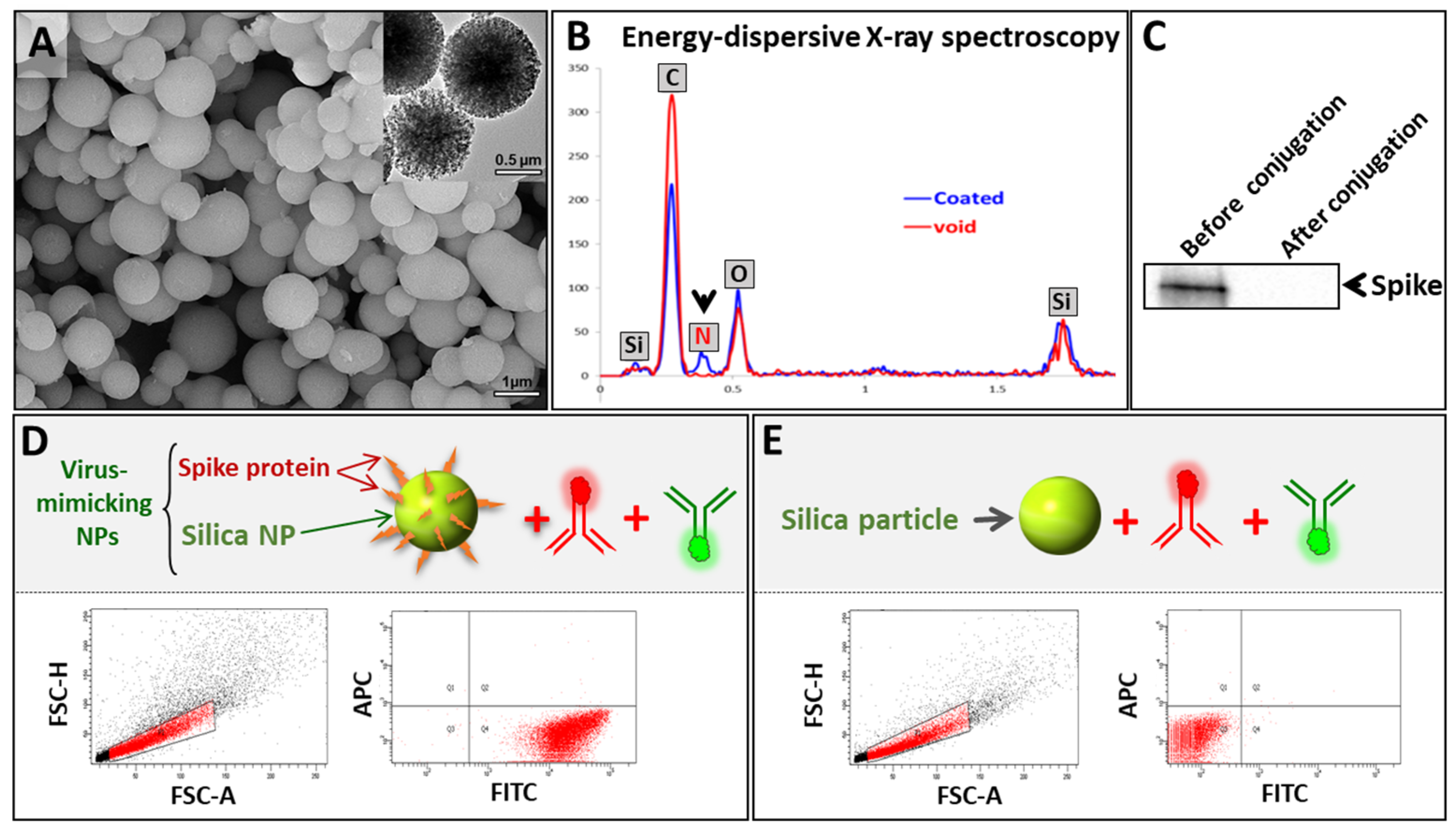
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of VM-SPs
3.3. Synthesis and Characterization of AS-MNPs
3.4. Optimization of MICaFVi
3.5. MICaFVi Detection of MERS-CoV Pseudoviral Particles (MERSpp)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, C.C.; Shih, T.P.; Ko, W.C.; Tang, H.J.; Hsueh, P.R. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): The epidemic and the challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostovtsev, V.V.; Green, L.G.; Fokin, V.V.; Sharpless, B. A Stepwise Huisgen Cycloaddition Process: Copper(I)-Catalyzed Regioselective Ligation of Azides and Terminal Alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 41, 2708–2711. [Google Scholar]
- Talic, S.; Shah, S.; Wild, H.; Gasevic, D.; Maharaj, A.; Ademi, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, W.; Mesa-Eguiagaray, I.; Rostron, J.; et al. Effectiveness of public health measures in reducing the incidence of COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and COVID-19 mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2021, 375, e068302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, A.A.T.; Fatima, K.; Mohammad, T.; Fatima, U.; Singh, I.K.; Singh, A.; Atif, S.M.; Hariprasad, G.; Hasan, G.M.; Hassan, M.I. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 genome, structure, evolution, pathogenesis and therapies: Structural genomics approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Al-Ahmed, S.H.; Haque, S.; Sah, R.; Tiwari, R.; Malik, Y.S.; Dhama, K.; Yatoo, M.I.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-COV: A comparative overview. Le Infez. Med. 2020, 28, 174–184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Fang, Z.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y. An updated review of SARS-CoV-2 detection methods in the context of a novel coronavirus pandemic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, V.; Negro, A.; Pirotti, T.; Trenti, T. Estimate false-negative RT-PCR rates for SARS-CoV-2. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucirka, L.M.; Lauer, S.A.; Laeyendecker, O.; Boon, D.; Lessler, J. Variation in False-Negative Rate of Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based SARS-CoV-2 Tests by Time Since Exposure. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanji, J.N.; Zelyas, N.; MacDonald, C.; Pabbaraju, K.; Khan, M.N.; Prasad, A.; Hu, J.; Diggle, M.; Berenger, B.M.; Tipples, G. False negative rate of COVID-19 PCR testing: A discordant testing analysis. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Duong Bang, D.; Wolff, A. 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Paving the Road for Rapid Detection and Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Micromachines 2020, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Greenblatt, M.; Ziegler, M.J.; Bromberg, V.; Huang, E.; Abdallah, H.; Tolomeo, P.; Lautenbach, E.; Glaser, L.; Kelly, B.J. Impact of Nasopharyngeal Specimen Quality on SARS-CoV-2 Test Sensitivity. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz Gulec, E.; Cesur, N.P.; Yesilyurt Fazlioğlu, G.; Kazezoğlu, C. Effect of different storage conditions on COVID-19 RT-PCR results. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6575–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pas, S.D.; Patel, P.; Reusken, C.; Domingo, C.; Corman, V.M.; Drosten, C.; Dijkman, R.; Thiel, V.; Nowotny, N.; Koopmans, M.P. First international external quality assessment of molecular diagnostics for Mers-CoV. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 69, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hao, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, R.; Lin, G.; Jia, T.; Zhang, D.; Chang, L.; Xie, J.; Li, J. External quality assessment for the molecular detection of MERS-CoV in China. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 75, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosten, C.; Seilmaier, M.; Corman, V.M.; Hartmann, W.; Scheible, G.; Sack, S.; Guggemos, W.; Kallies, R.; Muth, D.; Junglen, S. Clinical features and virological analysis of a case of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poissy, J.; Goffard, A.; Parmentier-Decrucq, E.; Favory, R.; Kauv, M.; Kipnis, E.; Mathieu, D.; Guery, B.; The, M. Kinetics and pattern of viral excretion in biological specimens of two MERS-CoV cases. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly-Cirino, C.; Mazzola, L.T.; Chua, A.; Oxenford, C.J.; Van Kerkhove, M.D. An updated roadmap for MERS-CoV research and product development: Focus on diagnostics. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4 (Suppl. S2), e001105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.X.; Liew, W.P.P.; Ong, H.K.; Yong, C.Y.; Shit, C.S.; Ho, W.Y.; Ng, S.Y.L.; Yeap, S.K. Current diagnostic approaches to detect two important betacoronaviruses: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 225, 153565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, Q.; Inchakalody, V.P.; Merhi, M.; Mestiri, S.; Taib, N.; Moustafa Abo El-Ella, D.; Bedhiafi, T.; Raza, A.; Al-Zaidan, L.; Mohsen, M.O.; et al. Emerging COVID-19 variants and their impact on SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, therapeutics and vaccines. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzada, M.; Altintas, Z. Nanomaterials for virus sensing and tracking. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5805–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun-Ur-Rashid, M.; Foyez, T.; Jahan, I.; Pal, K.; Imran, A.B. Rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 via nano-biosensor-implemented biomedical utilization: A systematic review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 9445–9465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, N.; Anik, M.I.; Hossain, M.K.; Khan, M.I.; Uddin, S.; Ashrafuzzaman, M.; Rahaman, M.M. Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Platforms to Combat COVID-19: Diagnostics, Preventions, Therapeutics, and Vaccine Developments. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 2431–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, A.; Mishra, A.; Bisht, H.; Tripathi, R.M. Nanomaterial Based Biosensors for Detection of Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2: A Review. J. Anal. Test. 2021, 5, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yu, W.; Sabet, K.A.; Bogumil, M.; Zhao, Y.; Hambalek, J.; Lin, S.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Garner, O.; Di Carlo, D.; et al. Ferrobotic swarms enable accessible and adaptable automated viral testing. Nature 2022, 611, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, P.L.; Yin, Y.; Lee, D.; Ko, S.H. Advancement in COVID-19 detection using nanomaterial-based biosensors. Exploration 2023, 3, 20210232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadrami, H.A.; Suaifan, G.; Zourob, M.M. A Portable Nanoprobe for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 S1 Protein. Biosensors 2022, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chugh, V.K.; Krishna, V.D.; di Girolamo, A.; Wang, Y.A.; Saha, R.; Liang, S.; Cheeran, M.C.J.; Wang, J.-P. One-Step, Wash-free, Nanoparticle Clustering-Based Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy Bioassay Method for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Nucleocapsid Proteins in the Liquid Phase. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 44136–44146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Qiao, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, K.Y.; et al. Structural and Functional Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry by Using Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904.e899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaeen, G.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Yousefinejad, S. Application of nanomaterials in treatment, anti-infection and detection of coronaviruses. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as drug carriers: Preparation, conjugation and delivery. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 929–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Saha, R.; Su, D.; Krishna, V.D.; Liu, J.; Cheeran, M.C.J.; Wang, J.-P. Magnetic-Nanosensor-Based Virus and Pathogen Detection Strategies before and during COVID-19. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 9560–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Rösch, E.L.; Viereck, T.; Schilling, M.; Ludwig, F. Toward Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 with Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Chugh, V.K.; Krishna, V.D.; Wang, Y.A.; Gordon, T.D.; Cheeran, M.C.J.; Wang, J.-P. Five-Minute Magnetic Nanoparticle Spectroscopy-Based Bioassay for Ultrafast Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 17503–17507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, G.; Lee, G.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, S.-H.; Choi, M.; Ku, K.B.; Lee, C.-S.; Jun, S.; Park, D.; Kim, H.G.; et al. Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Causative Virus (SARS-CoV-2) in Human Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens Using Field-Effect Transistor-Based Biosensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C.; Hsu, W.; Wang, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Fang, J.-M. Rapid and specific influenza virus detection by functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and mass spectrometry. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschmann, J.; Voepel, N.; Voß, L.; Rasche, S.; Schubert, M.; Kleines, M.; Krause, H.J.; Shaw, T.M.; Spiegel, H.; Schroeper, F. Development of Fast and Portable Frequency Magnetic Mixing-Based Serological SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody Detection Assay. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 643275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, F.; Xie, W.; Zhou, T.C.; OuYang, J.; Jin, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.; et al. Ultrasensitive supersandwich-type electrochemical sensor for SARS-CoV-2 from the infected COVID-19 patients using a smartphone. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 128899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Drelich, A.J.; Hopkins, C.M.; Mecozzi, S.; Li, L.; Kwon, G.; Hong, S. Gold nanoparticles in virus detection: Recent advances and potential considerations for SARS-CoV-2 testing development. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 14, e1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.N.; Richards, S.J.; Guy, C.S.; Congdon, T.R.; Hasan, M.; Zwetsloot, A.J.; Gallo, A.; Lewandowski, J.R.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Straube, A.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Binds Sialic Acids and Enables Rapid Detection in a Lateral Flow Point of Care Diagnostic Device. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasaud, A.; Alharbi, N.K.; Hashem, A.M. Generation of MERS-CoV Pseudotyped Viral Particles for the Evaluation of Neutralizing Antibodies in Mammalian Sera. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2099, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Ali, R.; Al-Zahrani, H.; Trivilegio, T.; Alanazi, A.H.; Khan, A.L.; Boudjelal, M.; AlKushi, A. Preparation of iron oxide mesoporous magnetic microparticles as novel multidrug carriers for synergistic anticancer therapy and deep tumor penetration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Yang, L.; Kuang, M.; Duan, H.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, H.; Wang, A. Antibody conjugated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for cancer cell separation in fresh whole blood. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9758–9765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.Y.; Ong, H.K.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, K.L.; Tan, W.S. Recent Advances in the Vaccine Development against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, L.; Li, F.; Jiang, S. MERS-CoV spike protein: A key target for antivirals. Expert Opin. Targets 2017, 21, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, S.; Vijay, R. Middle East respiratory syndrome vaccines. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 47, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Dominguez, S.R.; Holmes, K.V. Role of the spike glycoprotein of human Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in virus entry and syncytia formation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samman, N.; El-Boubbou, K.; Al-Muhalhil, K.; Ali, R.; Alaskar, A.; Alharbi, N.K.; Nehdi, A. MICaFVi: A Novel Magnetic Immuno-Capture Flow Virometry Nano-Based Diagnostic Tool for Detection of Coronaviruses. Biosensors 2023, 13, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050553
Samman N, El-Boubbou K, Al-Muhalhil K, Ali R, Alaskar A, Alharbi NK, Nehdi A. MICaFVi: A Novel Magnetic Immuno-Capture Flow Virometry Nano-Based Diagnostic Tool for Detection of Coronaviruses. Biosensors. 2023; 13(5):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050553
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamman, Nosaibah, Kheireddine El-Boubbou, Khawlah Al-Muhalhil, Rizwan Ali, Ahmed Alaskar, Naif Khalaf Alharbi, and Atef Nehdi. 2023. "MICaFVi: A Novel Magnetic Immuno-Capture Flow Virometry Nano-Based Diagnostic Tool for Detection of Coronaviruses" Biosensors 13, no. 5: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050553
APA StyleSamman, N., El-Boubbou, K., Al-Muhalhil, K., Ali, R., Alaskar, A., Alharbi, N. K., & Nehdi, A. (2023). MICaFVi: A Novel Magnetic Immuno-Capture Flow Virometry Nano-Based Diagnostic Tool for Detection of Coronaviruses. Biosensors, 13(5), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13050553






