Development and In-House Validation of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and a Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Dosage of Tenofovir in Human Saliva
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Competitive ELISA (cELISA) for TFV in Buffer
2.2. Development and Analytical Validation of the cELISA in Saliva
2.3. Monoclonal Antibody Labeling with Gold Nanoparticles
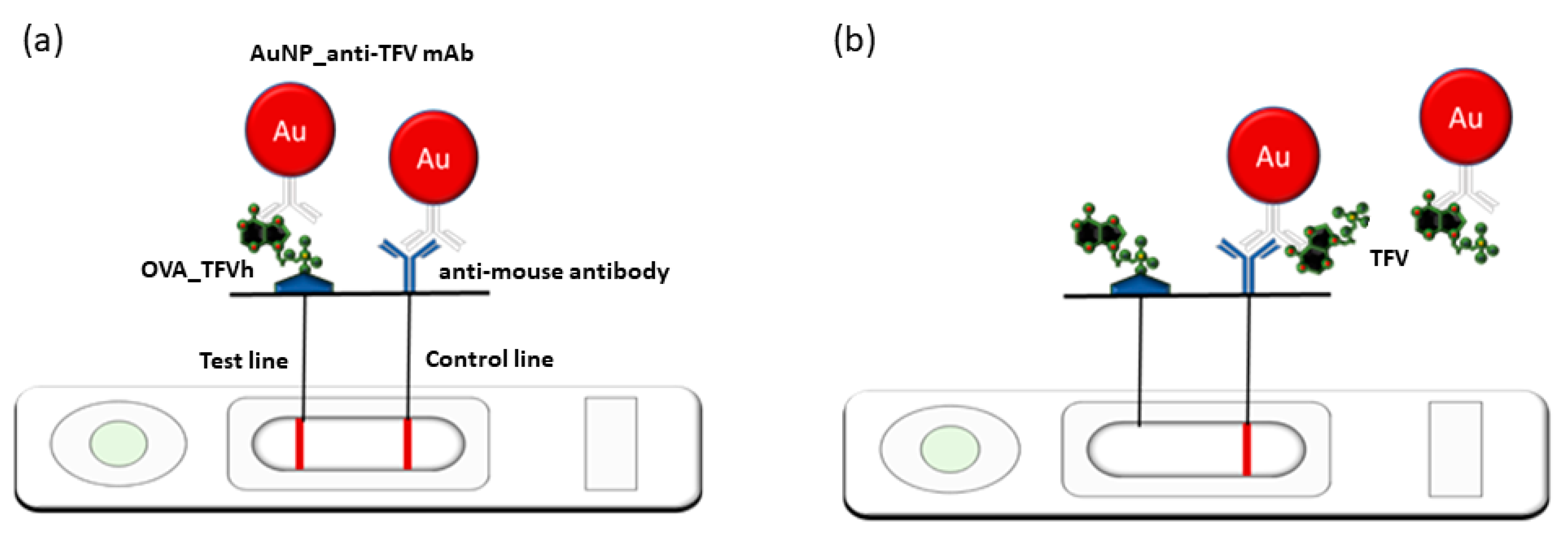
2.4. The LFIA Strip Preparation
2.5. The LFIA Test Procedure
2.6. Saliva Samples
3. Results and Discussion
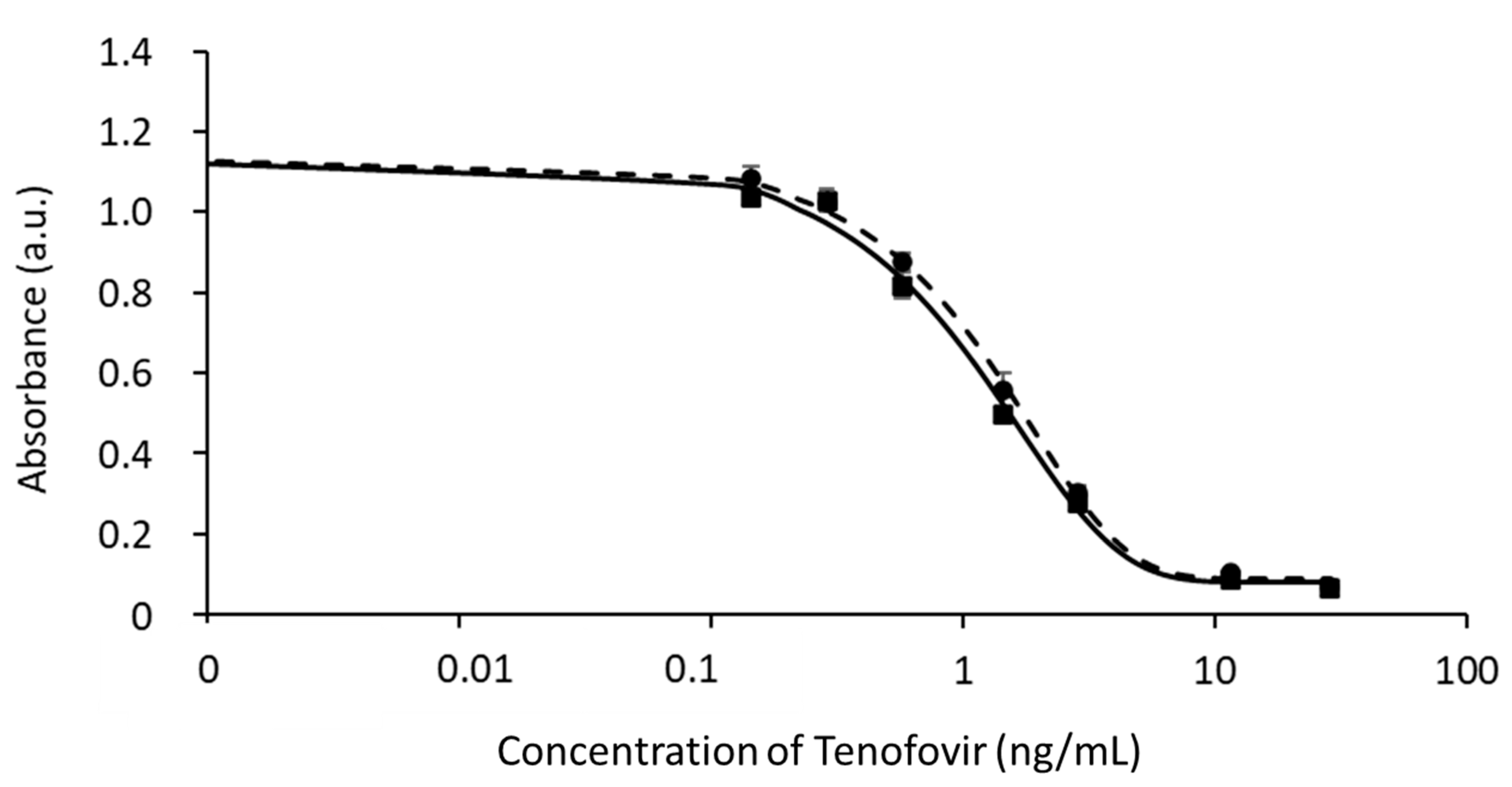
3.1. Development of the cELISA for TFV in Buffer
3.2. Application of the cELISA to Saliva
3.3. Analytical Validation of the cELISA Method for TFV in Saliva
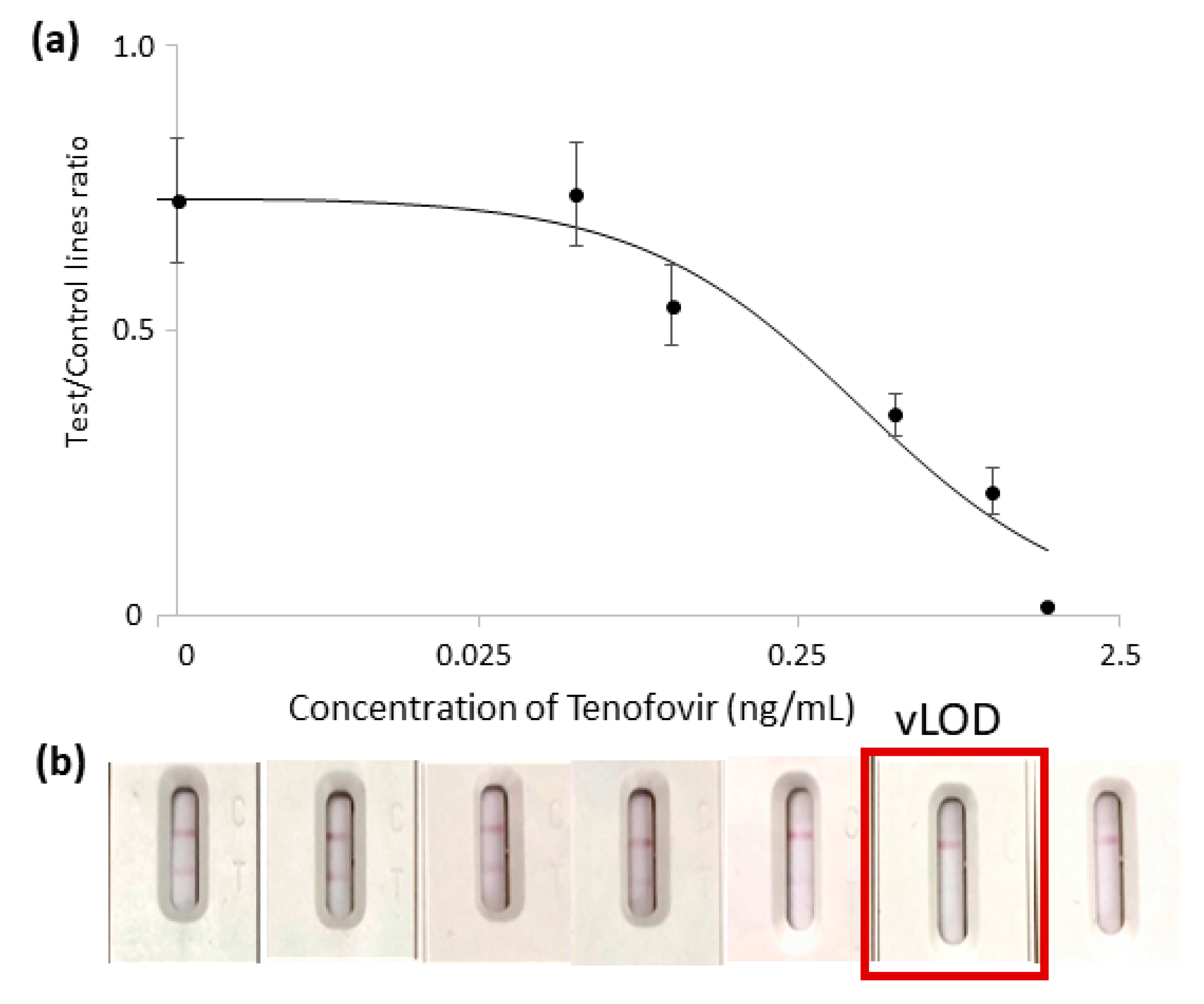
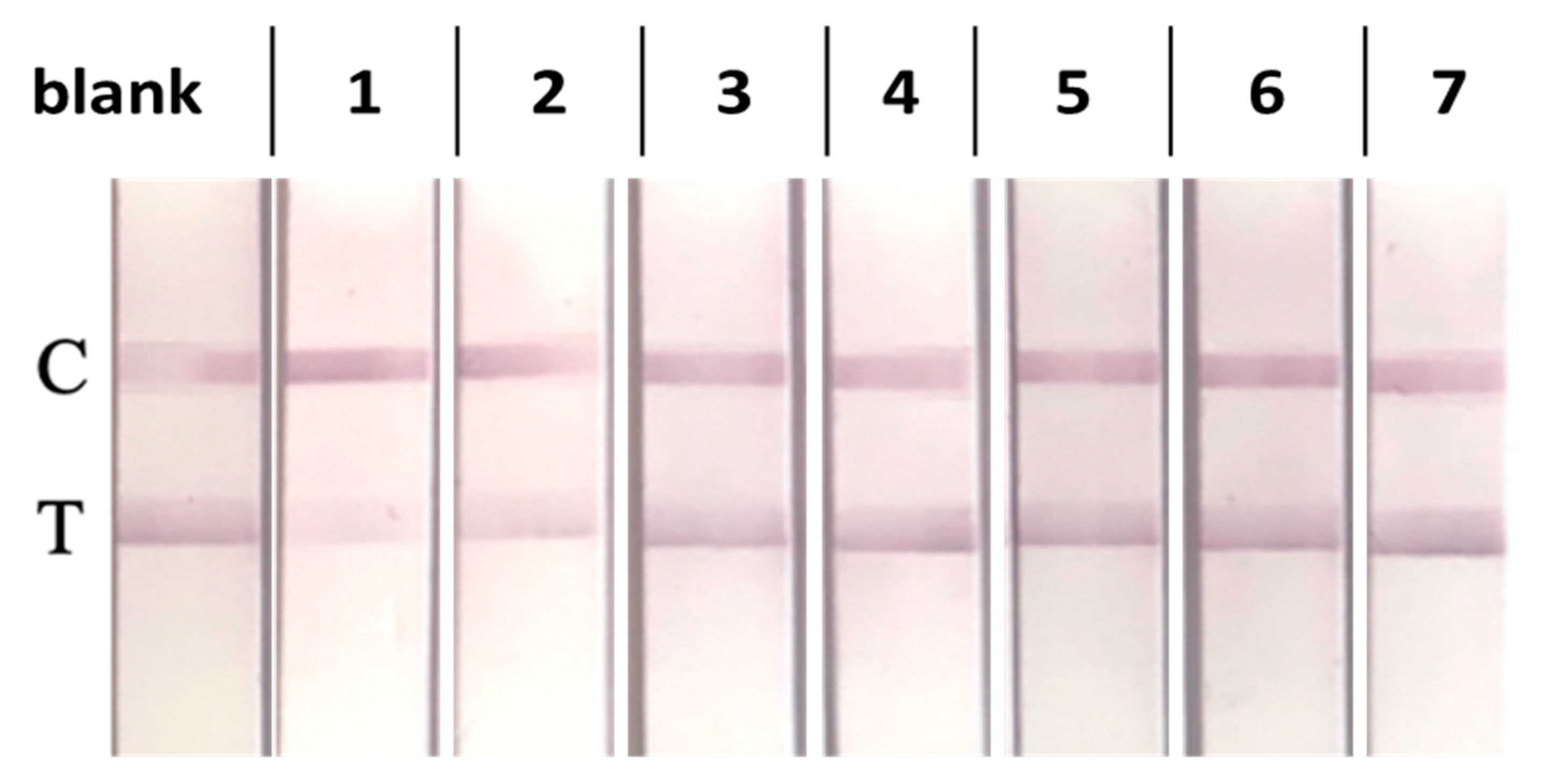
3.4. Development of an LFIA for Detecting TFV in Saliva
3.5. Selectivity of the LFIA in Saliva
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kearney, B.P.; Flaherty, J.F.; Shah, J. Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Clinical Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, R.; Carey, I.; Agarwal, K. Tenofovir alafenamide in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus: Rationale and clinical trial evidence. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1756284818786108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruane, P.J.; DeJesus, E.; Berger, D.; Markowitz, M.; Bredeek, U.F.; Callebaut, C.; Zhong, L.; Ramanathan, S.; Rhee, M.S.; Fordyce, M.W.; et al. Antiviral Activity, Safety, and Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics of Tenofovir Alafenamide as 10-Day Monotherapy in HIV-1–Positive Adults. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2013, 63, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Günthard, H.F.; Saag, M.S.; Benson, C.A.; Del Rio, C.; Eron, J.J.; Gallant, J.E.; Hoy, J.; Mugavero, M.J.; Sax, P.E.; Thompson, M.A.; et al. Antiretroviral Drugs for Treatment and Prevention of HIV Infection in Adults: 2016 Recommendations of the International Antiviral Society–USA Panel. JAMA 2016, 316, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tessema, B.; Biadglegne, F.; Mulu, A.; Getachew, A.; Emmrich, F.; Sack, U. Magnitude and determinants of nonadherence and nonreadiness to highly active antiretroviral therapy among people living with HIV/AIDS in Northwest Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. AIDS Res. Ther. 2010, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawana, T.D.; Nhachi, C.F.B.; Nathoo, K.; Ngara, B.; Okochi, H.; Louie, A.; Kuncze, K.; Katzenstein, D.; Metcalfe, J.; Gandhi, M.; et al. Brief Report: Ritonavir Concentrations in Hair Predict Virologic Outcomes in HIV-Infected Adolescents with Virologic Failure on Atazanavir-Based or Ritonavir-Based Second-Line Treatment. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2021, 88, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wyl, V.; Klimkait, T.; Yerly, S.; Nicca, D.; Furrer, H.; Cavassini, M.; Calmy, A.; Bernasconi, E.; Böni, J.; Aubert, V.; et al. Adherence as a Predictor of the Development of Class-Specific Resistance Mutations: The Swiss HIV Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcellin, F.; Spire, B.; Carrieri, M.P.; Roux, P. Assessing adherence to antiretroviral therapy in randomized HIV clinical trials: A review of currently used methods. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuny, C.; Deyà-Martínez, Á.; Chiappini, E.; Galli, L.; de Martino, M.; Noguera-Julian, A. Metabolic and Renal Adverse Effects of Antiretroviral Therapy in HIV-infected Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, S36–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werb, D.; Mills, E.J.; Montaner, J.S.; Wood, E. Risk of Resistance to Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy among HIV-Positive Injecting Drug Users: A Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezabhe, W.M.; Chalmers, L.; Bereznicki, L.R.; Peterson, G.M. Adherence to Antiretroviral Therapy and Virologic Failure. Medicine 2016, 95, e3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, E.; Park, B.-J.; Bang, J.H.; Lee, J.Y. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy and factors affecting low medication adherence among incident HIV-infected individuals during 2009–2016: A nationwide study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gengiah, T.N.; Moosa, A.; Naidoo, A.; Mansoor, L.E. Adherence Challenges with Drugs for Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis to Prevent HIV Infection; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 36, pp. 70–85. [Google Scholar]
- Iacob, S.A.; Iacob, D.G.; Jugulete, G. Improving the Adherence to Antiretroviral Therapy, a Difficult but Essential Task for a Successful HIV Treatment—Clinical Points of View and Practical Considerations. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nardo, F.; Chiarello, M.; Cavalera, S.; Baggiani, C.; Anfossi, L. Ten Years of Lateral Flow Immunoassay Technique Applications: Trends, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Sensors 2021, 21, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zaman, M.H. Low-cost tools for diagnosing and monitoring HIV infection in low-resource settings. Bull. World Health Organ. 2012, 90, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, F.; Baggiani, C.; Giovannoli, C.; Spano, G.; Anfossi, L. Multicolor immunochromatographic strip test based on gold nanoparticles for the determination of aflatoxin B1 and fumonisins. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, K.H. Lateral Flow Immunoassay; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2015; Volume 1318, pp. 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Drain, P.K.; Kubiak, R.W.; Siriprakaisil, O.; Klinbuayaem, V.; Quame-Amaglo, J.; Sukrakanchana, P.-O.; Tanasri, S.; Punyati, P.; Sirirungsi, W.; Cressey, R.; et al. Urine Tenofovir Concentrations Correlate with Plasma and Relate to Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Adherence: A Randomized, Directly Observed Pharmacokinetic Trial (TARGET Study). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonsart, J.; Saragosti, S.; Taouk, M.; Peytavin, G.; Bushman, L.; Charreau, I.; Hance, A.; Goldwirt, L.; Morel, S.; Mammano, F.; et al. Single-dose pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral tenofovir and emtricitabine in blood, saliva and rectal tissue: A sub-study of the ANRS IPERGAY trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 72, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalera, S.; Agulló, C.; Mercader, J.V.; Di Nardo, F.; Chiarello, M.; Anfossi, L.; Baggiani, C.; D’Avolio, A.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Abad-Fuentes, A. Monoclonal Antibodies with Subnanomolar Affinity to Tenofovir for Monitoring Adherence to Antiretroviral Therapies: From Hapten Synthesis to Prototype Development. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10439–10449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, D. Immunoassay for Beginners. In The Immunoassay Handbook. Theory and Applications of Ligand Binding, ELISA and Related Techniques; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Software. Available online: http://gruppochemiometria.it/index.php/software (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Cox, K.L.; Devanarayan, V.; Kriauciunas, A.; Manetta, J.; Montrose, C.; Sittampalam, S. Immunoassay Methods. In Assay Guidance Manual [Internet]; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; Bethesda: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22553884/ (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Di Nardo, F.; Cavalera, S.; Baggiani, C.; Chiarello, M.; Pazzi, M.; Anfossi, L.; Nardo, F.D.; Cavalera, S.; Baggiani, C.; Chiarello, M.; et al. Enzyme Immunoassay for Measuring Aflatoxin B1 in Legal Cannabis. Toxins 2020, 12, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capodicasa, C.; Bastiani, E.; Serra, T.; Anfossi, L.; Catellani, M. Design of a Diagnostic Immunoassay for Aflatoxin M1 Based on a Plant-Produced Antibody. Toxins 2022, 14, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimling, J.; Maier, M.; Okenve, B.; Kotaidis, V.; Ballot, H.; Plech, A. Turkevich Method for Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis Revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15700–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalera, S.; Pezzoni, G.; Grazioli, S.; Brocchi, E.; Baselli, S.; Lelli, D.; Colitti, B.; Serra, T.; Di Nardo, F.; Chiarello, M.; et al. Investigation of the “Antigen Hook Effect” in Lateral Flow Sandwich Immunoassay: The Case of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochańska, B.; Smoleński, R.T.; Knap, N. Determination of adenine nucleotides and their metabolites in human saliva. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2000, 47, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bill, C.; Danielson, J.A.; Jones, R.S. Salivary intercellular adenosine triphosphate testing in primary caretakers: An examination of statistical significance versus diagnostic predictability. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2017, 3, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, S.P.; Williamson, R.T. A review of saliva: Normal composition, flow, and function. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.; Wild, D. Calibration Curve Fitting. In The Immunoassay Handbook; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 323–336. ISBN 9780080970370. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, C.P.; Semenova, V.A.; Elie, C.M.; Romero-Steiner, S.; Greene, C.; Li, H.; Stamey, K.; Steward-Clark, E.; Schmidt, D.S.; Mothershed, E.; et al. Specific, Sensitive, and Quantitative Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Human Immunoglobulin G Antibodies to Anthrax Toxin Protective Antigen. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, N.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, X.; Liang, G.; Han, Z.; Meng, H. A novel and sensitive chemiluminescence immunoassay based on AuNCs@pepsin@luminol for simultaneous detection of tetrabromobisphenol A bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ether and tetrabromobisphenol A mono(hydroxyethyl) ether. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1035, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Ling, S.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S. The Preparation and Identification of a Monoclonal Antibody against Domoic Acid and Establishment of Detection by Indirect Competitive ELISA. Toxins 2017, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, D.; Mitchell, R.A. How to Obtain Reproducible Quantitative ELISA Results; Oxford Biomedical Research Inc.: Oxford, MI, USA, 1997; pp. 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Reimer, G.J.; Gee, S.J.; Hammock, B.D. Comparison of a Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunoassay and an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Analysis of Atrazine in Water. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3353–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, S.; Ge, D.; Zhu, N.; Wang, K.; Zhu, G.; Xu, W.; Xu, H. An ultrasensitive competitive immunosensor using silica nanoparticles as an enzyme carrier for simultaneous impedimetric detection of tetrabromobisphenol A bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ether and tetrabromobisphenol A mono(hydroxyethyl) ether. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byzova, N.A.; Safenkova, I.V.; Slutskaya, E.S.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Less is More: A Comparison of Antibody–Gold Nanoparticle Conjugates of Different Ratios. Bioconjugate Chem. 2017, 28, 2737–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safenkova, I.; Zherdev, A.; Dzantiev, B. Factors influencing the detection limit of the lateral-flow sandwich immunoassay: A case study with potato virus X. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lastours, V.; Fonsart, J.; Burlacu, R.; Gourmel, B.; Molina, J.-M. Concentrations of Tenofovir and Emtricitabine in Saliva: Implications for Preexposure Prophylaxis of Oral HIV Acquisition. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4905–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anfossi, L.; Di Nardo, F.; Profiti, M.; Nogarol, C.; Cavalera, S.; Baggiani, C.; Giovannoli, C.; Spano, G.; Ferroglio, E.; Mignone, W.; et al. A versatile and sensitive lateral flow immunoassay for the rapid diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4123–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loynachan, C.N.; Thomas, M.R.; Gray, E.R.; Richards, D.A.; Kim, J.; Miller, B.S.; Brookes, J.C.; Agarwal, S.; Chudasama, V.; McKendry, R.A.; et al. Platinum Nanocatalyst Amplification: Redefining the Gold Standard for Lateral Flow Immunoassays with Ultrabroad Dynamic Range. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, E.; Takagi, R.; Sudo, K.; Kato, S. Determination of abacavir, tenofovir, darunavir, and raltegravir in human plasma and saliva using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 114, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| TFV Added (ng/mL) | TFV Mean Concentration ± SD a (ng/mL) | Mean Recovery ± SD a (%) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.3 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 73.4 ± 0.6 | 8.2 |
| 2.7 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 106.8 ± 11.9 | 11.1 |
| 5.4 | 7.2 ± 0.6 | 133.6 ± 11.1 | 8.3 |
| TFV (ng/mL) a | Intra-Assay (%), n = 4 | Inter-Assay (%) n = 3 | Accuracy (Mean n = 4 × 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 28.7 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 85.8 |
| 11.5 | 9.6 | 4.2 | 120.3 |
| 2.9 | 13.4 | 3.5 | 99.0 |
| 1.4 | 24.0 | 3.1 | 96.7 |
| 0.6 | 49.6 | 11.6 | 106.4 |
| 0.3 | 63.4 | 28.2 | 111.2 |
| 0.1 | 75.5 | 17.0 | 145.6 |
| Compound | CR% |
|---|---|
| TDF | 0.8% |
| TAF | 0.1% |
| DTG | <0.003% |
| EVG | <0.003% |
| ATP | <0.03% |
| Adenine | <0.03% |
| Caffeine | <0.03% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavalera, S.; Serra, T.; Abad-Fuentes, A.; Mercader, J.V.; Abad-Somovilla, A.; Nardo, F.D.; D’Avolio, A.; De Nicolò, A.; Testa, V.; Chiarello, M.; et al. Development and In-House Validation of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and a Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Dosage of Tenofovir in Human Saliva. Biosensors 2023, 13, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060667
Cavalera S, Serra T, Abad-Fuentes A, Mercader JV, Abad-Somovilla A, Nardo FD, D’Avolio A, De Nicolò A, Testa V, Chiarello M, et al. Development and In-House Validation of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and a Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Dosage of Tenofovir in Human Saliva. Biosensors. 2023; 13(6):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060667
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavalera, Simone, Thea Serra, Antonio Abad-Fuentes, Josep V. Mercader, Antonio Abad-Somovilla, Fabio Di Nardo, Antonio D’Avolio, Amedeo De Nicolò, Valentina Testa, Matteo Chiarello, and et al. 2023. "Development and In-House Validation of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and a Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Dosage of Tenofovir in Human Saliva" Biosensors 13, no. 6: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060667
APA StyleCavalera, S., Serra, T., Abad-Fuentes, A., Mercader, J. V., Abad-Somovilla, A., Nardo, F. D., D’Avolio, A., De Nicolò, A., Testa, V., Chiarello, M., Baggiani, C., & Anfossi, L. (2023). Development and In-House Validation of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and a Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Dosage of Tenofovir in Human Saliva. Biosensors, 13(6), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13060667









