A Novel Acetone Sensor for Body Fluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
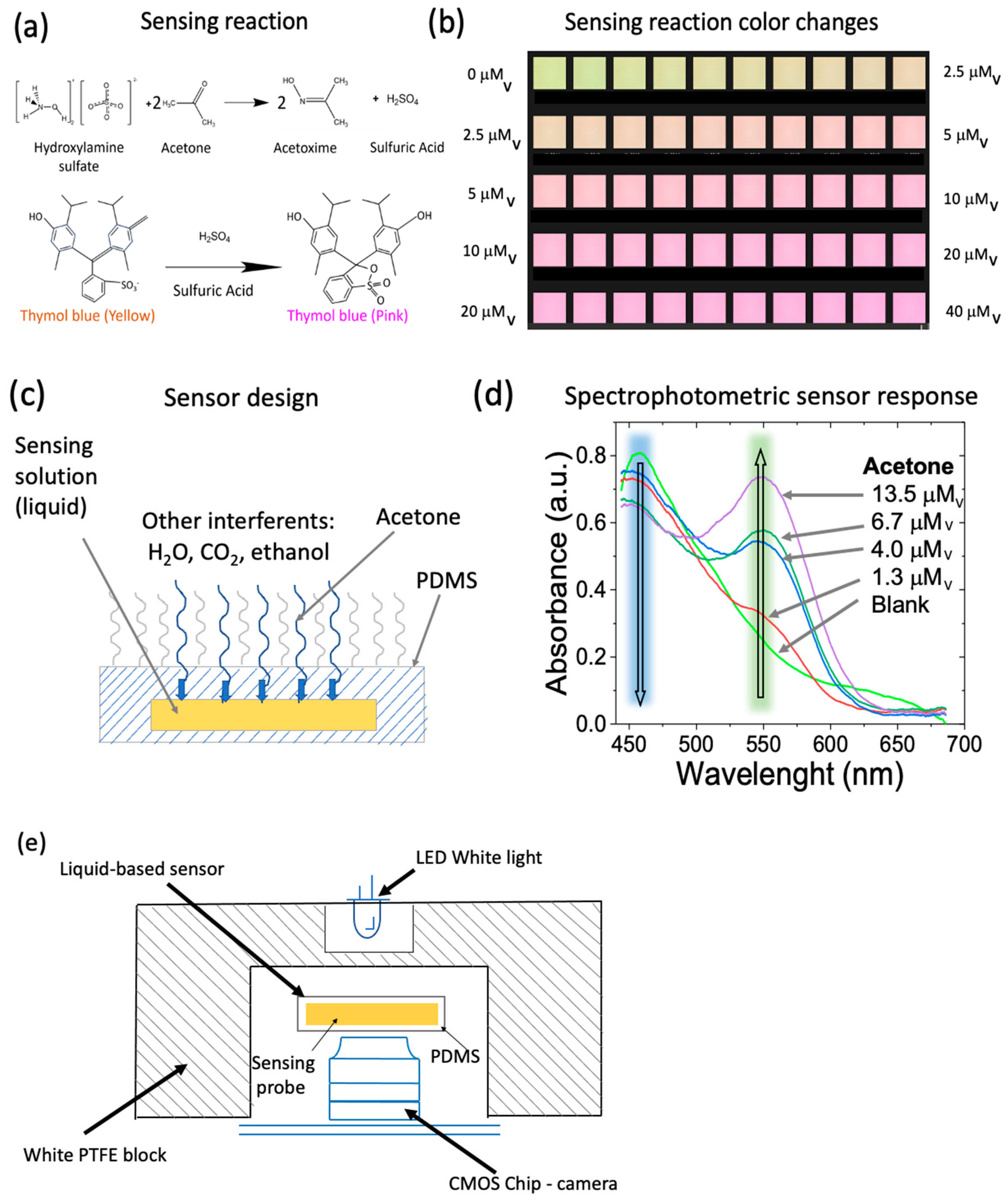
2.1. Sensing Technique
2.2. Sensor Design and Detection Device
2.3. Sample Handling
2.4. Human Subjects
2.4.1. Breath Ketone Measurements
2.4.2. Standard Blood Ketone Measurements
3. Results
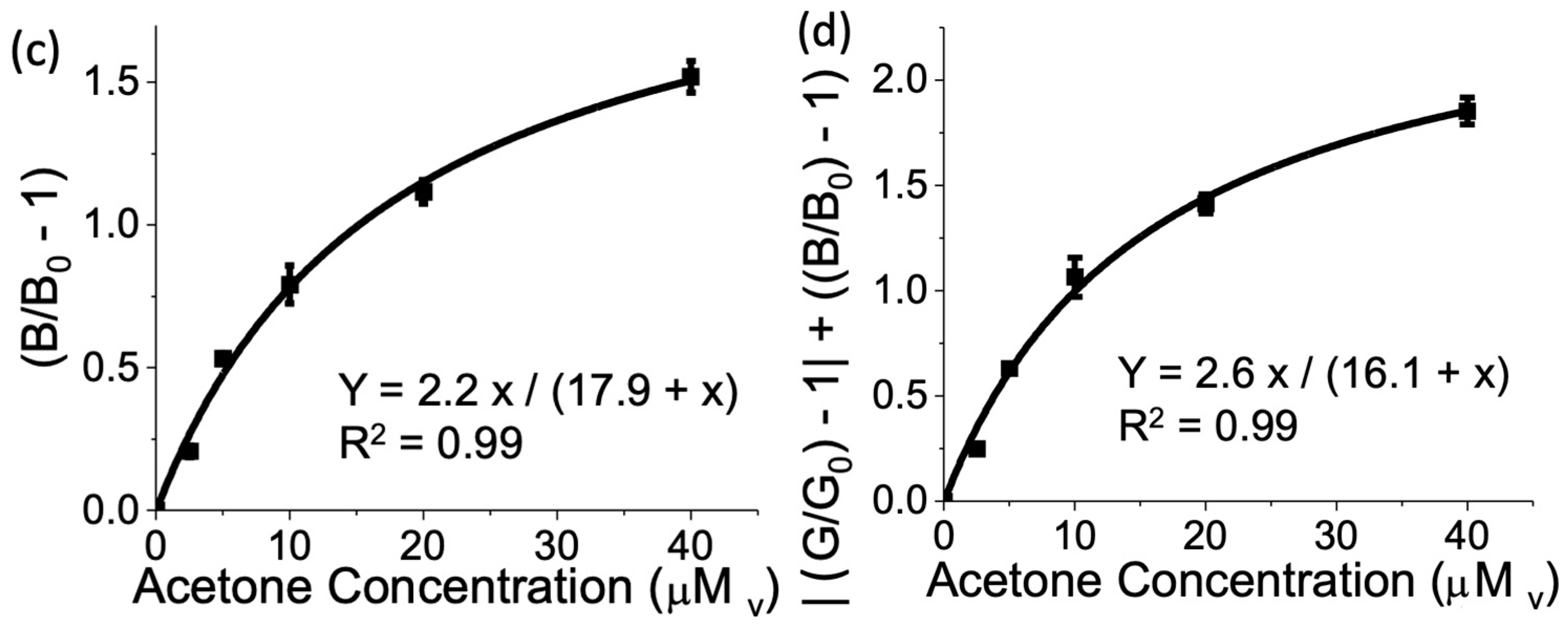
3.1. Sensor Calibration
3.2. Sensor Reproducibility
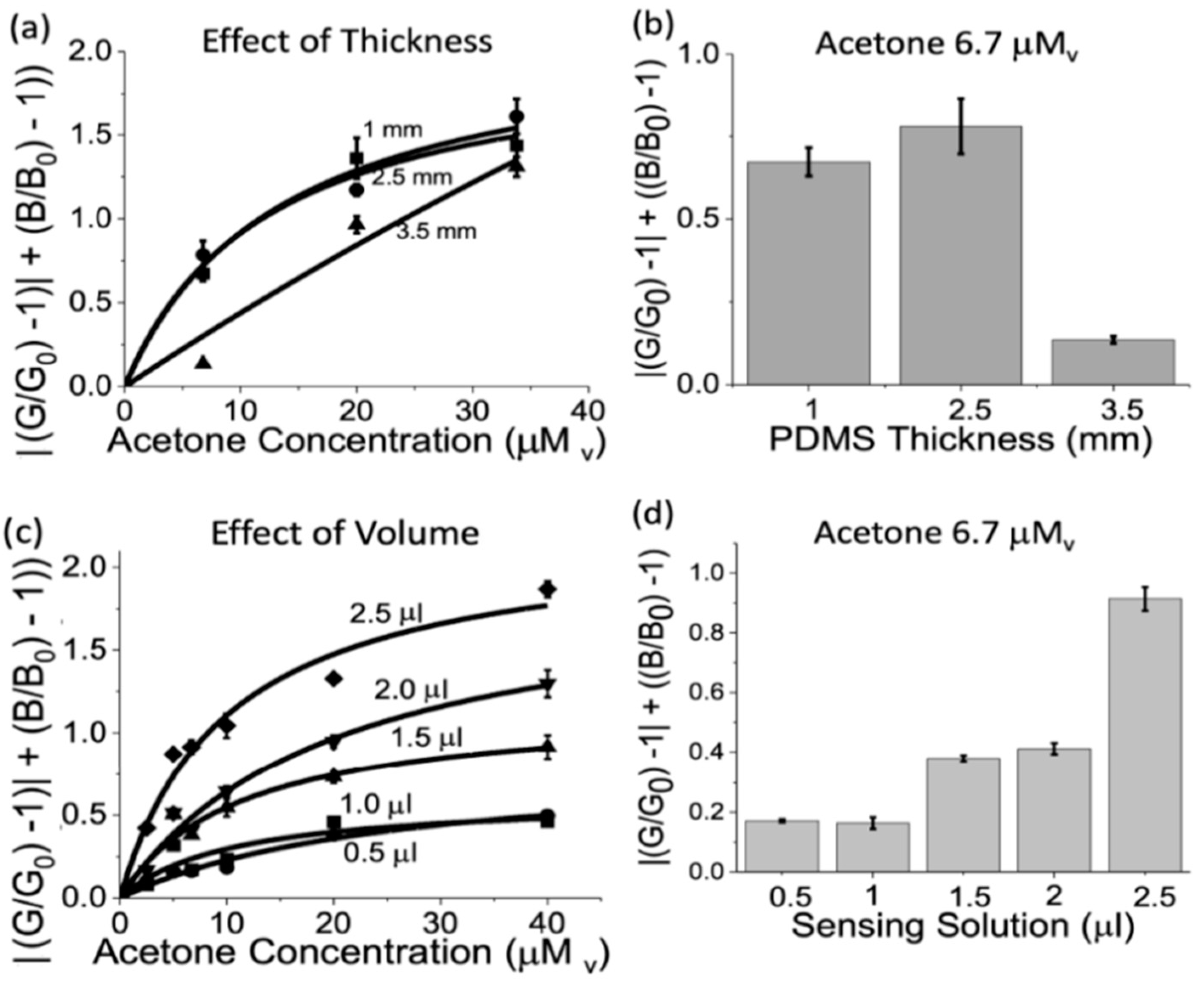
3.3. Sensor Geometry Optimization
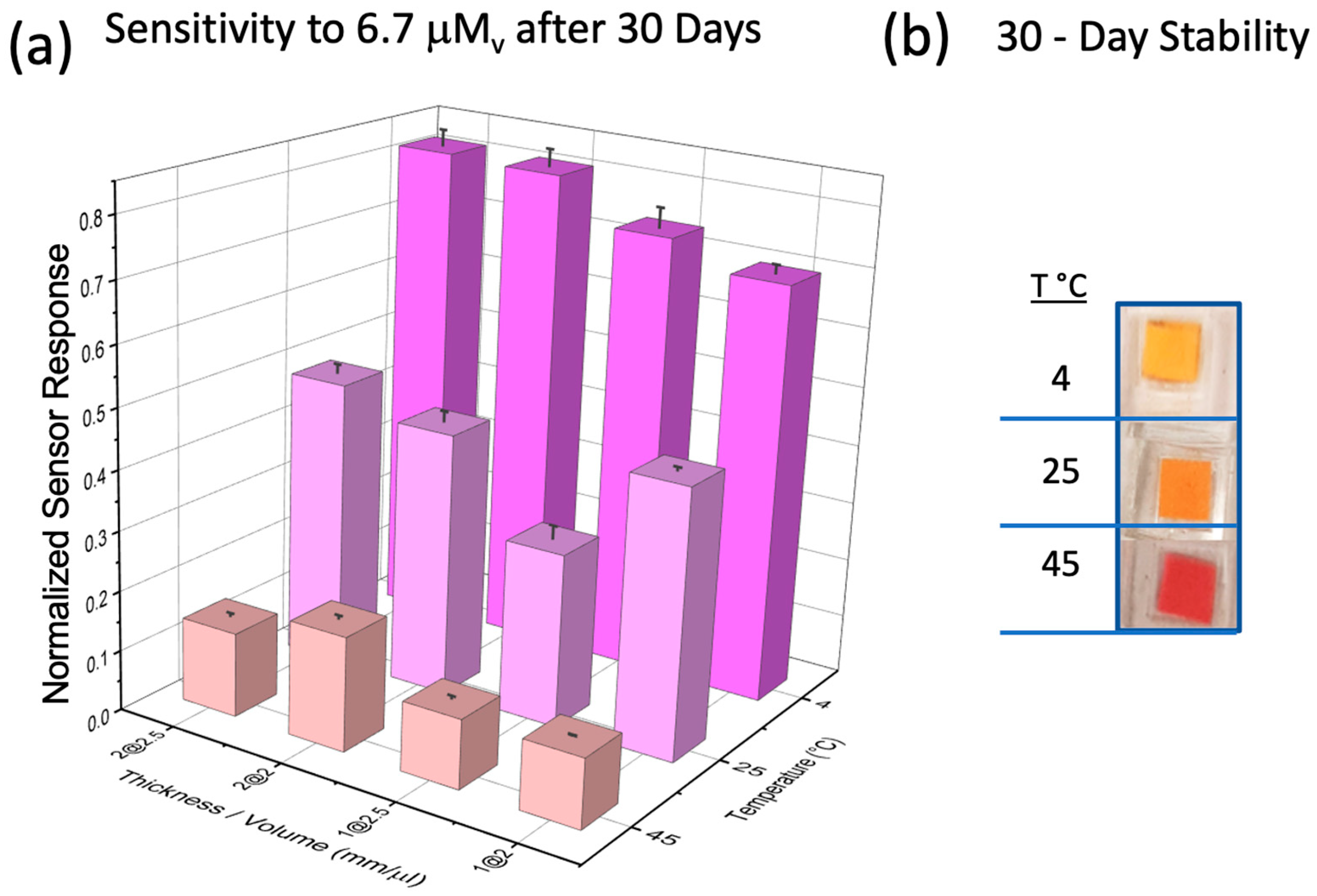
3.4. Sensor Stability
3.5. Sensor Interferent Study
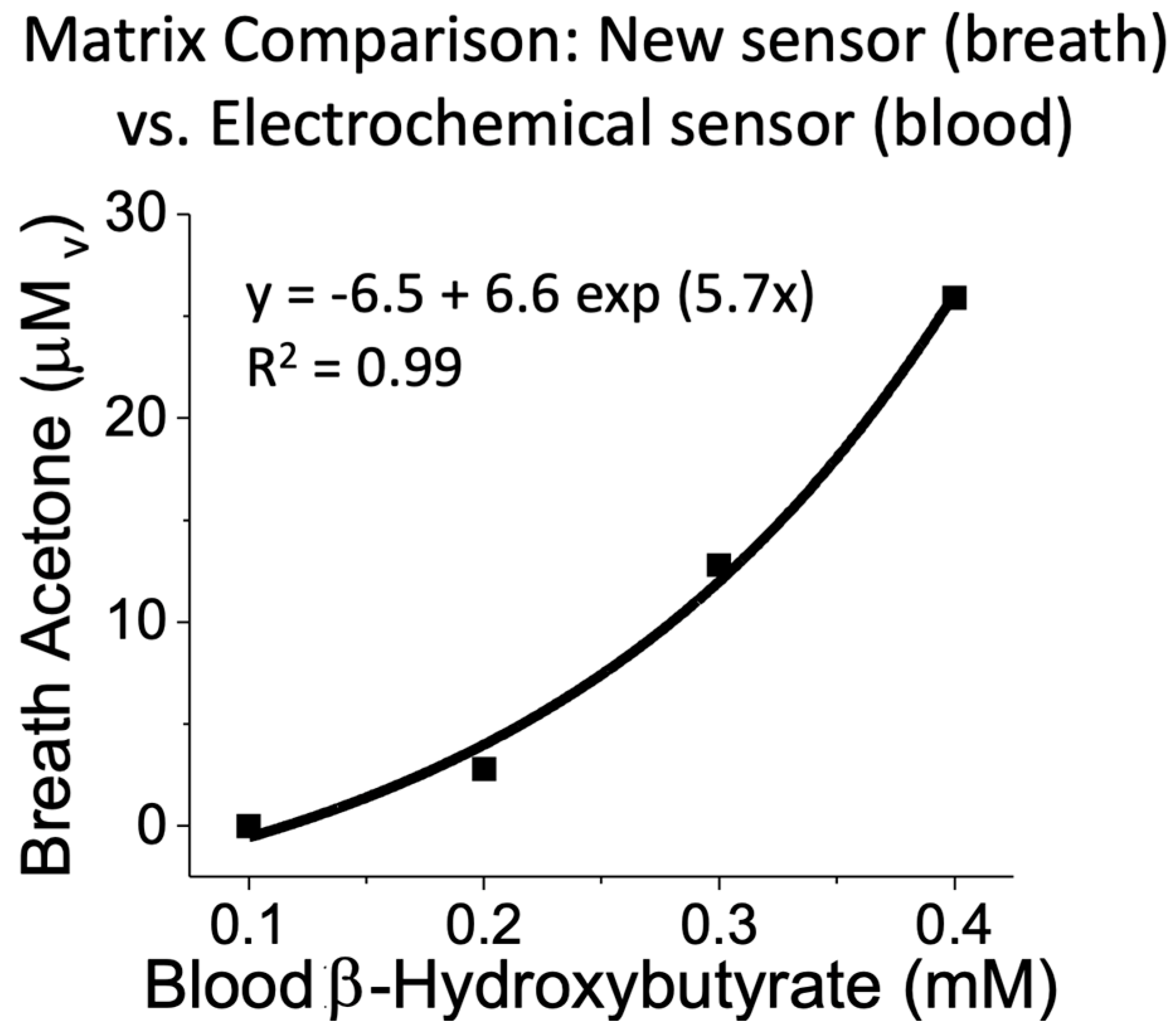
3.6. Sensor Calibration and Real Sample Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsow, F.; Xian, X.J.; Bridgeman, D.; Forzani, E.S.; Tao, N.J. Self-Contained Wearable Metabolic Analyzer. US20210378546A1, 9 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Forzani, E.S.; Tao, N.J. Metabolic Analyzer. US20130150746, 13 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tsow, F.; Xian, X.; Forzani, E.; Tao, N.J. An Improved Portable Metabolic Analyzer System. US10250369795A1, 24 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, N.J.; Forzani, E.S. Metabolic Analyzer. U.S. Patent 10,143,401, 4 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tsow, F.; Xian, X.J.; Forzani, E.S.; Tao, N.J. Portable Metabolic Analyzer. U.S. Patent 10,078,074, 18 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Xian, X.; Terrera, M.; Krishnan, R.; Miller, D.; Bridgeman, D.; Tao, K.; Zhang, L.; Tsow, F.; Forzani, E.; et al. A pocket-sized metabolic analyzer for assessment of resting energy expenditure. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, A.; Quach, A.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.J.; Terrera, M.; Jackemeyer, D.; Xian, X.; Tsow, F.; Tao, N.; Forzani, E. Breath Acetone as Biomarker for Lipid Oxidation and Early Ketone Detection. Glob. J. Obes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2014, 1, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar, A.; Quach, A.; AZhang, H.; Terrera, M.; Jackemeyer, D.; Xian, X.; Tsow, F.; Tao, N.; Forzani, E. Acetone as biomarker for ketosis buildup capability-a study in healthy individuals under combined high fat and starvation diets. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, F.; Prabhakar, A.; Qin, X.C.; Forzani, E.S.; Tao, N.J. Colorimetric Sensor for Online Accurate Detection of Breath Acetone. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArdle, W.D.; Katch, F.I.; Katch, V.L. Exercise Physiology: Nutrition, Energy, and Human Performance; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McGarry, J.; Foster, D. Regulation of hepatic fatty acid oxidation and ketone body production. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1980, 49, 395–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, R.; Bond, M. Kinetics of the decarboxylation of acetoacetic acid. Aust. J. Chem. 1967, 20, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard Jr, G.; Owen, O.; Haff, A.; Paul, P.; Bortz, W. Ketone-body production and oxidation in fasting obese humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1974, 53, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, R.D. Dr. Atkins’ New Diet Revolution; M. Evans: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kossoff, E.H.; Zupec-Kania, B.A.; Amark, P.E.; Ballaban-Gil, K.R.; Christina Bergqvist, A.; Blackford, R.; Buchhalter, J.R.; Caraballo, R.H.; Helen Cross, J.; Dahlin, M.G. Optimal clinical management of children receiving the ketogenic diet: Recommendations of the International Ketogenic Diet Study Group. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.M.; Kossoff, E.H.; Hartman, A.L. The ketogenic diet: One decade later. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Cenci, L.; Grimaldi, K.A. Effect of Ketogenic Mediterranean diet with phytoextracts and low carbohydrates/high-protein meals on weight, cardiovascular risk factors, body composition and diet compliance in Italian council employees. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupari, M.; Lommi, J.; Ventilä, M.; Karjalainen, U. Breath acetone in congestive heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 1995, 76, 1076–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umpierrez, G.E.; Kitabchi, A.E. Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Treat. Endocrinol. 2003, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardern, R.; Quinn, N. Emergency management of diabetic ketoacidosis in adults. Emerg. Med. J. EMJ 2003, 20, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, P.; Matz, R. Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus in adults: Experience in treating diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar nonketotic coma with low-dose insulin and a uniform treatment regimen. Diabetes Care 1983, 6, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, T.; Matthews, D. Recent advances in the monitoring and management of diabetic ketoacidosis. Qjm 2004, 97, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, R.A.; Malone, J.I.; Nathan, D.M.; Peterson, C.M. Tests of glycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Csako, G. False-positive results for ketone with the drug mesna and other free-sulfhydryl compounds. Clin. Chem. 1987, 33, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnardeaux, A.; Somerville, P.; Kaye, M. A study on the reliability of dipstick urinalysis. Clin. Nephrol. 1994, 41, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, M.R.; Okada, P.; White, P.C. Bedside ketone determination in diabetic children with hyperglycemia and ketosis in the acute care setting. Pediatr. Diabetes 2004, 5, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cone, E.J. Oral fluid testing: New technology enables drug testing without embarrassment. J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 2006, 34, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saasa, V.; Malwela, T.; Beukes, M.; Mokgotho, M.; Liu, C.P.; Mwakikunga, B. Sensing Technologies for Detection of Acetone in Human Breath for Diabetes Diagnosis and Monitoring. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güntner, A.T.; Kompalla, J.F.; Landis, H.; Theodore, S.J.; Geidl, B.; Sievi, N.A.; Kohler, M.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Gerber, P.A. Guiding Ketogenic Diet with Breath Acetone Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Likhodii, S.S.; Cunnane, S.C. Breath acetone is a reliable indicator of ketosis in adults consuming ketogenic meals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Likhodii, S.S.; Rarama, E.; Benoit, S.; Liu, Y.-M.C.; Chartrand, D.; Curtis, R.; Carmant, L.; Lortie, A.; Comeau, F.J. Breath acetone predicts plasma ketone bodies in children with epilepsy on a ketogenic diet. Nutrition 2006, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueta, I.; Saito, Y.; Hosoe, M.; Okamoto, M.; Ohkita, H.; Shirai, S.; Tamura, H.; Jinno, K. Breath acetone analysis with miniaturized sample preparation device: In-needle preconcentration and subsequent determination by gas chromatography–mass spectroscopy. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassopoulos, C.; Barnett, D.; Russell Fraser, T. Breath-acetone and blood-sugar measurements in diabetes. Lancet 1969, 293, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa-Veloso, K.; Rarama, E.; Comeau, F.; Curtis, R.; Cunnane, S. Epilepsy and the ketogenic diet: Assessment of ketosis in children using breath acetone. Pediatr. Res. 2002, 52, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovey, F.; Cros, J.; Tuzson, B.; Seyssel, K.; Schneiter, P.; Emmenegger, L.; Tappy, L. Breath acetone as a marker of energy balance: An exploratory study in healthy humans. Nutr. Diabetes 2018, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Španěl, P.; Smith, D. Progress in SIFT-MS: Breath analysis and other applications. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2011, 30, 236–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Huang, J.; Abbassi-Ghadi, N.; Spanel, P.; Smith, D.; Hanna, G.B. SIFT-MS Analysis of Exhaled Breath for Volatile Organic Compound Profiling of Esophago-Gastric Cancer. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6121–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diskin, A.M.; Španěl, P.; Smith, D. Time variation of ammonia, acetone, isoprene and ethanol in breath: A quantitative SIFT-MS study over 30 days. Physiol. Meas. 2003, 24, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, C.; Španěl, P.; Smith, D. A longitudinal study of ammonia, acetone and propanol in the exhaled breath of 30 subjects using selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry, SIFT-MS. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.; Spanel, P.; Davies, S. Trace gases in breath of healthy volunteers when fasting and after a protein-calorie meal: A preliminary study. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 87, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott-Laboratories. Abbott Breath Acetone Analyzer. FDA approval pre-market notification: 510 (k). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpcd/classification.cfm?id=454 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Abbott Breath Acetone Analyzer. FDA 510K application: K875029. 1988. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm?ID=K875029 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Kundu, S.K.; George, R.W.; March, S.C.; Rutnarak, S. Breath Component Monitoring Device. U.S. Patent 5,174,959, 29 December 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, S.K.; Bruzek, J.A.; Nair, R.; Judilla, A.M. Breath acetone analyzer-Diagnostic tool to monitor dietary fat loss. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landini, B.E.; Bravard, S.T. Breath Acetone Concentration Measured Using a Palm-Size Enzymatic Sensor System. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Hiyama, S. Breath Acetone Analyzer to Achieve “Biochip Mobile Terminal”. NTT DOCOMO Tech. J. 2013, 14, 51–57. Available online: https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/binary/pdf/corporate/technology/rd/technical_journal/bn/vol14_1/vol14_1_051en.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2013).
- Forzani, E.; ASU Biodesign Institute’s Center for Bioelectronics & Biosensors, Tempe, AZ, USA. Acetone Breath Analysis system: Reusable, no continuous monitoring, semiconductor technology with limited selectivity (high interferents’ level). Unpublished work. Results available upon request to eforzani@asu.edu. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alkedeh, O.; Priefer, R. The Ketogenic Diet: Breath Acetone Sensing Technology. Biosensors 2021, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, L.M.; Satterfield, B.C.; Martineau, R.L. Method and Apparatus for Analyzing Acetone in Breath. U.S. Patent 10352940, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Smeeton, T.M.; Zanola, M.; Barrett, J.; Berryman-Bousquet, V. A compact breath acetone analyser based on an ultraviolet light emitting diode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-B.; Byun, H.-G.; So, M.-S.; Huh, J.-S. Analysis of diabetic patient’s breath with conducting polymer sensor array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Xia, M. Carbon Nanotube-Based Ultra-Sensitive Breath Acetone Sensor for Non-Invasive Diabetes Diagnosis. 2012. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/reader/52955880 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Righettoni, M.; Tricoli, A.; Gass, S.; Schmid, A.; Amann, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Breath acetone monitoring by portable Si: WO3 gas sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 738, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, G.; Bonavita, A.; Micali, G.; Donato, N. Design and development of a breath acetone MOS sensor for ketogenic diets control. Sens. J. IEEE 2010, 10, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, L.M.; Ahmad, S.A.; Smith, Z. Breath Ketone Measurement System with Analysis Unit that Communicates with Mobile Application. U.S. Patent US10,278,640 B2, 7 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, L.M.; Satterfield, B.C.; Martineau, R.L. Method and Apparatus for Analysing Acetone in Breath. U.S. Patent US10,352,940 B2, 16 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, L.M.; Satterfield, B.C.; Martineau, R.L. Method and Apparatus for Analyzing Acetone in Breath. U.S. Patent US 2020/0110092 A1, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, L.M.; Satterfield, B.C.; Martineau, R.L. Method and Apparatus for Analyzing Acetone in Breath. U.S. Patent 0176447 A1, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, L.M.; Satterfield, B.; Martineau, R. Method and Apparatus for Analyzing Acetone in Breath. U.S. Patent 0132858 A1, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, L.M.; Satterfield, B.; Martineau, R. Method and Apparatus for Analyzing Acetone in Breath. U.S. Patent 9518991, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, L.M.; Smith, Z.B.; Ahmad, S.A.; Kim, C. Measuring an Analyte in Breath Using a Porous Structure Containing a Reactant. U.S. Patent 10591460, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Marasco, M. Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride for the Quick Estimation of Acetone. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1926, 18, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, N.; Nagashima, K. An automatic monitor of formaldehyde in air by a monitoring tape method. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://www.zefon.com/analytical/download/151d.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2013).
- Massick, S.M.; Vakhtin, A. Breath acetone detection. In Proceedings of the Optics East 2006, Boston, MA, USA, 17 October 2006; p. 63860O. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. Determination of acetone in human breath by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and solid-phase microextraction with on-fiber derivatization. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 810, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-W.; Que Hee, S.S. A new passive sampler for regulated workplace ketones. AIHAJ-Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. 2000, 61, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.K.; Pesce, A.J.E. Clinical Chemistry: Theory, Analysis, Correlation; Mosby, Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Grote, C.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid-Phase Microextraction for the Analysis of Human Breath. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooth, G.; Carlström, S. Therapeutic fasting. Acta Med. Scand. 1970, 187, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, G.A., Jr.; Haff, A.C.; Skutches, C.L.; Paul, P.; Holroyde, C.P.; Owen, O.E. Plasma acetone metabolism in the fasting human. J. Clin. Investig. 1979, 63, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osorio Perez, O.; Nguyen, N.A.; Hendricks, A.; Victor, S.; Mora, S.J.; Yu, N.; Xian, X.; Wang, S.; Kulick, D.; Forzani, E. A Novel Acetone Sensor for Body Fluids. Biosensors 2024, 14, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14010004
Osorio Perez O, Nguyen NA, Hendricks A, Victor S, Mora SJ, Yu N, Xian X, Wang S, Kulick D, Forzani E. A Novel Acetone Sensor for Body Fluids. Biosensors. 2024; 14(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsorio Perez, Oscar, Ngan Anh Nguyen, Asher Hendricks, Shaun Victor, Sabrina Jimena Mora, Nanxi Yu, Xiaojun Xian, Shaopeng Wang, Doina Kulick, and Erica Forzani. 2024. "A Novel Acetone Sensor for Body Fluids" Biosensors 14, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14010004
APA StyleOsorio Perez, O., Nguyen, N. A., Hendricks, A., Victor, S., Mora, S. J., Yu, N., Xian, X., Wang, S., Kulick, D., & Forzani, E. (2024). A Novel Acetone Sensor for Body Fluids. Biosensors, 14(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14010004







