Abstract
Gaussia luciferase (GLuc) is the preeminent secreted luciferase widely used in cell-based reporter assays. By employing sequence-guided mutagenesis informed by alignments of diverse copepod luciferase sequences, we identified key amino acids that significantly enhance bioluminescence (BL) intensity. Among the mutated proteins expressed in bacteria, five individual mutations (M60L, K88Q, F89Y, I90L, or S103T) independently increased BL intensity by 1.8 to 7.5-fold compared to wild-type GLuc in the presence of coelenterazine substrates. Remarkably, the combination of all five mutations in GLuc (designated as GLuc5) resulted in an unexpected 29-fold enhancement in BL intensity. Subsequent evaluation of the GLuc5-secreted reporter in transfected mammalian cells confirmed its superior BL performance across multiple cell lines. These findings suggest that the mutated residues are likely crucial for enhancing BL intensity in GLuc, supporting its potential to serve as a highly sensitive biosensor or reporter for a wide range of biological applications.
1. Introduction
Bioluminescence (BL) assays using luciferases often surpass fluorescence or chemiluminescence assays due to their superior sensitivity, linear dynamic range, and minimal background signal [1,2,3]. Luciferases catalyze the oxidation of substrates (primarily luciferin or coelenterazine) to produce light. To date, luciferases from diverse organisms, including fireflies, Renilla, copepods, and bacteria, have been cloned and characterized [4,5,6,7,8]. Firefly luciferase (FLuc), Renilla luciferase (RLuc), and Gaussia luciferase (GLuc) are widely employed in bioassays. While FLuc is dependent on adenosine triphosphate (ATP), oxygen, and Mg2+ for the oxidation of luciferin, RLuc, and GLuc can catalyze the oxidation of coelenterazine without requiring ATP or Mg2+. Among the coelenterazine-dependent luciferases, RLuc has been extensively studied and has a well-characterized structure [9].
GLuc, derived from the marine copepod Gaussia princeps, has garnered significant attention as a smaller (185 amino acids, ~19.9 kDa) and brighter luciferase compared to FLuc and RLuc [8]. The primary advantage of GLuc over other luciferases is its natural secretion, enabling non-destructive, real-time monitoring of biological processes in the extracellular medium. This makes GLuc particularly valuable for bioanalysis in live cells [10]. Applications of GLuc span diverse fields, including live imaging [10,11], protein–protein interactions [12], protein dynamics [13], tumor progression monitoring [14], and high-throughput screening [15]. Along with its advantages, structural and functional understandings of GLuc have been reported [16,17,18,19]. Given that GLuc’s unique bioluminescence-generating mechanism stems from conformational changes induced by substrate binding rather than multiple catalytic sites [16], we were motivated to engineer novel mutants based on the evolutionary relatedness and sequence similarity of luciferases.
Here, we report on the rational engineering of GLuc to enhance BL via sequence-guided mutagenesis. Protein engineering efforts have successfully enhanced and stabilized RLuc variants [20,21,22,23]. These modified RLuc mutants underpin the development of numerous bimolecular and high-throughput screening assays [24,25]. Similar endeavors have been undertaken with GLuc, employing gene shuffling to achieve substantial increases in luminescence [15,26]. Maguire C. A. et al. reported a GLuc variant exhibiting glow-type emission kinetics in the presence of the coelenterazine and nonionic surfactant, Triton X-100, suitable for high-throughput screening [15]. Welsh J. P. et al. described a double mutant with an extended luminescence half-life compared to wild-type GLuc [27]. Nonetheless, the use of a nonionic surfactant might introduce additional variables and complicate downstream applications, and the overall luminescence intensity of GLuc has not been fully explored.
To investigate the functional roles of conserved amino acids in copepod luciferases, we performed a comprehensive sequence analysis, incorporating the known structural data of GLuc [17,28]. Through BLAST searches and multiple sequence alignments, we identified highly conserved residues within GLuc. These residues were targeted for site-directed mutagenesis, either individually or in combination, and the resulting mutant proteins were expressed in bacteria to assess their impact on BL. The mutant exhibiting the highest BL intensity was further characterized by mammalian cells transfected with the pCMV vector construct.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Comparative Sequence Analysis for Site-Directed GLuc Mutagenesis
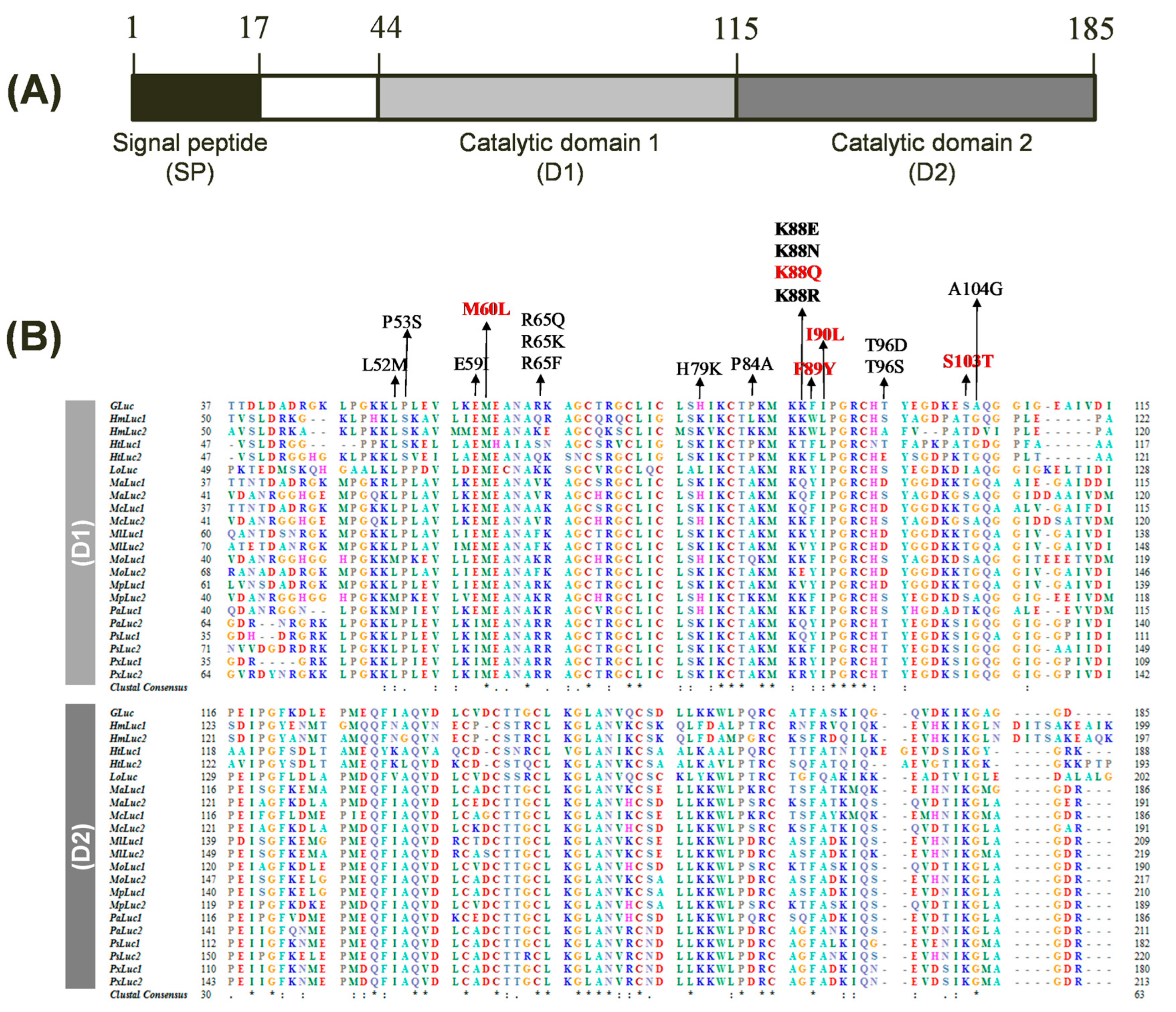
GLuc, a secreted BL reporter protein, has gained widespread recognition due to its exceptional brightness, compact size, and extracellular secretion. However, the precise active site and critical amino acid residues responsible for GLuc’s catalytic activity have remained elusive. In 2008, fundamental studies identified two distinct catalytic domains within GLuc, where both domains were found to be active when expressed individually [29]. In 2011, a computational analysis suggested that the GLuc active site resides within amino acids 71–140, the most hydrophilic region of the protein, based on comparisons with the chromophore region of green fluorescent protein and coelenterazine, along with hydrophobicity analysis [30]. The study also proposed a few mutations (I90L, F89W/I90L, and others) that led to enhanced BL intensities. Recent molecular-directed evolution studies on GLuc have identified additional mutations, such as M60I, that result in altered glow-type light emission kinetics [15,26]. Notably, all reported mutations have been confined to the first catalytic domain, and mutating corresponding amino acids in the second domain has not yielded any significant effects [26]. Based on the known structural and functional features of GLuc, we conducted a comprehensive sequence analysis of GLuc and its homologs. Our analysis identified twenty-one closely related luciferases from the copepod family, sharing approximately 37–73% sequence identity (Table 1). As previously observed [29], the primary structure of GLuc exhibits two catalytic domains (D1 and D2) composed of tandem repeat sequences, each consisting of 71 amino acid residues, located at positions 44–114 and 115–185, respectively (Figure 1A). The multiple sequence alignment of GLuc with its related copepod luciferases identified several highly conserved residues within these domains, suggesting their potential importance for GLuc’s function (Figure 1B). To investigate the functional significance of these consensus residues, we selected several candidate amino acids for mutagenesis based on their sequence conservation and predicted roles in BL activity. Focusing on the first repeated catalytic domain (D1), known to be more essential than D2 [26], we selected 13 amino acid sites (L52, P53, E59, M60, R65, H79, P84, K88, F89, I90, T96, S103, and A104) for mutagenesis within the D1 region (positions 44–114). We included three underlined residues known for their role in enhancing bioluminescence in GLuc: M60L [15], F89Y [30], and I90L [30]. The remaining 10 amino acids are either semi-conserved residues from the consensus sequence or frequently substituted residues based on sequence similarity. Cysteine residues in D1 were excluded from mutagenesis due to their structural role rather than catalytic function. Additionally, we excluded amino acids that were identical to the consensus sequence (marked with asterisks) and those previously shown to have no effect on luciferase activity. Mutant GLuc proteins with targeted substitutions were expressed, and their BL activity was assessed.

Table 1.
Luciferase sequence similarity among Copepod species revealed by protein BLAST research.
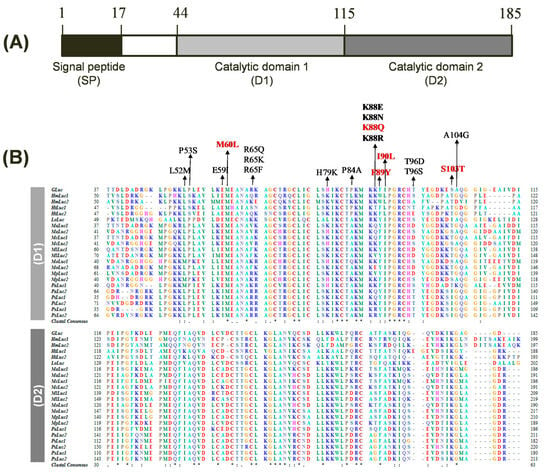
Figure 1.
Structure and sequence alignment of Gaussia luciferase (GLuc). (A) Domain architecture of GLuc encompassing a signal peptide (SP) and two repeated catalytic domains (D1 and D2). The protein comprises 185 amino acids. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of GLuc and 21 copepod luciferase homologs, focusing on the D1 (top) and D2 (bottom). Amino acid residues are color-coded based on their physicochemical properties. Identical residues across all sequences are indicated by asterisks (*), while conserved substitutions are represented by a colon (:) and period (.). Gaps introduced for optimal alignment are shown as dashes (–). Amino acid positions are numbered on the left and right. The amino acids targeted for mutagenesis are indicated by arrows, with GLuc5 mutation sites highlighted in red.
2.2. Single Site-Directed Mutagenesis of GLuc for Enhanced BL
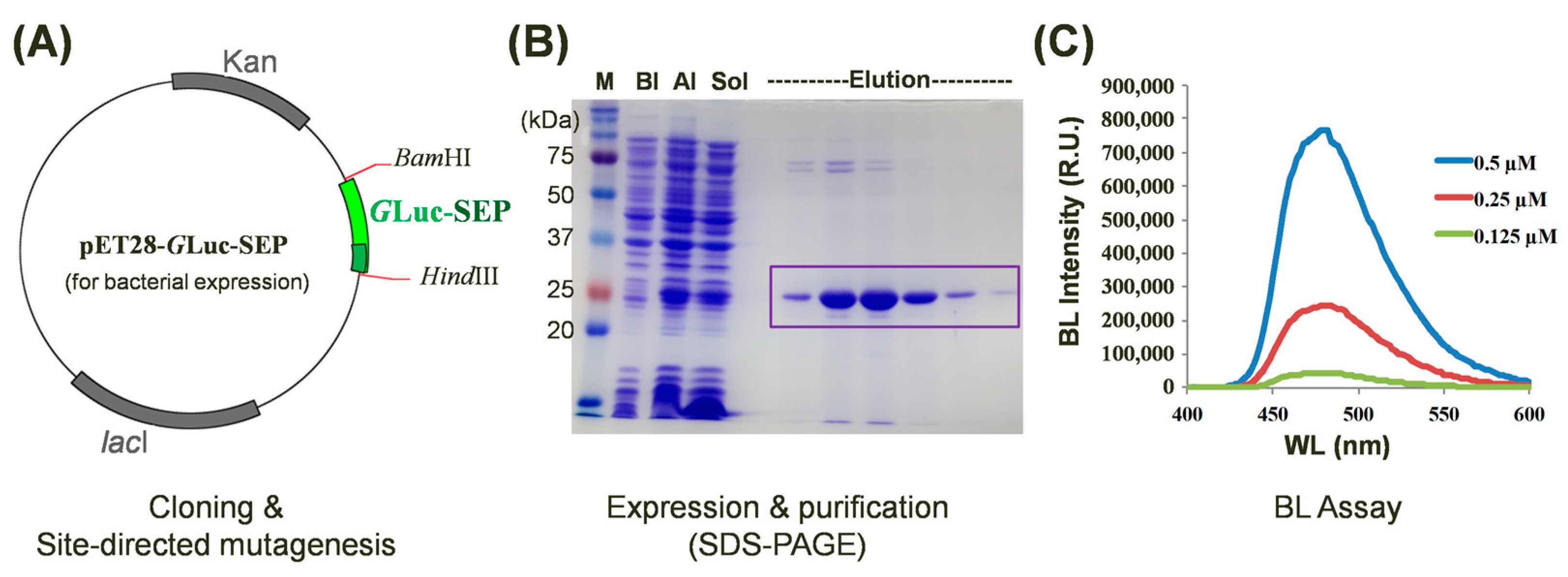
To investigate the impact of single amino acid substitutions on GLuc’s BL activity, we generated a series of site-directed mutants derived from the wild-type protein. For the efficient comparison of BL intensities among mutant proteins, we initially constructed a plasmid for bacterial expression. GLuc’s expression in bacterial systems is often hindered by the formation of five disulfide bonds because they increase the risk of misfolding when GLuc is bacterially produced, resulting in a low yield [31]. For the bacterial expression of GLuc, various strategies have been explored to enhance the soluble expression and purification of GLuc in bacterial systems [32,33,34]. One effective approach involves the insertion of an SEP-tag (nine Asp residues) at the C-terminus of GLuc [17,33]. We incorporated a C-terminal SEP-tag into the pET28 vector (termed pET28-GLuc-SEP) and utilized this construct for protein expression and mutagenesis (Figure 2A). The recombinant GLuc-SEP protein was successfully expressed in E. coli and purified to homogeneity. The molecular weight of the purified GLuc protein, as determined by SDS-PAGE analysis, was approximately 24 kDa (Figure 2B), which is consistent with its calculated molecular weight based on the amino acid sequence. To assess the impact of mutations on BL intensity, purified GLuc-SEP mutants were subjected to BL assays at varying concentrations (Figure 2C).
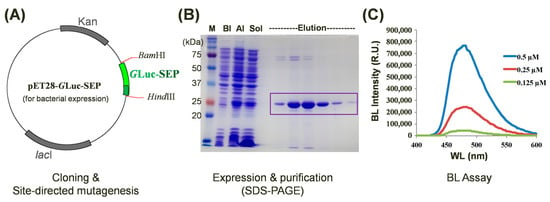
Figure 2.
Characterization of site-directed GLuc mutants with enhanced bioluminescence (BL) intensity. (A) A schematic representation of the pET28-GLuc-SEP plasmid used for bacterial expression. The WT or mutated GLuc-SEP gene was inserted between BamHI and HindIII restriction sites. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified GLuc-SEP protein. M, BI, AI, and Sol denote size markers before induction, after induction, and as a soluble fraction, respectively. The target protein is indicated by the box. (C) Assay of BL intensity of purified GLuc-SEP mutants at various concentrations. The BL intensities of the GLuc mutants were compared to those of the -type GLuc-SEP to verify BL enhancement.
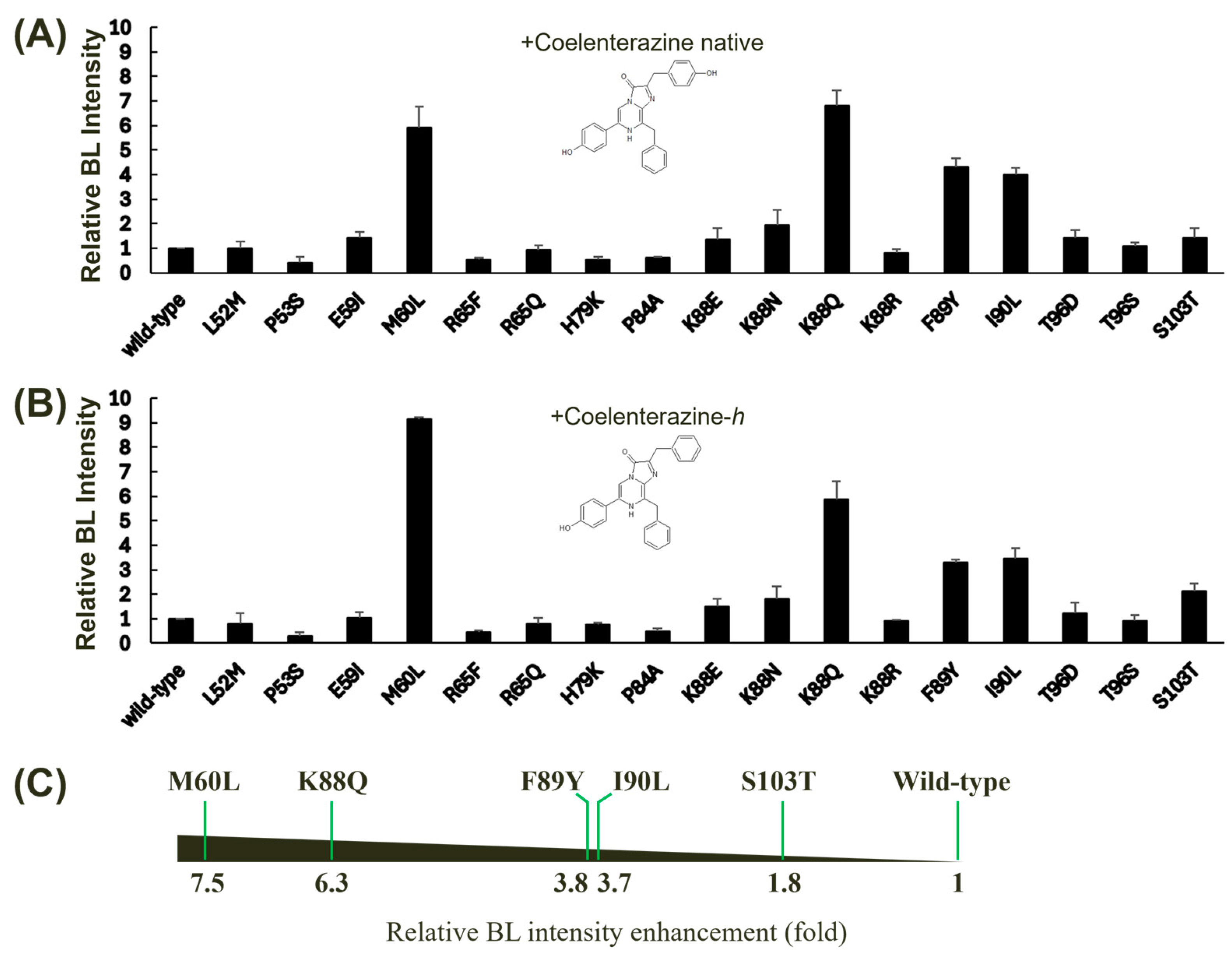
Despite the high conservation of cysteine residues among copepod luciferases, we excluded them from our site-directed mutagenesis experiments. Previous studies have demonstrated that cysteine residues within GLuc play a crucial role in maintaining protein structural stability through disulfide bond formation rather than directly influencing BL activity. It has been reported that the fifth disulfide bond in GLuc is dispensable for bioluminescence, as evidenced by complementation experiments involving two inactive GLuc domains [35]. The BL intensities of these mutants were measured using two distinct substrates: coelenterazine native (Figure 3A) and coelenterazine-h (Figure 3B). Our analysis revealed that several mutations led to significant enhancements in GLuc’s BL intensity, particularly when using coelenterazine-h as a substrate. This result also suggests that the region encompassing amino acids 60–103 plays a crucial role in substrate specificity, given the structural difference between coelenterazine native and coelenterazine-h, which involves an additional −OH group in the native form. Our findings corroborate the hypothesis that the GLuc active site resides within amino acids 71–140, as previously suggested, based on hydrophobicity analysis [21]. Collectively, five of the tested single mutants, M60L, K88Q, F89Y, I90L, and S103T, exhibited relatively high increases in BL intensity compared to the wild-type GLuc. Among these mutants, M60L and K88Q demonstrated the highest levels of BL enhancement. The M60I substitution has been previously reported to extend the light emission [15]. F89Y and I90L have also been shown to enhance BL in GLuc [30]. Notably, the M60L, K88Q, F89Y, and I90L mutants exhibited substantial increases in BL intensity, averaging between 3.7- and 7.5-fold compared to the wild-type protein (Figure 3C). These findings highlight the critical role of these amino acid residues in modulating GLuc’s catalytic efficiency and substrate specificity.
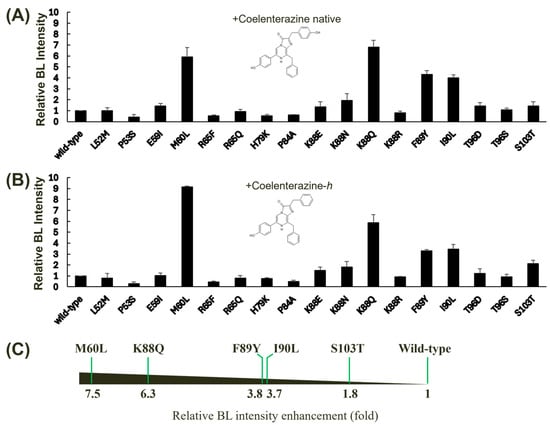
Figure 3.
Effect of single mutagenesis on the BL activity of GLuc. Single mutants were derived from wild-type GLuc via site-directed mutagenesis, and their BL intensities were assessed using two different substrates: coelenterazine native (A) and coelenterazine-h (B). The BL intensity of GLuc was measured at 482 nm. Error bars represent the standard deviations from three independent experiments. (C) A horizontal bar chart summarizing the relative BL intensity enhancement (fold increase) for selected mutants compared to the wild type is shown. The fold increase was calculated by taking the average of the values in (A,B). The mutants exhibiting significant increases in BL intensity are displayed.
2.3. Multiple Site-Directed Mutagenesis of GLuc for Enhanced BL
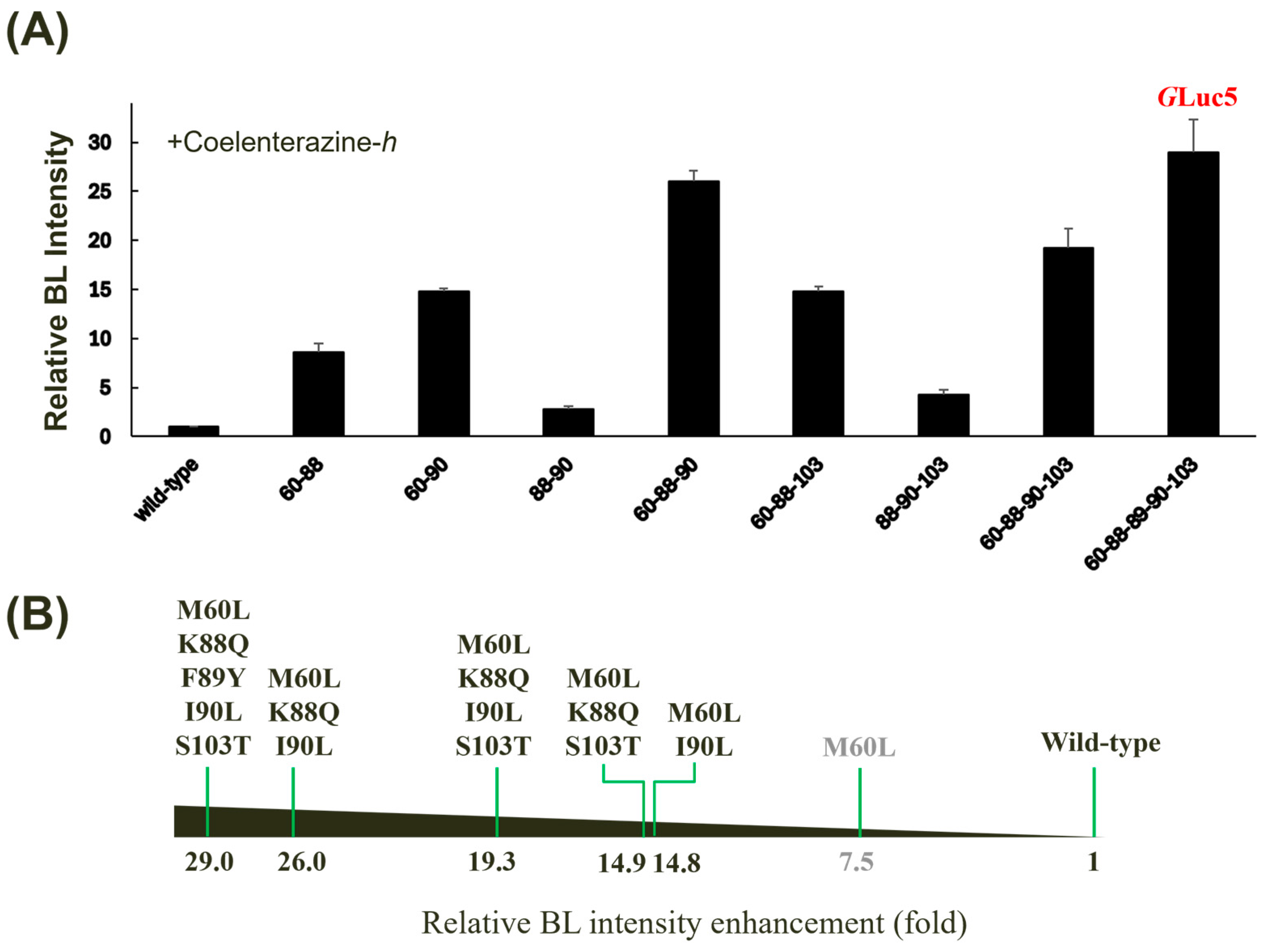
To investigate the synergistic effects of multiple amino acid substitutions on GLuc’s BL activity, we generated a series of combinatorial mutants based on the conserved positions (Figure 1B). When evaluated with coelenterazine-h, the quintuple mutant (M60L, K88Q, F89Y, I90L, and S103T, denoted GLuc5) exhibited the highest BL intensity (~29-fold versus wild-type) among all tested combinations, surpassing every single mutant (Figure 4A). While some double (M60L/I90L), triple (M60L/K88Q/I90L and M60L/L88Q/S103T), or quadruple mutants (M60L/K88Q/I90L/S103T) exhibited significant enhancements in BL activity, some multiple mutant combinations surprisingly exhibited decreased BL intensity compared to their single mutant counterparts (Figure 4B). The M60L substitution appears to be a key determinant of the observed enhancements, as combinations lacking this mutation showed only moderate increases in BL intensity. While a luciferase-based application was not implemented in the current study, GLuc5 has the potential to be directly applied in biosensors, as demonstrated by our previous research on measuring protease activity using peptide-linked luciferase [36].
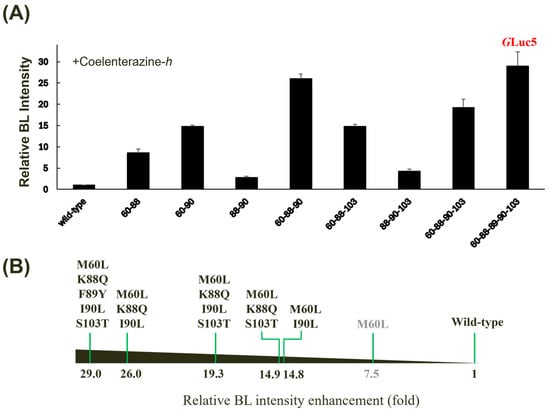
Figure 4.
Effect of multiple mutagenesis on the BL activity of GLuc. (A) Relative BL intensity of multiple mutants compared to the wild type when incubated with coelenterazine-h. Error bars represent the standard deviations from three independent experiments. (B) A horizontal bar chart summarizing the relative fold increase in BL intensity for selected mutants is shown.
2.4. BL Reporter Assay in Cell Culture Medium by Transfection of the GLuc5 Variant
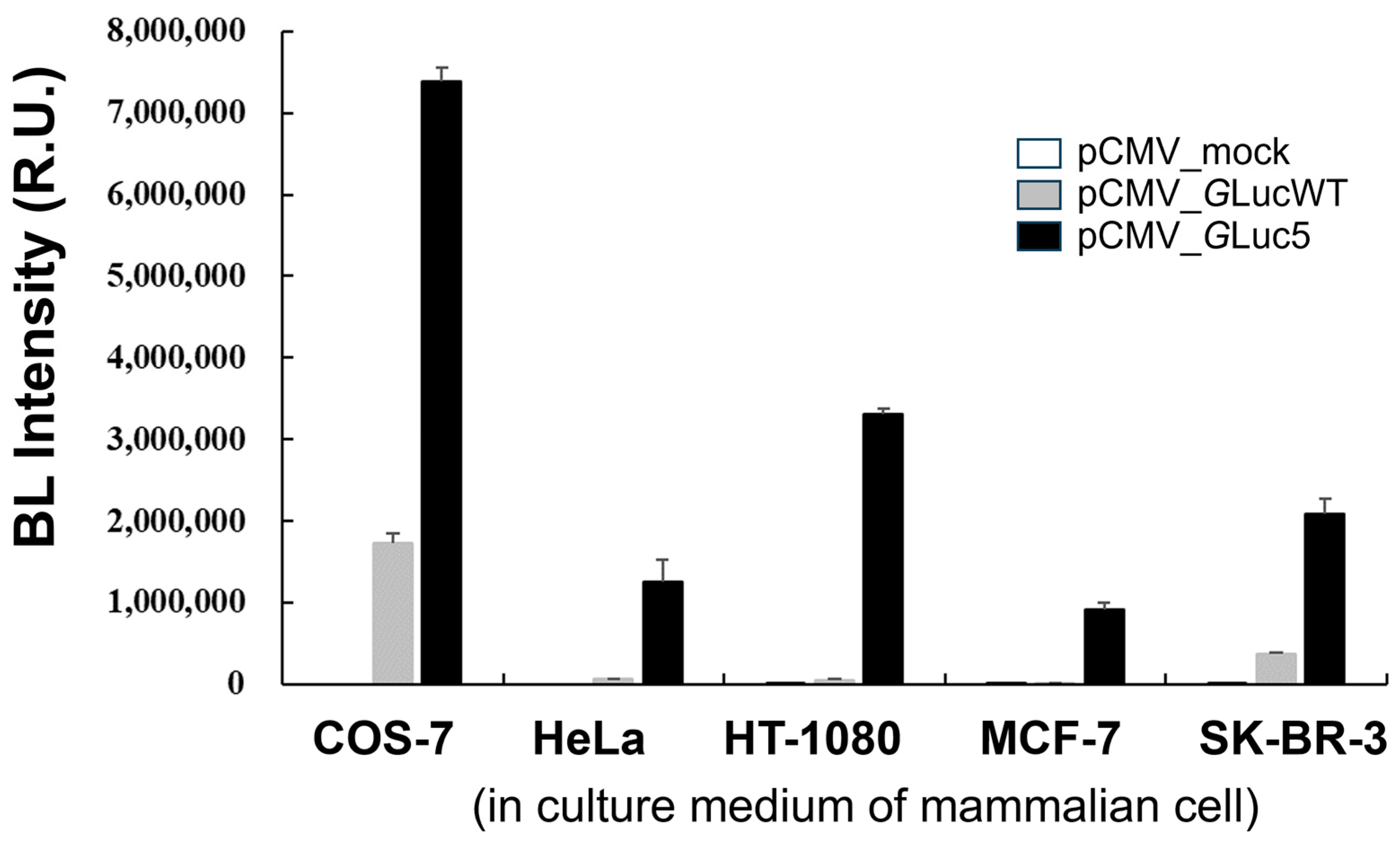
The codon-optimized GLuc used in the present study has been recognized as a promising reporter protein [8], offering a valuable tool for monitoring various biological processes in conditioned media of cultured cells, as well as in the blood and urine [10,37]. GLuc is highly stable in culture media, with a half-life of approximately six days, allowing samples to be stored at 4 °C for several days without a significant loss of reporter activity [37]. To investigate the usefulness of the multi-site-directed mutant GLuc5 in mammalian cells, BL intensity was compared across various mammalian cell lines transfected with different pCMV constructs (Figure 5). It is noteworthy that the gene encoding GLuc contains a secreted signal peptide sequence at its N-terminus functionally. Among the cell lines tested, COS-7 showed the highest BL intensity, particularly when transfected with the pCMV_GLuc5 vector, leading to a substantial increase in BL intensity. Although BL intensity varied widely among different cell lines transfected with the same GLuc constructs, other cell lines, including HeLa, HT-1080, MCF-7, and SK-BR-3, also exhibited significant increases in BL intensity when transfected with the pCMV_GLuc5 vector compared to the mock and pCMV_GLucWT controls. This variability in BL intensity among different cell lines suggests that transfection efficiency, substrate penetration, and/or other cellular factors may influence GLuc activity, highlighting the need for further investigation into the underlying mechanisms. Overall, this result indicates that the GLuc5 variant significantly enhances BL intensity across different cell lines, supporting its potential as a highly sensitive reporter for a wide range of biological applications, particularly in monitoring gene expression and cellular processes in various cell types. It is noteworthy that compared to the fluorescence measurement, BL offers superior sensitivity and enables the quantification of protein expression at lower concentrations. Consequently, we anticipate that the enhanced sensitivity of the engineered GLuc holds significant promise for applications such as BL resonance energy transfer (BRET) and BL imaging.
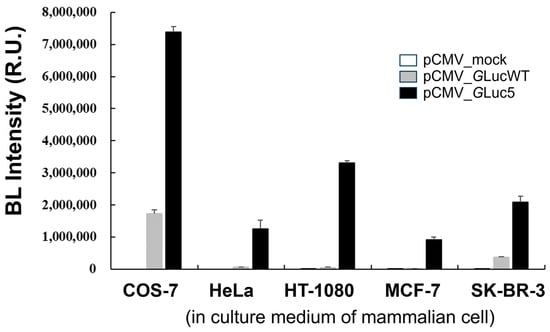
Figure 5.
A comparison of BL intensity in mammalian cell lines transfected with pCMV constructs. BL intensity was measured in the culture medium of five mammalian cell lines (COS-7, HeLa, HT-1080, MCF-7, and SK-BR-3) following transfection with an empty pCMV vector (mock, white bar), a pCMV vector expressing wild-type GLuc (GLucWT, gray bar), or a pCMV vector expressing the GLuc5 variant (black bar). Error bars represent the standard deviations from three independent experiments.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
The pCMV-GLuc plasmid, coelenterazine-native, and coelenterazine-h were purchased from Nanolight Technology (Pinetop, AZ, USA) and used for cloning with specific primers. All the primers were sourced from Macrogen (Seoul, Republic of Korea). All other reagents were purchased from commercial suppliers and were of the highest available purity grade.
3.2. Sequence-Guided Mutagenesis
A protein-BLAST search was initially conducted using the GLuc amino acid sequence to identify related copepod luciferase sequences. Subsequently, multiple sequence alignment was performed with the resulting luciferase sequences from the BLAST search, and highly consensus amino acids were selected for site-directed mutagenesis and characterization. The GenBank accession numbers for the luciferase sequences are as follows: Metridia asymmetrica 1 (MaLuc_1, BAN91823), Metridia asymmetrica 2 (MaLuc_2, BAN91824), Metridia curticauda 1 (McLuc_1, BAN91825) Metridia curticauda 2 (McLuc_2, BAN91826), Metridia pacifica 1 (MpLuc_1, BAG48249), Metridia pacifica 2 (MpLuc_2, BAG48250), Metridia okhotensis 1 (MoLuc_1, BAM11213), Metridia okhotensis 2 (MoLuc_2, BAL63033), Metridia longa 1 (MlLuc_1, ABW06650), M. longa 2 (MlLuc_2, AAR17541), Pleuromamma abdominalis 1 (PaLuc_1, BAL63034), Pleuromamma abdominalis 2 (PaLuc_2, BAL63035), Pleuromamma scutullata 1 (PsLuc_1, BAN91827), Pleuromamma scutullata 2 (PsLuc_2, BAN91828), P. xiphias 1 (PxLuc_1, BAN91832), Pleuromamma xiphias 2 (PxLuc_2, BAN91829), Lucicutia ovaliformis (LoLuc, BAN91831), Heterorhabdus tanneri 1 (HtLuc_1, BAL63039), Heterorhabdus tanneri 2 (HtLuc_2, BAL63040), Heterostylites major 1 (HmLuc_1, BAL63041), and Heterostylites major 2 (HmLuc_2, BAL63042). Site-directed mutagenesis was performed using pET_GLuc-SEP plasmid, which carries the GLuc gene with a C-terminal solubility enhancement peptide (SEP)-tag. The pET_GLuc-SEP was constructed by cloning the GLuc sequence from the pCMV-GLuc vector. The SEP-tag, consisting of six Asp residues, was added to the C-terminus to enhance solubility, as previously suggested [33], using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The resulting GLuc-SEP was then cloned into the pET28 vector. Single or multiple mutations at pET_GLuc-SEP were created by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis, as previously described [38]. This method involved the amplification of a target gene with mutagenic primers, followed by the digestion of parental methylated DNA with DpnI. The resulting PCR product, which was not methylated, was then transformed into E. coli DH5α cells. Subsequent selection and screening steps allowed for the identification of clones containing the desired mutation. All wild-type and mutant sequences were analyzed using the Macrogen sequencing service in Republic of Korea.
3.3. Expression and Purification of GLuc Mutants
The pET28_GLuc-SEP expression plasmid was transformed into E. coli strain BL21 cells and the transformed bacteria were grown at 37 °C in 250 mL of Luria–Bertani broth containing 50 µg/mL of kanamycin until the optical density at 600 nm reached 0.7. Protein expression was induced by adding 0.5 mM IPTG, and the cells were further incubated for an additional 5 h at 25 °C. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 7000 rpm for 10 min. The harvested cell pellet was resuspended in a 12.5 mL lysis buffer (50 mM Tris containing 300 mM NaCl, 1 mg/mL lysozyme, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and 0.5% Triton X-100, pH 8.0) and disrupted by ultrasonication. The crude cell extract was centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 20 min, and the supernatant was filtered and incubated with 1 mL of Ni-NTA beads for 1 h with shaking at 4 °C. The flow-through was removed, and the beads were washed three times with a wash buffer (50 mM Tris containing 300 mM NaCl and 20 mM imidazole, pH 8.0). The bound proteins were eluted with a linear gradient of 0–0.5 M imidazole in a wash buffer. Fractions containing the expressed protein were dialyzed and concentrated in 50 mM Tris (containing 50 mM NaCl, pH 8.0). Mutant proteins were purified in a similar manner. The protein concentration in the soluble fraction was determined using the theoretical extinction coefficient calculated from the amino acid sequences.
3.4. Protein-Based BL Assay of Bacteria-Expressed GLuc Mutants
BL assays were conducted in a total volume of 100 µL of 50 mM Tris (containing 50 mM NaCl, pH 8.0) with purified GLuc protein and coelenterazine substrates. Briefly, 50 µL of either coelenterazine-native or coelenterazine-h solution (final concentration of 10 µg/mL) was mixed with 50 μL of purified GLuc (final concentration of 250 nM), and the BL intensity was immediately measured using a plate reader (Varioskan; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at a wavelength of 400–600 nm. For analysis, the intensities of the mutant proteins at 482 nm (the wavelength of maximum intensity, λmax) were compared with those of the wild type, and enhanced candidates were selected for further characterization.
3.5. Secretion-Based BL Assay of Mammalian Cell-Expressed GLuc Mutants
To optimize mammalian cell transfection and luciferase secretion into the culture medium, two plasmids (pCMV_GLucWT and pCMV_GLuc5) were constructed using the pCMV3_untagged plasmid (Sino Biological, Beijing, China) as a backbone. The DNA sequence encoding GLuc_WT (or GLuc5 mutant), including the N-terminal signal sequence but excluding the SEP sequence, was amplified from the plasmid pET28_GLucWT-SEP (or pET28_GLuc5-SEP) by PCR. The forward primer (5′-CCC AAG CTT ATG GGA GTC AAA GTT CTG TTT GCC C-3′) included a HindIII restriction site, while the reverse primer (5′-GCT CTA GAT TAG TCA CCA CCG GCC CCC TTG-3′) included a XbaI site. Mammalian cell lines (COS-7, HeLa, HT-1080, MCF-7, and SK-BR-3) were cultured in a suitable growth medium with 10% FBS (DMEM for COS-7 and HeLa; RPMI1640 for HT-1080, MCF-7, and SK-BR-7) at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator until they reached 70–80% confluence. Cells were transfected with plasmids encoding wild-type GLuc (pCMV_GLucWT) and the GLuc5 mutant (pCMV_GLuc5) using the FuGene HD transfection reagent (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The empty plasmid (pCMV_mock) served as a negative control. Cells were transfected for 48 h in a serum-free medium to allow for protein expression. Subsequently, the cell culture supernatant was collected by centrifuging at 300× g for 5 min to remove cell debris. The resulting supernatant, containing secreted GLucWT or GLuc5, was transferred to a clean tube. BL was measured using a microplate reader immediately following the 2:1 mixing of volumes of a culture supernatant (100 µL) and coelenterazine-h solution (50 µL) in PBS within a white 96-well plate. The final concentration of coelenterazine-h was 6.7 µg/mL. BL intensity was determined at the maximal peak within the 400–600 nm wavelength range.
4. Conclusions
Despite its widespread use of GLuc in diverse biological applications, its performance can be significantly enhanced through rational protein engineering. We demonstrate that sequence-guided mutagenesis, informed by a comprehensive analysis of copepod luciferases, enabled the development of GLuc variants with substantially increased BL intensity. Among the single and multiple mutants generated, individual mutations within the first catalytic domain, including M60L, K88Q, F89Y, I90L, and S103T, were particularly effective at improving BL emissions. Notably, the quintuple mutant GLuc5 exhibited a remarkable 29-fold increase in BL intensity compared to the wild-type protein, both in bacterial expression systems and in culture media secreted by five mammalian cell lines. These findings highlight the potential of GLuc5 as a promising candidate for a wide range of BL-based applications, including gene expression studies and protein–protein interaction analysis.
Author Contributions
Validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, V.G.; validation, investigation, E.H.K.; validation, B.O.; conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, Y.-P.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (Nos. 2022R1A2B5B02002324 and 2022R1A4A1030421); the Basic Science Research Programs (2020R1A6A1A06046728) through the NRF, funded by the Ministry of Education; and the Korea Environment Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI) through the Aquatic Ecosystem Conservation Research Program, funded by the Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) (No. 2020003030007, 1485019157).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Billard, P.; DuBow, M.S. Bioluminescence-based assays for detection and characterization of bacteria and chemicals in clinical laboratories. Clin. Biochem. 1998, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.K.; Moon, M.; Park, J.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.P. Self-luminescent photodynamic therapy using breast cancer targeted proteins. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Wood, K.V. Bioluminescent assays for high-throughput screening. Assay Drug. Dev. Technol. 2007, 5, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, W.W.; McCann, R.O.; Longiaru, M.; Cormier, M.J. Isolation and expression of a cDNA encoding Renilla reniformis luciferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4438–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, S.V.; Burakova, L.P.; Vysotski, E.S. High-active truncated luciferase of copepod Metridia longa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Masuda, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Nishikawa, S.; Shigeri, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Mizuno, H. Two forms of secreted and thermostable luciferases from the marine copepod crustacean, Metridia pacifica. Gene 2008, 425, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.J.; Thompson, T.B.; Thoden, J.B.; Baldwin, T.O.; Rayment, I. The 1.5-A resolution crystal structure of bacterial luciferase in low salt conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 21956–21968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannous, B.A.; Kim, D.E.; Fernandez, J.L.; Weissleder, R.; Breakefield, X.O. Codon-optimized Gaussia luciferase cDNA for mammalian gene expression in culture and in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loening, A.M.; Fenn, T.D.; Gambhir, S.S. Crystal structures of the luciferase and green fluorescent protein from Renilla reniformis. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 374, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannous, B.A. Gaussia luciferase reporter assay for monitoring biological processes in culture and in vivo. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enjalbert, B.; Rachini, A.; Vediyappan, G.; Pietrella, D.; Spaccapelo, R.; Vecchiarelli, A.; Brown, A.J.; d’Enfert, C. A multifunctional, synthetic Gaussia princeps luciferase reporter for live imaging of Candida albicans infections. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 4847–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, I.; Michnick, S.W. A highly sensitive protein-protein interaction assay based on Gaussia luciferase. Nat. Meth. 2006, 3, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Sato, M.; Tao, H. Split Gaussia luciferase-based bioluminescence template for tracing protein dynamics in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.; Yamashita, H.; Au, P.; Tannous, B.A.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Secreted Gaussia luciferase as a biomarker for monitoring tumor progression and treatment response of systemic metastases. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, C.A.; Deliolanis, N.C.; Pike, L.; Niers, J.M.; Tjon-Kon-Fat, L.A.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Tannous, B.A. Gaussia luciferase variant for high-throughput functional screening applications. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7102–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionova, M.D.; Markova, S.V.; Vysotski, E.S. Bioluminescent and structural features of native folded Gaussia luciferase. J. Photoch. Photobio. B 2018, 183, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Tsuda, K.; Unzai, S.; Saotome, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Yamazaki, T. Solution structure of Luciferase with five disulfide bonds and identification of a putative coelenterazine binding cavity by heteronuclear NMR. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkema, F.M.; Nordentoft, M.K.; Didriksen, A.K.; Corneliussen, A.S.; Willemoës, M.; Winther, J.R. Flash properties of Gaussia luciferase are the result of covalent inhibition after a limited number of cycles. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmuro-Matsuyama, Y.; Matsui, H.; Kanai, M.; Furuta, T. Glow-type conversion and characterization of a minimal luciferase via mutational analyses. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 5554–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loening, A.M.; Dragulescu-Andrasi, A.; Gambhir, S.S. A red-shifted Renilla luciferase for transient reporter-gene expression. Nat. Meth. 2010, 7, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loening, A.M.; Fenn, T.D.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S. Consensus guided mutagenesis of Renilla luciferase yields enhanced stability and light output. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2006, 19, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loening, A.M.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S. Red-shifted Renilla reniformis luciferase variants for imaging in living subjects. Nat. Meth. 2007, 4, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.; von Arnim, A.G. Mutational optimization of the coelenterazine-dependent luciferase from Renilla. Plant Meth. 2008, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragulescu-Andrasi, A.; Chan, C.T.; De, A.; Massoud, T.F.; Gambhir, S.S. Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) imaging of protein-protein interactions within deep tissues of living subjects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12060–12065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacart, J.; Corbel, C.; Jockers, R.; Bach, S.; Couturier, C. The BRET technology and its application to screening assays. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degeling, M.H.; Bovenberg, M.S.; Lewandrowski, G.K.; de Gooijer, M.C.; Vleggeert-Lankamp, C.L.; Tannous, M.; Maguire, C.A.; Tannous, B.A. Directed molecular evolution reveals Gaussia luciferase variants with enhanced light output stability. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3006–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.P.; Patel, K.G.; Manthiram, K.; Swartz, J.R. Multiply mutated Gaussia luciferases provide prolonged and intense bioluminescence. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 389, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkema, F.M.; Escarpizo-Lorenzana, M.I.; Nordentoft, M.K.; Rabe, H.C.; Sahin, C.; Landreh, M.; Branca, R.M.; Sorensen, E.S.; Christensen, B.; Prestel, A.; et al. A suicidal and extensively disordered luciferase with a bright luminescence. Protein Sci. 2024, 33, e5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, S.; Sahara, Y. Identification of two catalytic domains in a luciferase secreted by the copepod Gaussia princeps. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Suzuki, H.; Sato, M.; Tao, H. Superluminescent variants of marine luciferases for bioassays. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8732–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneyx, F.; Mujacic, M. Recombinant protein folding and misfolding in Escherichia coli. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goerke, A.R.; Loening, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Swartz, J.R. Cell-free metabolic engineering promotes high-level production of bioactive Gaussia princeps luciferase. Metab. Eng. 2008, 10, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnayaka, T.; Tawa, M.; Nakamura, T.; Sohya, S.; Kuwajima, K.; Yohda, M.; Kuroda, Y. Solubilization and folding of a fully active recombinant Gaussia luciferase with native disulfide bonds by using a SEP-Tag. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011, 1814, 1775–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayaka, T.; Tawa, M.; Sohya, S.; Yohda, M.; Kuroda, Y. Biophysical characterization of highly active recombinant Gaussia luciferase expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010, 1804, 1902–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markova, S.V.; Larionova, M.D.; Vysotski, E.S. Shining light on the secreted luciferases of marine copepods: Current knowledge and applications. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.L.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.O.; Gye, M.C.; Kim, Y.P. Detection of matrix metalloproteinase activity by bioluminescence via intein-mediated biotinylation of luciferase. Sensors 2018, 18, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurdinger, T.; Badr, C.; Pike, L.; de Kleine, R.; Weissleder, R.; Breakefield, X.O.; Tannous, B.A. A secreted luciferase for monitoring of processes. Nat. Meth. 2008, 5, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, M.P.; Costa, G.L.; Schoettlin, W.; Cline, J.; Mathur, E.; Bauer, J.C. Site-directed mutagenesis of double-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain-reaction. Gene 1994, 151, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).