Simple, Visual, Point-of-Care SARS-CoV-2 Detection Incorporating Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Target DNA–Protein Crosslinking Enhanced Chemiluminescence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Preparation of the SARS-CoV-2 N Gene Plasmid
2.4. Preparation of the IVT RNA
2.5. Preparation of RPA Products
2.6. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Analysis
2.7. SARS-CoV-2 Detection
2.8. Specificity Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Detection
2.9. SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Complex Matrix Systems Simulating Clinical Specimens
3. Results and Discussion
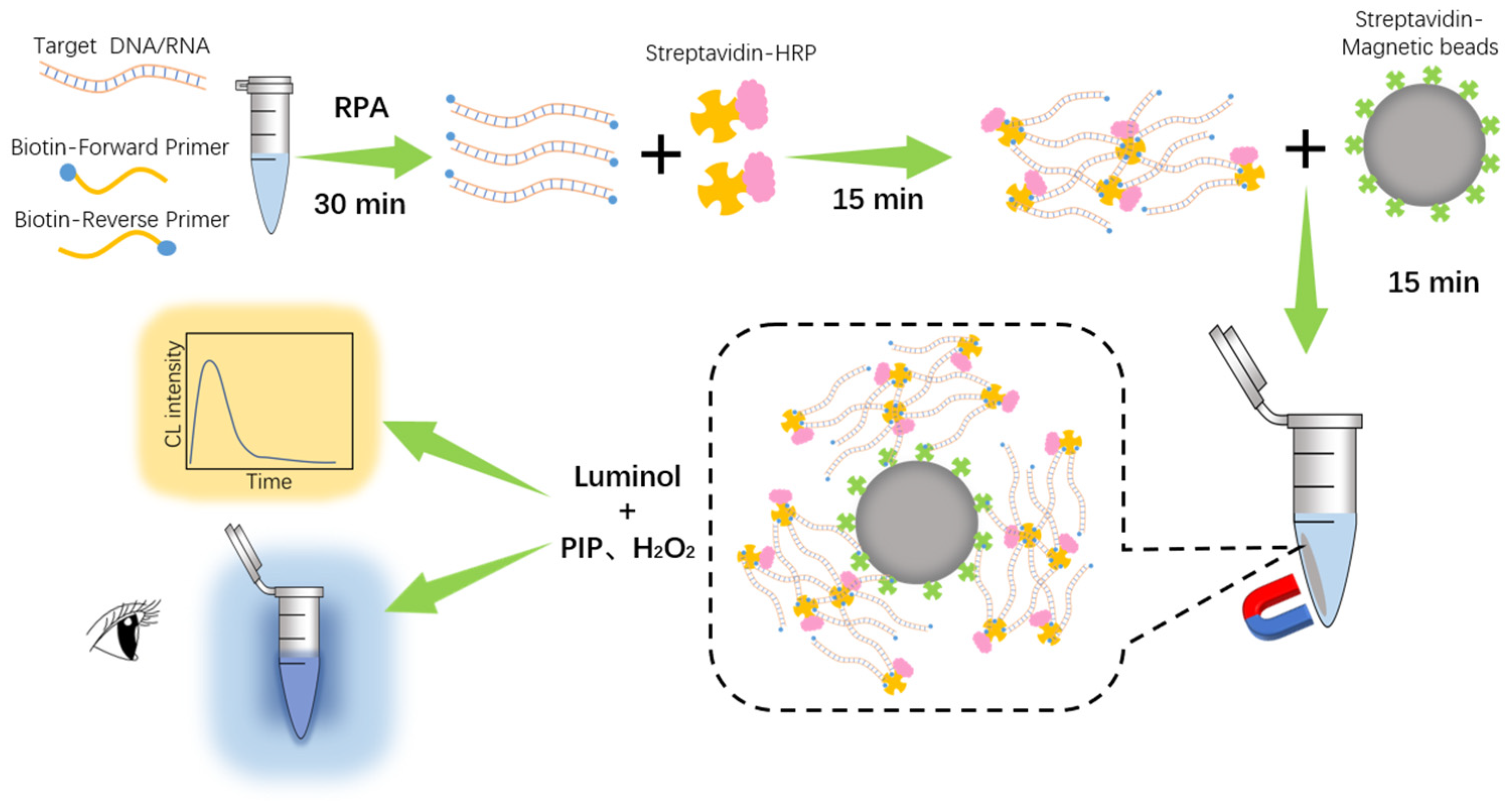
3.1. Working Principle of RPADPCL
3.2. Feasibility Analysis
3.3. Effect of Different Sample Addition Orders of SA-HRP and SA-MB on Signal Output
3.4. Optimization of Reaction Conditions to Enhance RPADPCL Target Detection Performance
3.5. Analytical Sensitivity of RPADPCL for the Detection of Plasmids Containing the SARS-CoV-2 N Gene Sequence
3.6. Analytical Sensitivity of RPADPCL for SARS-CoV-2 IVT RNA Detection
3.7. Specificity Analysis of RPADPCL
3.8. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Simulated Clinical Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carabelli, A.M.; Peacock, T.P.; Thorne, L.G.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; COVID-19 Genomics UK Consortium; Peacock, S.J.; Barclay, W.S.; de Silva, T.I.; Towers, G.J. SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: Immune escape, transmission and fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, P.V.; Ghafari, M.; Beer, M.; Lythgoe, K.; Simmonds, P.; Stilianakis, N.I.; Katzourakis, A. The evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhach, O.; Meyer, B.; Eckerle, I. SARS-CoV-2 viral load and shedding kinetics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- V’kovski, P.; Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Stalder, H.; Thiel, V. Coronavirus biology and replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.-X.; Liu, B.-Z.; Deng, H.-J.; Wu, G.-C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.-K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.-F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.-F. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Rao, Z. Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2 and implications for therapeutic development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L. SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Knox, K.S.; Rios, C.T.; Natt, B.; Bhattacharya, D.; Fain, M.J. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in older adults: What we may expect regarding pathogenesis, immune responses, and outcomes. Geroscience 2020, 42, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiso, M.; Yamayoshi, S.; Iida, S.; Furusawa, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Uraki, R.; Imai, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kawaoka, Y. In vitro and in vivo characterization of SARS-CoV-2 resistance to ensitrelvir. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Kumar, B.K.; Deekshit, V.K.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. Detection technologies and recent developments in the diagnosis of COVID-19 infection. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2021, 105, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalandra, R.; Yadav, A.K.; Verma, D.; Dalal, N.; Sharma, M.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A.; Solanki, P.R. Strategies and perspectives to develop SARS-CoV-2 detection methods and diagnostics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogels, C.B.; Brito, A.F.; Wyllie, A.L.; Fauver, J.R.; Ott, I.M.; Kalinich, C.C.; Petrone, M.E.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Catherine Muenker, M.; Moore, A.J. Analytical sensitivity and efficiency comparisons of SARS-CoV-2 RT–qPCR primer–probe sets. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafeef, M.; Dighe, K.; Moitra, P.; Pan, D. Rapid, ultrasensitive, and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 using antisense oligonucleotides directed electrochemical biosensor chip. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 17028–17045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiani, L.; Saroglia, M.; Galatà, G.; De Santis, R.; Fillo, S.; Luca, V.; Faggioni, G.; D’Amore, N.; Regalbuto, E.; Salvatori, P. Magnetic beads combined with carbon black-based screen-printed electrodes for COVID-19: A reliable and miniaturized electrochemical immunosensor for SARS-CoV-2 detection in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, C.; Qin, Y.; Tan, C.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, Y. A universal platform for one-pot detection of circulating non-coding RNA combining CRISPR-Cas12a and branched rolling circle amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2023, 1246, 340896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Liang, J.; Qiu, L.; Han, D.; Tan, W. Rapid one-pot detection of SARS-CoV-2 based on a lateral flow assay in clinical samples. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3325–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flower, B.; Brown, J.C.; Simmons, B.; Moshe, M.; Frise, R.; Penn, R.; Kugathasan, R.; Petersen, C.; Daunt, A.; Ashby, D. Clinical and laboratory evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 lateral flow assays for use in a national COVID-19 seroprevalence survey. Thorax 2020, 75, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Z.; Huang, L.; Dan, H.; Xiao, W.; Liang, J.; Zou, S.; Tang, Y. Differential diagnosis of PRV-infected versus vaccinated pigs using a novel EuNPs-virus antigen probe-based blocking fluorescent lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, P.; Poon, L.L.M.; Wang, Q. Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, C.; Mei, X.; Yang, L. Achieving broad availability of SARS-CoV-2 detections via smartphone-based analysis. Trac-Trend. Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. Trac-Trend. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, B.; Ochoa-Corona, F.M.; Paret, M.L. Recombinase polymerase amplification applied to plant virus detection and potential implications. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 546, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrmann, O.; Bachmann, I.; Spiegel, M.; Schramm, M.; Abd El Wahed, A.; Dobler, G.; Dame, G.; Hufert, F.T. Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 by low volume real-time single tube reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification using an exo probe with an internally linked quencher (exo-IQ). Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkaoui, D.; Heaney, J.; Huang, D.; Byott, M.; Miller, B.S.; Nastouli, E.; McKendry, R.A. Clinical validation of a rapid variant-proof RT-RPA assay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Tong, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Duan, J.; Lei, X.; Huang, M.; Qiu, Y. Fast and sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA using suboptimal protospacer adjacent motifs for Cas12a. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Qiu, Z.; Bi, Z.; Tian, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, X. Photocontrolled crRNA activation enables robust CRISPR-Cas12a diagnostics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2202034119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelite, T.R.; Uscanga-Palomeque, A.C.; Castellanos-Gonzalez, A.; Melby, P.C.; Travi, B.L. Isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification-lateral flow detection of SARS-CoV-2, the etiological agent of COVID-19. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 296, 114227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.K.; Dhau, J.S.; Gohel, H.; Mishra, Y.K.; Kateb, B.; Kim, N.-Y.; Goswami, D.Y. Electrochemical SARS-CoV-2 sensing at point-of-care and artificial intelligence for intelligent COVID-19 management. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7306–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.J.; Varshavsky, A. Formaldehyde-mediated DNA-protein crosslinking: A probe for in vivo chromatin structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 6470–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.; Weinfeld, M.; Murray, D. DNA–protein crosslinks: Their induction, repair, and biological consequences. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. 2005, 589, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, C.M. Semisynthetic DNA–protein conjugates for biosensing and nanofabrication. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2010, 49, 1200–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretyakova, N.Y.; Groehler, A., IV; Ji, S. DNA–protein cross-links: Formation, structural identities, and biological outcomes. Accounts Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1631–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K. Programmable self-assembly of DNA–protein hybrid hydrogel for enzyme encapsulation with enhanced biological stability. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeeva, I.I.; Vakh, C.S.; Bulatov, A.V.; Worsfold, P.J. Flow analysis with chemiluminescence detection: Recent advances and applications. Talanta 2018, 179, 246–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Y. Long-lasting chemiluminescence-based POCT for portable and visual pathogenic detection and in situ inactivation. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8382–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Huang, X.; Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; Fan, M.; Gong, Z. Applications of nanomaterial-based chemiluminescence sensors in environmental analysis. Trac-Trend. Anal. Chem. 2022, 158, 116879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Wang, D.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, X. Dual gold nanoparticle/chemiluminescent immunoassay for sensitive detection of multiple analytes. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 6628–6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapeluich, Y.L.; Rubtsova, M.Y.; Egorov, A.M. Enhanced chemiluminescence reaction applied to the study of horseradish peroxidase stability in the course of p-iodophenol oxidation. J. Biolumi. Chemilumi. 1997, 12, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, A. Enhancement effect of p-iodophenol on gold nanoparticle-catalyzed chemiluminescence and its applications in detection of thiols and guanidine. Talanta 2018, 182, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Qin, P.; He, J.; Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, X. Rapid and simultaneous visual screening of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virufses with customized isothermal amplification integrated lateral flow strip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 197, 113771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, E.; Jiang, L.; Tian, T.; Hu, M.; Yue, H.; Huang, M.; Lin, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, X. Simultaneous dual-gene diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 based on CRISPR/Cas9-mediated lateral flow assay. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2021, 60, 5307–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Boswell, S.A.; Chidley, C.; Lu, Z.-x.; Pettit, M.E.; Gaudio, B.L.; Fajnzylber, J.M.; Ingram, R.T.; Ward, R.H.; Li, J.Z. An enhanced isothermal amplification assay for viral detection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, D.; Zhu, M.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. A microfluidic-integrated lateral flow recombinase polymerase amplification (MI-IF-RPA) assay for rapid COVID-19 detection. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Tian, D.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lyon, C.J.; Lai, W.; Fusco, D.; Drouin, A.; Yin, X.; Hu, T. Ultra-sensitive and high-throughput CRISPR-p owered COVID-19 diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 164, 112316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.S.; Pan, J.; Li, F.; Zhu, M.; Xu, M.; Zhu, H.; Yu, Y.; Su, G. Reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification coupled with CRISPR-Cas12a for facile and highly sensitive colorimetric SARS-CoV-2 detection. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4126–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Ge, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, B.; Cui, L. A reverse-transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for the rapid detection of N gene of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Virology 2020, 549, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Du, B.; Cui, J.; Yan, C.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y. Reverse-transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for rapid detection of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9699–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Wahed, A.A.; Patel, P.; Maier, M.; Pietsch, C.; Rüster, D.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Kissenkötter, J.; Behrmann, O.; Frimpong, M.; Diagne, M.M. Suitcase lab for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 based on recombinase polymerase amplification assay. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 2627–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkaoui, D.; Huang, D.; Miller, B.S.; Turbé, V.; McKendry, R.A. Harnessing recombinase polymerase amplification for rapid multi-gene detection of SARS-CoV-2 in resource-limited settings. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Sfeir, M.M.; Ballesteros, E.; Liu, C. Autonomous lab-on-paper for multiplexed, CRISPR-based diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample No. | Spiked (Copies) | CL Intensity (a.u.) | Found a (Copies) | Recovery b (%) | RSD c (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 4.87 × 105 | 95 ± 15 | 95% | 15.8% |
| 4.93 × 105 | |||||
| 3.87 × 105 | |||||
| 2 | 300 | 1.29 × 106 | 309 ± 35 | 103% | 11.3% |
| 1.41 × 106 | |||||
| 1.14 × 106 |
| Sample No. | Spiked (Copies) | CL Intensity (a.u.) | Found a (Copies) | Recovery b (%) | RSD c (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 2.67 × 105 | 96 ± 13 | 96% | 13.5% |
| 2.92 × 105 | |||||
| 2.32 × 105 | |||||
| 2 | 500 | 9.51 × 105 | 432 ± 21 | 86.4% | 4.9% |
| 1.04 × 106 | |||||
| 9.79 × 105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Xu, N.; Feng, Y.; Fang, K.; Tan, C.; Tan, Y. Simple, Visual, Point-of-Care SARS-CoV-2 Detection Incorporating Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Target DNA–Protein Crosslinking Enhanced Chemiluminescence. Biosensors 2024, 14, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14030135
Chen H, Zhuang Z, Xu N, Feng Y, Fang K, Tan C, Tan Y. Simple, Visual, Point-of-Care SARS-CoV-2 Detection Incorporating Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Target DNA–Protein Crosslinking Enhanced Chemiluminescence. Biosensors. 2024; 14(3):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14030135
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hui, Zhiyuan Zhuang, Naihan Xu, Ying Feng, Kaixin Fang, Chunyan Tan, and Ying Tan. 2024. "Simple, Visual, Point-of-Care SARS-CoV-2 Detection Incorporating Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Target DNA–Protein Crosslinking Enhanced Chemiluminescence" Biosensors 14, no. 3: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14030135
APA StyleChen, H., Zhuang, Z., Xu, N., Feng, Y., Fang, K., Tan, C., & Tan, Y. (2024). Simple, Visual, Point-of-Care SARS-CoV-2 Detection Incorporating Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and Target DNA–Protein Crosslinking Enhanced Chemiluminescence. Biosensors, 14(3), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14030135






