Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Virus via Fiber-Optic and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Aptasensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. MCP–SELEX Procedure
2.3. Affinity Determination and Specificity Tests of Aptamers via ELONA
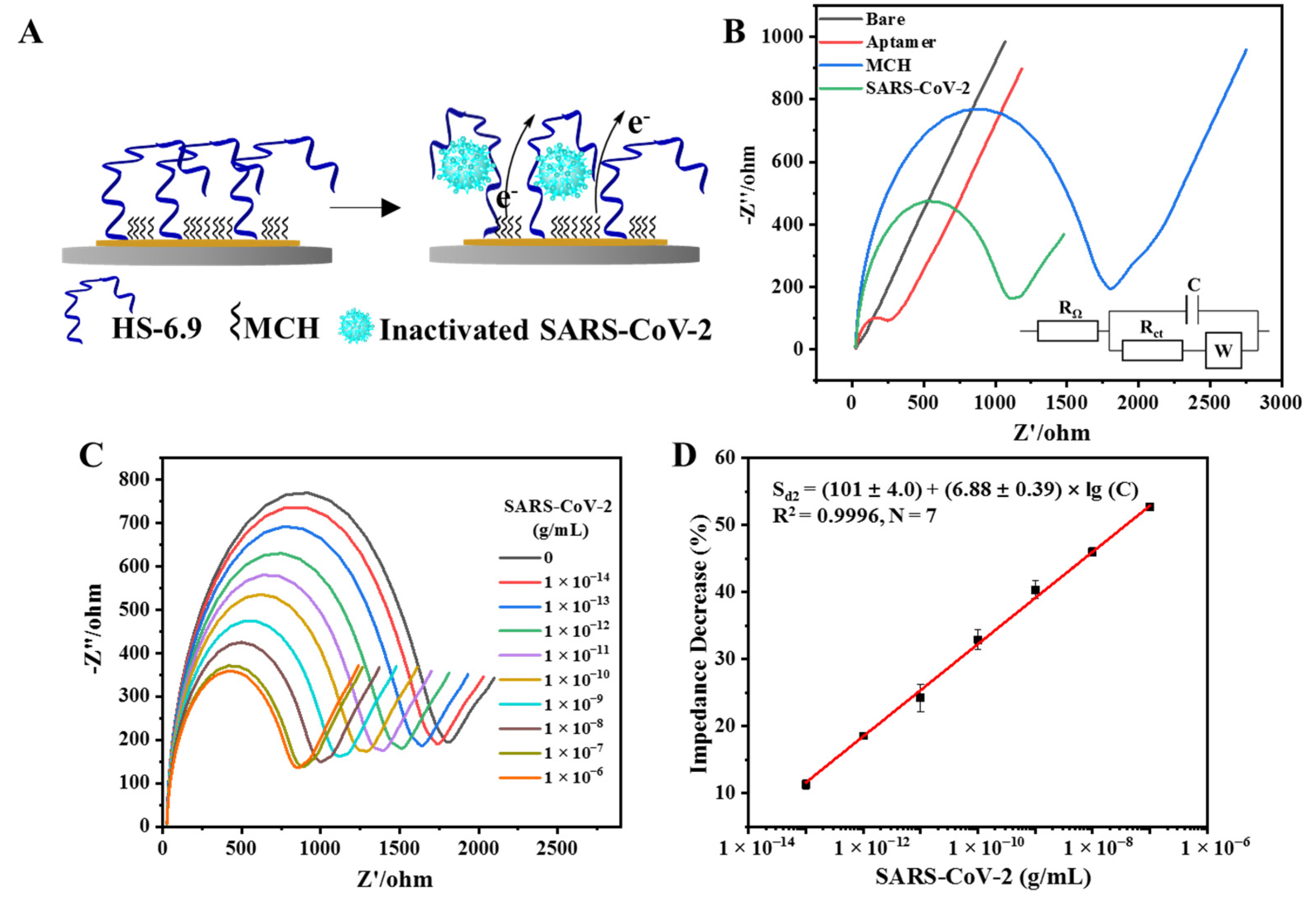
2.4. Fabrication of the FOEW Aptasensor
2.5. Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 with the FOEW Aptasensor
2.6. Fabrication of the EIS Aptasensor
2.7. Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 with the EIS Aptasensor
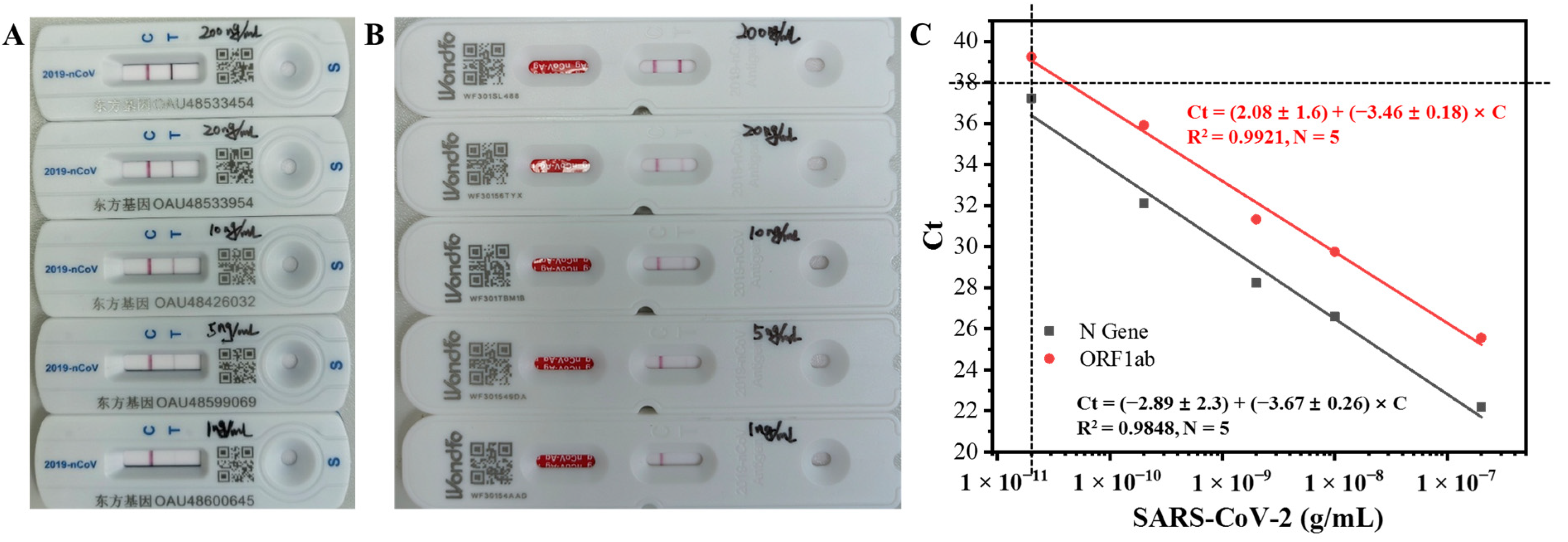
2.8. Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 with Commercial Colloidal Gold Test Strips and RT-PCR
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Aptamer Selection for Inactivated SARS-CoV-2
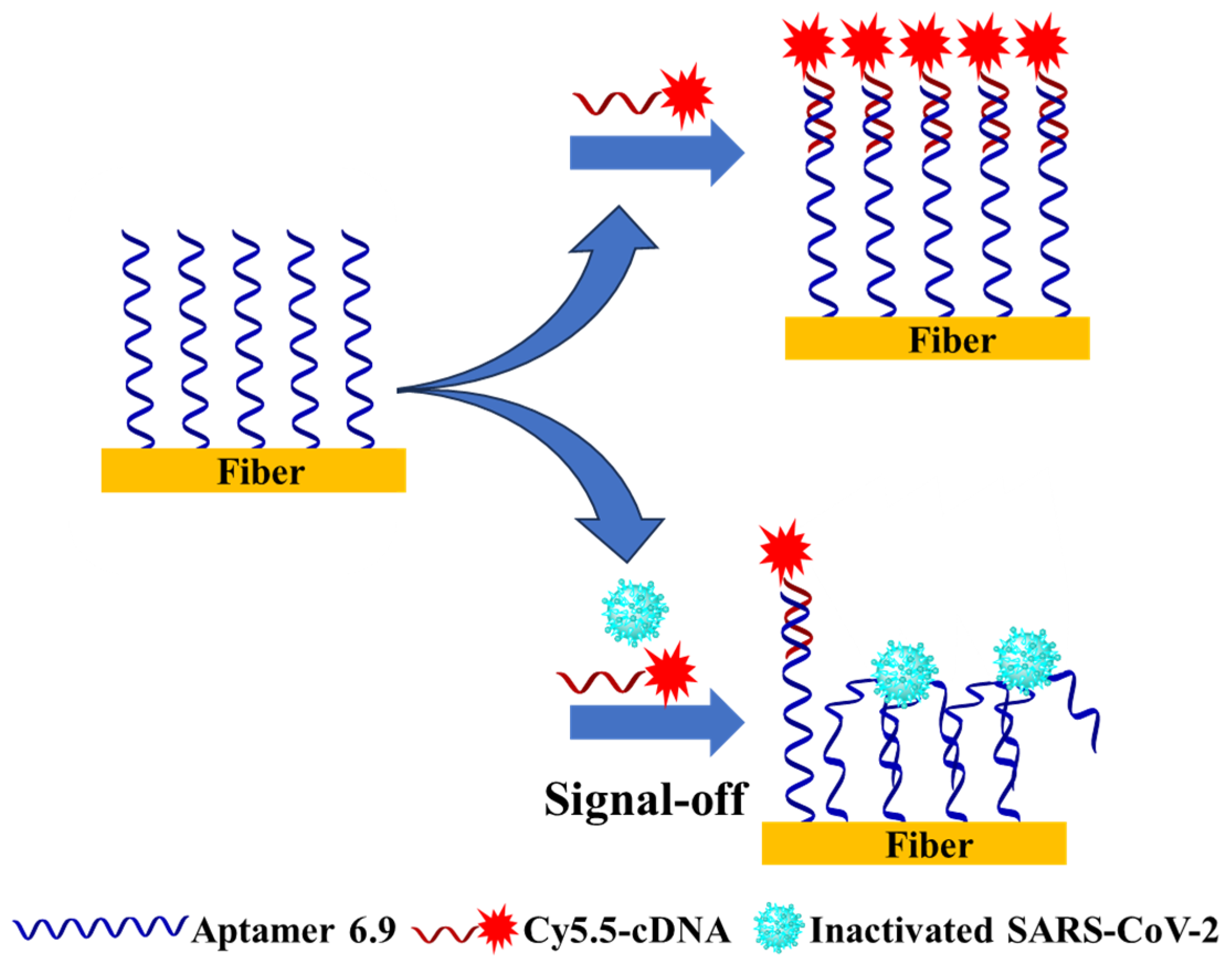
3.2. Establishment of the FOEW Aptasensor for the Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2
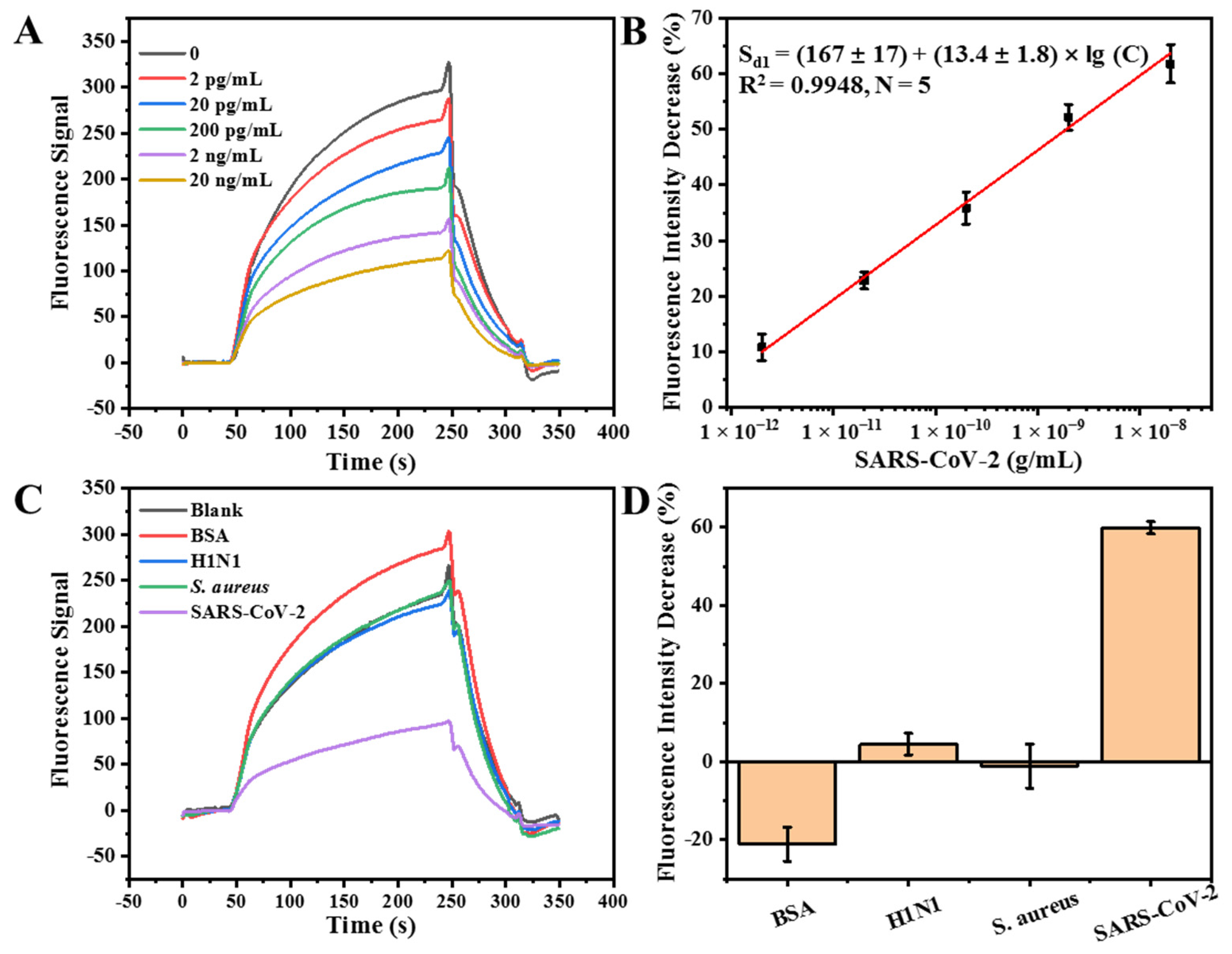
3.3. Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 with the FOEW Aptasensor
3.4. Establishment of the EIS Aptasensor for the Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2
3.5. Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 with the EIS Aptasensor
3.6. Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pekosz, A.; Parvu, V.; Li, M.; Andrews, J.C.; Manabe, Y.C.; Kodsi, S.; Gary, D.S.; Roger-Dalbert, C.; Leitch, J.; Cooper, C.K. Antigen-Based Testing but Not Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Correlates with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Viral Culture. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, R.; Moradi, N.; Abdi, M. RRT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2: Analytical Considerations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 516, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, W.R.; Lukas, H.; Torres, M.D.T.; Gao, W.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Low-Cost Biosensor Technologies for Rapid Detection of COVID-19 and Future Pandemics. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 1757–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Bao, N.; Kim, Y.; Jang, H.W. Rapid Assays of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Noble Biosensors by Nanomaterials. Nano Converg. 2024, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.M.; Rodríguez, D.N.; Palop, N.T.; Arenas, R.O.; Córdoba, M.M.; Mochón, M.D.O.; Cardona, C.G. Comparison of Commercial Lateral Flow Immunoassays and ELISA for SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubas-Atienzar, A.I.; Kontogianni, K.; Edwards, T.; Wooding, D.; Buist, K.; Thompson, C.R.; Williams, C.T.; Patterson, E.I.; Hughes, G.L.; Baldwin, L.; et al. Limit of Detection in Different Matrices of 19 Commercially Available Rapid Antigen Tests for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In Vitro Selection of RNA Molecules That Bind Specific Ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment: RNA Ligands to Bacteriophage T4 DNA Polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Csordas, A.T.; Wang, J.; Oh, S.S.; Eisenstein, M.S.; Soh, H.T. Rapid and Label-Free Strategy to Isolate Aptamers for Metal Ions. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7558–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Mitchell, N.M.; Banerjee, S.; Cheng, Z.; Taylor, S.; Kostic, A.M.; Wong, I.; Sajjath, S.; Zhang, Y.; Stevens, J.; et al. A Functional Group–Guided Approach to Aptamers for Small Molecules. Science 2023, 380, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Wang, Y.; Wen, C.; Davis, B.; Wang, X.; Lee, K.; Wang, Y. High-Affinity One-Step Aptamer Selection Using a Non-Fouling Porous Hydrogel. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xu, H.; Ding, H.; Huang, Y.; Cao, X.; Yang, G.; Li, J.; Xie, Z.; Meng, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Identification of an Aptamer Targeting HnRNP A1 by Tissue Slide-Based SELEX. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wan, J.; Wen, X.; Guo, Q.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, K. Identification of a New DNA Aptamer by Tissue-SELEX for Cancer Recognition and Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7369–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Tian, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, K.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. Aptamer-Based Lateral Flow Assay on-Site Biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 186, 113279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.F.; Ling, M.; Kacherovsky, N.; Pun, S.H. Aptamers 101: Aptamer Discovery and in Vitro Applications in Biosensors and Separations. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 4961–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandtke, T.; Wędrowska, E.; Szczur, M.; Przybylski, G.; Libura, M.; Kopiński, P. Aptamers-Diagnostic and Therapeutic Solution in SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasserre, P.; Balansethupathy, B.; Vezza, V.J.; Butterworth, A.; Macdonald, A.; Blair, E.O.; McAteer, L.; Hannah, S.; Ward, A.C.; Hoskisson, P.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Aptasensors Based on Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Low-Cost Gold Electrode Substrates. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.F.; Kacherovsky, N.; Liang, J.; Salipante, S.J.; Pun, S.H. SCORe: SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant RBD-Binding DNA Aptamer for Multiplexed Rapid Detection and Pseudovirus Neutralization. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 12683–12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aithal, S.; Mishriki, S.; Gupta, R.; Sahu, R.P.; Botos, G. SARS-CoV-2 Detection with Aptamer-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles. Talanta 2022, 236, 122841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Xiong, Y.; Ren, S.; Dwivedy, A.; Magazine, N.; Zhou, L.; Jin, X.; Zhang, T.; Cunningham, B.T.; Yao, S.; et al. Net-Shaped DNA Nanostructures Designed for Rapid/Sensitive Detection and Potential Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 20214–20228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Song, J.; Wei, X.; Huang, M.; Sun, M.; Zhu, L.; Lin, B.; Shen, H.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. Discovery of aptamers targeting the receptor-binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9895–9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Pasquardini, L.; Arcadio, F.; Lunelli, L.; Vanzetti, L.; Carafa, V.; Altucci, L.; Zeni, L. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein detection through a plasmonic d-shaped plastic optical fiber aptasensor. Talanta 2021, 233, 122532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, T.; Giroux, E.; Jovic, M.; Martic-Milne, S. Localized surface plasmon resonance aptasensor for selective detection of SARS-CoV-2 s1 protein. Analyst 2021, 146, 7207–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Xing, W.; Luo, H.; Ji, H.; Fang, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, L. CRISPR/Cas12a-Derived Electrochemical Aptasensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Nucleocapsid Protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 200, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Liu, X.; Ou, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Z. Discovery of Sandwich Type COVID-19 Nucleocapsid Protein DNA Aptamers. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 10235–10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mao, J.; Hou, M.; Hu, Z.; Sun, G.; Zhang, S. A Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Profiling Assay with High Sensitivity Comparable to Nucleic Acid Detection. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 14627–14634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liang, Z.; Hu, O.; He, Q.; Sun, D.; Chen, Z. An electrochemical dual-aptamer biosensor based on metal-organic frameworksmil-53 decorated with au@pt nanoparticles and enzymes for detection of COVID-19 nucleocapsid protein. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 387, 138553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, S.; Gopinath, S.C.B.; Ismail, Z.H.; Md Arshad, M.K.; Poopalan, P. Aptasensing nucleocapsid protein on nanodiamond assembled gold interdigitated electrodes for impedimetric SARS-CoV-2 infectious disease assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 197, 113735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-C.; Sun, A.Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-H.; Wang, S.-C.; Chau, L.-K. Integration of Power-Free and Self-Contained Microfluidic Chip with Fiber Optic Particle Plasmon Resonance Aptasensor for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein. Biosensors 2022, 12, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Lu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Ding, H.; Li, H.; Dong, J.; Huang, A.; Fang, T.; et al. Aptamer Selection and Application in Multivalent Binding-Based Electrical Impedance Detection of Inactivated H1N1 Virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Diao, D.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Ding, X.; Shangguan, D.; Lou, X. Speeding up in Vitro Discovery of Structure-Switching Aptamers via Magnetic Cross-Linking Precipitation. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13383–13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Y.; et al. Selection of Regioselective DNA Aptamer for Detection of Homocysteine in Nondeproteinized Human Plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 237, 115528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Song, D.; Jiang, B.; Guo, X.; Liu, W.; Long, F.; Song, H.; Hao, R. Rapid and Universal Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza A Virus Using a Reusable Dual-Channel Optic Fiber Immunosensor. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5325–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Zhu, A.; Wang, H. Optofluidics-Based DNA Structure-Competitive Aptasensor for Rapid on-Site Detection of Lead(II) in an Aquatic Environment. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 849, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, L.; Mei, X.; Xu, W. A Sandwich-Based Evanescent Wave Fluorescent Biosensor for Simple, Real-Time Exosome Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 200, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolai, S.; Tabib-Azar, M. Whole Virus Detection Using Aptamers and Paper-based Sensor Potentiometry. Med. Devices Sens. 2020, 3, e10112. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, T.; Ahn, J.H. Aptamer-Based Field-Effect Transistor for Detection of Avian Influenza Virus in Chicken Serum. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 5524–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmangali, A.; Dukenbayev, K.; Kanayeva, D. Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Using an Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Aptasensor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, D.K.; Bodily, T.; Karkisaval, A.G.; Dong, Y.; Natani, S.; Ramanathan, A.; Ramil, A.; Srivastava, S.; Bandaru, P.; Glinsky, G.; et al. Rapid Self-Test of Unprocessed Viruses of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants in Saliva by Portable Wireless Graphene Biosensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2206521119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Bao, L.; Mao, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, N.; Lv, Z.; et al. Development of an Inactivated Vaccine Candidate for SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldéus, T.; Nordenström, M.; Carlmark, A.; Wågberg, L.; Malmström, E. Insights into the EDC-Mediated PEGylation of Cellulose Nanofibrils and Their Colloidal Stability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Ding, H.; Xu, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, N.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Combining Use of a Panel of SsDNA Aptamers in the Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 4621–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razumovitch, J.; De França, K.; Kehl, F.; Wiki, M.; Meier, W.; Vebert, C. Optimal Hybridization Efficiency upon Immobilization of Oligonucleotide Double Helices. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 8383–8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Lai, R.Y.; Plaxco, K.W. Preparation of Electrode-Immobilized, Redox-Modified Oligonucleotides for Electrochemical DNA and Aptamer-Based Sensing. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2875–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Hench, L.L. Effect of Taper Geometries and Launch Angle on Evanescent Wave Penetration Depth in Optical Fibers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, Y.; Goda, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Yamaoka, S.; Miyahara, Y. Gold Nanoparticles with Ligand/Zwitterion Hybrid Layer for Individual Counting of Influenza A H1N1 Subtype Using Resistive Pulse Sensing. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, K.L.D.M.; Trombetta, R.; Nishitani, K.; Bello-irizarry, S.N.; Ninomiya, M.; Zhang, L.; Chung, H.L.; Mcgrath, J.L.; Daiss, J.L.; Awad, H.A.; et al. Evidence of Staphylococcus Aureus Deformation, Proliferation and Migration in Canaliculi of Live Cortical Bone in Murine Models of Osteomyelitis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2018, 32, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicker, L.R.; Kummari, S.; Keerthanaa, M.R.; Rao Bommi, J.; Koteshwara Reddy, K.; Yugender Goud, K. Trends and Challenges in Electroanalytical Biosensing Methodologies for Infectious Viral Diseases. Bioelectrochemistry 2024, 156, 108594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochia, R. Electrochemical Biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 Detection: Voltametric or Impedimetric Transduction? Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 147, 108190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, C.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Huang, A.; Wang, L.; Lou, X.; Gao, B.; Shao, N. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Virus via Fiber-Optic and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Aptasensors. Biosensors 2024, 14, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050231
Xiao C, Wang N, Zhao Y, Liu X, Li H, Huang A, Wang L, Lou X, Gao B, Shao N. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Virus via Fiber-Optic and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Aptasensors. Biosensors. 2024; 14(5):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050231
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Can, Nan Wang, Yuechao Zhao, Xuemei Liu, Hui Li, Aixue Huang, Lin Wang, Xinhui Lou, Bo Gao, and Ningsheng Shao. 2024. "Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Virus via Fiber-Optic and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Aptasensors" Biosensors 14, no. 5: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050231
APA StyleXiao, C., Wang, N., Zhao, Y., Liu, X., Li, H., Huang, A., Wang, L., Lou, X., Gao, B., & Shao, N. (2024). Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Virus via Fiber-Optic and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Aptasensors. Biosensors, 14(5), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios14050231




