Attention Affecting Response Inhibition in Overweight Adults with Food Addiction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
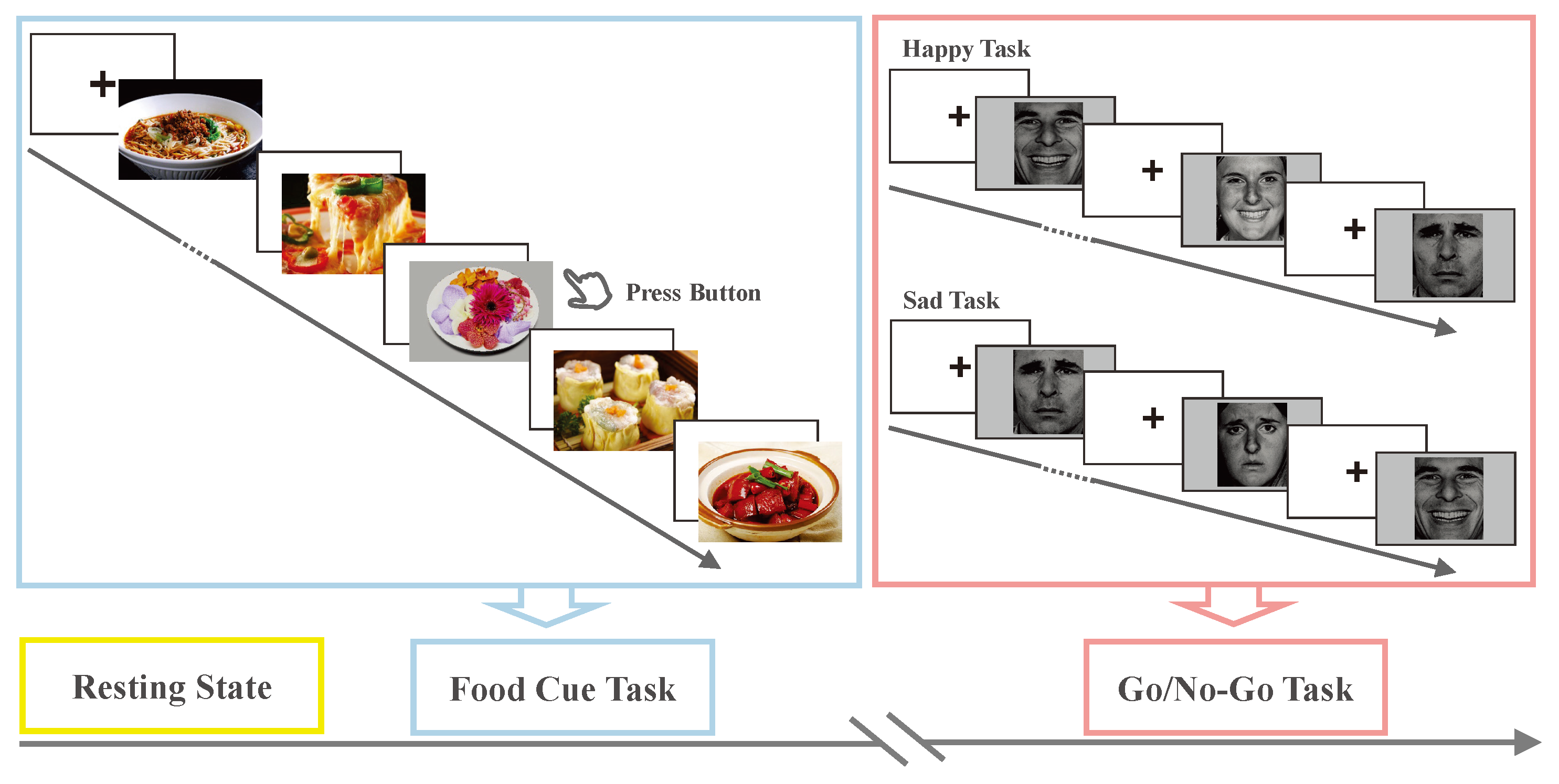
2.2. Experimental Design and Task Paradigm
2.3. EEG Microstate Analysis
2.4. ERP Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Behavioral Test
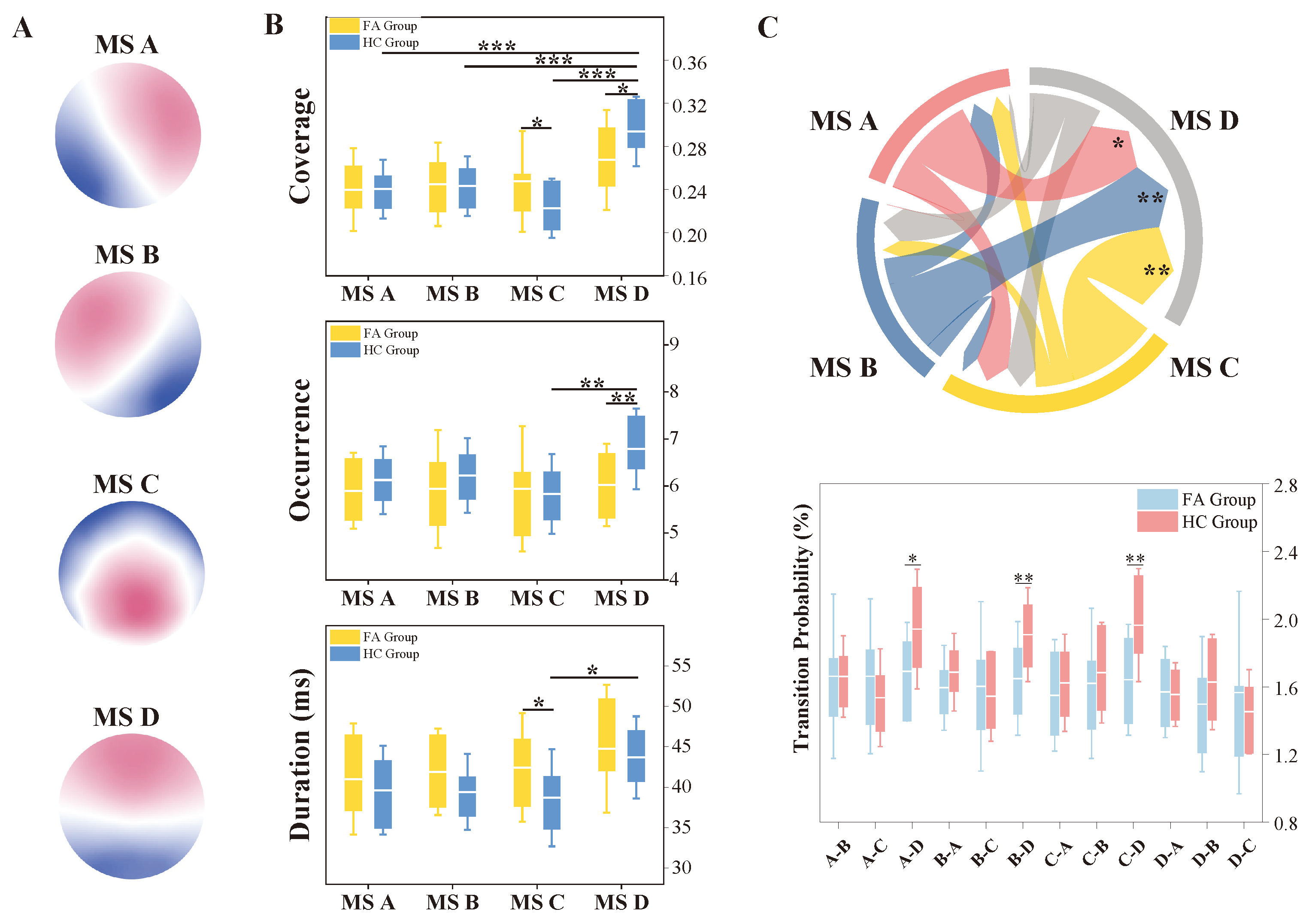
3.3. EEG Microstate Characteristics
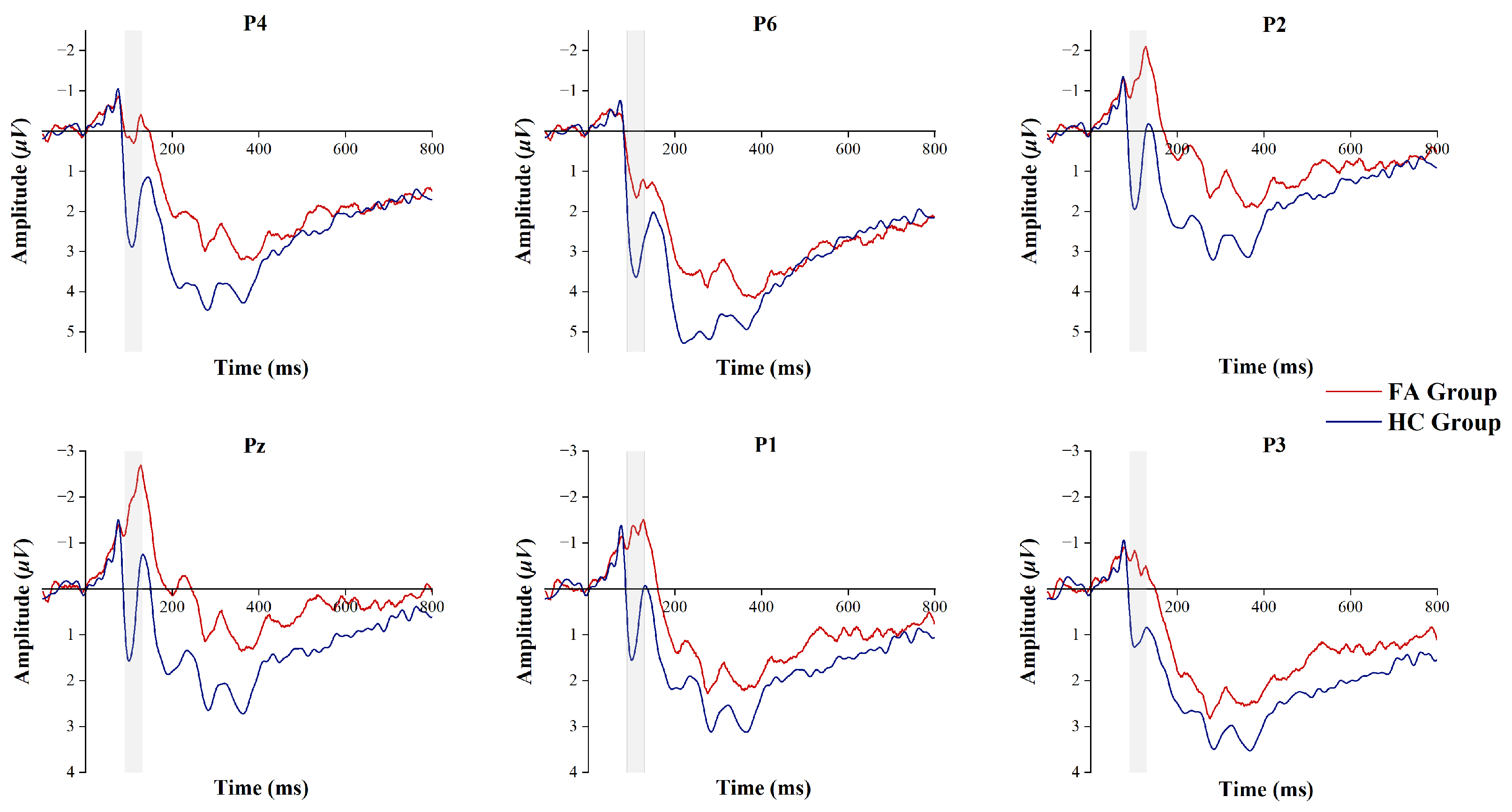
3.4. P100 Component
3.5. Correlations Between EEG Characteristics and Behavioral Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schulte, E.; Gearhardt, A. Attributes of the food addiction phenotype within overweight and obesity. Eat. Weight. Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2021, 26, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, D.; Manning, P.; Leong, S.L.; Ross, S.; Sutherland, W.; Horwath, C.; Vanneste, S. The brain, obesity and addiction: An EEG neuroimaging study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzerouk, F.; Gierski, F.; Ducluzeau, P.H.; Bourbao-Tournois, C.; Gaubil-Kaladjian, I.; Bertin, É.; Kaladjian, A.; Ballon, N.; Brunault, P. Food addiction, in obese patients seeking bariatric surgery, is associated with higher prevalence of current mood and anxiety disorders and past mood disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 267, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pursey, K.M.; Stanwell, P.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Collins, C.E.; Burrows, T.L. The prevalence of food addiction as assessed by the Yale Food Addiction Scale: A systematic review. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4552–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.C.; Sedgmond, J.; Maizey, L.; Chambers, C.D.; Lawrence, N.S. Food addiction: Implications for the diagnosis and treatment of overeating. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhardt, A. Current Considerations Regarding Food Addiction. J. Behav. Addict. 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, N.S.; Porter, L.; Staiger, P.K. The ‘Go’s and the ‘No-Go’s of response-inhibition training to food: Lessons learned from trials. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2022, 48, 101229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, B.; Lawrence, N.S. Giving pork the chop: Response inhibition training to reduce meat intake. Appetite 2019, 141, 104315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGreen, J.; Kemps, E.; Tiggemann, M. The effectiveness of Go/No-Go and Stop-Signal training in reducing food consumption and choice: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Appetite 2024, 195, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Roefs, A.; Nederkoorn, C. Fluctuations in attentional bias for food and the role of executive control. Appetite 2022, 168, 105761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.; Lee, M.; Higgs, S. Food-specific response inhibition, dietary restraint and snack intake in lean and overweight/obese adults: A moderated-mediation model. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardee, J.E.; Phaneuf, C.; Cope, L.; Zucker, R.; Gearhardt, A.; Heitzeg, M. Neural correlates of inhibitory control in youth with symptoms of food addiction. Appetite 2020, 148, 104578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meule, A.; Lutz, A.; Vögele, C.; Kübler, A. Women with elevated food addiction symptoms show accelerated reactions, but no impaired inhibitory control, in response to pictures of high-calorie food-cues. Eat. Behav. 2012, 13, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stice, E.; Yokum, S.; Nelson, T.D.; Berkman, E.; Veling, H.; Lawrence, N. Efficacy of a combined food-response inhibition and attention training for weight loss. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2022, 46, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.L.; Lee, J.H. Attentional bias to high-calorie food in binge eaters with high shape/weight concern. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 606296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Associations with overeating and obesity. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2010, 12, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, E.M.; Yokum, S.; Jahn, A.; Gearhardt, A.N. Food cue reactivity in food addiction: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 208, 112574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajehpour, H.; Mohagheghian, F.; Bakht, S.; Samadzadehaghdam, N.; Eqlimi, E.; Makkiabadi, B. Event-related potential correlates of biased cognitive processing and control in substance abusers: A review. Front. Biomed. Technol. 2019, 6, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, V.P.; Fan, S.; Hillyard, S.A. Identification of early visual evoked potential generators by retinotopic and topographic analyses. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1994, 2, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviram-Friedman, R.; Kafri, L.; Baz, G.; Alyagon, U.; Zangen, A. Prisoners of addictive cues: Biobehavioral markers of overweight and obese adults with food addiction. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, J.; Ardelt-Gattinger, E.; Paulmichl, K.; Weghuber, D.; Blechert, J. Dietary restraint and impulsivity modulate neural responses to food in adolescents with obesity and healthy adolescents. Obesity 2015, 23, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehr, T.; Wiedenmann, P.; Herrmann, M. Nicotine Stroop and addiction memory—An ERP study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2006, 62, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohue, S.E.; Woldorff, M.G.; Hopf, J.M.; Harris, J.A.; Heinze, H.J.; Schoenfeld, M.A. An electrophysiological dissociation of craving and stimulus-dependent attentional capture in smokers. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 16, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, G.; Kornreich, C.; Maurage, P.; Noël, X.; Letesson, C.; Verbanck, P.; Campanella, S. Early attentional modulation by alcohol-related cues in young binge drinkers: An event-related potentials study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, M.; Schmidt, R.; Hilbert, A. Abnormalities in the EEG power spectrum in bulimia nervosa, binge-eating disorder, and obesity: A systematic review. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2019, 27, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.D.; Zhang, H.W.; Xu, T.; Liu, L.; Cai, H.T.; Liu, Z.Q.; Li, Q.; Zheng, H.; Xu, T.; Yuan, T.F. How impulsiveness influences obesity: The mediating effect of resting-state brain activity in the dlPFC. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 873953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, A.; Vainik, U.; Garcia-Garcia, I.; Dagher, A. Overlapping neural endophenotypes in addiction and obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Kang, Q.; Li, X.; Tian, M.; Lv, H.; He, J. Temporal and spatial variability of dynamic microstate brain network in disorders of consciousness. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britz, J.; Van De Ville, D.; Michel, C.M. BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Jia, H.; Wu, X.; Yu, D.; Feng, Y. Altered resting-state EEG microstate parameters and enhanced spatial complexity in male adolescent patients with mild spastic diplegia. Brain Topogr. 2017, 30, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ke, Y.; Ni, G.; Liu, S.; Ming, D. Evidence for modulation of EEG microstates by mental workload levels and task types. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2023, 45, e26552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Lyu, X.; Zheng, Q.; He, H.; Jin, R.; Peng, W. Temporal dynamics of electroencephalographic microstates during sustained pain. Cerebral Cortex 2023, 33, 8594–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.B.; Li, X.Y.; Xu, M.; He, Z.J.; Jiang, H. The effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on electroencephalography microstates of patients with heroin-addiction. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2023, 329, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Férat, V.; Arns, M.; Deiber, M.P.; Hasler, R.; Perroud, N.; Michel, C.M.; Ros, T. Electroencephalographic microstates as novel functional biomarkers for adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2022, 7, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushnie, A.K.; Tang, W.; Heilbronner, S.R. Connecting Circuits with Networks in Addiction Neuroscience: A Salience Network Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S. Differences in EEG microstate induced by gaming: A comparison between the gaming disorder individual, recreational game users and healthy controls. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 32549–32558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yue, J.; Wang, Y.; Zou, F.; Zhang, M.; Wu, X. Negative effects of mobile phone addiction tendency on spontaneous brain microstates: Evidence from resting-state EEG. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 636504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunault, P.; Berthoz, S.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Gierski, F.; Kaladjian, A.; Bertin, E.; Tchernof, A.; Biertho, L.; de Luca, A.; Hankard, R.; et al. The modified Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0: Validation among non-clinical and clinical French-speaking samples and comparison with the full Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 480671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escrivá-Martínez, T.; Galiana, L.; Herrero, R.; Rodríguez-Arias, M.; Fernández-Aranda, F.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Baños, R.M. Food addiction and its relationship with other eating behaviours among Spanish university students. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Schulte, E.M.; Cui, G.; Li, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, H. Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the modified Yale Food Addiction Scale version 2.0 (C-mYFAS 2.0): Prevalence of food addiction and relationship with resilience and social support. Eat. Weight. Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2022, 27, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, E.M.; Gearhardt, A.N. Development of the modified Yale food addiction scale version 2.0. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2017, 25, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tong, T.; Gao, Y.; Liang, C.; Yu, H.; Li, S.; Yan, X.; Wang, L. Translation of the Chinese version of the modified Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0 and its validation among college students. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammela, L.I.; Pääkkönen, A.; Karhunen, L.J.; Karhu, J.; Uusitupa, M.I.; Kuikka, J.T. Brain electrical activity during food presentation in obese binge-eating women. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2010, 30, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobera, I.J. Neurophysiological Basis of Food Craving. In State of the Art of Therapeutic Endocrinology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A.; Kaneko, D.; De Kruijf, I.; Ushiama, S.; Van Schaik, M.G.; Brouwer, A.M.; Kallen, V.; Van Erp, J.B.F. CROCUFID: A cross-cultural food image database for research on food elicited affective responses. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, J.; Young, K.D.; Hong, W.; Ma, R.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hampson, M.; Hendler, T.; Zhang, X. Effect of deactivation of activity patterns related to smoking cue reactivity on nicotine addiction. Brain 2019, 142, 1827–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, L.; Nation, K. Go or no-go? Developmental improvements in the efficiency of response inhibition in mid-childhood. Dev. Sci. 2008, 11, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, U.; Chen, E.; Neighbors, C.; Hunter, D.; Lo, T.; Larimer, M. Difficulties regulating emotions: Do binge eaters have fewer strategies to modulate and tolerate negative affect? Eat. Behav. 2007, 8, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.D.; Ekman, P. Facial areas and emotional information. J. Commun. 1975, 25, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, L.; Zhang, J. +microstate: A MATLAB toolbox for brain microstate analysis in sensor and cortical EEG/MEG. Neuroimage 2022, 258, 119346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Dai, L.; Sun, Z.; Liang, Z. Adaptive Spatial-Temporal Aware Graph Learning for EEG-Based Emotion Recognition. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2024, 5, 0088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.; Faber, P.L.; Galderisi, S.; Herrmann, W.M.; Kinoshita, T.; Koukkou, M.; Mucci, A.; Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Saito, N.; Wackermann, J.; et al. EEG microstate duration and syntax in acute, medication-naive, first-episode schizophrenia: A multi-center study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2005, 138, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baradits, M.; Bitter, I.; Czobor, P. Multivariate patterns of EEG microstate parameters and their role in the discrimination of patients with schizophrenia from healthy controls. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 288, 112938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, N.; Luo, X.; Zheng, S.; Yao, D.; Zhao, M.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Calhoun, V.D.; Sun, L.; Sui, J. Aberrant brain dynamics and spectral power in children with ADHD and its subtypes. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2023, 32, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, M.; Liu, P.; Hu, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, A.; Sun, N.; Wang, Y.; et al. EEG microstates as markers of major depressive disorder and predictors of response to SSRIs therapy. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 116, 110514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.; Bu, J.; Zeng, G.Q.; Gou, H.; Liu, M.; Cui, G.; Zhang, X. Correlation between abnormal brain network activity and electroencephalogram microstates on exposure to smoking-related cues. BJPsych Open 2023, 9, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xue, T.; Ren, Y.; Lv, X.; et al. Altered resting-state electroencephalography microstate characteristics in young male smokers. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1008007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, I.; Jurado, M.Á.; Garolera, M.; Segura, B.; Sala-Llonch, R.; Marqués-Iturria, I.; Pueyo, R.; Sender-Palacios, M.J.; Vernet-Vernet, M.; Narberhaus, A.; et al. Alterations of the salience network in obesity: A resting-state fMRI study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visintin, E.; Panfilis, C.D.; Antonucci, C.; Capecci, C.; Marchesi, C.; Sambataro, F. Parsing the intrinsic networks underlying attention: A resting state study. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 278, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, I.H.; Tsai, S.Y.; Duann, J.R. Inhibition control and error processing in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: An event-related potentials study. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2011, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, L.; Pan, T.; Nie, Y. Automatic processing advantage of cartoon face in internet gaming disorder: Evidence from P100, N170, P200, and MMN. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G.; Kornreich, C.; Dan, B.; Verbanck, P.; Campanella, S. Electrophysiological correlates of alcohol-and non-alcohol-related stimuli processing in binge drinkers: A follow-up study. J. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 28, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashhoon, Y.; Betts, J.; Farmer, S.L.; Lukas, S.E. Early onset tobacco cigarette smokers exhibit deficits in response inhibition and sustained attention. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018, 184, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| FA Group (n = 20) | HC Group (n = 23) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (Male/Female) | 14/6 | 11/12 | 0.142 |
| Age (years) | 24.44 ± 6.26 | 23.18 ± 2.88 | 0.390 |
| Education (years) | 17.52 ± 2.75 | 16.47 ± 1.33 | 0.114 |
| c-mYFAS 2.0 | 5.05 ± 2.63 | 0.35 ± 0.49 | <0.001 |
| BMI | 28.96 ± 4.37 | 21.29 ± 2.00 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Pei, G.; Zhao, J.; Xu, M.; Cao, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Funahashi, S.; Ding, L.; et al. Attention Affecting Response Inhibition in Overweight Adults with Food Addiction. Biosensors 2025, 15, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030180
Liu X, Pei G, Zhao J, Xu M, Cao L, Zhang J, Liu T, Wu J, Funahashi S, Ding L, et al. Attention Affecting Response Inhibition in Overweight Adults with Food Addiction. Biosensors. 2025; 15(3):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030180
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaotong, Guangying Pei, Jiayuan Zhao, Mengzhou Xu, Lizhi Cao, Jian Zhang, Tiantian Liu, Jinglong Wu, Shintaro Funahashi, Lei Ding, and et al. 2025. "Attention Affecting Response Inhibition in Overweight Adults with Food Addiction" Biosensors 15, no. 3: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030180
APA StyleLiu, X., Pei, G., Zhao, J., Xu, M., Cao, L., Zhang, J., Liu, T., Wu, J., Funahashi, S., Ding, L., & Wang, L. (2025). Attention Affecting Response Inhibition in Overweight Adults with Food Addiction. Biosensors, 15(3), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15030180





