Movement Recognition and Muscle Force Estimation of Wrist Based on Electromyographic Signals of Forearm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
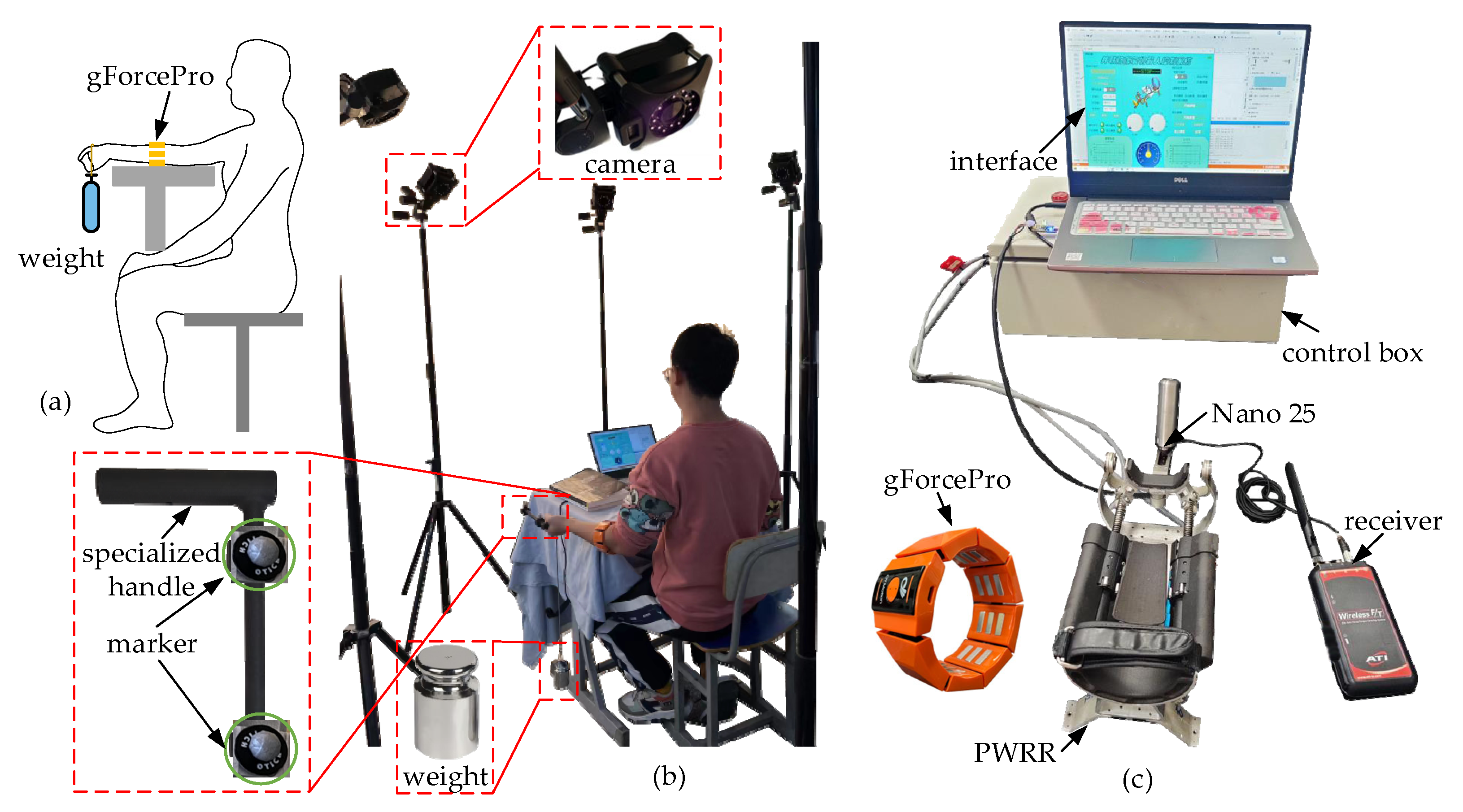
2.1. Experimental Platform
2.2. Movement Recognition Algorithm of Wrist
2.3. Muscle Force Estimation Model
3. Results
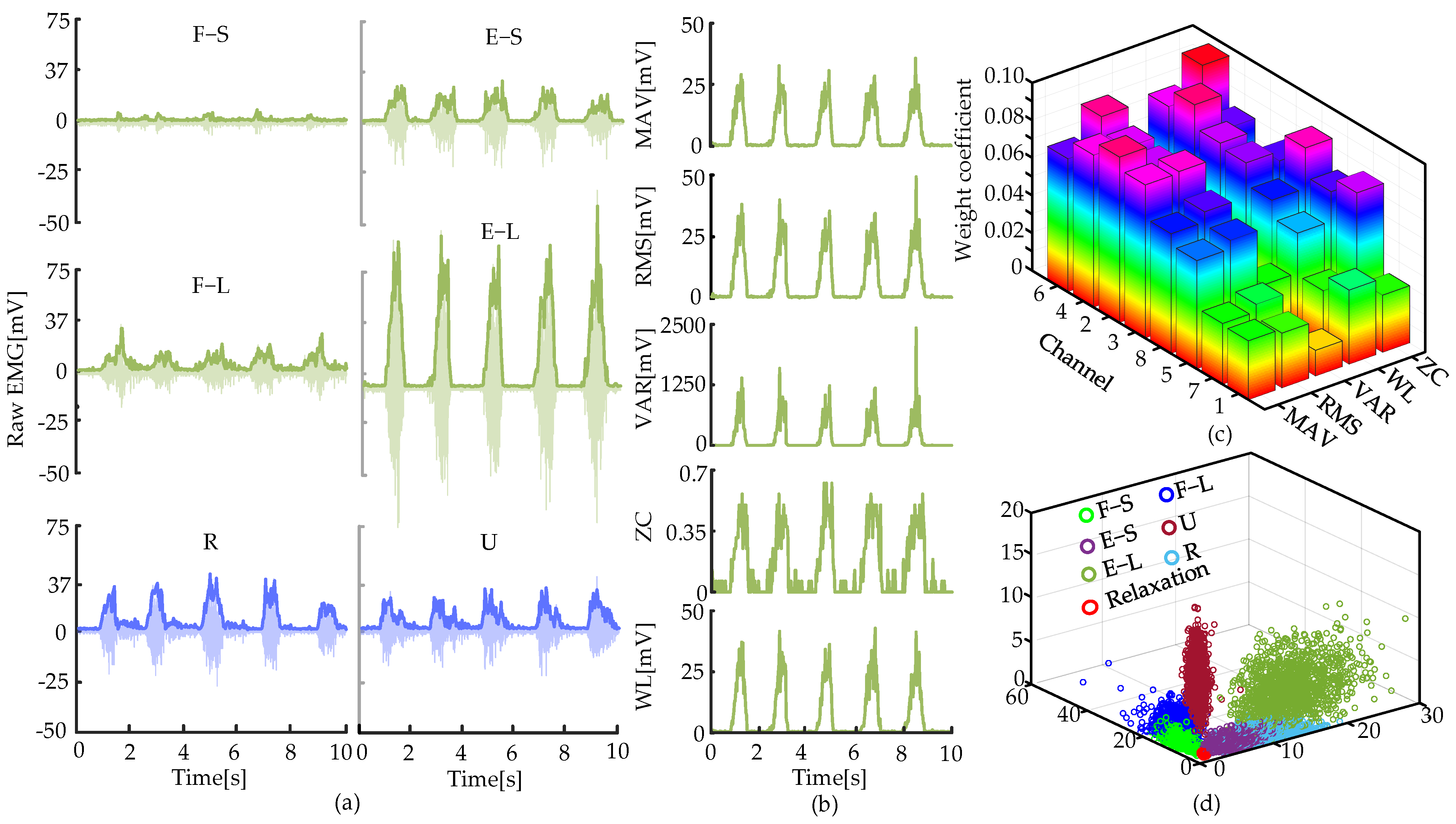
3.1. Verification of the Movement Recognition Algorithm
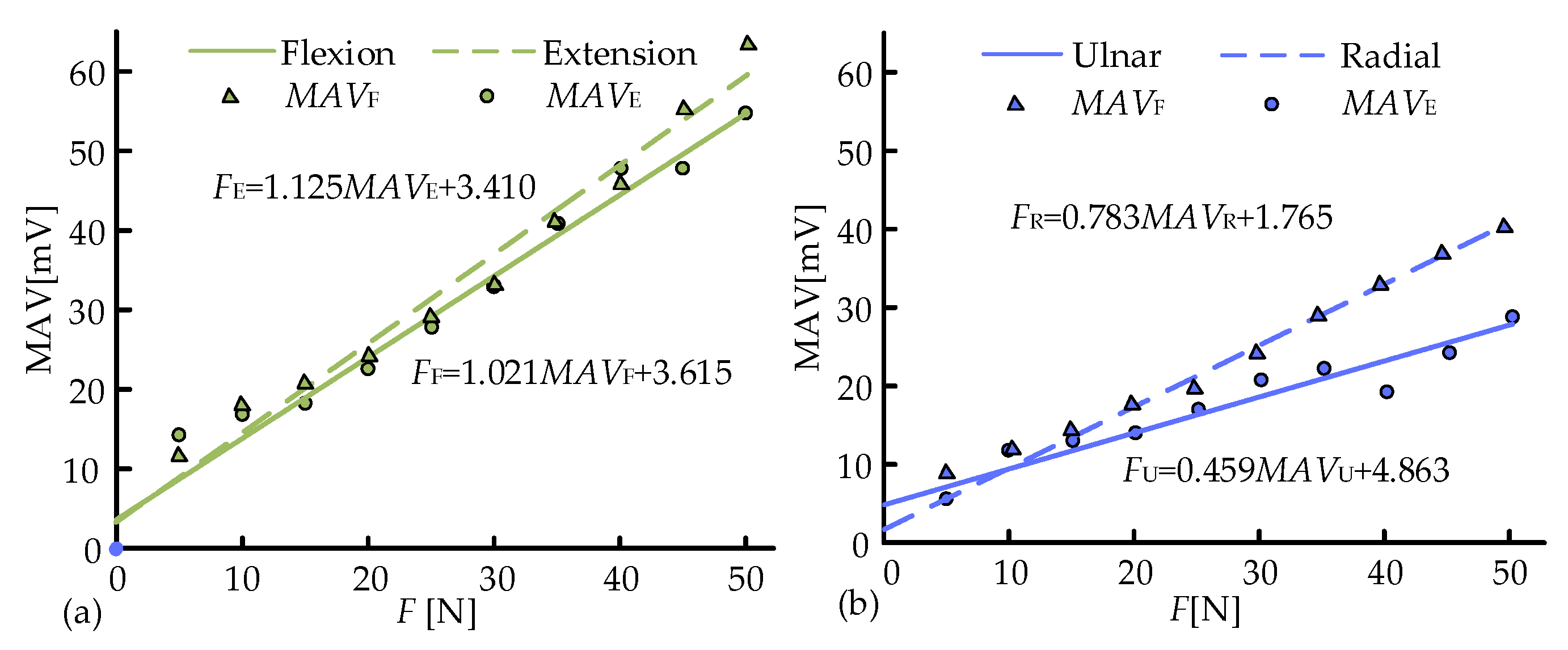
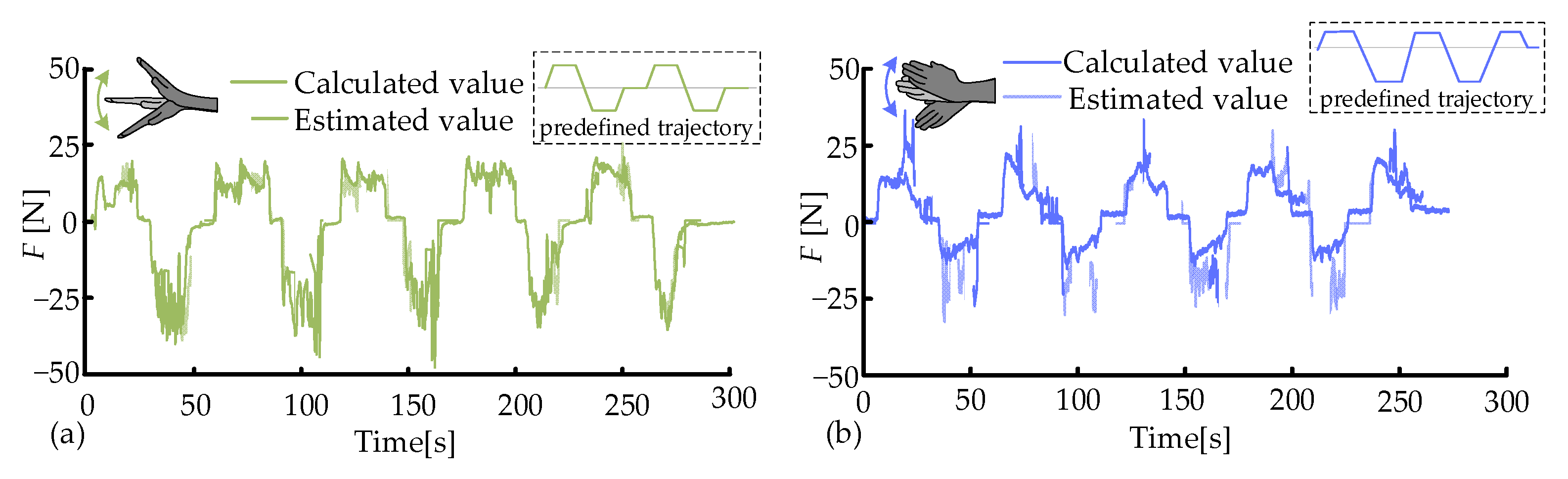
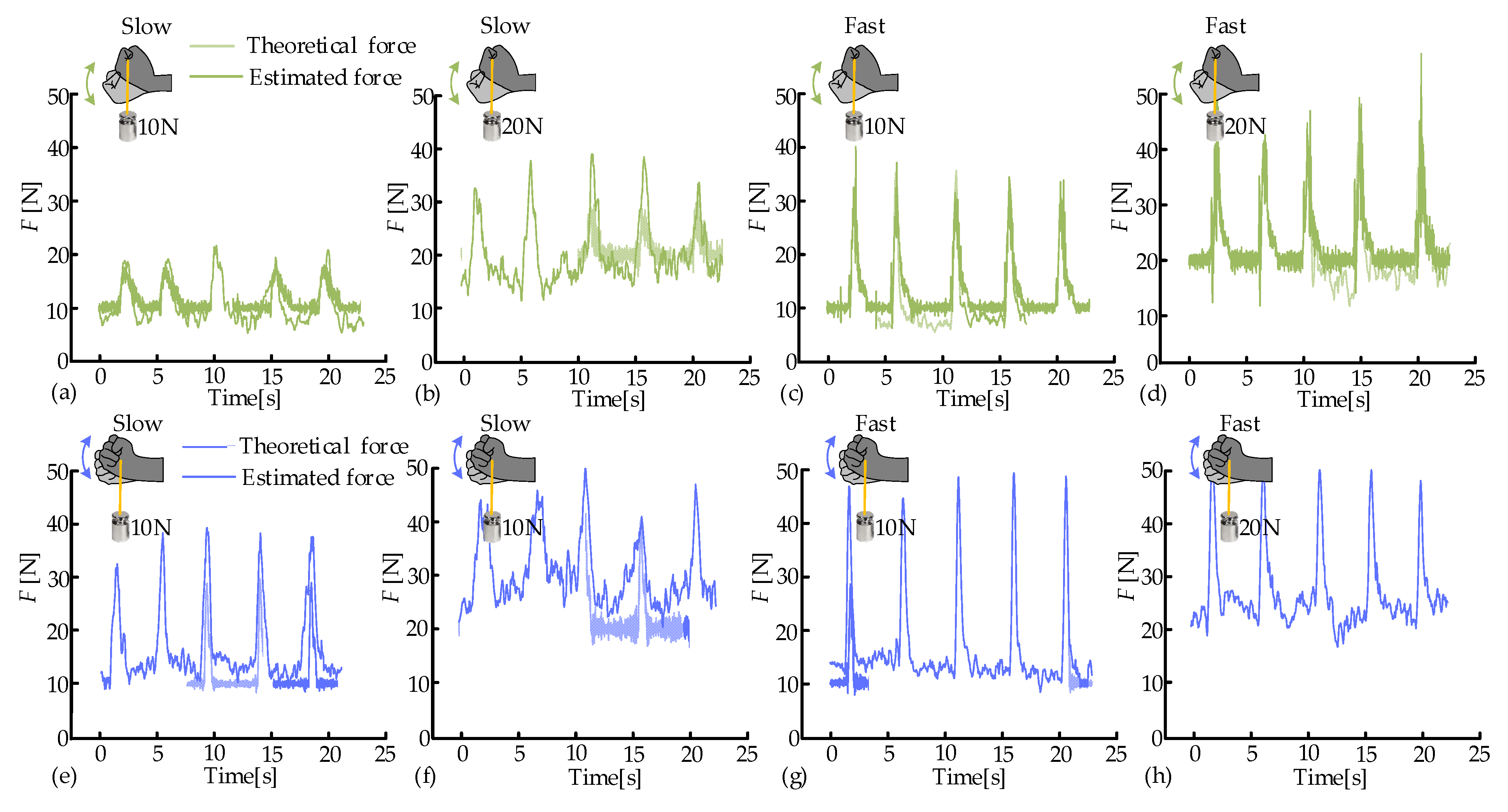
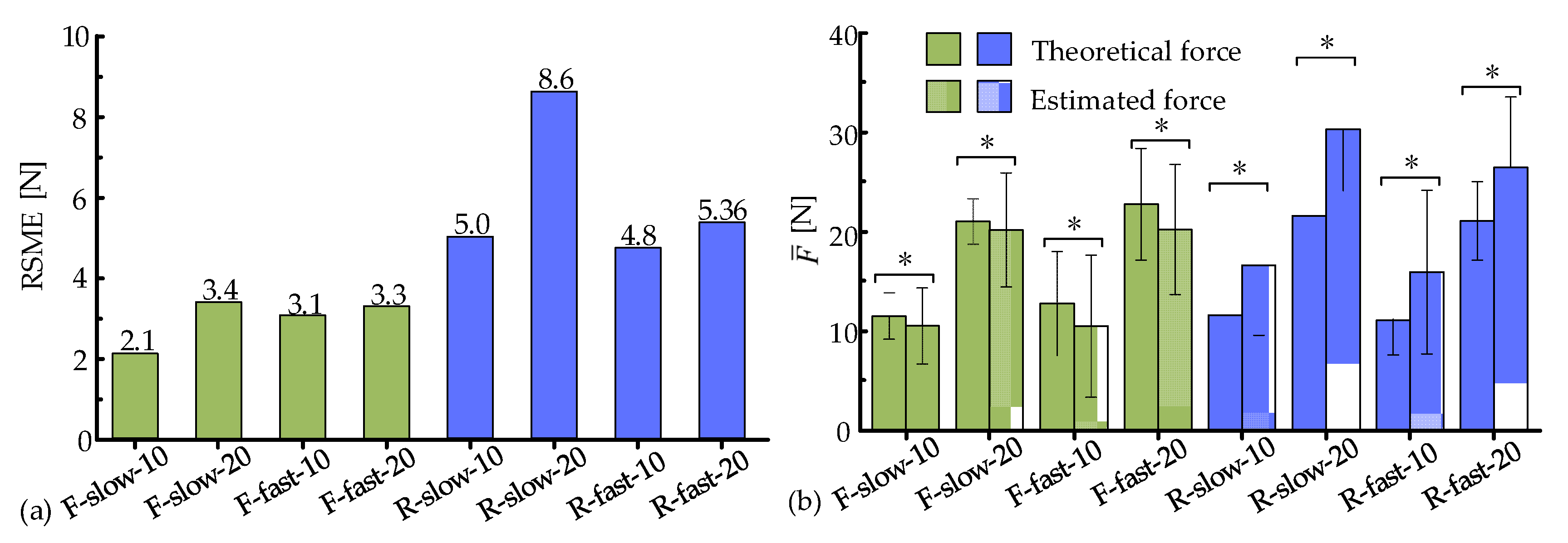
3.2. Muscle Force Estimation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| sEMG | Surface electromyography |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| HD-EMG | High-density electromyography |
| SAE-DNN | Stacked autoencoders and deep neural network |
| BPNN | Backpropagation neural network |
| MAV | Mean absolute values |
| WL | Waveform length |
| ZC | Zero crossing |
| VAR | Variance |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| NMF | Non-negative matrix factorization |
References
- Eschweiler, J.; Li, J.; Quack, V.; Rath, B.; Baroncini, A.; Hildebrand, F.; Migliorini, F. Anatomy, biomechanics, and loads of the wrist joint. Life 2022, 12, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, B.R.; McDowell, S.K.; Worthen-Chaudhari, L.C. Poststroke upper extremity rehabilitation: A review of robotic systems and clinical results. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2007, 14, 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, O.; O’Malley, M.K.; Boake, C.; Levin, H.S.; Yozbatiran, N.; Reistetter, T.A. Normalized movement quality measures for therapeutic robots strongly correlate with clinical motor impairment measures. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 18, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.L.; Winstein, C.J.; Miller, J.P.; Taub, E.; Uswatte, G.; Morris, D.; Giuliani, C.; Light, K.E.; Nichols-Larsen, D. Effect of constraint-induced movement therapy on upper extremity function 3 to 9 months after stroke: The EXCITE randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2006, 296, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Qin, J.; Wu, Z.Z.; Duan, L.H.; Li, Z.Q. Development of a novel finger and wrist rehabilitation robot for finger and wrist training. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2015—2015 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Macao, China, 1–4 November 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Murgia, A.; Kyberd, P.J.; Chappell, P.H.; Light, C.M. Marker placement to describe the wrist movements during activities of daily living in cyclical tasks. Clin. Biomech. 2004, 19, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, P.S.; Burgar, C.G.; Shor, P.C.; Majmundar, M.; Van der Loos, M. Robot-assisted movement training compared with conventional therapy techniques for the rehabilitation of upper-limb motor function after stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Liu, Z.; Meng, W.; Liu, Q.; Xie, S.Q. Machine learning in robot-assisted upper limb rehabilitation: A focused review. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2021, 15, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, H.; Yu, H. Human–Robot interaction evaluation-Based AAN control for upper limb rehabilitation robots driven by series elastic actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 3437–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Kim, Y.H. Robot-assisted therapy in stroke rehabilitation. J. Stroke 2013, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, L.; Elangovan, N.; Contu, S.; Khosravani, S.; Konczak, J.; Masia, L. Robot-aided assessment of wrist proprioception. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.J.; Klein, J.; Minakata, K.; Le, V.; Bobrow, J.E.; Reinkensmeyer, D.J. A low-cost parallel robot and trajectory optimization method for wrist and forearm rehabilitation using the wii. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd IEEE Ras & Embs International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 19–22 October 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 869–874. [Google Scholar]
- Andrikopoulos, G.; Nikolakopoulos, G.; Manesis, S. Design and development of an exoskeletal wrist prototype via pneumatic artificial muscles. Meccanica 2015, 50, 2709–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, E.; Elias, A. A review of parallel robots: Rehabilitation, assistance, and humanoid applications for neck, shoulder, wrist, hip, and ankle joints. Robotics 2023, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsberts, A.; Atzori, M.; Castellini, C.; Müller, H.; Caputo, B. Movement error rate for evaluation of machine learning methods for sEMG-Based hand movement classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.Z.; Lewek, M.D.; Sawicki, G.S. A neuromechanics-Based powered ankle exoskeleton to assist walking post-stroke: A feasibility study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujiuchi, N.; Mizuno, H.; Koizumi, T.; Yamada, S. 7—Motion discrimination technique for forearms using real-time EMG signals. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Guangzhou, China, 11–14 December 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 441–445. [Google Scholar]
- Xao, F.Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Y.H.; Zhao, J. Continuous estimation of joint angle from electromyography using multiple time-delayed features and random forests. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 39, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Ma, K.; Huang, S.; Li, G.; Cai, S. A continuous estimation model of upper limb joint angles by using surface electromyography and deep learning method. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 174940–174950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukano, K.; Iiazawa, K.; Soeda, T.; Shirai, A.; Capi, G. Deep learning for gesture recognition based on surface EMG data. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Advanced Mechatronic Systems (ICAMechS), Tokyo, Japan, 9–12 December 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Liu, H. An EMG-Based deep learning approach for multi-DoF wrist movement decoding. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 7099–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian, G.; Etemad, A.; Morin, E. Generalized EMG-Based isometric contact force estimation using a deep learning approach. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 70, 103012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, C.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X.Y. Multi-DoF continuous estimation for wrist torques using stacked autoencoder. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 57, 101733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, C.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. Wrist torque estimation via electromyographic motor unit decomposition and image reconstruction. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 25, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. Surface electromyography image-driven torque estimation of multi-DoF wrist movements. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, Z.O.; Xiao, Z.G.; Menon, C. Surface EMG pattern recognition for real-time control of a wrist exoskeleton. Biomed. Eng. Online 2010, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokhar, Z.O.; Xiao, Z.G.; Sheridan, C.; Menon, C. A novel wrist rehabilitation/assistive device. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 13th International Multitopic Conference, Islamabad, Pakistan, 14–15 December 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rechy-Ramirez, E.J.; Marin-Hernandez, A.; Rios-Figueroa, H.V. A human–computer interface for wrist rehabilitation: A pilot study using commercial sensors to detect wrist movements. Vis. Comput. 2019, 35, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.V. The heat of shortening and the dynamic constants of muscle. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1938, 126, 136–195. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Qi, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ferrigno, G.; De Momi, E. Deep neural network approach in EMG-Based force estimation for human–robot interaction. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Zaidi, R.; Xie, S.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Z.Q. A CNN-LSTM hybrid model for erist kinematics estimation using surface electromyography. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Jamwal, P.K.; Van Vliet, P.; Ghayesh, M.H. State-of-the-art robotic devices for wrist rehabilitation: Design and control aspects. IEEE T. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2020, 50, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, B.; Sadedel, M.; Mohammadi, M. Innovative integration of meta-heuristic algorithms with adaptive tsk fuzzy systems for inverse kinematics in a new wrist and forearm rehabilitation exoskeleton. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam, M.; Moghaddam, M.M. EMG-driven fatigue-based self-adapting admittance control of a hand rehabilitation robot. J. Biomech. 2022, 138, 111104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Yu, Z.D.; Su, P.; Li, J.F.; Ge, R.D. Design of a parallel wrist rehabilitation robot and analysis of physiological effect on training. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 29, 3401–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farago, E.; MacIsaac, D.; Suk, M.; Chan, A.D.C. A review of techniques for surface electromyography signal quality analysis. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 16, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wan, J.; Jin, Y.; Yu, X.; Fang, Y. EEG- and EMG-driven poststroke rehabilitation: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 23649–23660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Ji, S.; Gao, C.; Fu, J. Estimation of muscle forces of lower limbs based on CNN–LSTM neural network and wearable sensor system. Sensors 2024, 24, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sittiruk, T.; Sengchuai, K.; Booranawong, A.; Phukpattaranont, P. Implementation of a real-time force estimation system based on sEMG signals and gaussian process regression: Human–robot interaction in rehabilitation. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 13731–13747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, T.; Lloyd, D.; Manal, K.; Besier, T.F. Neuromusculoskeletal modeling: Estimation of muscle forces and joint moments and movements from measurements of neural command. J. Appl. Biomech. 2004, 20, 367–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharian, N.; Moghimi, S.; Kalani, H. Estimation biting force based using EMG signals and Laguerre estimation technique. In Proceedings of the 2015 23rd Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, Tehran, Iran, 10–14 May 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Yu, Y.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. Non-invasive analysis of motor unit activation during simultaneous and continuous wrist movements. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X. Wrist torque estimation by combining motor unit discharges with musculoskeletal model. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 4249–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Jiao, Z.; Li, Y.; Chang, Y. Movement Recognition and Muscle Force Estimation of Wrist Based on Electromyographic Signals of Forearm. Biosensors 2025, 15, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040259
Zhang L, Jiao Z, Li Y, Chang Y. Movement Recognition and Muscle Force Estimation of Wrist Based on Electromyographic Signals of Forearm. Biosensors. 2025; 15(4):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040259
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Leiyu, Zhenxing Jiao, Yongzhen Li, and Yawei Chang. 2025. "Movement Recognition and Muscle Force Estimation of Wrist Based on Electromyographic Signals of Forearm" Biosensors 15, no. 4: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040259
APA StyleZhang, L., Jiao, Z., Li, Y., & Chang, Y. (2025). Movement Recognition and Muscle Force Estimation of Wrist Based on Electromyographic Signals of Forearm. Biosensors, 15(4), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15040259




