One-Pot Colorimetric Nucleic Acid Test Mediated by Silver Nanoparticles for DNA Extraction and Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Bacterial Samples
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization of PEI-AgNPs
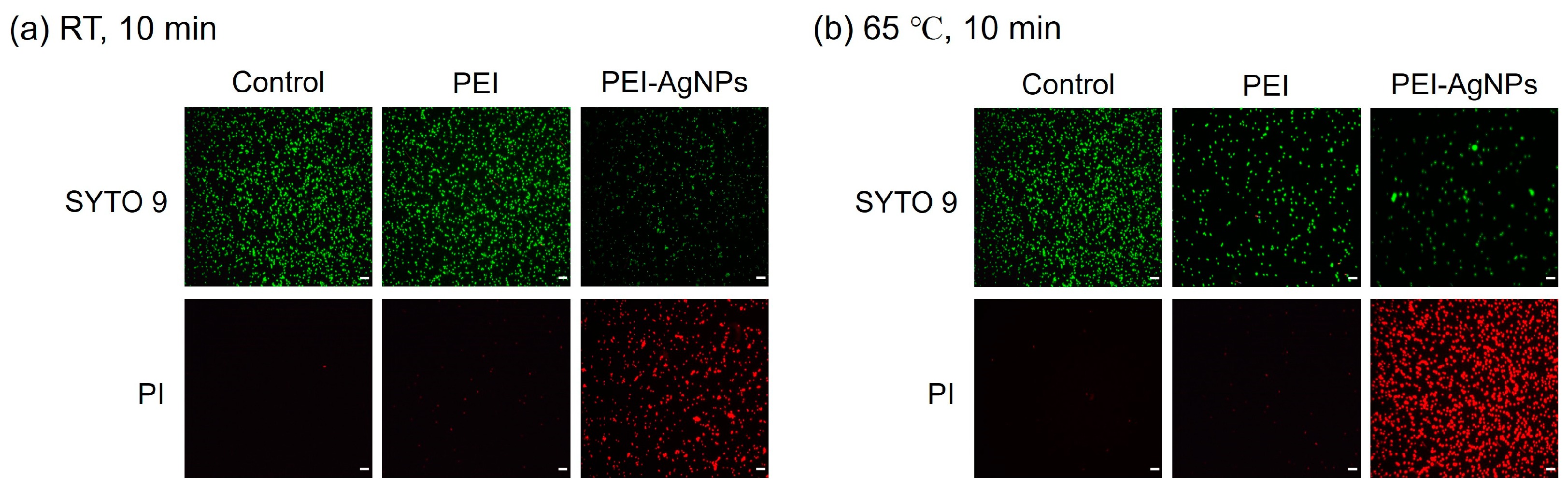
2.4. Live/Dead Bacterial Viability Assay
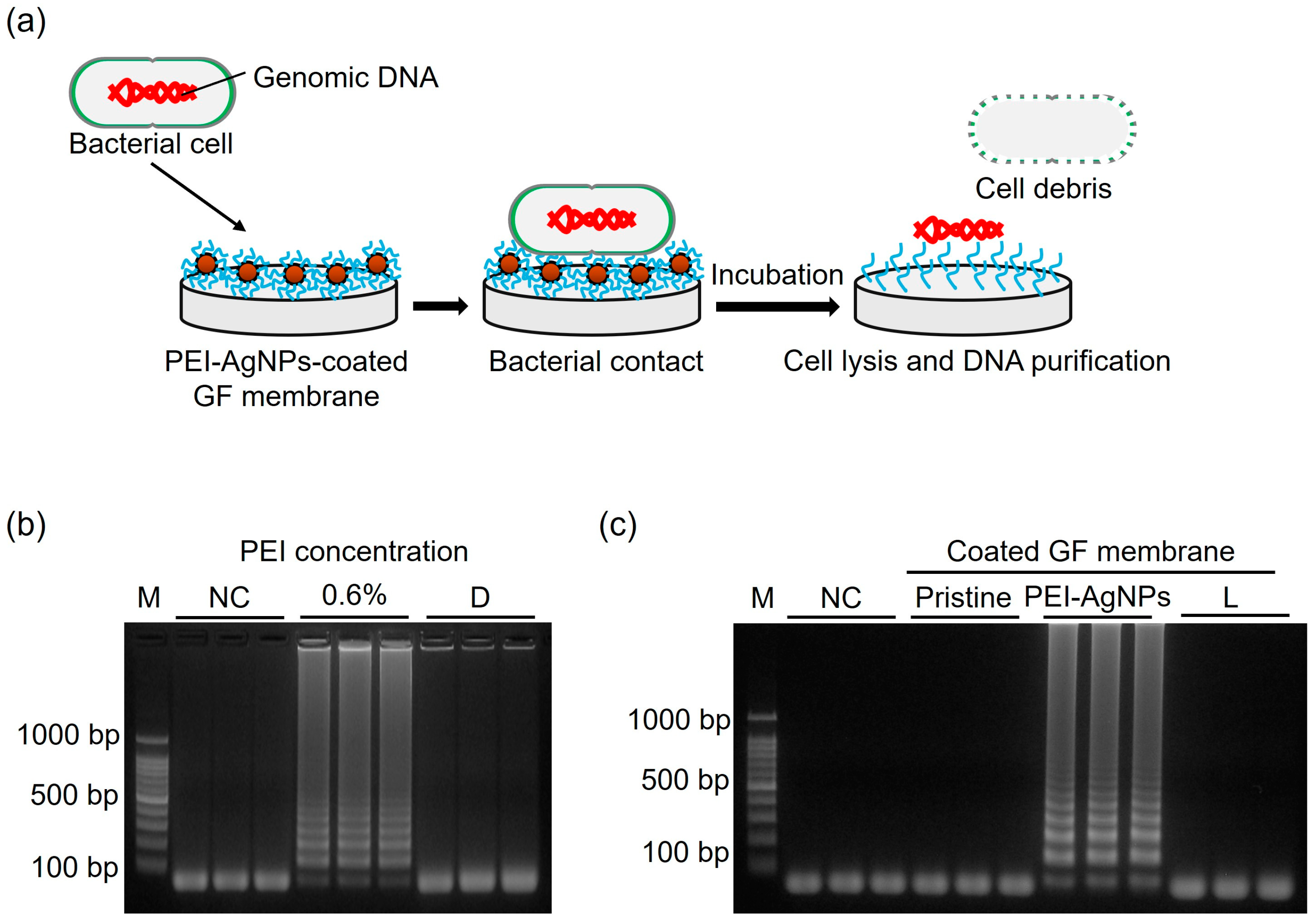
2.5. Extraction of Genomic DNA
2.6. LAMP Reaction
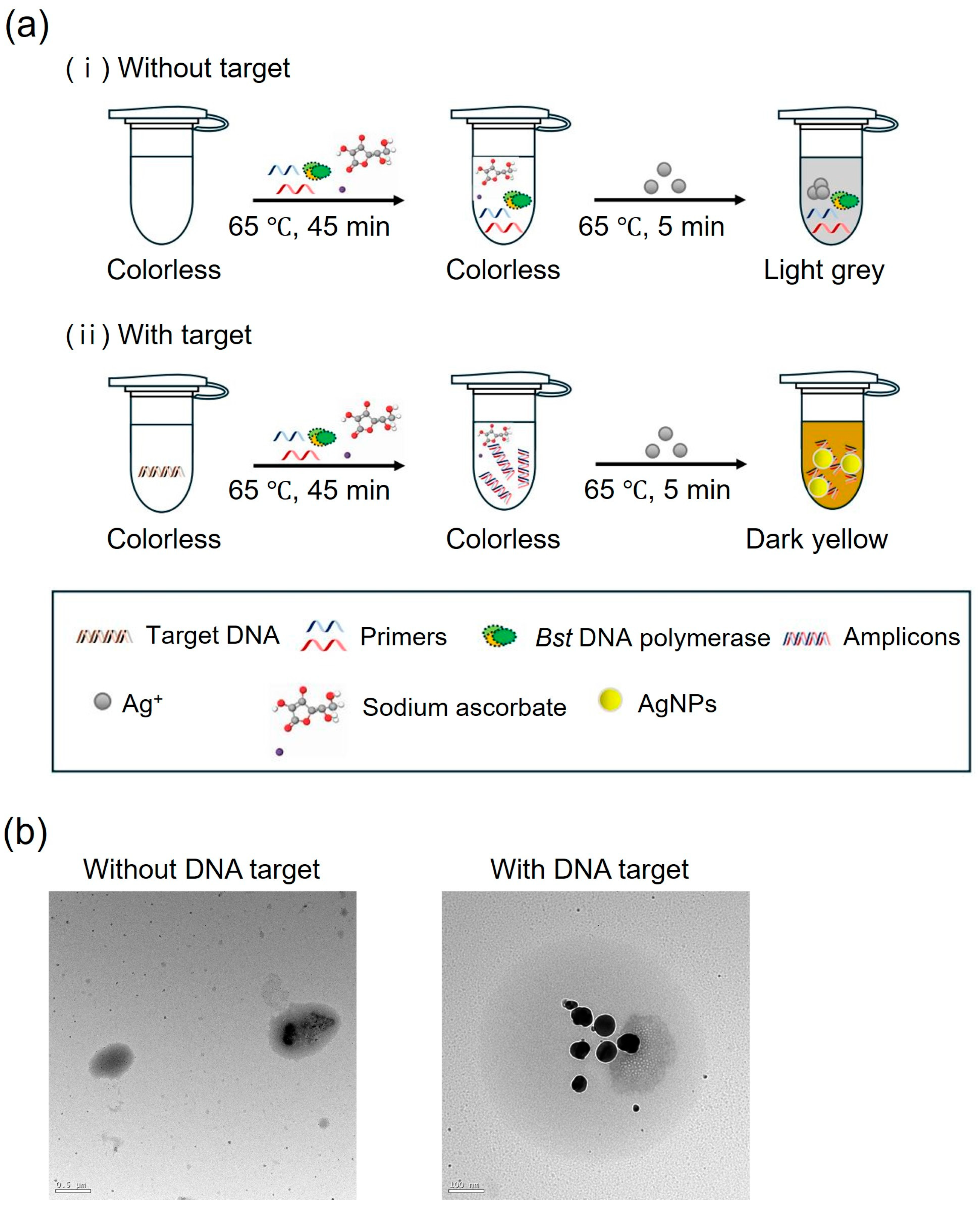
2.7. Colorimetric Detection
2.8. Fabrication and Operation of the One-Pot Colorimetric NAT Platform
3. Results and Discussion
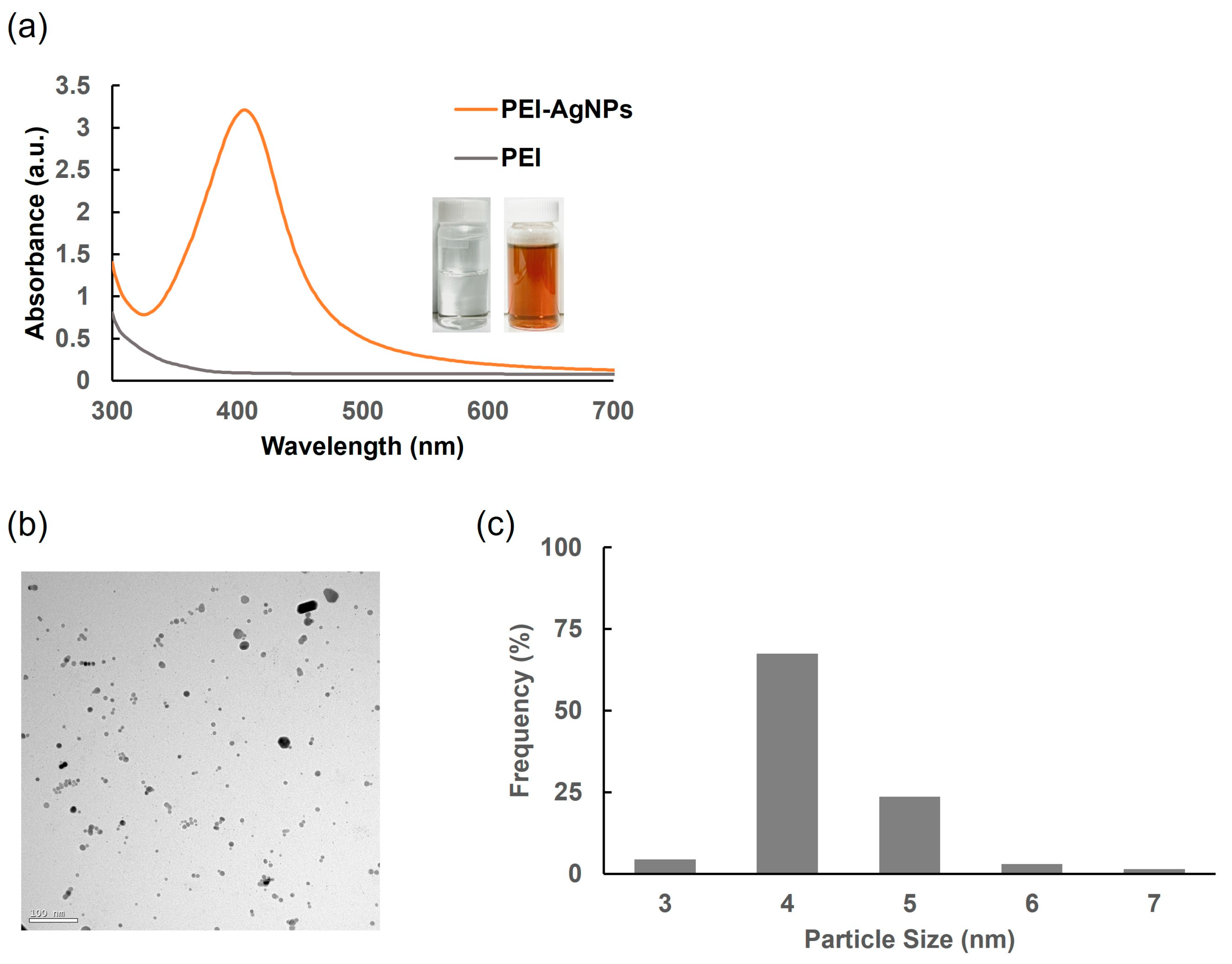
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of PEI-AgNPs
3.2. Effect of PEI-AgNPs on Cell Lysis
3.3. DNA Extraction Performance
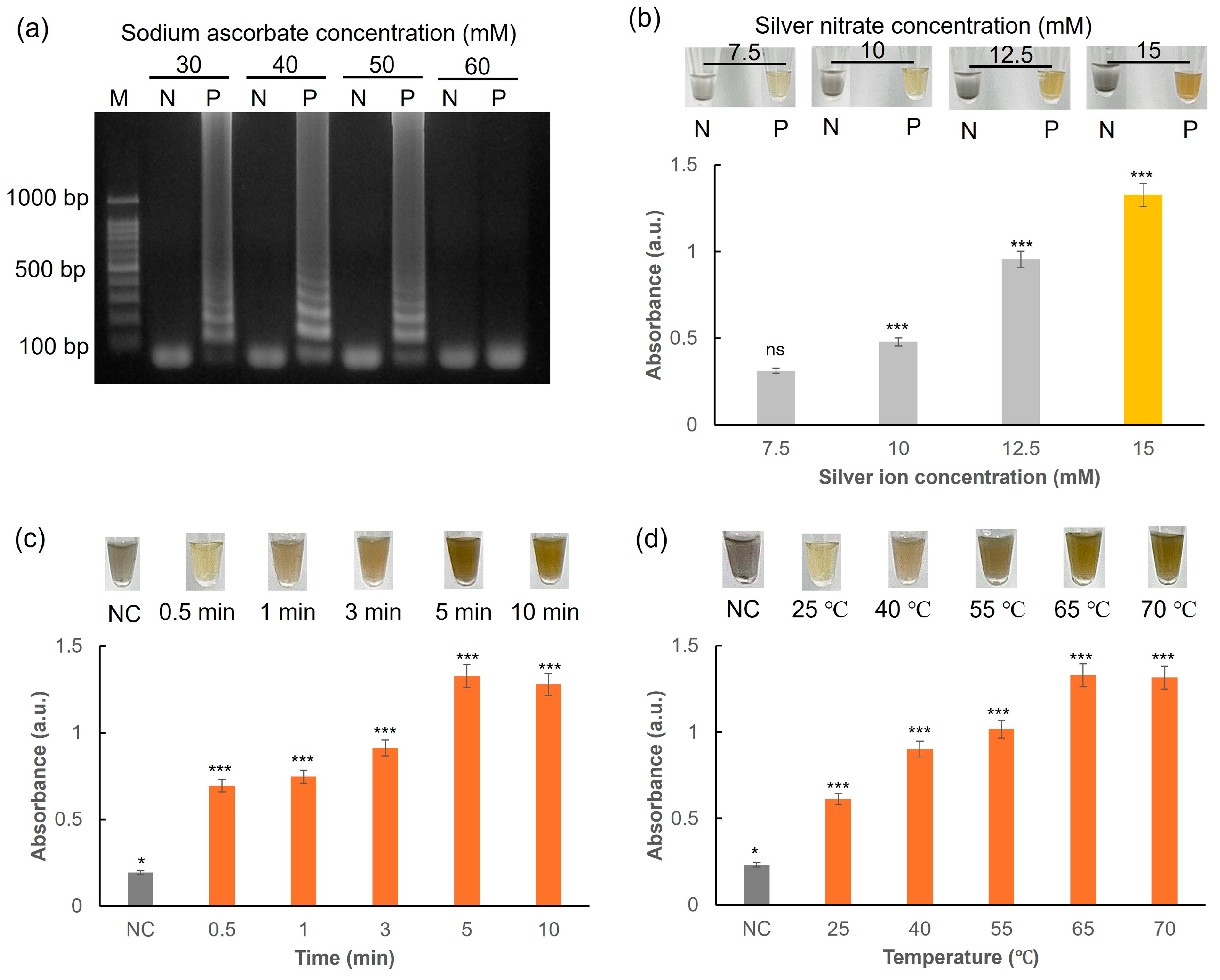
3.4. Sodium Ascorbate-Induced AgNPs for LAMP Colorimetric Detection
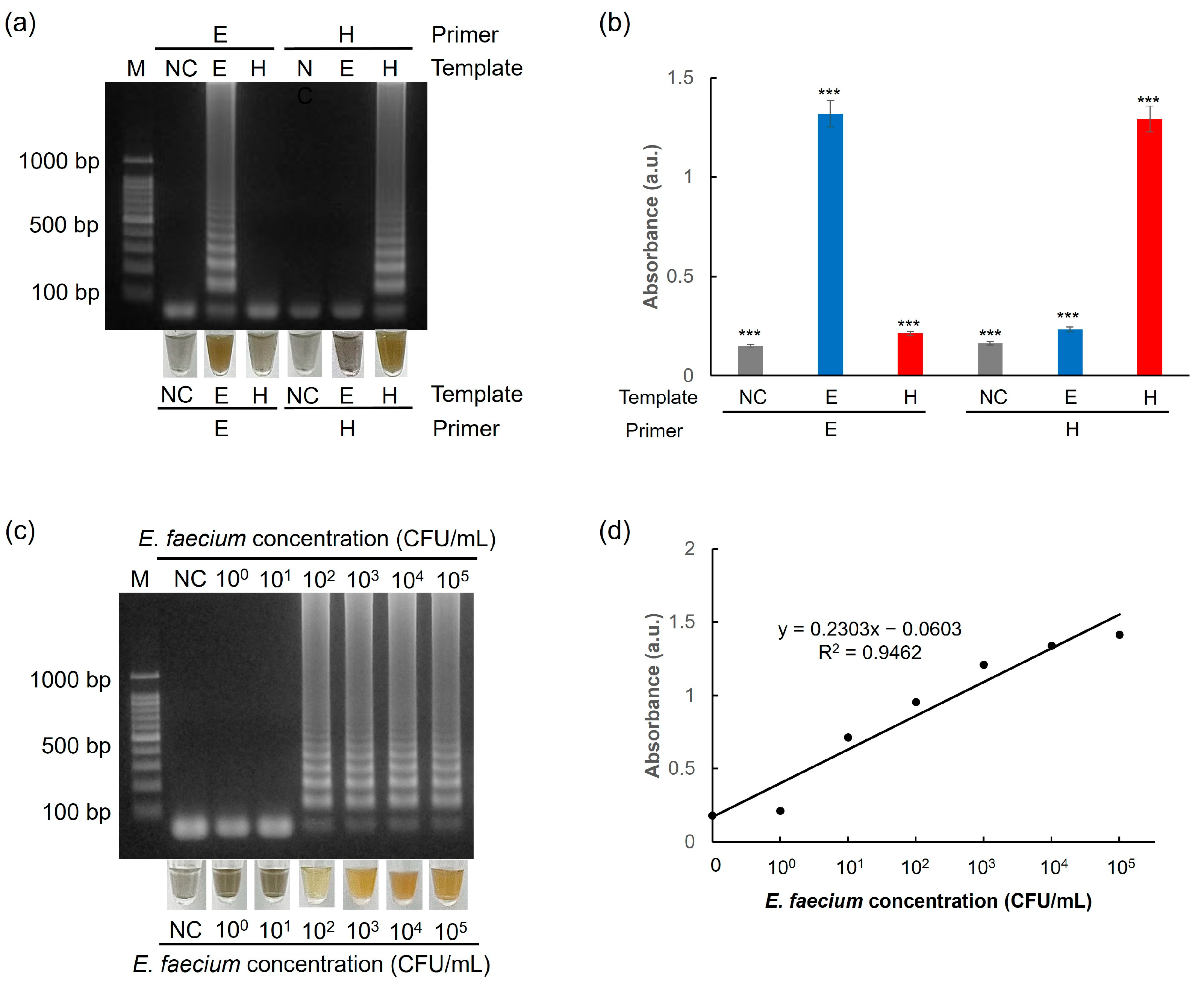
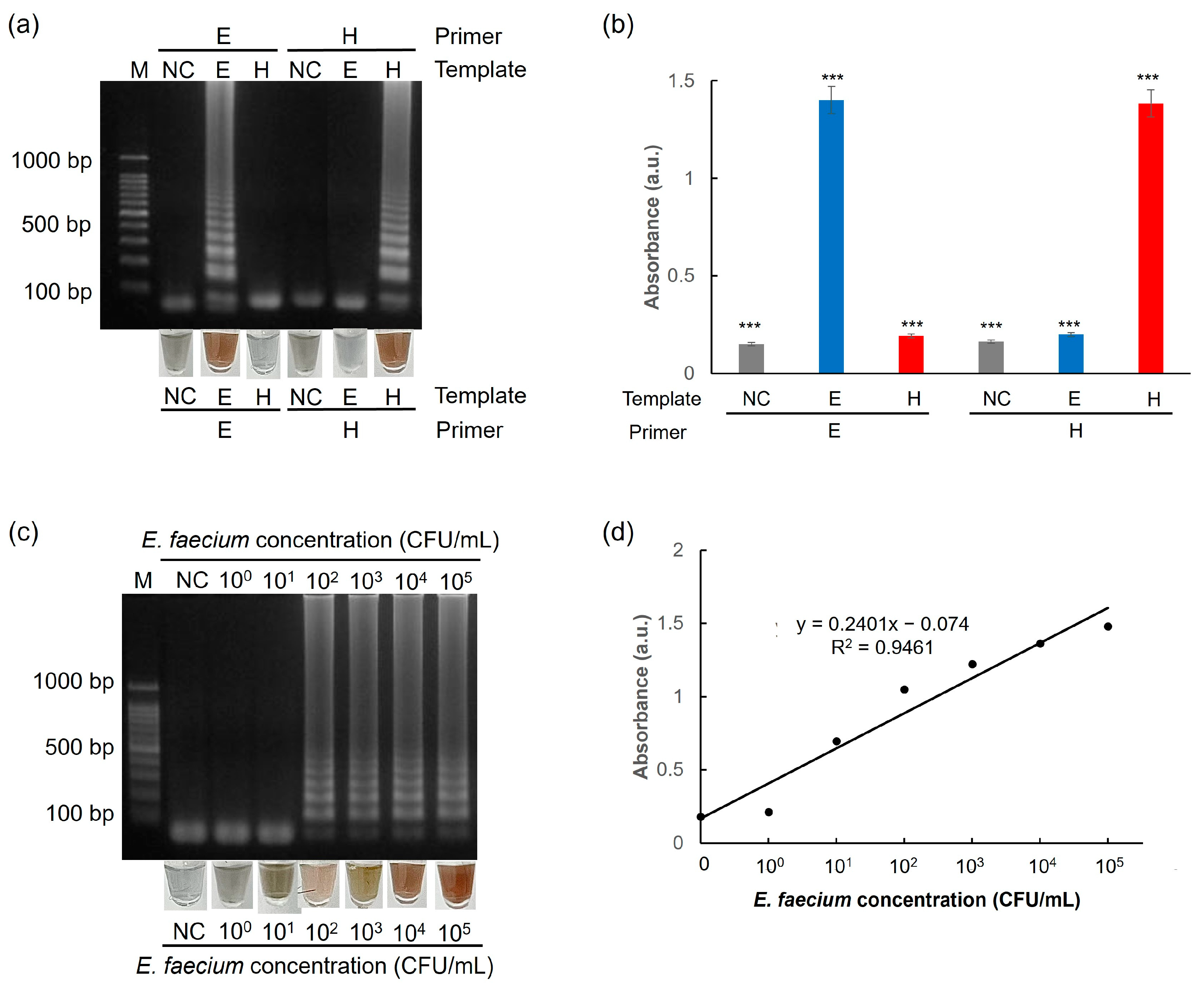
3.5. Selectivity and Sensitivity of the One-Pot Colorimetric NAT Platform
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, P.; Liu, R. Multiplex detection of nucleic acids using a low cost microfluidic chip and a personal glucose meter at the point-of-care. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3824–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, A.; Ornob, A.; Yu, H.; Damhorst, G.; Chen, W.; Sun, F.; Bhuiya, A.; Cunningham, B.; Bashir, R. Hands-free smartphone-based diagnostics for simultaneous detection of Zika, Chikungunya, and Dengue at point-of-care. Biomed. Microdevices 2017, 19, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsky, H.C.; Freije, C.A.; Kosoko-Thoroddsen, T.-S.F.; Sabeti, P.C.; Myhrvold, C. CRISPR-based surveillance for COVID-19 using genomically-comprehensive machine learning design. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, Y.; Matubara, H.; Tanizawa, T.; Nabeya, Y.; Kawahira, H.; Akai, T.; Hoshino, I.; Hayashi, H. Rapid diagnosis of micrometastasis of gastric cancer using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shkodenko, L.; Laushkina, V.; Rubel, M.; Sergeeva, E. Finger-Actuated Microfluidic Platform for Colorimetric Isothermal Diagnostics of Neisseria meningitidis and Herpes Simplex Virus. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2024, 50, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mateos, P.; Ngamsom, B.; Ameyo, D.; Wakaba, P.; Shiluli, C.; Iles, A.; Gitaka, J.; Pamme, N. Integrated microscale immiscible phase extraction and isothermal amplification for colorimetric detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 5129–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El-Nour, K.M.; Eftaiha, A.A.; Al-Warthan, A.; Ammar, R.A. Synthesis and applications of silver nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 3, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, S.S. Role of silver nanoparticles in colorimetric detection of biomolecules. Biomed. Nurs. 2019, 5, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichetti, A.; Mavridi-Printezi, A.; Mordini, D.; Montalti, M. Effect of size, shape and surface functionalization on the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, H.H.; Garza-Treviño, E.N.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Singh, D.K. Silver nanoparticles are broad-spectrum bactericidal and virucidal compounds. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Zheng, J. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: Structural effects. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, G.; Boruah, H.; Gautom, T.; Hazarika, D.J.; Barooah, M.; Boro, R.C. Chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles as cell lysis agent for bacterial genomic DNA isolation. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 045015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.H.; Woo, M.-K.; Yoon, H.Y.; Jang, J.W.; Wu, J.H.; Lim, C.-S.; Kim, Y.K. Isolation of DNA using magnetic nanoparticles coated with dimercaptosuccinic acid. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 447, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.; Gu, Y.; Han, J.; Li, C.-X.; Sun, J.; Liu, P. Chitosan-modified filter paper for nucleic acid extraction and “in situ PCR” on a thermoplastic microchip. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3568–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, C.N.; Diudea, M.V.; Putz, M.V.; Grudziński, I.P. Linear and branched PEIs (polyethylenimines) and their property space. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.G.; Oh, E.J.; Chung, H.Y.; Han, S.I.; Kim, E.J.; Seo, S.Y.; Do Ghim, H.; Yeum, J.H.; Choi, J.H. Antimicrobial polyethyleneimine-silver nanoparticles in a stable colloidal dispersion. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.N.D.; La, H.C.; Lee, N.Y. Fully integrated and foldable microdevice encapsulated with agarose for long-term storage potential for point-of-care testing of multiplex foodborne pathogens. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2754–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.L.; Stabler, R.A.; Lee, N.Y. Fabrication of a foldable all-in-one point-of-care molecular diagnostic microdevice for the facile identification of multiple pathogens. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 314, 128057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.; Chandran, P.; Khan, S.S. Biofunctionalized silver nanoparticles: Advances and prospects. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 105, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Moshe, A.; Markovich, G. Synthesis of single crystal hollow silver nanoparticles in a fast reaction-diffusion process. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, D.A.; Shah, M.R.; Malik, M.I. Polyethyleneimine stabilized silver nanoparticles as an efficient and selective colorimetric assay for promethazine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1223, 340216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, F.; McGoverin, C.; Swift, S.; Vanholsbeeck, F. Rapid evaluation of bacterial viability using the optrode—A near real time portable fluorimeter. In Proceedings of the Australian Conference on Optical Fibre Technology, Sydney, Australia, 5–8 September 2016; p. AW3C.6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, N.; Guo, N.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of polyethylenimine (PEI) functionalized silver nanoparticles by a hydrothermal method and their antibacterial activity study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 42, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanoff, D.D., Jr.; Chumanov, G. Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanoparticles and arrays. ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, L.; Prevost, M.; Barbeau, B.; Coallier, J.; Desjardins, R. LIVE/DEAD® BacLight™: Application of a new rapid staining method for direct enumeration of viable and total bacteria in drinking water. J. Microbiol. Methods 1999, 37, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K. Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2001, 56, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.; Rangasamy, S.; Purushothaman, B.; Song, J.M. The application of bactericidal silver nanoparticles in wound treatment. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2015, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Immobilized silver nanoparticles enhance contact killing and show highest efficacy: Elucidation of the mechanism of bactericidal action of silver. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7328–7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W. Quantifying the interactions between PEI and double-stranded DNA: Toward the understanding of the role of PEI in gene delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21055–21062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, A.A.; Jadaon, M.M.; Abdulsamad, A.M.; Dashti, H.M. Heat treatment of bacteria: A simple method of DNA extraction for molecular techniques. Kuwait Med. J. 2009, 41, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Hu, A.; Pan, J.; Deng, G.; Hua, C.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L. A novel microfluidic device integrated with chitosan-modified capillaries for rapid ZIKV detection. Micromachines 2020, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błasiak, J.; Kowalik, J. Protective action of sodium ascorbate against the DNA-damaging effect of malaoxon. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1999, 65, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Luo, Y.; Turner, E.; Feng, H. Efficacy of sodium chlorite as an inhibitor of enzymatic browning in apple slices. Food Chemistry 2007, 104, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.H.; Mandal, A.M.; Heidelberg, T.; Hussen, R.S.D.; Goh, E.W. Ionic magnetic core–shell nanoparticles for DNA extraction. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 38818–38830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedi, N.; Farjadian, F.; Farhadi, A.; Rafiei Dehbidi, G.; Ranjbaran, R.; Zare, F.; Ali Okhovat, M.; Nikouyan, N.; Behzad-Behbahani, A. High yield gold nanoparticle-based DNA isolation method for human papillomaviruses genotypes from cervical cancer tissue samples. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 14, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieu, N.M.; Nam, N.H.; Huyen, N.T.; Van Anh, N.T.; Nghia, P.T.; Khoa, N.B.; Toan, N.L.; Luong, N.H. Synthesis of SiO2-Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Using Ultrasound and Its Application in DNA Extraction from Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Human Cancer Tissues. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 3738–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Baghban, N.; Soylak, M. Solid-phase extraction (SPE) of salmon sperm DNA using a polyaniline@ molybdenum (IV) sulfide@ multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) nanocomposite with spectrophotometric detection. Anal. Lett. 2023, 56, 1632–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Target Gene | Primer Name | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| esp gene (Enterococcus faecium) | F3 | CCAGAACACTTATGGAACAG |
| B3 | GTTGGGCTTTGTGACCTG | |
| FIP | CGTGTCTCCGCTCTCTTCTTTTTATTT-GCAAGATATTGATGGTG | |
| BIP | ATCGGGAAACCTGAATTAGAAGAA-GAACTCGTGGATGAATACTTTC | |
| LB | TGATGTTGACACAACAGTTAAGGG | |
| hlyA gene (Listeria monocytogenes) | F3 | TTGCGCAACAAACTGAAGC |
| B3 | GCTTTTACGAGAGCACCTGG | |
| FIP | CGTGTTTCTTTTCGATTGGCGTCTTTTTTTCATCCATGGCACCACC | |
| BIP | CCACGGAGATGCAGTGACAAATGTTTTGGATTTCTTCTTTTTCTCCACAAC | |
| LB | GCCAAGAAAAGGTTACAAAGATGG |
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic nanoparticles | - High binding efficiency | - Use of magnets | [36] |
| - Easy magnetic separation | - Higher cost | ||
| Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) | - Tunable surface | - Expensive | [37] |
| - High sensitivity | - Complex synthesis | ||
| Silica-coated nanoparticles | - High DNA purity | - Time consuming | [38] |
| - Wide applicability | - Relatively expensive | ||
| Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) | - High surface area | - Difficult for purification | [39] |
| - Strong adsorption | - Potential for cytotoxicity | ||
| PEI-AgNP-coated GF membrane | - Simple, low-cost, instrument-free | - Limited binding capacity | This study |
| - Fast extraction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.K.; Trinh, K.T.L.; Lee, N.Y. One-Pot Colorimetric Nucleic Acid Test Mediated by Silver Nanoparticles for DNA Extraction and Detection. Biosensors 2025, 15, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050271
Park SK, Trinh KTL, Lee NY. One-Pot Colorimetric Nucleic Acid Test Mediated by Silver Nanoparticles for DNA Extraction and Detection. Biosensors. 2025; 15(5):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050271
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seung Kyun, Kieu The Loan Trinh, and Nae Yoon Lee. 2025. "One-Pot Colorimetric Nucleic Acid Test Mediated by Silver Nanoparticles for DNA Extraction and Detection" Biosensors 15, no. 5: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050271
APA StylePark, S. K., Trinh, K. T. L., & Lee, N. Y. (2025). One-Pot Colorimetric Nucleic Acid Test Mediated by Silver Nanoparticles for DNA Extraction and Detection. Biosensors, 15(5), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050271







