Strategies Using Bio-Layer Interferometry Biosensor Technology for Vaccine Research and Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. BLI Applications on Vaccine Research and Development
3. Epitope Design and Epitope Capture Approaches
3.1. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Epitopes
3.2. Epitope Scaffolding
3.3. Epitope Binning
4. Antibody Design and Antibody Capture Strategies
4.1. High-Throughput Antibody Screening
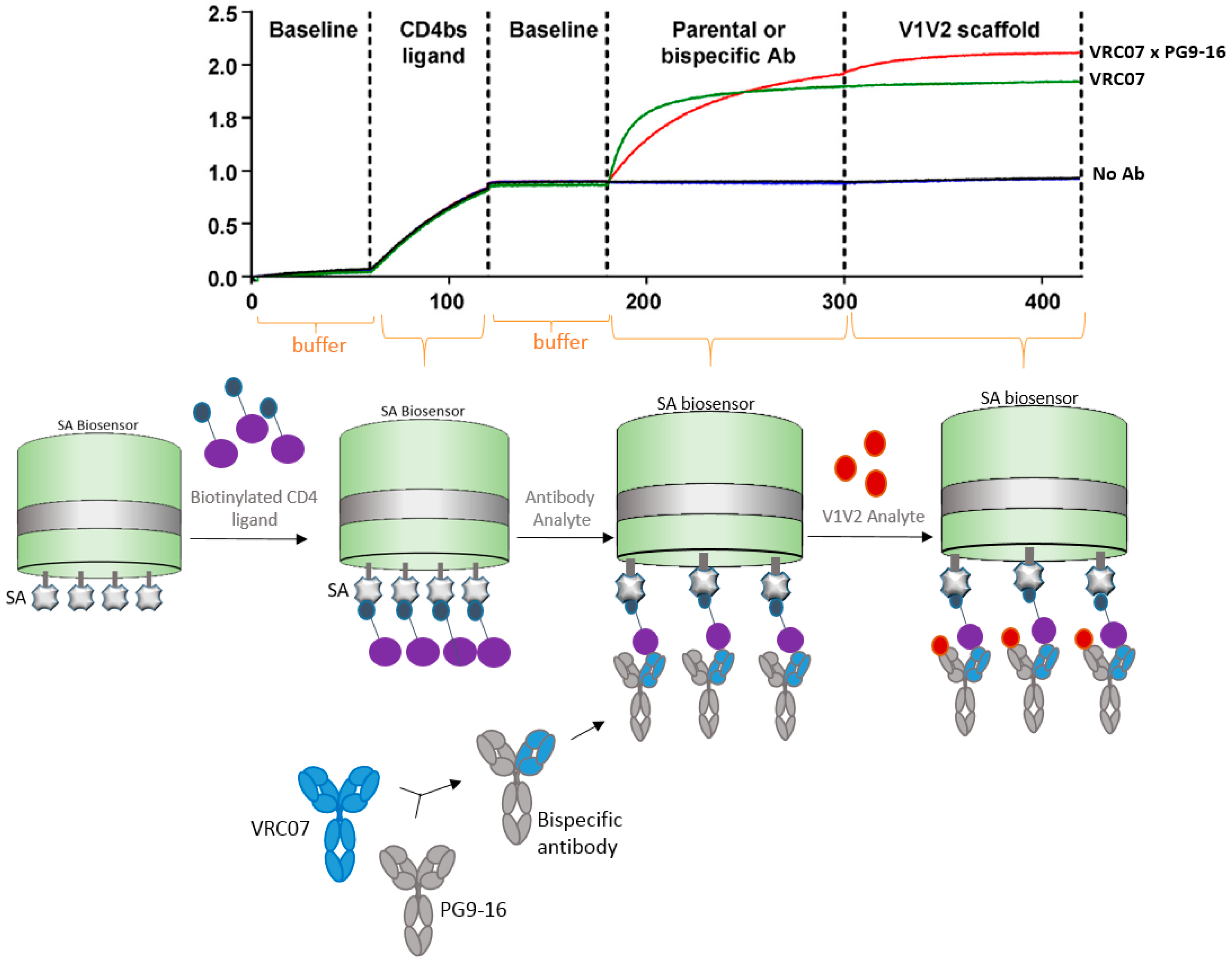
4.2. Bispecific Antibody Capture
5. Virus Capture Strategies
5.1. VLP (Virus-Like Particles) Capture
5.2. Whole Virus Capture
6. Nucleic Acid Capture
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Disease | Organism | Citation n# | Selected Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIV | Lentivirus, virus | 53 | [29] |
| Flu/Influenza | Orthomyxoviridae, virus | 36 | [25] |
| Ebola virus | Filoviridae, virus | 8 | [24] |
| Dengue | Flavivirus, virus | 6 | [37] |
| Smallpox, variola | Vaccinia virus (VACV) orthopoxvirus, virus | 6 | [6] |
| Staph infection | Staphylococcus aureus, bacteria | 5 | [38] |
| Malaria | Plasmodium falciparum, protozoa | 4 | [39] |
| Chikungunya infection | Chikungunya (CHIKV), virus | 3 | [30] |
| Tuberculosis | Mycobacterium tuberculosis, bacteria | 2 | [40] |
| Middle East Respiratory syndrome | MERS-CoV coronavirus, virus | 2 | [41] |
| Hepatitis C (HCV) | Hepacivirus, virus | 2 | |
| Anthrax toxin | Bacillus anthracis, bacteria | 2 | [42] |
| Zika | Flavivirus, virus | 2 | [43] |
| Herpes | Herpesviridae, virus | 2 | [44] |
| Respiratory infection | Syncytial virus (RSV), virus | 1 | [45] |
| Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) | Enterovirus 71 (EV71), virus | 1 | [46] |
| HMPV | Metapneumovirus, virus | 1 | [47] |
| Schistosomiasis | Schistosoma japonicum, Trematoda worm | 1 | [48] |
| CMV infection, congenital infections | cytomegalovirus (HCMV), virus | 1 | [49] |
| Whooping cough | Bordetella pertussis, bacillus | 1 | [50] |
| Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) | Clostridium difficile, bacteria | 1 | [51] |
| Marburg virus disease | Marburg filoviridae, virus | 1 | [52] |
| Diphtheria | Corynebacterium diphtheria, bacteria | 1 | [53] |
| Gastroenteritis, urinary infections, neonatal meningitis | Escherichia coli, bacteria | 1 | [54] |
| Listeriosis | Listeria monocytogenes, bacteria | 1 | [55] |
| Lung infection, opportunistic pathogen | Pseudomonas aeruginosa, bacteria | 1 | [56] |
| Otitis, pulmonary infections | Moraxella catarrhalis, bacteria | 1 | [57] |
| Vaginitis | Trichomonas vaginalis, protozoan | 1 | [58] |
| Chlamydia infection | Chlamydia trachomatis, bacteria | 1 | [59] |
| Pulmonary, urinary infections | Klebsiella pneumoniae, bacteria | 1 | [14] |
| Encephalitis | Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), virus | 1 | [60] |
References
- Hearty, S.; Conroy, P.J.; Ayyar, B.V.; Byrne, B.; O’Kennedy, R. Surface plasmon resonance for vaccine design and efficacy studies: Recent applications and future trends. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 645–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaraswamy, S.; Tobias, R. Label-free kinetic analysis of an antibody-antigen interaction using biolayer interferometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1278, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Apiyo, D.O. Biolayer Interferometry (Octet) for Label-free Biomolecular Interaction Sensing. In Handbook of Surface Plasmon Resonance, 2nd ed.; Schasfoort, R.B.M., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; pp. 356–397. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, G.C.; Hougland, M.D.; Rajendra, Y. High-throughput mAb expression and purification platform based on transient CHO. Biotechnol. Prog. 2015, 31, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchelkunov, S.N. An Increasing Danger of Zoonotic Orthopoxvirus Infections. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaever, T.; Meng, X.; Matho, M.H.; Schlossman, A.; Li, S.; Sela-Culang, I.; Ofran, Y.; Buller, M.; Crump, R.W.; Parker, S.; et al. Potent Neutralization of Vaccinia Virus by Divergent Murine Antibodies Targeting a Common Site of Vulnerability in L1 Protein. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11339–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, D.R. Scaffolding to build a rational vaccine design strategy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17859–17860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhu, J. Computational tools for epitope vaccine design and evaluation. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 11, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Cheng, Y.; Kong, L.; Azadnia, P.; Giang, E.; Kim, J.; Wood, M.R.; Wilson, I.A.; Law, M.; Zhu, J. Approaching rational epitope vaccine design for hepatitis C virus with meta-server and multivalent scaffolding. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleishman, S.J.; Whitehead, T.A.; Ekiert, D.C.; Dreyfus, C.; Corn, J.E.; Strauch, E.-M.; Wilson, I.A.; Baker, D. Computational design of proteins targeting the conserved stem region of influenza hemagglutinin. Science 2011, 332, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, J.S.; Correia, B.E.; Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Graham, B.S.; Schief, W.R.; Kwong, P.D. Design and Characterization of Epitope-Scaffold Immunogens that Present the Motavizumab Epitope from Respiratory Syncytial Virus. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 409, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Y.; Gorman, J.; Ofek, G.; Srivatsan, S.; Druz, A.; Lees, C.R.; Lu, G.; Soto, C.; et al. Transplanting supersites of HIV-1 vulnerability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cvitkovic, R.; Pennini, M.E.; Chang, C.S.; Pelletier, M.; Bonnell, J.; Koksal, A.C.; Wu, H.; Dall’Acqua, W.F.; et al. Anti-MrkA Monoclonal Antibodies Reveal Distinct Structural and Antigenic Features of MrkA. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdiche, Y.N.; Miles, A.; Eckman, J.; Foletti, D.; Van Blarcom, T.J.; Yeung, Y.A.; Pons, J.; Rajpal, A. High-Throughput Epitope Binning Assays on Label-Free Array-Based Biosensors Can Yield Exquisite Epitope Discrimination That Facilitates the Selection of Monoclonal Antibodies with Functional Activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdiche, Y.N.; Lindquist, K.C.; Stone, D.M.; Rajpal, A.; Pons, J. Label-Free Epitope Binning Assays of Monoclonal Antibodies Enable the Identification of Antigen Heterogeneity. J. Immunol. Methods 2012, 382, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdiche, Y.N.; Malashock, D.S.; Pons, J. Probing the binding mechanism and affinity of tanezumab, a recombinant humanized anti-NGF monoclonal antibody, using a repertoire of biosensors. Protein Sci. 2008, 17, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lad, L.; Clancy, S.; Kovalenko, M.; Liu, C.; Hui, T.; Smith, V.; Pagratis, N. High-Throughput Kinetic Screening of Hybridomas to Identify High-Affinity Antibodies Using Bio-Layer Interferometry. J. Biomol. Screen. 2015, 20, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdiche, Y.N.; Malashock, D.S.; Pinkerton, A.; Pons, J. Exploring blocking assays using Octet, ProteOn, and Biacore biosensors. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 386, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Könitzer, J.D.; Pramanick, S.; Pan, Q.; Augustin, R.; Bandholtz, S.; Harriman, W.; Izquierdo, S. Generation of a highly diverse panel of antagonistic chicken monoclonal antibodies against the GIP receptor. MAbs 2017, 9, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamat, V.; Rafique, A. Designing Binding Kinetic Assay on the Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI) Biosensor to Characterize Antibody-Antigen Interactions. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 536, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PREVAIL II Writing Group; Multi-National PREVAIL II Study Team. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of ZMapp for Ebola Virus Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 13, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin, L.; Whaley, K.J.; Olinger, G.G.; Jacobs, M.; Gopal, R.; Qiu, X.; Kobinger, G.P. Antibody therapeutics for Ebola virus disease. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 27, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornholdt, Z.A.; Turner, H.L.; Murin, C.D.; Li, W.; Sok, D.; Souders, C.A.; Piper, A.E.; Goff, A.; Shamblin, J.D.; Wollen, S.E.; et al. Isolation of potent neutralizing antibodies from a survivor of the 2014 Ebola virus outbreak. Science 2016, 351, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.N.; Weber, K.M.; Limmer, R.A.; Horne, B.J.; Stevens, J.; Schwerzmann, J.; Wrammert, J.; McCausland, M.; Phipps, A.J.; Hancock, K.; et al. Evaluation of multiplex assay platforms for detection of influenza hemagglutinin subtype specific antibody responses. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 243, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, W.; Brown, J.H.; Cusack, S.; Paulson, J.C.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature 1988, 333, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.M.; Hancock, K.; Xu, X. Serologic assays for influenza surveillance, diagnosis and vaccine evaluation. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurie, K.L.; Huston, P.; Riley, S.; Katz, J.M.; Willison, D.J.; Tam, J.S.; Mounts, A.W.; Hoschler, K.; Miller, E.; Vandemaele, K.; et al. Influenza serological studies to inform public health action: Best practices to optimize timing, quality and reporting. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 7, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asokan, M.; Rudicell, R.S.; Louder, M.; McKee, K.; O’Dell, S.; Stewart-Jones, G.; Wang, K.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Choe, M.; et al. Bispecific Antibodies Targeting Different Epitopes on the HIV-1 Envelope Exhibit Broad and Potent Neutralization. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12501–12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvarajah, S.; Sexton, N.R.; Kahle, K.M.; Fong, R.H.; Mattia, K.-A.; Gardner, J.; Lu, K.; Liss, N.M.; Salvador, B.; Tucker, D.F.; et al. A Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Targeting the Acid-Sensitive Region in Chikungunya Virus E2 Protects from Disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Martin, S.R.; Haire, L.F.; Wharton, S.A.; Daniels, R.S.; Bennett, M.S.; McCauley, J.W.; Collins, P.J.; Walker, P.A.; Skehel, J.J.; et al. Receptor binding by an H7N9 influenza virus from humans. Nature 2013, 499, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuck, P.; Zhao, H. The Role of Mass Transport Limitation and Surface Heterogeneity in the Biophysical Characterization of Macromolecular Binding Processes by SPR Biosensing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 627, 15–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wei, T.; Jin, J.; Rose, A.; Wang, R.; Lin, M.-H.; Spann, K.; Harrich, D. Binding of the eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1A with the 5′UTR of HIV-1 genomic RNA is important for reverse transcription. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, J.G. Predicting the Uncertain Future of Aptamer-Based Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Molecules 2015, 20, 6866–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, A.D.; Kim, D.; Liu, R. Highly Stable Aptamers Selected from a 2′-Fully Modified fGmH RNA Library for Targeting Biomaterials. Biomaterials 2015, 36, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, S.C.; Kumar, P.K. Aptamers that bind to the hemagglutinin of the recent pandemic influenza virus H1N1 and efficiently inhibit agglutination. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8932–8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costin, J.M.; Jenwitheesuk, E.; Lok, S.-M.; Hunsperger, E.; Conrads, K.A.; Fontaine, K.A.; Rees, C.R.; Rossmann, M.G.; Isern, S.; Samudrala, R.; et al. Structural Optimization and De Novo Design of Dengue Virus Entry Inhibitory Peptides. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, J.; Kodali, S.; Matsuka, Y.V.; McNeil, L.K.; Mininni, T.; Scully, I.L.; Vernachio, J.H.; Severina, E.; Girgenti, D.; Jansen, K.U.; et al. A Recombinant Clumping Factor A-Containing Vaccine Induces Functional Antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus That Are Not Observed after Natural Exposure. Clin. Vaccine Immun. 2012, 19, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.D.; Baldeviano, G.C.; Lucas, C.M.; Lugo-Roman, L.A.; Crosnier, C.; Bartholdson, S.J.; Diouf, A.; Miura, K.; Lambert, L.E.; Ventocilla, J.A.; et al. A PfRH5-Based Vaccine Is Efficacious against Heterologous Strain Blood-Stage Plasmodium falciparum Infection in Aotus Monkeys. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Ly, D.; Li, N.S.; Altman, J.D.; Piccirilli, J.A.; Moody, D.B.; Adams, E.J. Molecular basis of mycobacterial lipid antigen presentation by CD1c and its recognition by αβ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 11, E4648–E4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shi, W.; Joyce, M.G.; Modjarrad, K.; Zhang, Y.; Leung, K.; Lees, C.R.; Zhou, T.; Yassine, H.M.; Kanekiyo, M.; et al. Evaluation of candidate vaccine approaches for MERS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Li, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Yin, K.; Liu, J.; Zai, X.; Li, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Generation and Characterization of Human Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Anthrax Protective Antigen following Vaccination with a Recombinant Protective Antigen Vaccine. J. Clin. Vaccine Immun. 2015, 22, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba-Spaeth, G.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Rouvinski, A.; Vaney, M.C.; Medits, I.; Sharma, A.; Simon-Lorière, E.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; Haouz, A.; et al. Structural basis of potent Zika-dengue virus antibody cross-neutralization. Nature 2016, 536, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, T.M.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Gallagher, J.R.; Lin, Y.; Lou, H.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Wald, A.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Patient-Specific Neutralizing Antibody Responses to Herpes Simplex Virus Are Attributed to Epitopes on gD, gB, or Both and Can Be Type Specific. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9213–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krarup, A.; Truan, D.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, P.; Bogaert, L.; Bouchier, P.; Bisschop, I.J.M.; Widjojoatmodjo, M.N.; Zahn, R.; Schuitemaker, H.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. A highly stable prefusion RSV F vaccine derived from structural analysis of the fusion mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Su, W.; An, D.; Gao, F.; Kong, W.; Jiang, C. Identification of a Common Epitope between Enterovirus 71 and Human MED25 Proteins Which May Explain Virus-Associated Neurological Disease. Viruses 2015, 7, 1558–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, J.E.; Cox, R.G.; Hastings, A.K.; Boyd, K.L.; Wadia, J.; Chen, Z.; Burton, D.R.; Williamson, R.A.; Williams, J.V. A Broadly Neutralizing Human Monoclonal Antibody Exhibits In Vivo Efficacy against Both Human Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Gobert, G.N.; Cai, P.; Mou, R.; Nawaratna, S.; Fang, G.; Villinger, F.; McManus, D.P. Suppression of the Insulin Receptors in Adult Schistosoma japonicum Impacts on Parasite Growth and Development: Further Evidence of Vaccine Potential. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauvar, L.M.; Liu, K.; Park, M.; DeChene, N.; Stephenson, R.; Tenorio, E.; Ellsworth, S.L.; Tabata, T.; Petitt, M.; Tsuge, M.; et al. A High-Affinity Native Human Antibody Neutralizes Human Cytomegalovirus Infection of Diverse Cell Types. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millen, H.; Watanabe, M.; Komatsu, E.; Yamaguchi, F.; Nagasawa, Y.; Suzuki, E.; Monaco, H.; Weiss, A. Single Amino Acid Polymorphisms of Pertussis Toxin Subunit S2 (PtxB) Affect Protein Function. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anosova, N.G.; Cole, L.E.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Brown, A.M.; Mundle, S.; Zhang, J.; Ray, S.; Ma, F.; Garrone, P.; et al. A Combination of Three Fully Human Toxin A- and Toxin B-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies Protects against Challenge with Highly Virulent Epidemic Strains of Clostridium difficile in the Hamster Model. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flyak, A.I.; Ilinykh, P.A.; Murin, C.D.; Garron, T.; Shen, X.; Fusco, M.L.; Hashiguchi, T.; Bornholdt, Z.A.; Slaughter, J.C.; Sapparapu, G.; et al. Mechanism of Human Antibody-Mediated Neutralization of Marburg Virus. Cell 2015, 160, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevigny, L.M.; Booth, B.J.; Rowley, K.J.; Leav, B.A.; Cheslock, P.S.; Garrity, K.A.; Sloan, S.E.; Thomas, W., Jr.; Babcock, G.J.; Wang, Y. Identification of a Human Monoclonal Antibody to Replace Equine Diphtheria Antitoxin for Treatment of Diphtheria Intoxication. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3992–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szijártó, V.; Guachalla, L.M.; Visram, Z.C.; Hartl, K.; Varga, C.; Mirkina, I.; Zmajkovic, J.; Badarau, A.; Gerhild, Z.; Pleban, C.; et al. Bactericidal Monoclonal Antibodies Specific to the Lipopolysaccharide O Antigen from Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Clone ST131-O25b:H4 Elicit Protection in Mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reniere, M.L.; Whiteley, A.T.; Hamilton, K.L.; John, S.M.; Lauer, P.; Brennan, R.G.; Portnoy, D.A. Glutathione activates virulence gene expression of an intracellular pathogen. Nature 2015, 517, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGiandomenico, A.; Warrener, P.; Hamilton, M.; Guillard, S.; Ravn, P.; Minter, R.; Camara, M.M.; Venkatraman, V.; Macgill, R.S.; Lin, J.; et al. Identification of broadly protective human antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa exopolysaccharide Psl by phenotypic screening. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Al-Jubair, T.; Voraganti, C.; Andersson, T.; Mukherjee, O.; Su, Y.-C.; Zipfel, P.; Riesbeck, K. Moraxella catarrhalis Binds Plasminogen to Evade Host Innate Immunity. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3458–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichorova, R.N.; Yamamoto, H.S.; Fashemi, T.; Foley, E.; Ryan, S.; Beatty, N.; Dawood, H.; Hayes, G.R.; St-Pierre, G.; Sato, S.; et al. Trichomonas vaginalis. Lipophosphoglycan Exploits Binding to Galectin-1 and -3 to Modulate Epithelial Immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 998–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Dong, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, G. Chlamydial Plasmid-Encoded Virulence Factor Pgp3 Neutralizes the Antichlamydial Activity of Human Cathelicidin LL-37. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 4701–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Jin, R.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; Gong, R.; Xiao, G.F.; Wang, W. Peptide inhibitor of Japanese encephalitis virus infection targeting envelope protein domain III. Antivir. Res. 2014, 104, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petersen, R.L. Strategies Using Bio-Layer Interferometry Biosensor Technology for Vaccine Research and Development. Biosensors 2017, 7, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040049
Petersen RL. Strategies Using Bio-Layer Interferometry Biosensor Technology for Vaccine Research and Development. Biosensors. 2017; 7(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040049
Chicago/Turabian StylePetersen, Rejane L. 2017. "Strategies Using Bio-Layer Interferometry Biosensor Technology for Vaccine Research and Development" Biosensors 7, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040049
APA StylePetersen, R. L. (2017). Strategies Using Bio-Layer Interferometry Biosensor Technology for Vaccine Research and Development. Biosensors, 7(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios7040049





