pH-Responsive “Smart” Hydrogel for Controlled Delivery of Silver Nanoparticles to Infected Wounds
Abstract
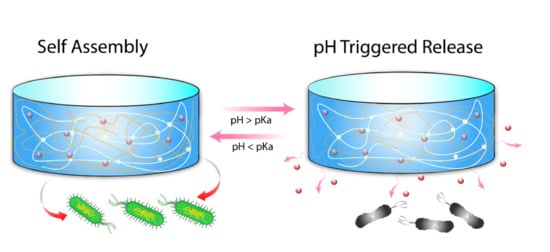
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of AgNPs@MSA
2.2. Preparation of pH-Responsive Hydrogel
2.3. pH-Dependent Swelling and Rheological Properties of the Hydrogel
2.4. Hydrogel Morphology
2.5. pH-Dependent Release Kinetics
2.6. Antibacterial Activity
2.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of AgNPs
3.3. Characterization of AgNPs
3.4. Preparation of pH-Responsive Hydrogel
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.6. pH-Responsive Swelling
3.7. Rheological Characterization
3.8. pH-Responsive Analysis of Hydrogel Loaded with Crystal Violet
3.9. pH-Dependent Release of AgNP- Loaded Hydrogel
3.10. In Vitro Antibacterial Assessment
Bacterial Culture
3.11. Zone of Inhibition
3.12. Live/Dead Bacterial Viability Assay
3.13. In vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilev, K.; Cook, J.; Griesser, H.J. Antibacterial surfaces for biomedical devices. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2009, 6, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, G.; Shi, D.; Wang, M.; Webster, T.J. Reducing Bacterial Infections and Biofilm Formation Using Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Antibacterial Surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzello, L.; Pompa, P.P. Nanosilver-based antibacterial drugs and devices: Mechanisms, methodological drawbacks, and guidelines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1501–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, H.; Garg, S.; Vasilev, K.; Kopecki, Z.; Cowin, A.J. Silver-based wound dressings: Current issues and future developments for treating bacterial infections. Wound Pract. Res. 2020, 28, 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Jose Ruben, M.; Luis, E.J.; Alejandra, C.; Katherine, H.; Juan, B.K.; Tapia, R.J.; Jose, Y.M. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K.; Setyawati, M.I.; Leong, D.T.; Xie, J. Antimicrobial silver nanomaterials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 357, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, Z. Boosting antibacterial activity with mesoporous silica nanoparticles supported silver nanoclusters. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 555, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Mun, G.L.K.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Human Cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Elkhooly, T.A.; Liu, X.; Cavallaro, A.; Taheri, S.; Vasilev, K.; Feng, Q. Silver nanoparticle based coatings enhance adipogenesis compared to osteogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells through oxidative stress. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1466–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Yu, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, G.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Y. Bioinspired Multifunctional Hybrid Hydrogel Promotes Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haidari, H.; Kopecki, Z.; Bright, R.; Cowin, A.J.; Garg, S.; Goswami, N.; Vasilev, K. Ultrasmall AgNP-Impregnated Biocompatible Hydrogel with Highly Effective Biofilm Elimination Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 41011–41025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, S.; Cavallaro, A.; Christo, S.N.; Majewski, P.; Barton, M.; Hayball, J.D.; Vasilev, K. Antibacterial Plasma Polymer Films Conjugated with Phospholipid Encapsulated Silver Nanoparticles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilev, K. Nanoengineered antibacterial coatings and materials: A perspective. Coatings 2019, 9, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, H.; Zhang, Q.; Melville, E.; Kopecki, Z.; Song, Y.; Cowin, A.J.; Garg, S. Development of Topical Delivery Systems for Flightless Neutralizing Antibody. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afinjuomo, F.; Fouladian, P.; Parikh, A.; Barclay, T.G.; Song, Y.; Garg, S. Preparation and Characterization of Oxidized Inulin Hydrogel for Controlled Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavallaro, A.; Taheri, S.; Vasilev, K. Responsive and “smart” antibacterial surfaces: Common approaches and new developments. Biointerphases 2014, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, N.; Bhardwaj, A.; Mehta, S.; Mehta, A. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 748–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kocak, G.; Tuncer, C.; Bütün, V. pH-Responsive polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, J.R.; Harris, K.L.; Jubin, K.; Bainbridge, N.J.; Jordan, N.R. The effect of pH in modulating skin cell behaviour. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 671–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Ochoa, M.; Waimin, J.F.; Rahimi, R.; Ziaie, B. A pH-regulated drug delivery dermal patch for targeting infected regions in chronic wounds. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Cai, X.; Xiao, J.; Cheng, Y. A pH-responsive hydrogel with potent antibacterial activity against both aerobic and anaerobic pathogens. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dong, S.; Xu, W.; Tu, S.; Yan, L.; Zhao, C.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Antibacterial Hydrogels. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, C.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. pH-Switchable Antimicrobial Nanofiber Networks of Hydrogel Eradicate Biofilm and Rescue Stalled Healing in Chronic Wounds. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11686–11697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, E.; Dennison, S.R.; Harris, F.; Phoenix, D.A. pH dependent antimicrobial peptides and proteins, their mechanisms of action and potential as therapeutic agents. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halacheva, S.S.; Freemont, T.J.; Saunders, B.R. pH-responsive physical gels from poly(meth)acrylic acid-containing crosslinked particles: The relationship between structure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4065–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haidari, H.; Goswami, N.; Bright, R.; Kopecki, Z.; Cowin, A.J.; Garg, S.; Vasilev, K. The interplay between size and valence state on the antibacterial activity of sub-10 nm silver nanoparticles. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2365–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hibbins, A.R.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Marimuthu, T.; Toit, L.C.D.; Pillay, V. Design of a Versatile pH-Responsive Hydrogel for Potential Oral Delivery of Gastric-Sensitive Bioactives. Polymers 2017, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozlovskaya, V.; Kharlampieva, E.; Mansfield, M.L.; Sukhishvili, S.A. Poly(methacrylic acid) Hydrogel Films and Capsules: Response to pH and Ionic Strength, and Encapsulation of Macromolecules. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, A.R.; Peppas, N.A. Swelling/deswelling of anionic copolymer gels. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Wang, L.L.; Chung, J.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Atluri, P.; Burdick, J.A. Methods To Assess Shear-Thinning Hydrogels for Application As Injectable Biomaterials. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michl, T.D.; Tran, D.T.T.; Kuckling, H.F.; Zhalgasbaikyzy, A.; Ivanovská, B.; García, L.E.G.; Visalakshan, R.M.; Vasilev, K. It takes two for chronic wounds to heal: Dispersing bacterial biofilm and modulating inflammation with dual action plasma coatings. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7368–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Guo, G.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, H.; Wahafu, T.; Shen, H.; Liu, X.; et al. Silver-nanoparticles-modified biomaterial surface resistant to staphylococcus: New insight into the antimicrobial action of silver. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, Q.; Lou, D.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Qiao, B.; Dong, S.; Ma, L.; Gao, C.; Wu, Z. Smart Flexible Electronics-Integrated Wound Dressing for Real-Time Monitoring and On-Demand Treatment of Infected Wounds. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.E.; Kopecki, Z.; Anderson, P.J.; Cowin, A.J. In vitro analysis of the effect of Flightless I on murine tenocyte cellular functions. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; He, S.; Sun, X.; Shen, Y.; Yan, M.; Zhao, C. Injectable, NIR/pH-Responsive Nanocomposite Hydrogel as Long-Acting Implant for Chemophotothermal Synergistic Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20361–20375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, A.; Ata, S.; Islam, A. Stimuli responsive biopolymer (chitosan) based blend hydrogels for wound healing application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haidari, H.; Kopecki, Z.; Sutton, A.T.; Garg, S.; Cowin, A.J.; Vasilev, K. pH-Responsive “Smart” Hydrogel for Controlled Delivery of Silver Nanoparticles to Infected Wounds. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010049
Haidari H, Kopecki Z, Sutton AT, Garg S, Cowin AJ, Vasilev K. pH-Responsive “Smart” Hydrogel for Controlled Delivery of Silver Nanoparticles to Infected Wounds. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaidari, Hanif, Zlatko Kopecki, Adam T. Sutton, Sanjay Garg, Allison J. Cowin, and Krasimir Vasilev. 2021. "pH-Responsive “Smart” Hydrogel for Controlled Delivery of Silver Nanoparticles to Infected Wounds" Antibiotics 10, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010049
APA StyleHaidari, H., Kopecki, Z., Sutton, A. T., Garg, S., Cowin, A. J., & Vasilev, K. (2021). pH-Responsive “Smart” Hydrogel for Controlled Delivery of Silver Nanoparticles to Infected Wounds. Antibiotics, 10(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010049