Defining the Scope of Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions on the Prescription Quality of Antibiotics for Surgical Intra-Abdominal Infections
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Analyzed Variables and Definitions
2.4. Antimicrobial Stewardship
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Baseline Characteristics and Indications for Emergency Surgery
3.2. Impact on Prescription Behavior
3.3. Postoperative Antibiotic Therapy
3.4. Postoperative Outcomes and Complications
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance. About AMR. 15 February 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- The White House. FACT SHEET: Obama Adminstration Releases National Action Plan to Combat Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. 27 March 2015. Available online: https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/03/27/fact-sheet-obama-administration-releases-national-action-plan-combat-ant (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Gesundheit Bf. Bundesministerium für Gesundheit. 10-Punkte-Plan zur Bekämpfung Resistenter Erreger. 25 March 2015. Available online: https://www.bundesgesundheitsministerium.de/ministerium/meldungen/2015/10-punkte-plan-zu-antibiotika-resistenzen.html (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Bundesgesetzblatt. Gesetz zur Änderung des Infektionsschutzgesetzes und Weiterer Gesetze. 28 July 2011. Available online: https://www.bgbl.de (accessed on 20 August 2015).
- Versporten, A.; Zarb, P.; Caniaux, I.; Gros, M.-F.; Drapier, N.; Miller, M.; Jarlier, V.; Nathwani, D.; Goossens, H.; Koraqi, A.; et al. Antimicrobial consumption and resistance in adult hospital inpatients in 53 countries: Results of an internet-based global point prevalence survey. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghdassi, S.J.S.; Gastmeier, P.; Piening, B.C.; Behnke, M.; Diaz, L.A.P.; Gropmann, A.; Rosenbusch, M.-L.; Kramer, T.S.; Hansen, S. Antimicrobial usage in German acute care hospitals: Results of the third national point prevalence survey and comparison with previous national point prevalence surveys. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charani, E.; Castro-Sanchez, E.; Sevdalis, N.; Kyratsis, Y.; Drumright, L.; Shah, N.; Holmes, A. Understanding the Determinants of Antimicrobial Prescribing Within Hospitals: The Role of “Prescribing Etiquette”. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartelli, M.; Chichom-Mefire, A.; Labricciosa, F.M.; Hardcastle, T.; Abu-Zidan, F.M.; Adesunkanmi, A.K.; Ansaloni, L.; Bala, M.; Balogh, Z.J.; Beltrán, M.A.; et al. The management of intra-abdominal infections from a global perspective: 2017 WSES guidelines for management of intra-abdominal infections. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2017, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartelli, M.; Labricciosa, F.M.; Ciotti, M.; Pagani, L.; Ansaloni, L.; Brink, A.J.; Carlet, J.; Khanna, A.K.; Chichom-Mefire, A.; Coccolini, F.; et al. The Global Alliance for Infections in Surgery: Defining a model for antimicrobial stewardship—results from an international cross-sectional survey. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2017, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, C.; Zak, M.; Avery, L.; Brown, J.E. Treatment Modalities and Antimicrobial Stewardship Initiatives in the Management of Intra-Abdominal Infections. Antibiotics 2016, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazuski, J.E.; Tessier, J.M.; May, A.K. The Surgical Infection Society Revised Guidelines on the Management of In-tra-Abdominal Infection. Surg. Infect. 2017, 18, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomkin, J.S.; Mazuski, J.; Bradley, J.S.; Rodvold, K.A.; Goldstein, E.J.C.; Baron, E.J.; O’Neill, P.J.; Chow, A.W.; Dellinger, E.P.; Eachempati, S.R.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Complicated Intra-abdominal Infection in Adults and Children: Guidelines by the Surgical Infection Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linder, M.M.; Wacha, H.; Feldmann, U.; Wesch, G.; Streifensand, R.A.; Gundlach, E. The Mannheim peritonitis index. An instrument for the intraoperative prognosis of peritonitis. Der Chir. 1987, 58, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangram, A.J.; Horan, T.C.; Pearson, M.L.; Silver, L.C.; Jarvis, W.R. Guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 1999. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Am. J. Infect. Control. 1999, 27, 133–134. [Google Scholar]
- de With, K.; Wilke, K.; Kern, W.V. AWMF-S3-Leitlinie Strategien zur Sicherung Rationaler Antibiotika-Anwendung im Krankenhaus. 31 January 2019. Available online: https://www.awmf.org/leitlinien/detail/ll/092-001.html (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Barlam, T.F.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Abbo, L.M. Implementing an Antibiotic Stewardship Program: Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratzler, D.W.; Houck, P.M. Surgical Infection Prevention Guideline Writers, W. Antimicrobial prophylaxis for surgery: An ad-visory statement from the National Surgical Infection Prevention Project. Am. J. Surg. 2005, 189, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, M.J.; Lin, M.Y.; Weinstein, R.A.; Trick, W.E. Spread of Carbapenem-ResistantEnterobacteriaceaeAmong Illinois Healthcare Facilities: The Role of Patient Sharing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cassier, P.; Lallechère, S.; Aho, S. Cephalosporin and fluoroquinolone combinations are highly associated with CTX-M β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli: A case-control study in a French teaching hospital. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 17, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazuski, J.E.; Sawyer, R.; Nathens, A.; DiPiro, J.T.; Schein, M.; Kudsk, K.A.; Yowler, C. Antibiotics as an Adjunct to Source Control: Revised Surgical Infection Society Guidelines for Antimicrobial Therapy of Intra-abdominal Infections. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. Source Control 2003, 2003, 427–441. [Google Scholar]
- Popovski, Z.; Mercuri, M.; Main, C.; Sne, N.; Walsh, K.; Sung, M.; Rice, T.; Mertz, D. Multifaceted intervention to optimize antibiotic use for intra-abdominal infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 70, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubrovskaya, Y.; Papadopoulos, J.; Scipione, M.R.; Altshuler, J.; Phillips, M.; Mehta, S.A. Antibiotic Stewardship for Intra-abdominal Infections: Early Impact on Antimicrobial Use and Patient Outcomes. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2012, 33, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.G.; Claridge, J.A.; Nathens, A.B.; Rotstein, O.D.; Duane, T.M.; Evans, H.L.; Cook, C.H.; O’Neill, P.J.; Mazuski, J.E.; Askari, R.; et al. Trial of Short-Course Antimicrobial Therapy for Intraabdominal Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimbrell, A.R.; Novosel, T.J.; Collins, J.N. Do Postoperative Antibiotics Prevent Abscess Formation in Complicated Appendi-citis? Am. Surgeon. 2014, 80, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.D.; Cifu, A.S. Management of Acute Diverticulitis. JAMA 2017, 318, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartelli, M.; Weber, D.G.; Kluger, Y.; Ansaloni, L.; Coccolini, F.; Abu-Zidan, F.; Augustin, G.; Ben-Ishay, O.; Biffl, W.L.; Bouliaris, K.; et al. 2020 update of the WSES guidelines for the management of acute colonic diverticulitis in the emergency setting. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2020, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, T.; Strasberg, S.M.; Solomkin, J.S.; Pitt, H.A.; Gomi, H.; Yoshida, M.; Mayumi, T.; Miura, F.; Gouma, D.J.; Garden, O.J.; et al. TG13: Updated Tokyo Guidelines for the management of acute cholangitis and cholecystitis. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2013, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duane, T.M.; Zuo, J.X.; Wolfe, L.G.; Bearman, G.; Edmond, M.B.; Lee, K.; Cooksey, L.; Stevens, M.P. Surgeons Do Not Listen: Evaluation of Compliance with Antimicrobial Stewardship Program Recommendations. Am. Surg. 2013, 79, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartelli, M.; Labricciosa, F.M.; Scoccia, L.; Bellesi, J.; Mazzoccanti, M.R.; Scaloni, G.; Gentilozzi, B.; Chiodera, A. Non-Restrictive Antimicrobial Stewardship Program in a General and Emergency Surgery Unit. Surg. Infect. 2016, 17, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, M.C.; Edye, M. Educational Antimicrobial Stewardship Intervention Ineffective in Changing Surgical Prophylactic Anti-biotic Prescribing. Surg Infect. 2016, 17, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, P.; Peden, C.; Brown, E.; Charani, E.; Michie, S.; Ramsay, C.R.; Marwick, C.A. interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing practices for hospital inpatients (updated protocol). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachouras, D.; Hopkins, S. Antimicrobial stewardship: We know it works; time to make sure it is in place everywhere. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2, ED000119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuts, E.C.; Hulscher, M.E.J.L.; Mouton, J.W.; Verduin, C.M.; Stuart, J.W.T.C.; Overdiek, H.W.P.M.; Van Der Linden, P.D.; Natsch, S.; Hertogh, C.M.P.M.; Wolfs, T.F.W.; et al. Current evidence on hospital antimicrobial stewardship objectives: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, H. Antibiotic consumption and link to resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Patients, No. (%) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Total (n = 767) | Baseline (n = 495) | ASP (n = 272) | |
| Sex ratio (M:F) | 411:356 | 268:227 | 143:129 | 0.68 |
| Age, mean (range), y | 53.3 (18–96) | 52.6 (18–96) | 54.5 (18–89) | 0.21 |
| Body weight, mean (SD), kg | 80.4 (20.8) | 79.9 (19.8) | 81.4 (22.4) | 0.70 |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 27.0 (6.3) | 26.8 (5.8) | 27.5 (7.1) | 0.79 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 75 (9.8) | 54 (10.9) | 21 (7.7) | 0.16 |
| Liver cirrhosis | 11 (1.4) | 6 (1.2) | 5 (1.8) | 0.49 |
| Current immunosuppressive drugs | 50 (6.5) | 24 (4.8) | 26 (9.6) | 0.011 |
| ASA classification | ||||
| I | 107 (14.0) | 65 (13.1) | 42 (15.4) | 0.22 |
| II | 355 (46.3) | 234 (47.3) | 121 (44.5) | |
| III | 220 (28.7) | 140 (28.3) | 80 (29.4) | |
| IV | 78 (10.2) | 54 (10.9) | 24 (8.8) | |
| CCI | ||||
| 0 | 273 (35.6) | 185 (37.4) | 88 (32.4) | 0.28 |
| 1–2 | 162 (21.1) | 93 (18.8) | 69 (25.4) | |
| 3–4 | 170 (22.2) | 120 (24.2) | 50 (18.4) | |
| >4 | 162 (21.1) | 97 (19.6) | 65 (23.9) | |
| Community-acquired IAI | 602 (78.5) | 379 (76.6) | 223 (82.0) | 0.081 |
| Hospital-acquired IAI | 165 (21.5) | 116 (23.4) | 49 (18.0) | |
| Preoperative a | ||||
| LOS, mean (SD), d | 1.8 (4.3) | 1.9 (4.6) | 1.5 (3.7) | 0.13 |
| Surgery | 118 (15.4) | 78 (15.8) | 40 (14.7) | 0.70 |
| Antibiotic therapy | 134 (17.5) | 85 (17.2) | 49 (18.0) | 0.77 |
| Duration ABT, mean (SD), d | 6.7 (5.8) | 6.6 (5.6) | 7.0 (6.3) | 0.56 |
| MDR | 51 (6.6) | 25 (5.1) | 26 (9.6) | 0.017 |
| Patients, No. (%) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Total (n = 767) | Baseline (n = 495) | ASP (n = 272) | |
| Time from indication to surgery, mean (median, SD), h | 6.6 (4.0, 6.4) | 6.6 (4.4, 6.5) | 6.5 (4.0, 6.2) | 0.97 |
| Indication for surgery | ||||
| Appendicitis | 293 (38.2) | 190 (38.4) | 103 (37.9) | <0.001 |
| Cholecystitis | 200 (26.1) | 151 (30.5) | 49 (18.0) | |
| Diverticulitis | 26 (3.4) | 15 (3.0) | 11 (4.0) | |
| Primary perforation a | 86 (11.2) | 55 (11.1) | 31 (11.4) | |
| Postoperative leakage | 70 (9.1) | 49 (9.9) | 21 (7.7) | |
| Intestinal obstruction | 85 (11.1) | 30 (6.1) | 55 (20.2) | |
| Abscess | 7 (0.9) | 5 (1.0) | 2 (0.7) | |
| Duration of surgery, mean (SD), min | 91 (54) | 91.9 (55.0) | 90.4 (52.3) | 0.61 |
| Peritonitis | 290 (37.8) | 168 (33.9) | 122 (44.9) | 0.003 |
| MPI b | 18.3 (10.4) | 17.3 (8.7) | 19.7 (8.8) | 0.030 |
| Sepsis | 112 (14.6) | 77 (15.6) | 35 (12.9) | 0.31 |
| Definitive source control | 713 (93.0) | 461 (93.1) | 252 (92.6) | 0.80 |
| Postoperative transfer | ||||
| General ward | 398 (51.9) | 256 (51.7) | 142 (52.2) | 0.44 |
| IMC | 88 (11.5) | 52 (10.5) | 36 (13.2) | |
| ICU | 281 (36.6) | 187 (37.8) | 94 (34.6) | |
| Patients, No. (%) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Total (n = 767) | Baseline (n = 495) | ASP (n = 272) | |
| Total days on ABT, mean (median, SD), d | 5.7 (3, 6.9) | 6.1 (3, 7.0) | 4.8 (1, 6.8) | 0.02 |
| Switches during ABT | ||||
| None | 427 (55.7) | 257 (51.9) | 170 (62.5) | 0.017 |
| 1 | 224 (29.2) | 151 (30.5) | 73 (26.8) | |
| > 1 | 116 (15.2) | 87 (17.5) | 29 (10.6) | |
| Time from indication to ABT, mean (median, SD), h | 3.6 (2.0, 4.8) | 3.6 (3, 4.5) | 3.7 (2, 5.4) | 0.12 |
| Surgeons’ recommendations a | ||||
| Missing | 430 (56.1) | 277 (56.0) | 153 (56.3) | <0.001 |
| PAT | 312 (40.7) | 212 (42.8) | 100 (36.8) | |
| No PAT | 25 (3.3) | 6 (1.2) | 19 (7.0) | |
| Postoperative antibiotic therapy | 404 (52.7) | 281 (56.8) | 123 (45.2) | 0.002 |
| Documented indication b | 93 (12.1) | 61 (12.3) | 32 (11.8) | 0.81 |
| Duration, mean (SD), d | 7.7 (5.6) | 8.1 (5.7) | 7.2 (5.4) | 0.08 |
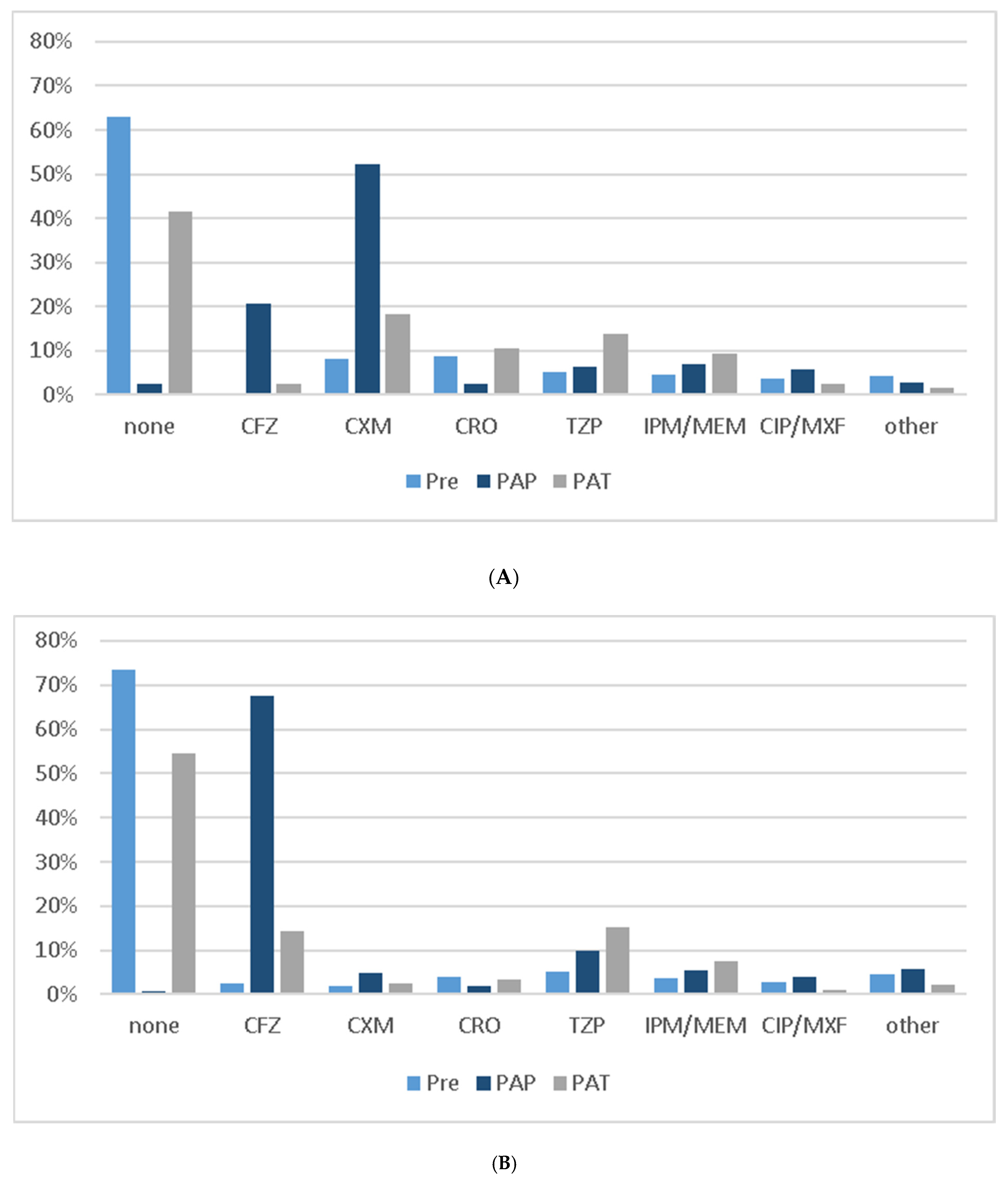
| EAT | ||||
| CFZ | 51 (12.6) | 12 (4.3) | 39 (31.7) | <0.001 |
| CXM | 91 (22.5) | 84 (29.9) | 7 (5.7) | |
| CRO | 60 (14.9) | 52 (18.5) | 8 (6.5) | |
| TZP | 108 (26.7) | 68 (24.2) | 40 (32.5) | |
| IPM/MEM | 66 (16.3) | 46 (16.4) | 20 (16.3) | |
| CIP/MXF | 14 (3.5) | 11 (3.9) | 3 (2.4) | |
| Other | 8 (1.9) | 6 (2.1) | 2 (1.6) | |
| Additional MTZ | 224 (55.4) | 164 (58.4) | 60 (48.8) | 0.01 |
| AMS assessment of PAT | ||||
| No indication | 59 (14.6) | 49 (17.4) | 10 (8.1) | 0.015 |
| Missing PAT c | 24 (6.6) | 12 (5.6) | 12 (8.1) | 0.36 |
| Too long | 184 (45.5) | 135 (48.0) | 49 (39.8) | 0.038 |
| Too short | 2 (0.5) | 0 | 2 (1.6) | |
| Too broad | 89 (22.0) | 81 (28.8) | 8 (6.5) | <0.001 |
| Too narrow | 75 (18.6) | 48 (17.1) | 27 (22.0) | |
| Mismatch with MTZ d | 28 (4.5) | 15 (3.7) | 13 (6.0) | 0.18 |
| Perioperative use of CRO | 98 (12.8) | 80 (16.2) | 18 (6.6) | <0.001 |
| Perioperative use of CIP/MXF | 61 (8.0) | 42 (8.5) | 19 (7.0) | 0.46 |
| Postoperative Antibiotic Therapy, No. (%) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Total (n = 404) | Baseline (n = 281) | ASP (n = 123) | |
| Community-acquired IAI | 262 (43.5) | 177 (46.7) | 85 (38.1) | 0.040 |
| Hospital-acquired IAI | 142 (86.1) | 104 (89.7) | 38 (77.6) | 0.040 |
| Indication for surgery | ||||
| Appendicitis | 102 (34.8) | 68 (35.8) | 34 (33.0) | 0.63 |
| Cholecystitis | 102 (51.0) | 82 (54.3) | 20 (40.8) | 0.070 |
| Diverticulitis | 25 (96.2) | 14 (93.3) | 11 (100) | 0.38 |
| Primary perforation a | 84 (97.7) | 54 (98.2) | 30 (96.8) | 0.68 |
| Postoperative leakage | 66 (94.3) | 47 (95.9) | 19 (90.5) | 0.37 |
| Intestinal obstruction | 18 (21.2) | 11 (36.7) | 7 (12.7) | 0.010 |
| Abscess | 7 (100) | 5 (100) | 2 (100) | |
| Definitive source control | 353 (49.5) | 247 (53.6) | 106 (42.1) | 0.020 |
| Peritonitis | 252 (86.9) | 158 (94.0) | 94 (77.0) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 109 (97.3) | 76 (98.7) | 33 (94.3) | 0.18 |
| Surgeons’ recommendations for PAT | 299 (95.8) | 204 (96.2) | 95 (95.0) | 0.61 |
| Patients, No. (%) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Total (n = 767) | Baseline (n = 495) | ASP (n = 272) | |
| Postoperative organ support | ||||
| Vasopressor therapy | 195 (25.4) | 127 (25.7) | 68 (25.0) | 0.84 |
| Ventilation | 214 (27.9) | 135 (27.3) | 79 (29.0) | 0.60 |
| Dialysis | 21 (2.7) | 12 (2.4) | 9 (3.3) | 0.47 |
| Re-intervention | 169 (22.0) | 118 (23.8) | 51 (18.8) | 0.10 |
| Surgery | 135 (17.6) | 94 (19.0) | 41 (15.1) | 0.17 |
| Postoperative complications a | ||||
| None | 343 (44.7) | 211 (42.6) | 132 (48.5) | 0.14 |
| Minor (Grade I–IIIa) | 251 (32.7) | 174 (35.2) | 77 (28.3) | |
| Major (Grade IIIb–V) | 173 (22.6) | 110 (22.2) | 63 (23.3) | |
| Mortality (Grade V) | 30 (3.9) | 18 (3.6) | 12 (4.4) | 0.60 |
| Surgical site infection | 94 (12.3) | 62 (12.5) | 32 (11.8) | 0.76 |
| New MDR | 27 (3.5) | 13 (2.6) | 14 (5.1) | 0.07 |
| LOS, mean (SD), d | 10.5 (9.0) | 10.5 (9.0) | 10.4 (9.1) | 0.62 |
| No. of days in ICU or IMC, mean (SD), d | 4.1 (7.8) | 4.1 (7.8) | 4.0 (7.8) | 0.61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Surat, G.; Vogel, U.; Wiegering, A.; Germer, C.-T.; Lock, J.F. Defining the Scope of Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions on the Prescription Quality of Antibiotics for Surgical Intra-Abdominal Infections. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010073
Surat G, Vogel U, Wiegering A, Germer C-T, Lock JF. Defining the Scope of Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions on the Prescription Quality of Antibiotics for Surgical Intra-Abdominal Infections. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(1):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010073
Chicago/Turabian StyleSurat, Güzin, Ulrich Vogel, Armin Wiegering, Christoph-Thomas Germer, and Johan Friso Lock. 2021. "Defining the Scope of Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions on the Prescription Quality of Antibiotics for Surgical Intra-Abdominal Infections" Antibiotics 10, no. 1: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010073
APA StyleSurat, G., Vogel, U., Wiegering, A., Germer, C.-T., & Lock, J. F. (2021). Defining the Scope of Antimicrobial Stewardship Interventions on the Prescription Quality of Antibiotics for Surgical Intra-Abdominal Infections. Antibiotics, 10(1), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010073





