DksA Modulates Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
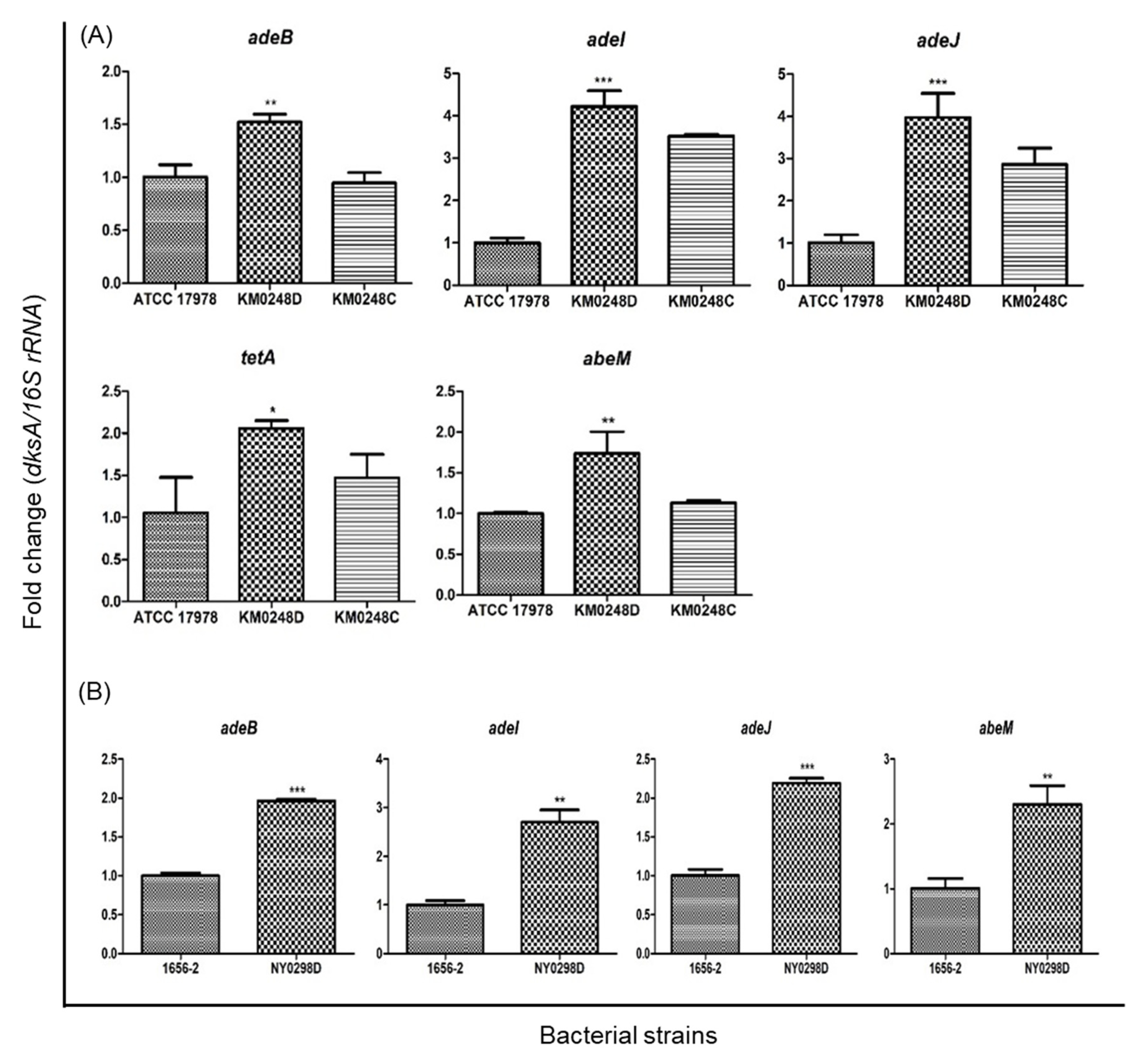
2.1. The Effect of dksA on the Antimicrobial Susceptibility of A. baumannii ATCC 17978
2.2. The Effect of dksA on the Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Cellular Morphology of a Clinical A. baumannii Strain
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Construction of the ∆dksA Mutant of 1656-2 Strain
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.4. RNA Isolation and qPCR
4.5. Gram Staining
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antunes, L.; Visca, P.; Towner, K.J. Acinetobacter baumannii: Evolution of a global pathogen. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 71, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eliopoulos, G.M.; Maragakis, L.L.; Perl, T.M. Acinetobacter baumannii: Epidemiology, antimicrobial resistance, and treatment options. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, M.; Park, K.S.; Bae, I.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.-J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Biology of Acinetobacter baumannii: Pathogenesis, antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and prospective treatment options. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.; Edwards, J.E., Jr.; Gilbert, D.; Scheld, M.; Bartlett, J.G. Bad bugs need drugs: An update on the development pipeline from the Antimicrobial Availability Task Force of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnet, S.; Courvalin, P.; Lambert, T. Resistance-nodulation-cell division-type efflux pump involved in aminoglycoside resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii strain BM4454. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 3375–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smani, Y.; Fàbrega, A.; Roca, I.; Sánchez-Encinales, V.; Vila, J.; Pachón, J. Role of OmpA in the multidrug resistance phenotype of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1806–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.-F.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Tu, C.-C.; Lan, C.-Y. Distribution of different efflux pump genes in clinical isolates of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and their correlation with antimicrobial resistance. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaviani, R.; Pouladi, I.; Niakan, M.; Mirnejad, R. Molecular detection of Adefg efflux pump genes and their contribution to antibiotic resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 8, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdi, S.N.; Ghotaslou, R.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Mehramouz, B.; Hasani, A.; Baghi, H.B.; Tanomand, A.; Narenji, H.; Yousefi, B.; Gholizadeh, P.; et al. AdeB efflux pump gene knockdown by mRNA mediated peptide nucleic acid in multidrug resistance Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, R.A.; Gaynes, R.; Edwards, J.R.; System, N.N.I.S. Overview of nosocomial infections caused by gram-negative bacilli. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Seifert, H.; Paterson, D.L. Acinetobacter baumannii: Emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 538–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, A.; Fernández, I.S.; Gordiyenko, Y.; Ramakrishnan, V. Ribosome-dependent activation of stringent control. Nature 2016, 534, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, J.W. Promoter-specific control of E. coli RNA polymerase by ppGpp and a general transcription factor. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul, B.J.; Barker, M.M.; Ross, W.; Schneider, D.A.; Webb, C.; Foster, J.W.; Gourse, R.L. DksA: A critical component of the transcription initiation machinery that potentiates the regulation of rRNA promoters by ppGpp and the initiating NTP. Cell 2004, 118, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magnusson, L.U.; Gummesson, B.; Joksimovic, P.; Farewell, A.; Nyström, T. Identical, independent, and opposing roles of ppGpp and DksA in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 5193–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenway, D.; England, R. The intrinsic resistance of Escherichia coli to various antimicrobial agents requires ppGpp and σs. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 29, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; Lu, L.; Wang, Z. Transcriptional analysis reveals the critical role of RNA polymerase-binding transcription factor, DksA, in regulating multi-drug resistance of Escherichia coli. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2018, 52, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Viducic, D.; Ono, T.; Murakami, K.; Susilowati, H.; Kayama, S.; Hirota, K.; Miyaka, Y. Functional analysis of spoT, relA and dksA genes on quinolone tolerance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa under nongrowing condition. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 50, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.W.; Kim, K.; Islam, M.M.; Lee, J.C.; Shin, M. Role of ppGpp-regulated efflux genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.I.; Kim, S.; Oh, M.H.; Na, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeon, Y.H.; Lee, J.C. Outer membrane protein A contributes to antimicrobial resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii through the OmpA-like domain. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 3012–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-M.; Cha, S.H.; Lim, S.-K.; Kim, J. Complete genome sequence of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strain 1656-2, which forms sturdy biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 6393–6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lonergan, Z.R.; Nairn, B.L.; Wang, J.; Hsu, Y.-P.; Hesse, L.E.; Beavers, W.N.; Chazin, W.J.; Trinidad, J.C.; VanNieuwenhze, M.S.; Giedroc, D.P. An Acinetobacter baumannii, zinc-regulated peptidase maintains cell wall integrity during immune-mediated nutrient sequestration. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 2009–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, B.J.; Berkmen, M.B.; Gourse, R.L. DksA potentiates direct activation of amino acid promoters by ppGpp. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7823–7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.; Son, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.C. Global regulator DksA modulates virulence of Acinetobacter baumannii. Virulence 2021, 12, 2750–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.H.; Jeon, H.; Oh, M.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.C. Screening of small molecules attenuating biofilm formation of Acinetobacter baumannii by inhibition of ompA promoter activity. J. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.H.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, J.; Choi, C.H.; Han, K. Simple method for markerless gene deletion in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3357–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twentylee-Fourth Informational Supplement, M100-S28; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- American Society for Microbiology. Gram Stain Protocols. Avaliable online: https://asm.org/getattachment/5c95a063-326b-4b2f-98ce-001de9a5ece3/gram-stain-protocol-2886.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2021).

| Antibacterial Agents | MIC (μg/mL) | Fold Change (KM0248D/WT) | MIC (μg/mL) | Fold Change (NY0298D/WT) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 17978 | KM0248D | KM0248C | 1656-2 | NY0298D | |||
| Nalidixic acid | 4 | 16 | 8 | 4 | >256 | >256 | 1 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.125 | 0.5 | 0.125 | 4 | 64 | 64 | 1 |
| Levofloxacin | 0.063 | 0.125 | 0.063 | 2 | 16 | 16 | 1 |
| Cefoxitin | 128 | 128 | 128 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 1 |
| Cefotaxime | 16 | 16 | 16 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 1 |
| Ceftazidime | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 | >256 | >256 | 1 |
| Imipenem | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 1 | 16 | 16 | 1 |
| Meropenem | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1 | 32 | 32 | 1 |
| Amikacin | 1.0 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 64 | 32 | 0.5 |
| Gentamicin | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 256 | 128 | 0.5 |
| Tobramycin | 0.5 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 128 | 64 | 0.5 |
| Tetracycline | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 32 | 32 | 1 |
| Tigecycline | 0.125 | 0.5 | 0.125 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Colistin | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Trimethoprim | >32 | >32 | >32 | 1 | 32 | 32 | 1 |
| Bacteria/Plasmids | Relevant Characteristics | Reference of Source |
|---|---|---|
| A. baumannii | ||
| ATCC 17978 | Wild-type strain | ATCC |
| KM0248D | ∆A1S_0248 of A. baumannii ATCC 17978 | [25] |
| KM0248C | A1S_0248 with T1 terminator in KM0248D | [25] |
| 1656-2 | Clinical isolate | [21] |
| NY0298D | ∆ABK1_0298 of A. baumannii 1656-2 | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pDM4 | Suicide vector, ori R6K; Cmr; sacB | GenBank accession no. KC795686 |
| pFL02 | pWH1266 with armA coding region and its promoter less nptI, and origin of replication with ermAM; Kmr, Eryr | [26] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, N.; Son, J.-H.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.-J.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.-C. DksA Modulates Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121472
Kim N, Son J-H, Kim K, Kim H-J, Shin M, Lee J-C. DksA Modulates Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(12):1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121472
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Nayeong, Joo-Hee Son, Kyeongmin Kim, Hyo-Jeong Kim, Minsang Shin, and Je-Chul Lee. 2021. "DksA Modulates Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii" Antibiotics 10, no. 12: 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121472
APA StyleKim, N., Son, J.-H., Kim, K., Kim, H.-J., Shin, M., & Lee, J.-C. (2021). DksA Modulates Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antibiotics, 10(12), 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121472






