Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Presence of the blaCTX-M-65 Gene in Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing and Multi-Drug-Resistant Clones of Salmonella Serovar Infantis Isolated from Broiler Chicken Environments in the Galapagos Islands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Determination of Serotype, AMR Phenotype, and Genotype
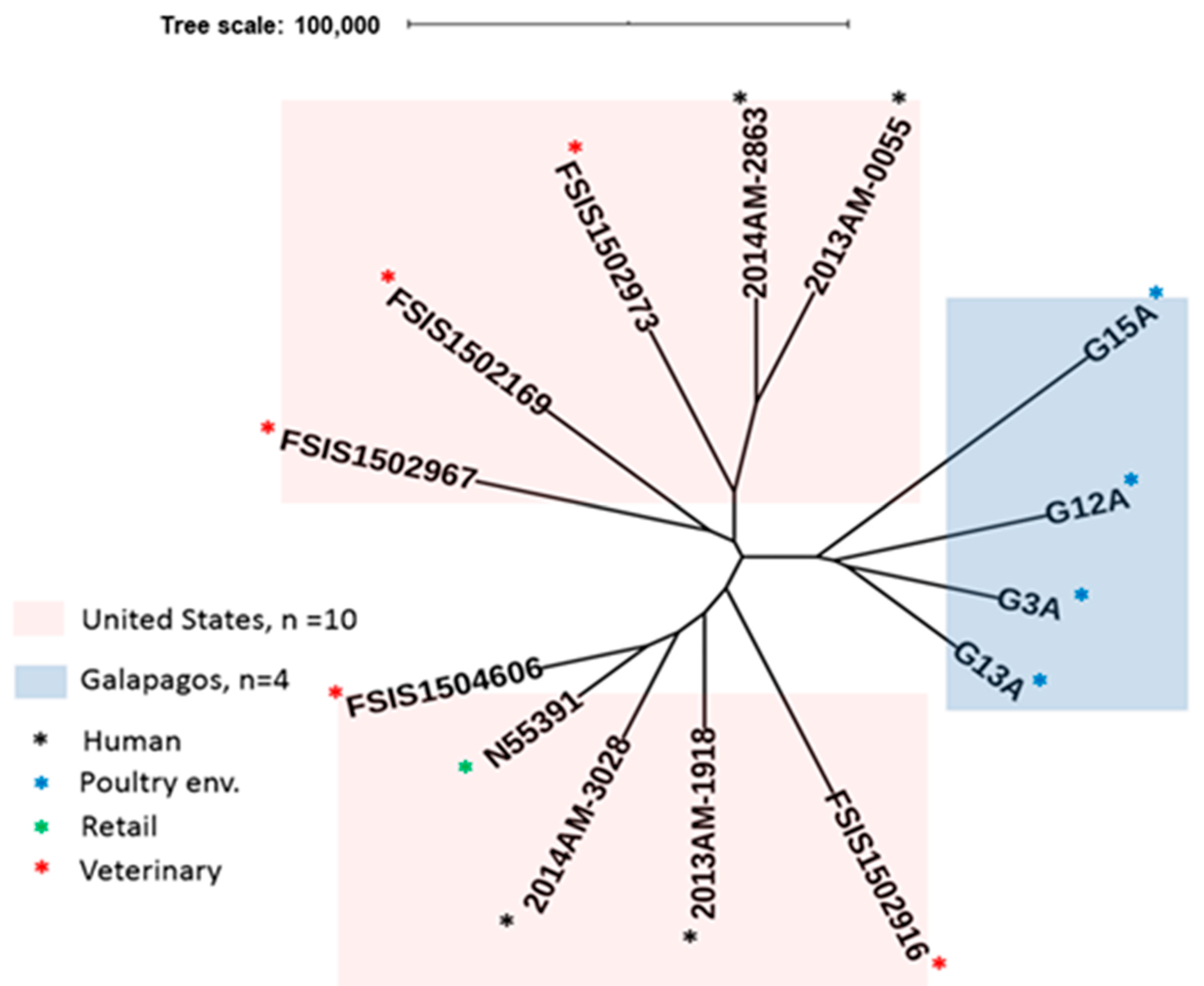
2.2. MLST and SNP Analysis
2.3. Prophage Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Potentially Pathogenic Clones of NTS Are Present in Poultry Farms in the Galapagos
3.2. NTS Isolates from the Galapagos Exhibit a Reduced Quinolone Susceptibility Phenotype
3.3. S. Infantis Isolates Possess IncFIB-Like Plasmids That Encode for ESBL Production
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Resistance Phenotyping
4.3. DNA Extraction and Whole-Genome Sequencing
4.4. Bioinformatic Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Acheson, D.; Hohmann, E.L. Nontyphoidal salmonellosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; International Collaboration on Enteric Disease ‘Burden of Illness’ Studies. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menton, M.M. Salmonella in domestic animals. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2000, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.; Domingues, S.; Da Silva, G.J. Plasmid-mediated colistin resistance in Salmonella enterica: A review. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, P.; Zhao, S.; Tate, H. Antimicrobial resistance in nontyphoidal Salmonella. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, S.-K.; Pusparajah, P.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Ser, H.-L.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. Salmonella: A review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanon, J.I.R. History of the use of antibiotic as growth promoters in European poultry feeds. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2466–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founou, L.L.; Founou, R.C.; Essack, S.Y. Antibiotic resistance in the food chain: A developing country-perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokma-Bakker, M.; Bondt, N.; Neijenhuis, F.; Mevius, D.J.; Ruiter, S. Antibiotic Use in Brazilian Broiler and Pig Production: An Indication and Forecast of Trends; Wageningen UR Livestock Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1570–8616. [Google Scholar]
- Donado-Godoy, P.; Castellanos, R.; León, M.; Arevalo, A.; Clavijo, V.; Bernal, J.; León, D.; Tafur, M.; Byrne, B.A.; Smith, W.A. The establishment of the Colombian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (COIPARS): A pilot project on poultry farms, slaughterhouses and retail market. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donado-Godoy, P.; Gardner, I.; Byrne, B.A.; Leon, M.; Perez-Gutierrez, E.; Ovalle, M.; Tafur, M.; Miller, W. Prevalence, risk factors, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Salmonella from commercial broiler farms in two important poultry-producing regions of Colombia. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, M.A.N.; Oliveira, D.C.N.d.; Rodrigues, D.D.P.; Freitas, D.R.C.D. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella in chicken carcasses at retail in 15 Brazilian cities. Rev. Panam. De Salud Pública 2011, 30, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattiello, S.P.; Drescher, G.; Barth, V.C.; Ferreira, C.A.; Oliveira, S.D. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica strains isolated from Brazilian poultry production. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 108, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinueza-Burgos, C.; Cevallos, M.; Ron-Garrido, L.; Bertrand, S.; De Zutter, L. Prevalence and diversity of Salmonella serotypes in Ecuadorian broilers at slaughter age. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinueza-Burgos, C.; Baquero, M.; Medina, J.; De Zutter, L. Occurrence, genotypes and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella collected from the broiler production chain within an integrated poultry company. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 299, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, K.C.; Fontes, L.C.; Moreno, A.M.; Astolfi-Ferreira, C.S.; Ferreira, A.J.; Lincopan, N. Emergence of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase CTX-M-2-producing Salmonella enterica serovars Schwarzengrund and Agona in poultry farms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3458–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziech, R.E.; Lampugnani, C.; Perin, A.P.; Sereno, M.J.; Sfaciotte, R.A.P.; Viana, C.; Soares, V.M.; Pinto, J.P.d.A.N.; dos Santos Bersot, L. Multidrug resistance and ESBL-producing Salmonella spp. isolated from broiler processing plants. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, F.M.; Carmo-Rodrigues, M.S.; Oliveira, V.G.S.; Gaspari, M.V.; dos Santos, A.; de Freitas, J.B.; Pignatari, A.C. β-Lactam resistance genes: Characterization, epidemiology, and first detection of bla CTX-M-1 and bla CTX-M-14 in Salmonella spp. isolated from poultry in Brazil—Brazil Ministry of Agriculture’s Pathogen Reduction Program. Microb. Drug Resist. 2016, 22, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Ghilardi-Rodrigues, Â.C.; Adams-Haduch, J.M.; Tavechio, A.T.; Doi, Y. CTX-M-2–producing Salmonella Typhimurium isolated from pediatric patients and poultry in Brazil. Microb. Drug Resist. 2009, 15, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos-Sánchez, K.; Tataje-Lavanda, L.; Villanueva-Pérez, D.; Bendezú, J.; Montalván, Á.; Zimic-Peralta, M.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Fernández-Díaz, M. Whole-genome sequencing of a Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Infantis strain isolated from broiler chicken in Peru. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00819–e00826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Salazar, E.; Gudiño, M.E.; Sevillano, G.; Zurita, J.; Guerrero-López, R.; Jaramillo, K.; Calero-Cáceres, W. Antibiotic resistance of Salmonella strains from layer poultry farms in central Ecuador. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 128, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.C.; Chen, J.C.; Watkins, L.K.F.; Campbell, D.; Folster, J.P.; Tate, H.; Wasilenko, J.; Van Tubbergen, C.; Friedman, C.R. CTX-M-65 extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Salmonella enterica serotype Infantis, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, H.; Folster, J.P.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, M.; Li, C.; Morales, C.; Tyson, G.H.; Mukherjee, S.; Brown, A.C. Comparative analysis of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase CTX-M-65-producing Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis isolates from humans, food animals, and retail chickens in the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00417–e00488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente-Rodríguez, D.; Bos, A.B.; Koerkamp, P.W.G. Rethinking livestock production systems on the Galápagos islands: Organizing knowledge-practice interfaces through reflexive interactive design. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 101, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, E.; Cann, I.K.O.; Mackie, R.I. Genomic fingerprinting and serotyping of Salmonella from Galápagos iguanas demonstrates island differences in strain diversity. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankau, E.W.; Cruz Bedon, L.; Mackie, R.I. Salmonella strains isolated from Galápagos iguanas show spatial structuring of serovar and genomic diversity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Lorenzetti, S.; Onorati, R.; Gentile, G.; Dell’Omo, G.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Battisti, A. Characterization of Salmonella occurring at high prevalence in a population of the land iguana Conolophus subcristatus in Galapagos islands, Ecuador. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmberg, S.D.; Osterholm, M.T.; Senger, K.A.; Cohen, M.L. Drug-resistant Salmonella from animals fed antimicrobials. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 311, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.-H.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chu, C.; Ou, J.T. Antimicrobial resistance in nontyphoid Salmonella serotypes: A global challenge. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist, M.J.; Greko, C.; Wallinga, D.B.; Beran, G.W.; Riley, D.G.; Thorne, P.S. The potential role of concentrated animal feeding operations in infectious disease epidemics and antibiotic resistance. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, S.V.; Pilataxi, M.L.; Burgos, C.V. Presencia y resistencia a los antimicrobianos de serovariedades de Salmonella enterica aisladas en una empresa avícola integrada del Ecuador. Rev. Ecuat. De Med. Y Cienc. Biológicas 2017, 38, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, L.Z.; Gomes, V.T.; Moreira, J.; de Oliveira, C.H.; Peres, B.P.; Silva, A.P.S.; Thakur, S.; La Ragione, R.M.; Moreno, A.M. First report of mcr-1-harboring Salmonella enterica serovar Schwarzengrund isolated from poultry meat in Brazil. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 93, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cunha-Neto, A.; Carvalho, L.A.; Castro, V.S.; Barcelos, F.G.; Carvalho, R.C.T.; Rodrigues, D.d.P.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Figueiredo, E.E.d.S. Salmonella Anatum, S. Infantis and S. Schwarzengrund in Brazilian Cheeses: Occurrence and antibiotic resistance profiles. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2019, 73, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jure, M.; Duprilot, M.; Musa, H.; López, C.; de Castillo, M.C.; Weill, F.-X.; Arlet, G.; Decré, D. Emergence of KPC-2-producing Salmonella enterica serotype Schwarzengrund in Argentina. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6335–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gymoese, P.; Kiil, K.; Torpdahl, M.; Østerlund, M.T.; Sørensen, G.; Olsen, J.E.; Nielsen, E.M.; Litrup, E. WGS based study of the population structure of Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, Q.; Fernandes, M.R.; Silva, K.C.; Monte, D.F.; Esposito, F.; Dropa, M.; Noronha, C.; Moreno, A.M.; Landgraf, M.; Negrão, F.J. Virulent nontyphoidal Salmonella producing CTX-M and CMY-2 β-lactamases from livestock, food and human infection, Brazil. Virulence 2018, 9, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monte, D.F.; Lincopan, N.; Berman, H.; Cerdeira, L.; Keelara, S.; Thakur, S.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Landgraf, M. Genomic features of high-priority Salmonella enterica serovars circulating in the food production chain, Brazil, 2000–2016. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Monte, D.F.; Lincopan, N.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Landgraf, M. Current insights on high priority antibiotic-resistant Salmonella enterica in food and foodstuffs: A review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 26, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robicsek, A.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C. The worldwide emergence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Switt, A.I.; Pezoa, D.; Sepulveda, V.; Gonzalez, I.; Rivera, D.; Retamal, P.; Navarrete, P.; Reyes-Jara, A.; Toro, M. Transduction as a potential dissemination mechanism of a clonal qnrB19-carrying plasmid isolated from Salmonella of multiple serotypes and isolation sources. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-J.; Ko, W.-C.; Chiou, C.-S.; Chen, H.-M.; Wang, L.-R.; Yan, J.-J. Emergence of Qnr determinants in human Salmonella isolates in Taiwan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cui, S.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.; Hu, C.; Jin, S.; Li, F.; Guo, Y.; Ran, L.; Ma, Y. Characterization of Salmonella enterica isolates from Infants and toddlers in Wuhan China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 63, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Karp, B.E.; Campbell, D.; Chen, J.C.; Folster, J.P.; Friedman, C.R. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance in human non-typhoidal Salmonella infections: An emerging public health problem in the United States. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaves, D.J.; Randall, L.; Gray, D.T.; Buckley, A.; Woodward, M.J.; White, A.P.; Piddock, L.J. Prevalence of mutations within the quinolone resistance-determining region of gyrA, gyrB, parC, and parE and association with antibiotic resistance in quinolone-resistant Salmonella enterica. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4012–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, G.L.; Panzenhagen, P.; Ferrari, R.G.; dos Santos, A.; Paschoalin, V.M.F.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Frequency of antimicrobial resistance genes in Salmonella From Brazil by in silico whole-genome sequencing analysis: An overview of the last four decades. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloeckaert, A.; Chaslus-Dancla, E. Mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Salmonella. Vet. Res. 2001, 32, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.; Chan, E.; Lam, A.; Cheng, A. Mutations in topoisomerase genes of fluoroquinolone-resistant salmonellae in Hong Kong. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3567–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nakaya, H.; Yasuhara, A.; Yoshimura, K.; Oshihoi, Y.; Izumiya, H.; Watanabe, H. Life-threatening infantile diarrhea from fluoroquinolone-fesistant Salmonella enteric Typhimurium with mutations in both gyrA and parC. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedenbach, D.J.; Toleman, M.; Walsh, T.R.; Jones, R.N. Analysis of Salmonella spp. with resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones isolated in North America and Latin America: Report from the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program (1997–2004). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006; 54, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, G.H.; Li, C.; Harrison, L.B.; Martin, G.; Hsu, C.H.; Tate, H.; Tran, T.T.; Strain, E.; Zhao, S. A multidrug-resistant Salmonella Infantis clone is spreading and recombining in the United States. Microb. Drug. Resist. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017/2018. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.; Karageorgopoulos, D.E. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing organisms. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 73, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossolini, G.; D’andrea, M.; Mugnaioli, C. The spread of CTX-M-type extended-spectrum β-lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantón, R.; González-Alba, J.M.; Galán, J.C. CTX-M enzymes: Origin and diffusion. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livermore, D.M.; Canton, R.; Gniadkowski, M.; Nordmann, P.; Rossolini, G.M.; Arlet, G.; Ayala, J.; Coque, T.M.; Kern-Zdanowicz, I.; Luzzaro, F. CTX-M: Changing the face of ESBLs in Europe. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, R.; Coque, T.M. The CTX-M β-lactamase pandemic. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierikx, C.; van Essen-Zandbergen, A.; Veldman, K.; Smith, H.; Mevius, D. Increased detection of extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli isolates from poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, R. Growing group of extended-spectrum β-lactamases: The CTX-M enzymes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartelle Gestal, M.; Zurita, J.; Paz y Mino, A.; Ortega-Paredes, D.; Alcocer, I. Characterization of a small outbreak of Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis that harbour CTX-M-65 in Ecuador. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 20, 406–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofacre, C.L.; Fricke, J.A.; Inglis, T. Antimicrobial drug use in poultry. Antimicrob. Ther. Vet. Med. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutil, L.; Irwin, R.; Finley, R.; Ng, L.K.; Avery, B.; Boerlin, P.; Bourgault, A.M.; Cole, L.; Daignault, D.; Desruisseau, A.; et al. Ceftiofur resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Heidelberg from chicken meat and humans, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierikx, C.M.; van der Goot, J.A.; Smith, H.E.; Kant, A.; Mevius, D.J. Presence of ESBL/AmpC-producing Escherichia coli in the broiler production pyramid: A descriptive study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinueza-Burgos, C.; Ortega-Paredes, D.; Narváez, C.; De Zutter, L.; Zurita, J. Characterization of cefotaxime resistant Escherichia coli isolated from broiler farms in Ecuador. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0207567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs–Horizontal Method for the Detection of Salmonella spp.–Amendment 1: Annex D: Detection of Salmonella spp. in Animal Faeces and in Environmental Samples from the Primary Production Stage; ISO 6579: 2002/Amd. 1: 2007; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Grimont, P.A.; Weill, F.-X. Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serovars. Who Collab. Cent. Ref. Res. Salmonella 2007, 9, 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for the Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Available online: http://eucast.org (accessed on 23 May 2020).
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 25th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, C.E.; Kruczkiewicz, P.; Laing, C.R.; Lingohr, E.J.; Gannon, V.P.; Nash, J.H.; Taboada, E.N. The Salmonella in silico typing resource (SISTR): An open web-accessible tool for rapidly typing and subtyping draft Salmonella genome assemblies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkau, A.; Mabon, P.; Sieffert, C.; Knox, N.C.; Cabral, J.; Iskander, M.; Iskander, M.; Weedmark, K.; Zaheer, R.; Katz, L.S. SNVPhyl: A single nucleotide variant phylogenomics pipeline for microbial genomic epidemiology. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treangen, T.J.; Ondov, B.D.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottawea, W.; Duceppe, M.-O.; Dupras, A.A.; Usongo, V.; Jeukens, J.; Freschi, L.; Emond-Rheault, J.-G.; Hamel, J.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Boyle, B.; et al. Salmonella enterica prophage sequence profiles reflect genome diversity and can be used for high discrimination subtyping. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropinski, A.M.; Sulakvelidze, A.; Konczy, P.; Poppe, C. Salmonella phages and prophages—Genomics and practical aspects. In Salmonella; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 133–175. [Google Scholar]
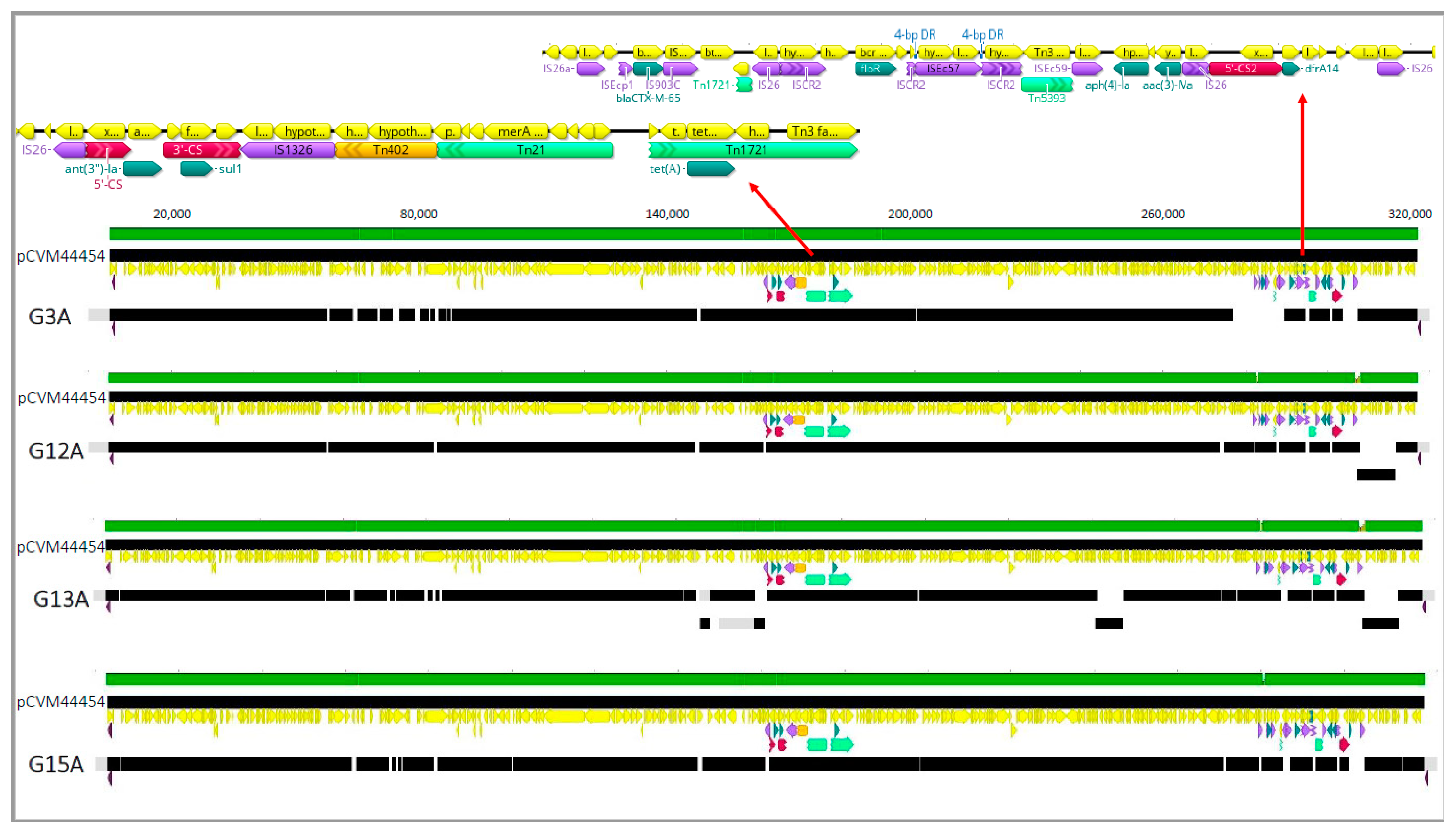


| Isolate | Serotype | SMX | GEN | CIP | AMP | CTX | TAZ | TET | TMP | CHL | NAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G3A | Infantis | (512) | (8) | (0.25) | 1 | 0.25 | 0.5 | (64) | (32) | (128) | (128) |
| G12A | Infantis | (1024) | (8) | (0.12) | (64) | (4) | (4) | (64) | (32) | (64) | (128) |
| G13A | Infantis | (1024) | (8) | (0.12) | (64) | (4) | (4) | (64) | (32) | (128) | (64) |
| G15A | Infantis | (1024) | (8) | (0.25) | (64) | (4) | (4) | (64) | (32) | (128) | (128) |
| G10A | Schwarzengrund | 64 | 1 | (0.50) | 1 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.25 | 8 | 16 |
| G11A | Schwarzengrund | 64 | 2 | 0.02 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.25 | 8 | 4 |
| Isolate | MLST | Plasmid | Β-Lactam | Quinolone | Tetracycline | Trimethoprim | Sulfonamide | Aminoglycoside |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G3A | ST-32 | IncFIB-like | - | gyrA D87Y | tet(A) | dfrA14 | sul1 | aph(4)-la, aadA1, aac(3)-IVa, aph(3′)-Ia |
| G12A | ST-32 | IncFIB-like | blaCTX-M-65 | gyrA D87Y | tet(A) | dfrA14 | sul1 | aph(4)-la, aadA1, aac(3)-IVa, aph(3′)-Ia |
| G13A | ST-32 | IncFIB-like | blaCTX-M-65 | gyrA D87Y | tet(A) | dfrA14 | sul1 | aph(4)-la, aadA1, aac(3)-IVa, aph(3′)-Ia |
| G15A | ST-32 | IncFIB-like | blaCTX-M-65 | gyrA D87Y | tet(A) | dfrA14 | sul1 | aph(4)-la, aadA1, aac(3)-IVa, aph(3′)-Ia |
| G10A | ST-96 | Col440II | - | qnrB19 | - | - | - | - |
| G11A | ST-96 | Col440II | - | qnrB19 | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burnett, E.; Ishida, M.; de Janon, S.; Naushad, S.; Duceppe, M.-O.; Gao, R.; Jardim, A.; Chen, J.C.; Tagg, K.A.; Ogunremi, D.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Presence of the blaCTX-M-65 Gene in Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing and Multi-Drug-Resistant Clones of Salmonella Serovar Infantis Isolated from Broiler Chicken Environments in the Galapagos Islands. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030267
Burnett E, Ishida M, de Janon S, Naushad S, Duceppe M-O, Gao R, Jardim A, Chen JC, Tagg KA, Ogunremi D, et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Presence of the blaCTX-M-65 Gene in Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing and Multi-Drug-Resistant Clones of Salmonella Serovar Infantis Isolated from Broiler Chicken Environments in the Galapagos Islands. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(3):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030267
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurnett, Elton, Maria Ishida, Sofia de Janon, Sohail Naushad, Marc-Olivier Duceppe, Ruimin Gao, Armando Jardim, Jessica C. Chen, Kaitlin A. Tagg, Dele Ogunremi, and et al. 2021. "Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Presence of the blaCTX-M-65 Gene in Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing and Multi-Drug-Resistant Clones of Salmonella Serovar Infantis Isolated from Broiler Chicken Environments in the Galapagos Islands" Antibiotics 10, no. 3: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030267
APA StyleBurnett, E., Ishida, M., de Janon, S., Naushad, S., Duceppe, M.-O., Gao, R., Jardim, A., Chen, J. C., Tagg, K. A., Ogunremi, D., & Vinueza-Burgos, C. (2021). Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals the Presence of the blaCTX-M-65 Gene in Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing and Multi-Drug-Resistant Clones of Salmonella Serovar Infantis Isolated from Broiler Chicken Environments in the Galapagos Islands. Antibiotics, 10(3), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10030267







