Antibiotic Use in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates After an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program
Abstract
1. Introduction
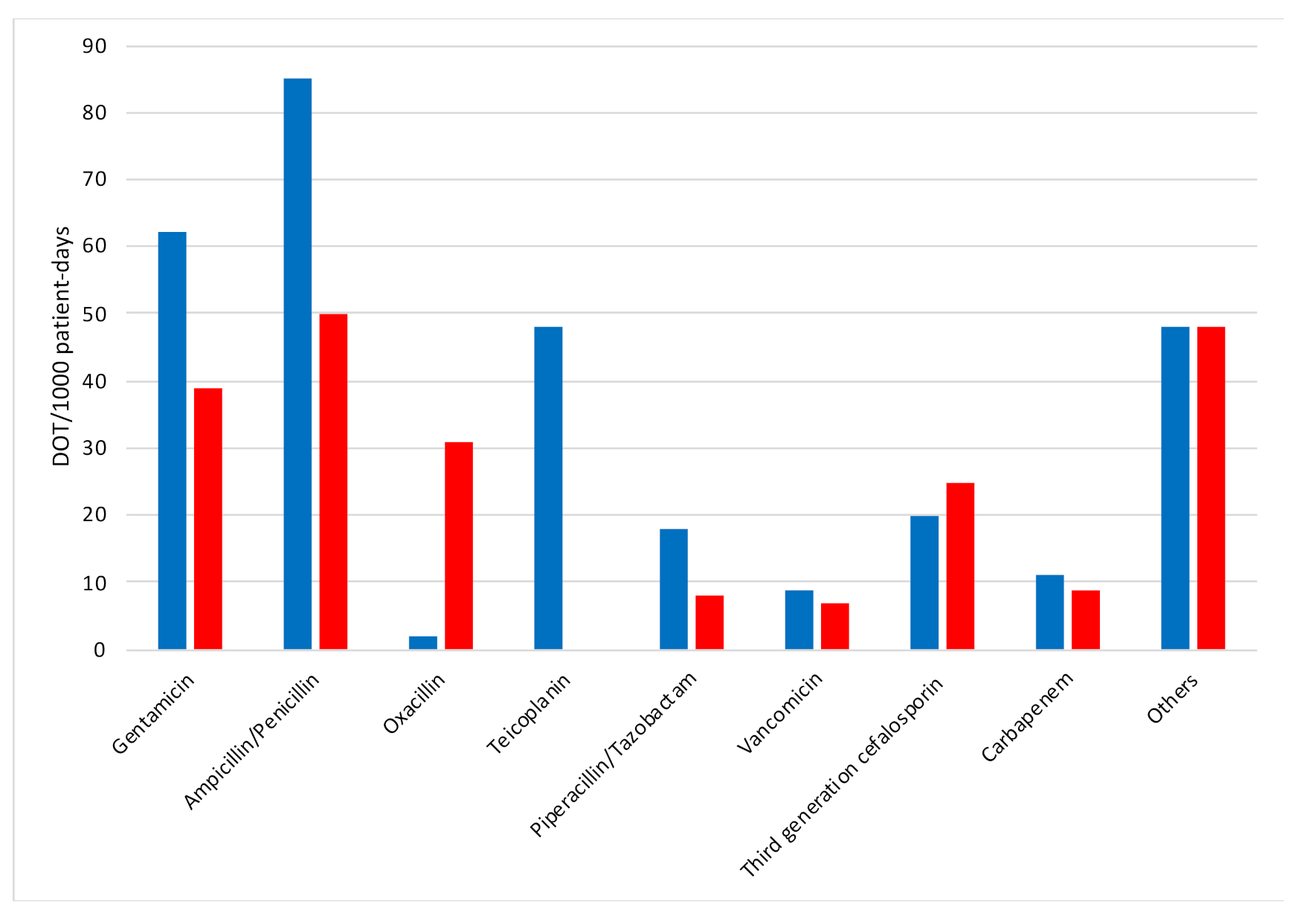
2. Results
2.1. Antibiotic Treatments According to Birth Weight
2.2. Neonates with A Low Risk of EOS
2.3. Neonatal Complications, Deaths and Reinstitution of Antibiotics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Data Collection
4.4. Data Relating to Antibiotic Therapies
4.5. Definitions
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, R.H.; Bloom, B.T.; Spitzer, A.R.; Gerstmann, D.R. Reported Medication Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Data from a Large National Data Set. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotten, C.M.; Taylor, S.; Stoll, B.; Goldberg, R.N.; Hansen, N.I.; Sánchez, P.J.; Ambalavanan, N.; Benjamin, D.K. For the Nichd Neonatal Research Network Prolonged Duration of Initial Empirical Antibiotic Treatment Is Associated With Increased Rates of Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Death for Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flannery, D.D.; Ross, R.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Tribble, A.C.; Puopolo, K.M.; Gerber, J.S. Temporal Trends and Center Variation in Early Antibiotic Use Among Premature Infants. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e180164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardas, M.; Gill, S.R.; Grier, A.; Pryhuber, G.S.; Gill, A.L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Guillet, R. The impact of postnatal antibiotics on the preterm intestinal microbiome. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 76, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficara, M.; Pietrella, E.; Spada, C.; Muttini, E.D.C.; Lucaccioni, L.; Iughetti, L.; Berardi, A. Changes of intestinal microbiota in early life. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2018, 33, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasethu, J.; Kawakita, T. Antibiotic stewardship in perinatal and neonatal care. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 22, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, J.; Walker, W.A. Necrotizing Enterocolitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaiassen, E.; Fjalstad, J.W.; Juvet, L.K.; Anker, J.N.V.D.; Klingenberg, C. Antibiotic exposure in neonates and early adverse outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1858–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Man, P.; Verhoeven, B.; Verbrugh, H.; Vos, M.; Anker, J.V.D. An antibiotic policy to prevent emergence of resistant bacilli. Lancet 2000, 355, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjalstad, J.W.; Esaiassen, E.; Juvet, L.K.; Anker, J.N.V.D.; Klingenberg, C. Antibiotic therapy in neonates and impact on gut microbiota and antibiotic resistance development: A systematic review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Puopolo, K.M. Clinical and Microbiologic Characteristics of Early-onset Sepsis Among Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sengupta, S.; Puopolo, K.M. Challenges and opportunities for antibiotic stewardship among preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2019, 104, F327–F332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.J.; Saiman, L. Principles and Strategies of Antimicrobial Stewardship in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Semin. Perinatol. 2012, 36, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantey, J.B.; Patel, S.J. Antimicrobial Stewardship in the NICU. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 28, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajar, P.; Saugstad, O.D.; Berild, D.; Dutta, A.; Greisen, G.; Lausten-Thomsen, U.; Mande, S.S.; Nangia, S.; Petersen, F.C.; Dahle, U.R.; et al. Antibiotic Stewardship in Premature Infants: A Systematic Review. Neonatology 2020, 117, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzniewicz, M.W.; Puopolo, K.M.; Fischer, A.; Walsh, E.M.; Li, S.; Newman, T.B.; Kipnis, P.; Escobar, G.J. A Quantitative, Risk-Based Approach to the Management of Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, A.; Fornaciari, S.; Rossi, C.; Patianna, V.; Reggiani, M.L.B.; Ferrari, F.; Neri, I.; Ferrari, F. Safety of physical examination alone for managing well-appearing neonates ≥35 weeks’ gestation at risk for early-onset sepsis. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2014, 28, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, T.; Takagi, K.; Arai, I.; Yasuhara, H.; Ebisu, R.; Ohgitani, A.; Kitagawa, D.; Oka, M.; Masuo, K.; Minowa, H. A simple and feasible antimicrobial stewardship program in a neonatal intensive care unit of a Japanese community hospital. J. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 25, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantey, J.B.; Wozniak, P.S.; Pruszynski, J.E.; Sánchez, P.J. Reducing unnecessary antibiotic use in the neonatal intensive care unit (SCOUT): A prospective interrupted time-series study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzegwu, N.I.; Rychalsky, M.R.; Nallu, L.A.; Song, X.; Deng, Y.; Natusch, A.M.; Baltimore, R.S.; Paci, G.R.; Bizzarro, M.J. Implementation of an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2017, 38, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, H.; Wang, L. Implementation of the Smart Use of Antibiotics Program to Reduce Unnecessary Antibiotic Use in a Neonatal ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinka, D.R.; Gandra, S.; Alvarez-Uria, G.; Torre, N.; Tadepalli, D.; Nayakanti, R.R. Impact of antibiotic policy on antibiotic consumption in a neonatal intensive care unit in India. Ind. Pediatr. 2017, 54, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puopolo, K.M.; Benitz, W.E.; Zaoutis, T.E.; Committee on Fetus and Newborn; Committee on Infectious Diseases. Management of Neonates Born at ≤34 6/7 Weeks’ Gestation with Suspected or Proven Early-Onset Bacterial Sepsis. Pediatrics 2018, 142, e20182896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardi, A.; Baroni, L.; Reggiani, M.L.B.; Ambretti, S.; Biasucci, G.; Bolognesi, S.; Capretti, M.G.; Carretto, E.; Ciccia, M.; Fiorini, V.; et al. The burden of early-onset sepsis in Emilia-Romagna (Italy): A 4-year, population-based study. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 3126–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, A.; Sforza, F.; Baroni, L.; Spada, C.; Ambretti, S.; Biasucci, G.; Bolognesi, S.; Capretti, M.; Carretto, E.; Ciccia, M.; et al. Epidemiology and complications of late-onset sepsis: An Italian area-based study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, A.; Ficara, M.; Pietrella, E.; Boncompagni, A.; Toffoli, C.; Bianchini, A.; Gargano, G.; Rizzo, V.; Azzalli, M.; Biasucci, G.; et al. Stewardship antimicrobica nel neonato e nel piccolo lattante. Med. Bambino 2017, 36, 493–501. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, W.D.; Jackson, G.L.; Sendelbach, D.; Ford, D.; Olesen, B.; Burton, K.M.; Pritchard, M.A.; Frawley, W.H. Neonatal Pneumonia: Comparison of 4 vs 7 Days of Antibiotic Therapy in Term and Near-Term Infants. J. Perinatol. 2000, 20, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhudasia, M.B.; Flannery, D.D.; Pfeifer, M.R.; Puopolo, K.M. Updated Guidance: Prevention and Management of Perinatal Group B Streptococcus Infection. NeoReviews 2021, 22, e177–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verani, J.R.; McGee, L.; Schrag, S.J. Division of Bacterial Diseases, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease—Revised guidelines from CDC, 2010. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2010, 59, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn, F.; Cooke, R.W.I.; Gamsu, H.R.; Greenough, A.; Hopkins, A.; Mcintosh, N.; Ogston, S.A.; Parry, G.J.; Silverman, M.; Shaw, J.C.L.; et al. The CRIB (clinical risk index for babies) score: A tool for assessing initial neonatal risk and comparing performance of neonatal intensive care units. The International Neonatal Network. Lancet 1993, 342, 193–198, Erratum in Lancet 1993, 342, 626. [Google Scholar]
- Vergnano, S.; Menson, E.; Kennea, N.; Embleton, N.; Russell, A.B.; Watts, T.; Robinson, M.J.; Collinson, A.; Heath, P.T. Neonatal infections in England: The NeonIN surveillance network. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2010, 96, F9–F14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Hsu, J.-F.; Chu, S.-M.; Lien, R.; Huang, H.-R.; Chiang, M.-C.; Fu, R.-H.; Lee, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-C. Incidence, Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors for Adverse Outcome in Neonates With Late-onset Sepsis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, e7–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermont Oxford Network. Available online: https://public.vtoxford.org/ (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- The Canadian Neonatal NetworkTM. Available online: http://www.canadianneonatalnetwork.org/portal/ (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- McCarthy, K.N.; Hawke, A.; Dempsey, E.M. Antimicrobial stewardship in the neonatal unit reduces antibiotic exposure. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Baseline (n = 111) | Intervention (n = 119) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prenatal steroids, n (%) | 96 (86) | 107 (90) | 0.42 |
| Maternal indication for delivery, n (%) | 28 (25) | 39 (33) | 0.48 |
| Histological chorioamnionitis, n (%) | 29 (26) | 31 (26) | 0.99 |
| Twin birth, n (%) | 28 (25) | 31 (26) | 0.99 |
| Prolonged membrane rupture (≥ 18 h), n (%) | 29 (26) | 34 (29) | 0.79 |
| Maternal fever during labor (> 38 °C), n (%) | 3 (3) | 6 (5) | 0.57 |
| Intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis, n (%) No Adequate Inadequate | 68 (61) 30 (27) 7 (6) | 55 (46) 48 (40) 10 (8) | 0.06 |
| Mode of delivery, n (%) Vaginal CS in labor or with membrane rupture CS before labor and with intact membranes | 21 (19) 30 (27) 60 (54) | 25 (21) 25 (21) 69 (58) | 0.56 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 61 (55) | 67 (56) | 0.94 |
| Gestational age, weeks, median (IQR) | 29 (26–31) | 29 (26–31) | 0.88 |
| Birth weight, g, median (IQR) | 1146 (857–1346) | 1109 (851–1398) | 0.85 |
| Apgar score at the 5th minute, median (IQR) | 8 (7–9) | 8 (6–9) | 0.03 |
| CRIB score, median (IQR) | 1 (1–4) | 1 (0–4) | 0.27 |
| Median length of stay, days (IQR) | 47 (29–75) | 46 (28–71) | 0.99 |
| First antibiotic treatment Total, n (%) † 48-h rule-out course, n (%) § Median duration, hours (IQR) | 82 (74) 3 (4) 168 (120–192) | 84 (71) 37 (44) 72 (48–72) | 0.68 <0.01 <0.01 |
| Days of therapy Total Median (IQR) | 1738 12 (0–23) | 1357 5 (0–16) | <0.01 <0.01 |
| Days of therapy/1000 patient-days | 302 | 215 | < 0.01 |
| Variables | Birth Weight < 1000 g, Baseline(n = 44) | Birth Weight < 1000 g, Intervention (n = 51) | p | Birth Weight 1000–1500 g, Baseline (n = 67) | Birth Weight 1000–1500 g, Intervention (n = 68) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median length of stay, days (IQR) | 73 (51–87) | 71 (21–96) | 0.86 | 37 (29–53) | 42 (28–56) | 0.76 |
| First antibiotic treatment Total, n (%) 48-h rule-out course, n (%) § Median duration, hours (IQR) | 39 (89) 2 (5) 168 (126–192) | 46 (90) 16 (35) 72 (48–96) | 0.93 <0.01 <0.01 | 43 (64) 1 (2) 168 (126–192) | 38 (56) 21 (55) 48 (48–72) | 0.42 <0.01 <0.01 |
| Days of therapy Total Median (IQR) | 1056 22 (12–36) | 893 11 (5–25) | 0.01 0.01 | 682 8 (0–15) | 454 3 (0–5) | 0.01 0.01 |
| Days of therapy/1000 patient-days | 367 | 266 | <0.01 | 238 | 154 | <0.01 |
| Early-onset sepsis, n (%) | 3 (7) | 3 (6) | 0.79 | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 0.99 |
| Late-onset sepsis, n (%) | 15 (34) | 13 (25) | 0.36 | 5 (7) | 4 (6) | 0.71 |
| Culture-negative sepsis, n (%) | 15 (34) | 9 (18) | 0.07 | 9 (13) | 4 (6) | 0.14 |
| Necrotizing enterocolitis, n (%) | 0 (0) | 3 (6) | 0.30 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.99 |
| Reinstitution of an antibiotic treatment, n (%) | 16 (36) | 19 (37) | 0.93 | 10 (15) | 4 (6) | 0.08 |
| Variables | Baseline (n = 26) | Intervention (n = 34) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male gender, n (%) | 12 (46) | 18 (53) | 0.79 |
| Gestational age, weeks, median (IQR) | 31 (29–32) | 30 (29–31) | 0.04 |
| Birth weight, g, median (IQR) | 1320 (1076–1456) | 1220 (990–1445) | 0.32 |
| Apgar score at the 5th min, median (IQR) | 9 (7–10) | 8 (7–9) | 0.05 |
| CRIB score, median (IQR) | 1 (0–1) | 1 (0–4) | 0.60 |
| Twins, n (%) | 4 (15) | 5 (15) | 0.77 |
| Maternal fever in labor (> 38 °C), n (%) | 0 (0) | 1 (3) | 0.89 |
| IAP, n (%) No Adequate Inadequate | 25 (96) 0 (0) 1 (4) | 27 (79) 6 (18) 1 (3) | 0.04 |
| Prenatal steroids, n (%) | 22 (85) | 31 (91) | 0.43 |
| Median length of stay, days (IQR) | 47 (38–57) | 46 (42–57) | 0.99 |
| First antibiotic treatment Total, n (%) 48-h rule-out course, n (%) § Median duration, hours (IQR) § | 13 (50) 0 (0) 144 (96–168) | 16 (48) 14 (88) 72 (48–72) | 0.97 <0.01 <0.01 |
| Days of therapy Total Median (IQR) | 233 2 (0–15) | 190 0 (0–6) | <0.01 <0.01 |
| Days of therapy/1000 patient-days | 194 | 113 | <0.01 |
| Variables | Baseline (n = 111) | Intervention (n = 119) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early-onset sepsis, n (%) | 3 (3) | 4 (3) | 0.93 |
| Late-onset sepsis, n (%) | 20 (18) | 17 (14) | 0.44 |
| Culture-negative sepsis, n (%) | 24 (22) | 13 (11) | 0.04 |
| Necrotizing enterocolitis, n (%) † | 1 (1) | 4 (3) | 0.20 |
| Reinstitution of an antibiotic treatment, n (%) | 26 (23) | 23 (19) | 0.55 |
| Reasons for the reinstitution of an antibiotic treatment, n (%) § Culture-proven sepsis Suspect of sepsis Surgical prophylaxis | 5 (19) 17 (65) 4 (15) | 7 (30) 14 (61) 2 (9) | 0.56 0.98 0.78 |
| Total case fatalities, n (%) | 11 (10) | 17 (14) | 0.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berardi, A.; Zinani, I.; Rossi, C.; Spaggiari, E.; D’Amico, V.; Toni, G.; Bedetti, L.; Lucaccioni, L.; Iughetti, L.; Lugli, L. Antibiotic Use in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates After an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040411
Berardi A, Zinani I, Rossi C, Spaggiari E, D’Amico V, Toni G, Bedetti L, Lucaccioni L, Iughetti L, Lugli L. Antibiotic Use in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates After an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(4):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040411
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerardi, Alberto, Isotta Zinani, Cecilia Rossi, Eugenio Spaggiari, Virginia D’Amico, Greta Toni, Luca Bedetti, Laura Lucaccioni, Lorenzo Iughetti, and Licia Lugli. 2021. "Antibiotic Use in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates After an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program" Antibiotics 10, no. 4: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040411
APA StyleBerardi, A., Zinani, I., Rossi, C., Spaggiari, E., D’Amico, V., Toni, G., Bedetti, L., Lucaccioni, L., Iughetti, L., & Lugli, L. (2021). Antibiotic Use in Very Low Birth Weight Neonates After an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program. Antibiotics, 10(4), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040411








