Antimicrobial Residues in Food from Animal Origin—A Review of the Literature Focusing on Products Collected in Stores and Markets Worldwide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
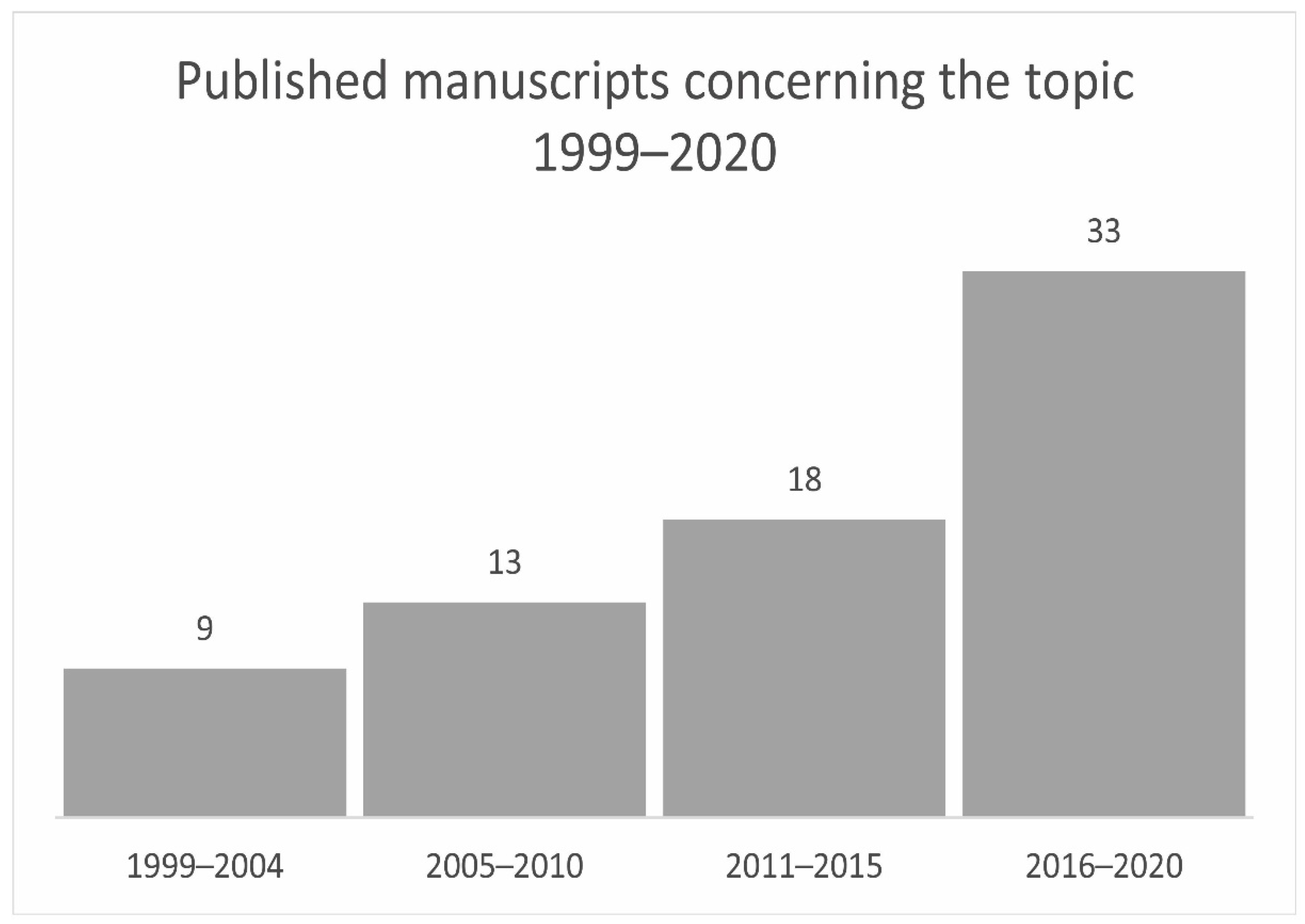
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Scientific Paper Selection
4.2. Data Extraction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Page, S.; Gautier, P. Use of antimicrobial agents in livestock. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2012, 31, 145–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.G.; Schellevis, F.; Stobberingh, E.; Goossens, H.; Pringle, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of antibiotic consumption on antibiotic resistance. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simoneit, C.; Burow, E.; Tenhagen, B.-A.; Käsbohrer, A. Oral administration of antimicrobials increase antimicrobial resistance in E. coli from chicken—A systematic review. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 118, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantziaras, I.; Boyen, F.; Callens, B.; Dewulf, J. Correlation between veterinary antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in food-producing animals: A report on seven countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. The Evolving Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance: Options for Action; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Muaz, K.; Riaz, M.; Akhtar, S.; Park, S.; Ismail, A. Antibiotic Residues in Chicken Meat: Global Prevalence, Threats, and Decontamination Strategies: A Review. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bager, F. DANMAP: Monitoring antimicrobial resistance in Denmark. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2000, 14, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Resistance monitoring in Denmark, 1997—DANMAP. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 1999, 74, 125–127. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, S. Reduced Antibiotic Use in Livestock: How Denmark TackledResistance. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, A160–A165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.S.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.A.; Laxminarayan, R.R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiseo, K.; Huber, L.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacanlı, M.; Başaran, N. Importance of antibiotic residues in animal food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ho, K.W.; Ying, G.-G.; Deng, W.-J. Veterinary antibiotics in food, drinking water, and the urine of preschool children in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraku, Y.; Sekine, A.; Nabeshi, H.; Midorikawa, K.; Murata, M.; Kumagai, Y.; Kawanishi, S. Mechanism of carcinogenesis induced by a veterinary antimicrobial drug, nitrofurazone, via oxidative DNA damage and cell proliferation. Cancer Lett. 2004, 215, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jester, E.L.E.; El Said, K.R.; Abraham, A.; Hooe-Rollman, J.; Plakas, S.M. Cyano Metabolite as a Biomarker of Nitrofurazone in Channel Catfish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.-F.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Li, Z.-G.; Cai, N.; Guan, W.-Q.; Huang, K.; Zhao, D.-H. Determination of 5-nitro-2-furaldehyde as marker residue for nitrofurazone treatment in farmed shrimps and with addressing the use of a novel internal standard. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeiza, G.K.; Ajayi, I.E.; Ode, O.J. Assessment of antimicrobial drug residues in beef in Abuja, the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria. Vet. Ital. 2012, 48, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Adesokan, H.K.; Agada, C.A.; Adetunji, V.O.; Akanbi, I.M. Oxytetracycline and penicillin-G residues in cattle slaughtered in south-western Nigeria: Implications for livestock disease management and public health. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2013, 84, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriuki, F.K.; Ogara, W.O.; Njeruh, F.M.; Mitema, E.S. Tetracycline residue levels in cattle meat from Nairobi salughter house in Kenya. J. Vet. Sci. 2001, 2, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basulira, Y.; Olet, S.A.; Alele, P.E. Inappropriate usage of selected antimicrobials: Comparative residue proportions in rural and urban beef in Uganda. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimera, Z.I.; Mdegela, R.H.; Mhaiki, C.J.; Karimuribo, E.D.; Mabiki, F.; Nonga, H.E.; Mwesongo, J. Determination of oxytetracycline residues in cattle meat marketed in the Kilosa district, Tanzania. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2015, 82, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morshdy, A.E.M.A.; El-Atabany, A.I.; Hussein, M.A.M.; Darwish, W.S. Oxytetracycline residues in bovine carcasses slaughtered at Mansoura Abattoir, Egypt. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 2013, 61, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Nonga, H.E.; Simon, C.; Karimuribo, E.D.; Mdegela, R.H. Assessment of Antimicrobial Usage and Residues in Commercial Chicken Eggs from Smallholder Poultry Keepers in Morogoro Municipality, Tanzania. Zoonoses Public Health 2009, 57, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezenduka, E.V.; Oboegbulem, S.I.; Nwanta, J.A.; Onunkwo, J.I. Prevalence of antimicrobial residues in raw table eggs from farms and retail outlets in Enugu State, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2010, 43, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesiyun, A.; Offiah, N.; Lashley, V.; Seepersadsingh, N.; Rodrigo, S.; Georges, K. Prevalence of Antimicrobial Residues in Table Eggs in Trinidad. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscoso, S.; Santos, F.S.D.L.; Andino, A.G.; Díaz-Sánchez, S.; Hanning, I. Detection of Quinolones in Commercial Eggs Obtained from Farms in the Espaíllat Province in the Dominican Republic. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeiza, G.K.; Kabir, J.; Mamman, M.; Ibrahim, H.; Fagbamila, I.O. Response of Nigerian farmers to a questionnaire on chloramphenicol application in commercial layers. Vet. Ital. 2012, 48, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Olatoye, O.; Kayode, S.T. Oxytetracycline residues in retail chicken eggs in Ibadan, Nigeria. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2012, 5, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbodi, F.E.; Nguku, P.; Okolocha, E.; Kabir, J. Determination of chloramphenicol residues in commercial chicken eggs in the Federal Capital Territory, Abuja, Nigeria. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, M. Residues of tetracycline compounds in poultry products in the eastern province of Saudi Arabia. Public Health 2000, 114, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, L.; Cubas-Delgado, F.; Sammel, M.; Smith, G.; Galligan, D.; Levy, M.; Hennessy, S. Antibiotic residues in milk from small dairy farms in rural Peru. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwandu, S.H.; Nonga, H.E.; Mdegela, R.H.; Katakweba, A.S.; Suleiman, T.S.; Ryoba, R. Assessment of Raw Cow Milk Quality in Smallholder Dairy Farms in Pemba Island Zanzibar, Tanzania. Vet. Med. Int. 2018, 2018, 1031726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moghadam, M.M.; Amiri, M.; Riabi, H.R.A.; Riabi, H.R.A. Evaluation of Antibiotic Residues in Pasteurized and Raw Milk Distributed in the South of Khorasan-e Razavi Province, Iran. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, FC31–FC35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempini, P.; Aly, S.; Karle, B.; Pereira, R. Multidrug residues and antimicrobial resistance patterns in waste milk from dairy farms in Central California. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8110–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siljanoski, A.; Ciglarič, R.; Pezdir, T.; Lainšček, P.R.; Dolenc, J.; Starič, J.; Šinigoj-Gačnik, K. Detection of tetracycline and other antimicrobial residues in milk from cows with clinical mastitis treated by combination therapy. J. Dairy Res. 2018, 85, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, E.; Oliveira, R.C.; Ferreira, G.M.Z.; Machinski, M. Occurrence of Antimicrobial Residues in Pasteurized Milk Commercialized in the State of Paraná, Brazil. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.; Mugoh, M.; Call, D.R.; Omulo, S. Antibiotic residues and antibiotic-resistant bacteria detected in milk marketed for human consumption in Kibera, Nairobi. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosgey, A.; Shitandi, A.; Marion, J.W. Antibiotic Residues in Milk from Three Popular Kenyan Milk Vending Machines. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 1520–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rama, A.; Lucatello, L.; Benetti, C.; Galina, G.; Bajraktari, D. Assessment of antibacterial drug residues in milk for consumption in Kosovo. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khanal, B.K.S.; Sadiq, M.B.; Singh, M.; Anal, A.K. Screening of antibiotic residues in fresh milk of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2017, 53, 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baazize-Ammi, D.; Dechicha, A.S.; Tassist, A.; Gharbi, I.; Hezil, N.; Kebbal, S.; Morsli, W.; Beldjoudi, S.; Saadaoui, M.R.; Guetarni, D. Screening and quantification of antibiotic residues in broiler chicken meat and milk in the central region of Algeria. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2019, 38, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Yu, Z.; Wu, W.; Ho, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Han, R. A Survey of 61 Veterinary Drug Residues in Commercial Liquid Milk Products in China. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitandi, A.; Sternesjö, Å. Factors Contributing to the Occurrence of Antimicrobial Drug Residues in Kenyan Milk. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, K.K.; Mensah, G.I.; Aning, K.G.; Nartey, N.; Nipah, G.K.; Bonsu, C.; Akyeh, M.L.; Smits, H.L. Microbiological quality and antibiotic residues in informally marketed raw cow milk within the coastal savannah zone of Ghana. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2010, 16, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baynes, R.E.; Lyman, R.; Anderson, K.L.; Brownie, C.F. A Preliminary Survey of Antibiotic Residues and Viable Bacteria in Milk from Three Caribbean Basin Countries. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vragović, N.; Bažulić, D.; Njari, B. Risk assessment of streptomycin and tetracycline residues in meat and milk on Croatian market. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, R.C.; Paschoal, J.A.; Reyes, F.G. Streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin residues in bovine milk from the Brazilian retail market. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2010, 3, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mdegela, R.; Ryoba, R.; Karimuribo, E.; Phiri, E.; Loken, T.; Reksen, O.; Mtengeti, E.; Urio, N. Prevalence of clinical and subclinical mastitis and quality of milk on smallholder dairy farms in Tanzania. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2009, 80, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prado, C.K.; Ferreira, F.D.; Bando, É.; Machinski, M. Oxytetracycline, tetracycline, chlortetracycline and doxycycline in pasteurised cow’s milk commercialised in Brazil. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2015, 8, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaki, M.; Berruga, M.; Althaus, R.; Molina, M.; Molina, A. Occurrence of Antibiotic Residues in Milk from Manchega Ewe Dairy Farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 3132–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Wang, J.; Han, R.; Xu, X.; Zhen, Y.; Qu, X.; Sun, P.; Li, S.; Yu, Z. Occurrence of several main antibiotic residues in raw milk in 10 provinces of China. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2013, 6, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.A.D.A.; Magnavita, A.P.A.; Ferrão, S.P.B.; Gualberto, S.A.; Faleiro, A.S.; Figueiredo, A.J.; Matarazzo, S.V. Daily ingestion of tetracycline residue present in pasteurized milk: A public health problem. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 3427–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi Sani A—Search Results—PubMed, (n.d.). Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=mohamadi+sani+a (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Cerkvenik, V. Analysis and monitoring of chloramphenicol residues in food of animal origin in Slovenia from 1991 to 2000. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwijila, L.R.; Omore, A.; Staal, S.; Mdoe, N.S.Y. Investigation of the Risk of Exposure to Antimicrobial Residues Present in Marketed Milk in Tanzania. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 2487–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, G.N.; Mikcha, J.M.G.; Bando, E.; Siqueira, V.L.D.; Machinski, M. Occurrence and Antibiotic Resistance of Coliform Bacteria and Antimicrobial Residues in Pasteurized Cow’s Milk from Brazil. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1684–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivaria, F.M.; Noordhuizen, J.P.T.M.; Kapaga, A.M. Evaluation of the hygienic quality and associated public health hazards of raw milk marketed by smallholder dairy producers in the Dar es Salaam region, Tanzania. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2006, 38, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusola, A.V.; Diana, B.E.; Ayoade, O.I. Assessment of Tetracycline, Lead and Cadmium Residues in Frozen Chicken Vended in Lagos and Ibadan, Nigeria. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 15, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Er, B.; Onurdağ, F.K.; Demirhan, B.; Özgacar, S.Ö.; Öktem, A.B.; Abbasoğlu, U. Screening of quinolone antibiotic residues in chicken meat and beef sold in the markets of Ankara, Turkey. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2212–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mustafa, Z.H.; Al-Ghamdi, M.S. Use of norfloxacin in poultry production in the eastern province of Saudi Arabia and its possible impact on public health. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2000, 10, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezenduka, E.V. Screening of antimicrobial residues in poultry meat in Enugu metropolis, Enugu State, South East Nigeria. Vet. Ital. 2019, 55, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdous, J.; Bradshaw, A.; Islam, S.K.M.A.; Zamil, S.; Islam, A.; Ahad, A.; Fournie, G.; Anwer, M.S.; Hoque, A. Antimicrobial Residues in Chicken and Fish, Chittagong, Bangladesh. EcoHealth 2019, 16, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huong, L.Q.; Hang, T.T.T.; Ngoc, P.T.; Van Tuat, C.; Erickson, V.I.; Padungtod, P. Pilot Monitoring of Antimicrobial Residues in Chicken and Pork in Vietnam. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong-Anh, N.T.; Van Chinh, D.; Tuyet-Hanh, T.T. Antibiotic Residues in Chickens and Farmers’ Knowledge of Their Use in Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam, in 2017. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2020, 32, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmatallah, N.; El Rhaffouli, H.; Amine, I.L.; Sekhsokh, Y.; Fihri, O.F.; El Houadfi, M. Consumption of antibacterial molecules in broiler production in Morocco. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 4, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sajid, A.; Kashif, N.; Kifayat, N.; Ahmad, S. Detection of antibiotic residues in poultry meat. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 29, 1691–1694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neogi, S.B.; Islam, M.; Islam, S.S.; Akhter, A.H.M.T.; Sikder, M.H.; Yamasaki, S.; Kabir, S.M.L. Risk of multi-drug resistant Campylobacter spp. and residual antimicrobials at poultry farms and live bird markets in Bangladesh. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapierre, L.; Quintrel, M.; Lagos-Susaeta, F.; Hervé-Claude, L.P.; Riquelme, R.; Oviedo, P.; Maino, M.; Cornejo, J. Assessment of Antimicrobial and Pesticide Residues in Food Products Sourced from Peasant Family Farming in Chile. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doğan, Y.N.; Pamuk, Ş.; Gürler, Z. Chloramphenicol and sulfonamide residues in sea bream (Sparus aurata) and sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fish from aquaculture farm. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41248–41252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.; Rosa, J.; Freitas, A.; Leston, S.; Barbosa, J.; Ramos, F. Detection and quantification of 47 antibiotic residues in farmed European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) using a multi-class and multi-residue UHPLC-MS/MS method. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, A.F.; Santos, L.; Rosa, J.; Leston, S.; Barbosa, J.; Pouca, A.S.V.; Freitas, A.; Ramos, F. Development and validation of a multi-residue and multi-class screening method of 44 antibiotics in salmon (Salmo salar) using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry: Application to farmed salmon. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1118–1119, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griboff, J.; Carrizo, J.C.; Bonansea, R.I.; Valdés, M.E.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Amé, M.V. Multiantibiotic residues in commercial fish from Argentina. The presence of mixtures of antibiotics in edible fish, a challenge to health risk assessment. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotte, A.R.; Daniel, D.; Braga, P.A.D.C.; Reyes, F.G.R. A simple and high-throughput method for multiresidue and multiclass quantitation of antimicrobials in pangasius (Pangasionodon hypophthalmus) fillet by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1124, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, L.R.; Tette, P.A.S.; Gloria, M.B.A.; Fernandes, C. A simple and rapid LC–MS/MS method for the determination of amphenicols in Nile tilapia. Food Chem. 2018, 262, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Compte, A.; Álvarez-Muñoz, D.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Barceló, D. Multi-residue method for the determination of antibiotics and some of their metabolites in seafood. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 104, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jansomboon, W.; Boontanon, S.K.; Boontanon, N.; Polprasert, C.; Da, C.T. Monitoring and determination of sulfonamide antibiotics (sulfamethoxydiazine, sulfamethazine, sulfamethoxazole and sulfadiazine) in imported Pangasius catfish products in Thailand using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniyappan, V.; Nagalingam, A.K.; Ranganathan, H.P.; Kandhikuppam, K.B.; Kothandam, H.P.; Vasu, S. Antibiotics in South Indian coastal sea and farmed prawns (Penaeus monodon). Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2013, 6, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, L.R.; Santos, F.A.; Ribeiro, A.C.S.; Fernandes, C.; Silva, L.H.; Gloria, M.B.A. Quinolones and tetracyclines in aquaculture fish by a simple and rapid LC-MS/MS method. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, C.; Booth, H.; Westacott, S.; Hawtin, P. Detection of antibacterial agents in warm water prawns. Commun. Dis. Public Health 1999, 2, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, N.; Fuchino, K. Survey of Residual Antibiotic Agents in Cultured Fish and Shellfish. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 42, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yen, N.T.P.; Nhung, N.T.; Van, N.T.B.; Van Cuong, N.; Chau, L.T.T.; Trinh, H.N.; Van Tuat, C.; Tu, N.D.; Lan, N.P.H.; Campbell, J.; et al. Antimicrobial residues, non-typhoidal Salmonella, Vibrio spp. and associated microbiological hazards in retail shrimps purchased in Ho Chi Minh city (Vietnam). Food Control. 2020, 107, 106756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Pei, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Zeng, W.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, K. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in mariculture farms, estuaries and the coast of the Beibu Gulf, China: Bioconcentration and diet safety of seafood. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansomboon, W.; Boontanon, S.K.; Boontanon, N.; Polprasert, C. Determination and health risk assessment of enrofloxacin, flumequine and sulfamethoxazole in imported Pangasius catfish products in Thailand. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2017, 53, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokh, S.; El Hawari, K.; Rahim, H.A.; Al Iskandarani, M.; Jaber, F. Antimicrobial residues survey by LC-MS in food-producing animals in Lebanon. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2020, 13, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensah, S.E.P.; Koudandé, O.D.; Sanders, P.; Laurentie, M.; Mensah, G.A.; Abiola, F.A. Antimicrobial residues in foods of animal origin in Africa: Public health risks. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2014, 33, 987. [Google Scholar]
- Njoga, E.O.; Onunkwo, J.I.; Okoli, C.E.; Ugwuoke, W.I.; Nwanta, J.A.; Chah, K.F. Assessment of antimicrobial drug administration and antimicrobial residues in food animals in Enugu State, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondieki, G.K.; Ombui, J.N.; Obonyo, M.; Gura, Z.; Githuku, J.; Orinde, A.B.; Gikunju, J.K. Antimicrobial residues and compositional quality of informally marketed raw cow milk, Lamu West Sub-County, Kenya, 2015. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2017, 28, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhung, N.T.; Van, N.T.B.; Van Cuong, N.; Duong, T.T.Q.; Nhat, T.T.; Hang, T.T.T.; Nhi, N.T.H.; Kiet, B.T.; Hien, V.B.; Ngoc, P.T.; et al. Antimicrobial residues and resistance against critically important antimicrobials in non-typhoidal Salmonella from meat sold at wet markets and supermarkets in Vietnam. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghani, A.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Rafieiyan, M.; Dallal, M.M.S.; Douraghi, M. Tetracycline and ciprofloxacin multiresidues in beef and chicken meat samples using indirect competitive ELISA. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2019, 40, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Okihashi, M.; Harada, K.; Konishi, Y.; Uchida, K.; Do, M.H.N.; Bui, H.D.T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, P.D.; Van Chau, V.; et al. Antibiotic Residue Monitoring Results for Pork, Chicken, and Beef Samples in Vietnam in 2012–2013. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5141–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, K.; Shahbazi, Y.; Nikousefat, Z. Monitoring and risk assessment of tetracycline residues in foods of animal origin. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitema, E.S.; Kikuvi, G.M.; Wegener, H.C.; Stohr, K. An assessment of antimicrobial consumption in food producing animals in Kenya. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 24, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, D.J. Antibiotic residues in poultry tissues and eggs: Human health concerns? Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla, P.; Doménech, E.; Escriche, I.; Beltrán, M.C.; Molina, M.P. Food Safety Margin Assessment of Antibiotics: Pasteurized Goat’s Milk and Fresh Cheese. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühne, M.; Körner, U.; Wenzel, S. Tetracycline residues in meat and bone meals. Part 2: The effect of heat treatments on bound tetracycline residues. Food Addit. Contam. 2001, 18, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratacós-Cubarsí, M.; Fernandez-García, A.; Picouet, P.; Valero-Pamplona, A.; García-Regueiro, J.-A.; Castellari, M. Formation of Tetracycline Degradation Products in Chicken and Pig Meat under Different Thermal Processing Conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4610–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, M.; Castillo, M.; Marti, P.; Althaus, R.L.; Molina, M.P. Effect of Heating on the Stability of Quinolones in Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5427–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, M.; Villegas, L.; Kortabitarte, M.; Althaus, R.; Molina, M. Effect of heat treatments on stability of β-lactams in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakila, R.J.; Vyla, S.A.P.; Kumar, R.S.; Jeyasekaran, G.; Jasmine, G.I. Stability of chloramphenicol residues in shrimp subjected to heat processing treatments. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Herrera, I.; Schneider, M.J.; Cole, K.; Farnell, M.B.; Blore, P.J.; Donoghue, D.J. Concentrations of Antibiotic Residues Vary between Different Edible Muscle Tissues in Poultry. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2217–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Herrera, I.; Donoghue, D.J. Antibiotic Residues Distribute Uniformly in Broiler Chicken Breast Muscle Tissue. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, A.L.; Herrick, K.A.; Afful, J.; Ahluwalia, N. Seafood Consumption in the United States, 2013–2016; NCHS Data Brief; U.S. Department of Health & Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 1–8.
- El Sheikha, A.F.; Montet, D. How to Determine the Geographical Origin of Seafood? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 56, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denver, S.; Jensen, J.D.; Christensen, T. Consumer preferences for reduced antibiotic use in Danish pig production. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 189, 105310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreyes, W.A.; Bahnson, P.B.; Funk, J.A.; Mckean, J.; Patchanee, P. Seroprevalence of Trichinella, Toxoplasma, and Salmonella in Antimicrobial-Free and Conventional Swine Production Systems. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2008, 5, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Fiol, F.S.; Balcão, V.M.; Barberato-Fillho, S.; Lopes, L.C.; Bergamaschi, C.C. Obesity: A New Adverse Effect of Antibiotics? Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, L.W.; Raphael, E.M.; Faerstein, E.M. Obesity in the United States—Dysbiosis from Exposure to Low-Dose Antibiotics? Front. Public Health 2013, 1, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Principi, N.; Esposito, S. Antibiotic administration and the development of obesity in children. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Yoo, J.Y.; Dutra, S.V.O.; Morgan, K.H.; Groer, M. The Association between Early-Life Gut Microbiota and Long-Term Health and Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Keyword Search | Primary Search Results | Remaining after Abstract Review | Remaining after Removal of Duplicates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial residues AND livestock | 381 | 16 | 8 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND seafood | 202 | 16 | 11 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND shrimp | 177 | 5 | 2 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND cattle | 1469 | 15 | 5 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND poultry | 1272 | 19 | 10 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND pork | 91 | 8 | 0 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND pig | 877 | 15 | 4 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND salmon | 95 | 5 | 0 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND milk | 1148 | 32 | 24 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND egg | 767 | 8 | 8 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND lamb | 274 | 1 | 0 |
| Antimicrobial residues AND sheep | 12 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 6765 | 141 | 73 |
| ELISA | U/HPLC | GC | LC-MS | Inhibitor Test | Test Kits | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | 4 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| Egg | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Milk | 4 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 12 |
| Pork/Pig | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Poultry | 2 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| Seafood | 2 | 7 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 2 |
| Sheep | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 14 | 29 | 1 | 20 | 5 | 21 |
| Antibiotic Detected | Cattle | Egg | Milk | Pork/Pig | Poultry | Seafood | Sheep | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amikacin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Amoxicilin | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 12 |
| Ampicilin | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Aparamycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ceftiofur | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Cephalexin | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Cephalothin | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Cephapirin | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Chloramphenicol | 0 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 12 |
| Chlortetracycline | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Clarithromycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Clindamycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Cloxacillin | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Doxycyclin | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Enrofloxacin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 7 |
| Erythromycin | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Florfenicol | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Flumequine | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Fluoroquinolon | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| Furazolidone | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Gentamycin | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 |
| Higromycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Kanamycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Lincomycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Neomycin | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Nitrofurantoin | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Norfloxacin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Oxytetracycline | 5 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 22 |
| Penicilin G | 7 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 |
| Quinolone | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| Roxithromycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Streptomycin | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Sulfanilamide | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Sulfadiazine | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 10 |
| Sulfaguanidine | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Sulfamethazine | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| Sulfisoxazole | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Sulfmethoxazole | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 5 |
| Sulfmethoxydiazine | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| Sulfmethoxypyridazine | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Sulfaquinoxaline | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Sulphanilamide | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tetracycline | 8 | 3 | 13 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 39 |
| Thiamphenicol | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Tobramycin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Trimethoprim | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| Trimetoprim | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tylmicosin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Treiber, F.M.; Beranek-Knauer, H. Antimicrobial Residues in Food from Animal Origin—A Review of the Literature Focusing on Products Collected in Stores and Markets Worldwide. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050534
Treiber FM, Beranek-Knauer H. Antimicrobial Residues in Food from Animal Origin—A Review of the Literature Focusing on Products Collected in Stores and Markets Worldwide. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(5):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050534
Chicago/Turabian StyleTreiber, Fritz Michael, and Heide Beranek-Knauer. 2021. "Antimicrobial Residues in Food from Animal Origin—A Review of the Literature Focusing on Products Collected in Stores and Markets Worldwide" Antibiotics 10, no. 5: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050534
APA StyleTreiber, F. M., & Beranek-Knauer, H. (2021). Antimicrobial Residues in Food from Animal Origin—A Review of the Literature Focusing on Products Collected in Stores and Markets Worldwide. Antibiotics, 10(5), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050534






