Determinants of Antimicrobial Resistance among the Different European Countries: More than Human and Animal Antimicrobial Consumption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Univariate Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Correlations
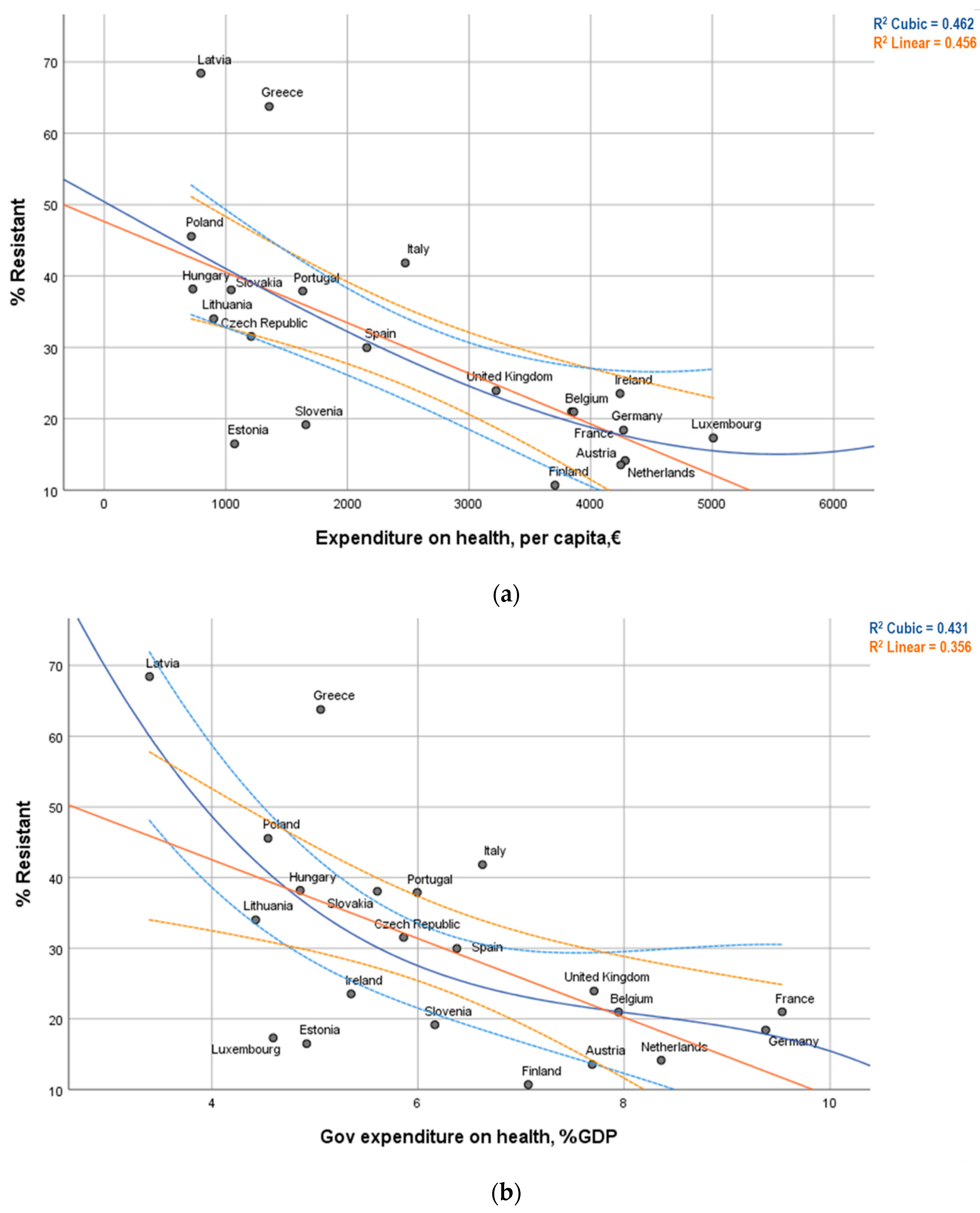
3.3. Graphical Visualization
3.4. Multiple Linear Regression Model
3.5. Multiple Linear Regression Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laxminarayan, R.; Matsoso, P.; Pant, S.; Brower, C.; Røttingen, J.-A.; Klugman, K.; Davies, S. Access to effective antimicrobials: A worldwide challenge. Lancet 2016, 387, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; Available online: http://www.who.int/antimicrobialresistance/global-action-plan/en/ (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- UN. Draft Political Declaration of the High Level Meeting of the General Assembly on Antimicrobial Resistance; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.un.org/pga/71/wp-content/uploads/ sites/40/2016/09/DGACM_GAEAD_ESCAB-antimicrobial resistance-Draft-Political-Declaration-1616108E.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- Robinson, T.P.; Bu, D.P.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Fèvre, E.M.; Gilbert, M.; Grace, D.; Hay, S.; Jiwakanon, J.; Kakkar, M.; Kariuki, S.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is the quintessential One Health issue. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC; OECD. Antimicrobial Resistance—Tackling the Burden in the European Union—Briefing Note for EU/EEA Countries; OECD: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fridkin, S.K.; Edwards, J.R.; Courval, J.M.; Hill, H.; Tenover, F.C.; Lawton, R.; Gaynes, R.P.; McGowan, J.E., Jr. Intensive Care Antimicrobial Resistance Epidemiology (ICARE) Project and the National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance (NNIS) System Hospitals (2001) The effect of vancomycin and third-generation cephalosporins on prevalence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in 126 U.S. adult intensive care units. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 135, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steinke, D.; Davey, P. Association between Antibiotic Resistance and Community Prescribing: A Critical Review of Bias and Confounding in Published Studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33 (Suppl. 3), S193–S205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, H.; Ferech, M.; Vander Stichele, R.; Elseviers, M.; ESAC Project Group. Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: A cross-national database study. Lancet 2005, 365, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.P.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, P.; Athukorala, P.-C.; Senanayake, S.; Khan, F. Antimicrobial Resistance: The Major Contribution of Poor Governance and Corruption to This Growing Problem. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- OECD. Percentage of hospitalised patients with at least one health care-associated infection and proportion of bacteria isolated from these infections resistant to antibiotics, 2015–2017. In Quality and Outcomes of Care; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, S.; Katrien, L.; Tommi, K.; Enrico, R.; Pete, K.; Luisa, M.M.; Béatrice, J.; Susan, H.; Sonja, H.; Outi, L.; et al. Prevalence of healthcare-associated infections, estimated incidence and composite antimicrobial resistance index in acute care hospitals and long-term care facilities: Results from two European point prevalence surveys, 2016 to 2017. Euro Surveill. 2018, 23, 1800516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collignon, P.; Beggs, J.J.; Walsh, T.R.; Gandra, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Anthropological and socio-economic factors contributing to global antimicrobial resistance: A univariate and multivariable analysis. Lancet Planet Health 2018, 2, e398–e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Lozano, J.M.; Lawes, T.; Nebot, C.; Beyaert, A.; Bertrand, X.; Hocquet, D.; Aldeyab, M.; Scott, M.; Conlon-Bingham, G.; Farren, D.; et al. A nonlinear time-series analysis approach to identify thresholds in associations between population antibiotic use and rates of resistance. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1160–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliemann, B.S.; Levin, A.S.; Moura, M.L.; Boszczowski, I.; Lewis, J.J. Socioeconomic Determinants of Antibiotic Consumption in the State of São Paulo, Brazil: The Effect of Restricting Over-The-Counter Sales. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Europe 2016. In Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net); ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017; Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/antimicrobial-resistance-surveillance-europe-2016 (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- European Medicines Agency; European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 30 European Countries in 2016, EMA/275982/2018. 2018. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-30-european-countries-2016-trends-2010-2016-eighth-esvac_en.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2020).
- Manageiro, V.; Jones-Dias, D.; Ferreira, E.; Caniça, M. Plasmid-Mediated Colistin Resistance (mcr-1) in Escherichia coli from Non-Imported Fresh Vegetables for Human Consumption in Portugal. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | SD | n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence of healthcare associated infections (HAI), % | 2.95 | 8.10 | 4.96 | 1.55 | 23 |
| Bacteria resistant to antibiotic (Resistant), % | 10.69 | 68.42 | 29.9251 | 15.72056 | 21 |
| Human antibiotic consumption at ambulatory care, DID | 9.20 | 31.00 | 17.4591 | 5.74669 | 22 |
| Human antibiotic consumption at hospital care, DID | 0.85 | 2.38 | 1.7226 | 0.43679 | 19 |
| Human antibiotic consumption (total), DID | 10 | 33 | 19.70 | 6.094 | 19 |
| Veterinary antibiotic overall sales, Tonnes | 0.59 | 2726.54 | 315.95 | 608.08 | 23 |
| Veterinary antibiotic sales for food-producing animals, Tonnes | 0.56 | 2724.89 | 314.55 | 620.95 | 22 |
| Veterinary antibiotic sales population correction unit, 1000 Tonnes | 54.62 | 8734.01 | 2156.80 | 2630.95 | 22 |
| Total expenditure on health, per capita, | 715.95 | 5785.41 | 2700.79 | 1605.21 | 23 |
| Total expenditure on health, % of GDP | 5.47 | 11.48 | 8.48 | 1.73 | 23 |
| Government expenditure on health, % of GDP | 3.40 | 9.54 | 6.40 | 1.70 | 23 |
| Years lost, /100,000 population, aged 75 years old | 3110.00 | 9122.00 | 4629.18 | 1668.09 | 17 |
| % Resistant | n | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Correlation | Coefficients | ||
| Prevalence of healthcare associated infections (HAI), % | r = 0.154 (p = 0.506) | rs = 0.045 (p = 0.845) | 21 |
| Human antibiotic consumption at ambulatory care, DID | r = 0.339 (p = 0.144) | rs = 0.387 (p = 0.092) | 20 |
| Human antibiotic consumption at hospital care, DID | r = 0.171 (p = 0.497) | rs = 0.164 (p = 0.515) | 18 |
| Human antibiotic consumption (total), DID | r = 0.275 (p = 0.269) | rs = 0.305 (p = 0.219) | 18 |
| Veterinary antibiotic overall sales, Tonnes | r = 0.037 (p = 0.873) | rs = 0.187 (p = 0.417) | 21 |
| Veterinary antibiotic sales for food-producing animals, Tonnes | r = 0.036 (p = 0.879) | rs = 0.188 (p = 0.427) | 20 |
| Veterinary antibiotic sales population correction unit, 1000 Tonnes | r = -0.124 (p = 0.603) | rs = 0.104 (p = 0.663) | 20 |
| Total expenditure on health, per capita, € | r = -0.675 ** (p = 0.001) | rs = −0.722 ** (p < 0.001) | 21 |
| Total expenditure on health, % of GDP | r = −0.428 (p = 0.053) | rs = −0.435 * (p = 0.049) | 21 |
| Government expenditure on health, % of GDP | r = −0.597 ** (p = 0.004) | rs = −0.534 * (p = 0.013) | 21 |
| Years lost /100,000 population, aged 75 years old | r = 0.305 (p = 0.269) | rs = 0.564 * (p = 0.028) | 15 |
| Variables | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| (Constant) | 19.741 | 8.275 | 2.386 | 0.044 | |
| Total expenditure on health, per capita, € | −0.007 | 0.002 | −0.668 | −4.158 | 0.003 |
| Human antibiotic consumption at ambulatory care, DID | 1.412 | 0.383 | 0.591 | 3.683 | 0.006 |
| Dependent Variable: % AMR rate R2 = 0.891; R2 adj = 0.742 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.C.; Nogueira, P.J.; Paiva, J.-A. Determinants of Antimicrobial Resistance among the Different European Countries: More than Human and Animal Antimicrobial Consumption. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070834
Silva AC, Nogueira PJ, Paiva J-A. Determinants of Antimicrobial Resistance among the Different European Countries: More than Human and Animal Antimicrobial Consumption. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(7):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070834
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Ana C., Paulo Jorge Nogueira, and José-Artur Paiva. 2021. "Determinants of Antimicrobial Resistance among the Different European Countries: More than Human and Animal Antimicrobial Consumption" Antibiotics 10, no. 7: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070834
APA StyleSilva, A. C., Nogueira, P. J., & Paiva, J.-A. (2021). Determinants of Antimicrobial Resistance among the Different European Countries: More than Human and Animal Antimicrobial Consumption. Antibiotics, 10(7), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10070834








