ESBL-Producing, Carbapenem- and Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Escherichia coli in Belgian and Dutch Broiler and Pig Farms: A Cross-Sectional and Cross-Border Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antibiotic Use in Belgian and Dutch Broiler and Pig Farms
2.2. ESBL-Producing, Carbapenem-Resistant and Ciprofloxacin-Resistant E. coli in Belgian and Dutch Broiler and Pig Farms
2.3. Associations between Antimicrobial Use and Resistance
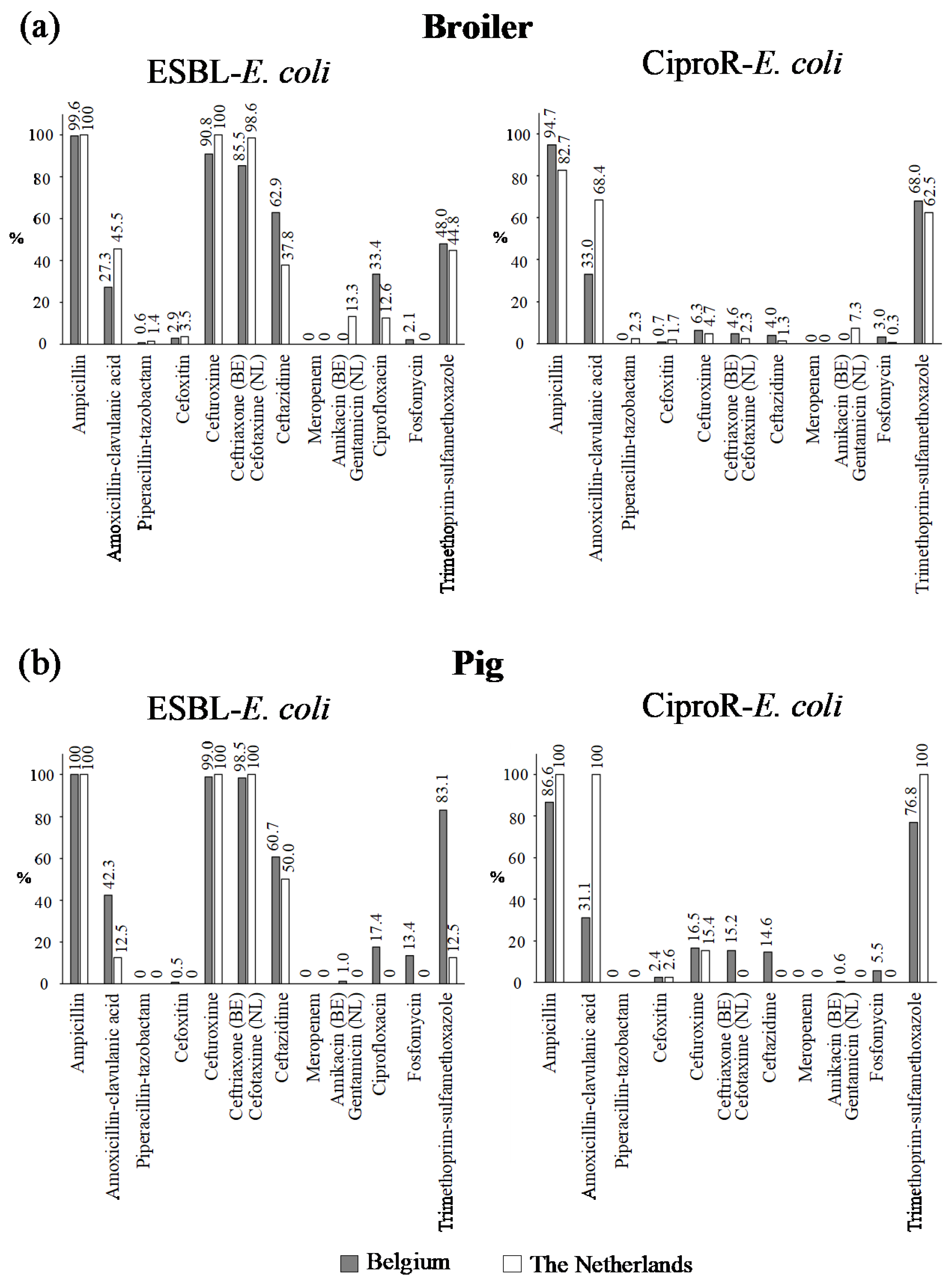
2.4. Antibiotic Resistance in ESBL-E. coli and CiproR-E. coli from Broiler Chickens and Pigs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design, Farm Selection and Farm Characteristics
4.2. Antibiotic Use
4.3. Collection of Fecal Samples
4.4. Microbiological Methods
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilbert, M.; Conchedda, G.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Cinardi, G.; Linard, C.; Nicolas, G.; Thanapongtharm, W.; D’Aietti, L.; Wint, W.; Newman, S.H.; et al. Income Disparities and the Global Distribution of Intensively Farmed Chicken and Pigs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burow, E.; Rostalski, A.; Harlizius, J.; Gangl, A.; Simoneit, C.; Grobbel, M.; Kollas, C.; Tenhagen, B.A.; Käsbohrer, A. Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia Coli from Pigs from Birth to Slaughter and Its Association with Antibiotic Treatment. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 165, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collignon, P.C.; Conly, J.M.; Andremont, A.; McEwen, S.A.; Aidara-Kane, A. World Health Organization Ranking of Antimicrobials According to Their Importance in Human Medicine: A Critical Step for Developing Risk Management Strategies to Control Antimicrobial Resistance From Food Animal Production. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, T.R. A One-Health Approach to Antimicrobial Resistance. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 854–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, P.; Knudsen, B.E.; Lukjancenko, O.; Duarte, A.S.R.; Van Gompel, L.; Luiken, R.E.C.; Smit, L.A.M.; Schmitt, H.; Garcia, A.D.; Hansen, R.B.; et al. Abundance and Diversity of the Faecal Resistome in Slaughter Pigs and Broilers in Nine European Countries. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, R.J.; Kim, S.S.; Mollenkopf, D.F.; Mathys, D.A.; Schuenemann, G.M.; Daniels, J.B.; Wittum, T.E. Antimicrobial-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Recovered from Companion Animal and Livestock Environments. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation Advisory Group on Integrated Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine: Ranking of Medically Important Antimicrobial for Risk Management of Antimicrobial Resistance Due to Non-Human Use- 6th Revision; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/312266/9789241515528-eng.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2019).
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2018/2019. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, P.M.; Loureiro, L.; Matos, A.J.F. Transfer of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria between Intermingled Ecological Niches: The Interface between Humans, Animals and the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorado-García, A.; Smid, J.H.; van Pelt, W.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Fluit, A.C.; van den Bunt, G.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Hordijk, J.; Dierikx, C.M.; Veldman, K.T.; et al. Molecular Relatedness of ESBL/AmpC-Producing Escherichia Coli from Humans, Animals, Food and the Environment: A Pooled Analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overdevest, I.; Willemsen, I.; Rijnsburger, M.; Eustace, A.; Li, X.; Hawkey, P.; Heck, M.; Savelkoul, P.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; van der Zwaluw, K.; et al. Extended-Spectrum B-Lactamase Genes of Escherichia Coli in Chicken Meat and Humans, The Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leverstein Hall, M.A.; Dierikx, C.M.; Cohen Stuart, J.; Voets, G.M.; van den Munckhof, M.P.; van Essen-Zandbergen, A.; Platteel, T.; Fluit, A.C.; van de Sande-Bruinsma, N.; Scharinga, J.; et al. Dutch Patients, Retail Chicken Meat and Poultry Share the Same ESBL Genes, Plasmids and Strains. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulder, M.; de Kiefte Jong, J.C.; Goessens, W.H.F.; de Visser, H.; Hofman, A.; Stricker, B.H.; Verbon, A. Risk Factors for Resistance to Ciprofloxacin in Community-Acquired Urinary Tract Infections Due to Escherichia Coli in an Elderly Population. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hijazi, S.M.; Fawzi, M.A.; Ali, F.M.; Abd El Galil, K.H. Prevalence and Characterization of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Healthy Children and Associated Risk Factors. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EUROSTAT. Total Livestock Density. 2016. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Agri-environmental_indicator_-_livestock_patterns (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- European Medicines Agency. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2018: Tenth ESVAC Report; EMA/24309/2020; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020.
- Nethmap-MARAN 2021- Consumption of Antimicrobial Agents and Antimicrobial Resistance among Medically Important Bacteria in The Netherlands. Available online: https://www.wur.nl/en/show/Nethmap-MARAN-2021.htm (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Belgian Veterinary Surveillance of Antibacterial Consumption National Consumption Report 2020; BELVETSAC 2020. Federal Agency for Medicines and Health Products: Brussels, Belgium. 2021. Available online: https://belvetsac.ugent.be (accessed on 25 July 2021).
- Callens, B.; Cargnel, M.; Sarrazin, S.; Dewulf, J.; Hoet, B.; Vermeersch, K.; Wattiau, P.; Welby, S. Associations between a Decreased Veterinary Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Commensal Escherichia Coli from Belgian Livestock Species (2011–2015). Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 157, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarrazin, S.; Joosten, P.; Van Gompel, L.; Luiken, R.E.C.; Mevius, D.J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Heederik, D.J.J.; Dewulf, J.; Wagenaar, J.; Graveland, H.; et al. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Antimicrobial Usage Patterns in 180 Selected Farrow-to-Finish Pig Farms from Nine European Countries Based on Single Batch and Purchase Data. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, P.; Sarrazin, S.; Van Gompel, L.; Luiken, R.E.C.; Mevius, D.J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Heederik, D.J.J.; Dewulf, J.; Graveland, H.; Schmitt, H.; et al. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Antimicrobial Usage at Farm and Flock Level on 181 Broiler Farms in Nine European Countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caekebeke, N.; Jonquiere, F.J.; Ringenier, M.; Tobias, T.J.; Postma, M.; van den Hoogen, A.; Houben, M.A.M.; Velkers, F.C.; Sleeckx, N.; Stegeman, J.A.; et al. Comparing Farm Biosecurity and Antimicrobial Use in High-Antimicrobial-Consuming Broiler and Pig Farms in the Belgian-Dutch Border Region. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 558455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, A.; Martel, A.; Persoons, D.; Dewulf, J.; Heyndrickx, M.; Catry, B.; Herman, L.; Haesebrouck, F.; Butaye, P. Diversity of Extended-Spectrum -Lactamases and Class C -Lactamases among Cloacal Escherichia Coli Isolates in Belgian Broiler Farms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Damme, I.; Garcia-Graells, C.; Biasino, W.; Gowda, T.; Botteldoorn, N.; De Zutter, L. High Abundance and Diversity of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Escherichia Coli in Faeces and Tonsils of Pigs at Slaughter. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 208, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in Zoonotic and Indicator Bacteria from Humans, Animals and Food in 2017/2018. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MARAN 2018- Monitoring of Antimicrobial Resistance and Antibiotic Usage in Animals in the Netherlands in 2017. Available online: https://www.wur.nl/upload_mm/7/b/0/5e568649-c674-420e-a2ca-acc8ca56f016_Maran 2018.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Dorado-García, A.; Mevius, D.J.; Jacobs, J.J.H.; Van Geijlswijk, I.M.; Mouton, J.W.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Heederik, D.J. Quantitative Assessment of Antimicrobial Resistance in Livestock during the Course of a Nationwide Antimicrobial Use Reduction in the Netherlands. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3607–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AMCRA. Activities and Achievements Related to the Reduction in Antibiotics Use and Resistance in Veterinary Medicine in Belgium in 2017. Available online: https://www.afsca.be/professionnals/publications/reportamcra/_documents/2017-06-30_AMR-Publiek-rapport_en.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2019).
- Van den Bogaard, A.E.; London, N.; Driessen, C.; Stobberingh, E.E. Antibiotic Resistance of Faecal Escherichia Coli in Poultry, Poultry Farmers and Poultry Slaughterers. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 47, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantziaras, I.; Boyen, F.; Callens, B.; Dewulf, J. Correlation between Veterinary Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance in Food-Producing Animals: A Report on Seven Countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Netherlands Veterinary Medicines Authority SDa Expert Panel. Usage of Antibiotics in Agricultural Livestock in The Netherlands in 2016; Trends and Benchmarking of Livestock Farms and Veterinarians. Available online: https://www.autoriteitdiergeneesmiddelen.nl/en/news/21/sda-report-usage-of-antibiotics-in-agricultural-livestock-in-the-netherlands-in-2016 (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Dierikx, C.; van der Goot, J.; Fabri, T.; Fabri, T.; Van Essen-Zandbergen, A.; Smith, H.; Mevius, D. Extended-Spectrum-Beta -Lactamase- and AmpC- Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia Coli in Dutch Broilers and Broiler Farmers. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaak, H.; van Hoek, A.H.A.M.; Hamidjaja, R.A.; van der Plaats, R.Q.J.; Kerkhof-de Heer, L.; de Roda Husman, A.M.; Schets, F.M. Distribution, Numbers, and Diversity of ESBL-Producing, E. Coli in the Poultry Farm Environment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinivasagam, H.N.; Tran, T.; Maddock, L.; Gale, A.; Blackall, P.J. Mechanically Ventilated Broiler Sheds: A Possible Source of Aerosolized Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Escherichia Coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7417–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persoons, D.; Dewulf, J.; Smet, A.; Herman, L.; Heyndrickx, M.; Martel, A.; Catry, B.; Butaye, P.; Haesebrouck, F. Antimicrobial Use in Belgian Broiler Production. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 105, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Kluytmans Bergh, M.; Lammens, C.; Perales Selva, N.; Buiting, A.; Leroux-roels, I.; Saegeman, V.; Savelkoul, P. Microbiological Methods to Detect Intestinal Carriage of Highly-Resistant Microorganisms (HRMO) in Humans and Livestock in the i-4-1-Health Dutch- Belgian Cross-Border Project. Preprints 2019, 2019120216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. EUCAST Clinical Breakpoint Tables v. 8.1, Valid from 2018-05-15. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. EUCAST Guidelines for Detection of Resistance Mechanisms and Specific Resistances of Clinical and/or Epidemiological Importance Version 2.0. 2017. Available online: https://eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Resistance_mechanisms/EUCAST_detection_of_resistance_mechanisms_170711.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S.C. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
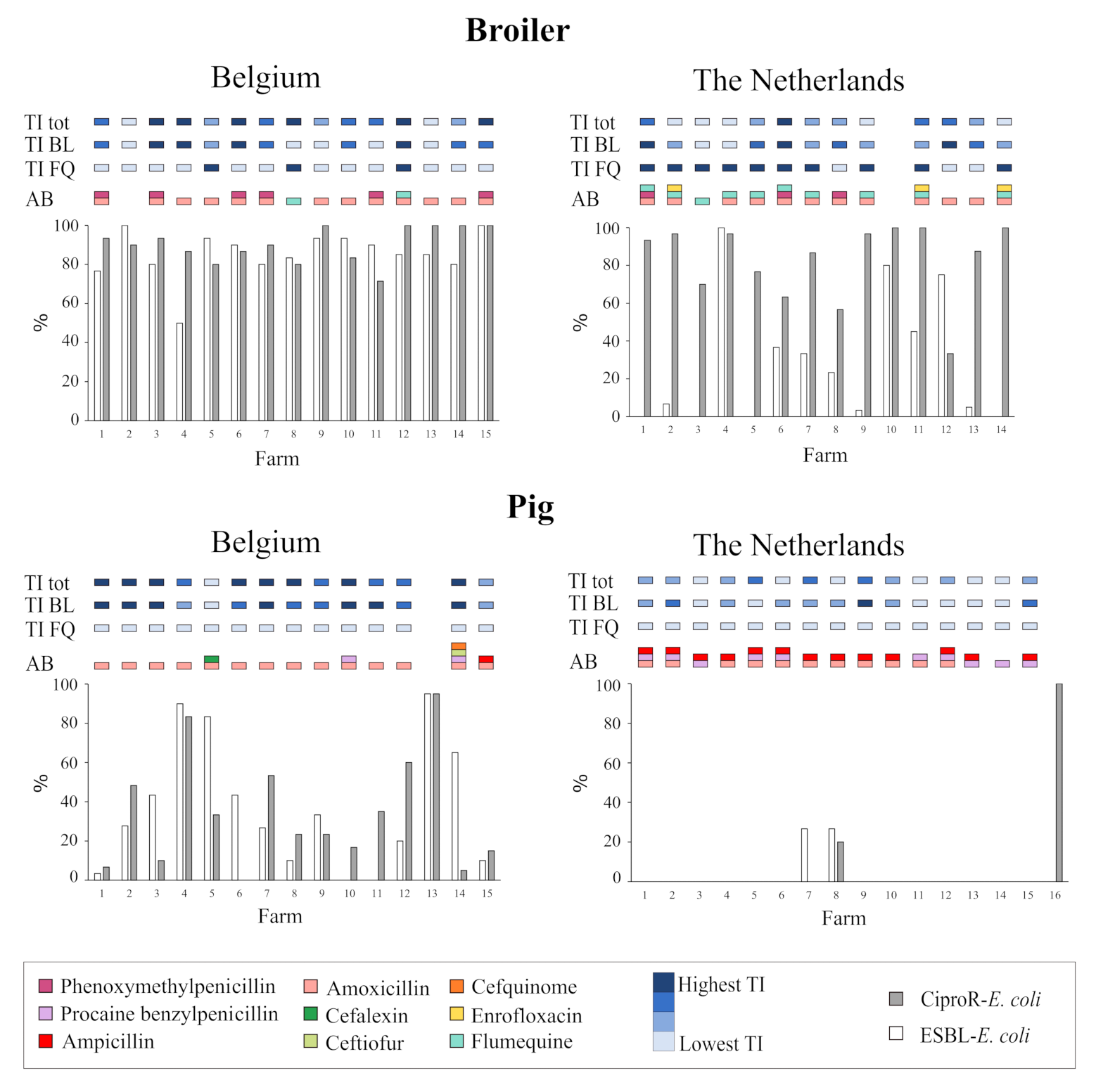
| Broiler | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Samples | Percentage Positive Samples (%) | Number of Positive Farms | Min–Max within Farm Percentage (Percentage Positive Samples per Farm) | Median Percentage (%) | Interquartile Range (%) | OR NL vs. BE (95% CI) | ||
| ESBL-E. coli | BE | 399 | 85 | 15/15 | 50–100 | 85 | 80–93 | 1 (reference) |
| NL | 380 | 27 | 10/14 | 0–100 | 15 | 0.83–43 | 0.007 (0.001–0.048) | |
| CiproR-E. coli | BE | 283 | 88 | 15/15 | 71–100 | 90 | 85–100 | 1 (reference) |
| NL | 303 | 82 | 14/14 | 33–100 | 90 | 72–97 | 0.60 (0.24–1.47) | |
| Pig | ||||||||
| Number of Samples | Percentage Positive Samples (%) | Number of Positive Farms | Min–Max within Farm Percentage (Percentage Positive Samples per Farm) | Median Percentage (%) | Interquartile Range (%) | OR NL vs. BE (95% CI) | ||
| ESBL-E. coli | BE | 399 | 37 | 13/15 | 0–95 | 28 | 10–54 | 1 (reference) |
| NL | 418 | 4.0 | 2/16 | 0–27 | 0 | 0–0 | 0.004 (0–0.042) | |
| CiproR-E. coli | BE | 399 | 33 | 14/15 | 0–95 | 23 | 13–51 | 1 (reference) |
| NL | 328 | 11 | 2/13 | 0–100 | 0 | 0–0 | 0.006 (0–0.098) | |
| ESBL-E. coli | CiproR-E. coli | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broiler | Category total TI | OR | 95% CI | Category total TI | OR | 95% CI |
| Belgium, total TI < 2.9 | 1 (reference) | Belgium, total TI < 2.9 | 1 (reference) | |||
| The Netherlands | 0.02 | 0–0.09 | The Netherlands | 0.46 | 0.19–1.07 | |
| Total TI 2nd quartile [2.9– <6.2] | 0.80 | 0.07–8.03 | Total TI 2nd quartile [2.9– <6.2] | 0.33 | 0.10–0.95 | |
| Total TI 3rd quartile [6.2– <12.2] | 1.20 | 0.1–12.22 | Total TI 3rd quartile [6.2– <12.2] | 0.40 | 0.11–1.24 | |
| Total TI 4th quartile [12.2– <28] | 0.95 | 0.08–11.54 | Total TI 4th quartile [12.2– <28] | 0.31 | 0.09–0.98 | |
| Category TI beta-lactam | OR | 95% CI | Category TI fluoroquinolone | OR | 95% CI | |
| Belgium, TI_BL < 1.2 | 1 (reference) | Belgium, no fluroquinolone use | 1 (reference) | |||
| The Netherlands | 0.02 | 0–0.11 | The Netherlands | 0.45 | 0.16–1.22 | |
| TI beta-lactam 2nd quartile [1.2– <3.4] | 0.28 | 0.02–3.30 | Fluoroquinolone use | 1.69 | 0.63–4.77 | |
| TI beta-lactam 3rd quartile [3.4– <7.4] | 0.27 | 0.03–2.28 | ||||
| TI beta-lactam 4th quartile [7.4– <16] | 0.33 | 0.03–2.81 | ||||
| ESBL-E. coli | CiproR-E. coli | |||||
| Pig | Category total TI | OR | 95% CI | Category total TI | OR | 95% CI |
| Belgium, total TI < 12.9 | 1 (reference) | Belgium, total TI < 12.9 | 1 (reference) | |||
| The Netherlands | 0.01 | 0.00–0.11 | The Netherlands | 0.01 | 0–0.05 | |
| Total TI 2nd quartile [12.9– <23.2] | 0.04 | 0.00–1.77 | Total TI 2nd quartile [12.9– <23.2] | 0.07 | 0–1.61 | |
| Total TI 3rd quartile [23.2– <44] | 0.63 | 0.03–15.90 | Total TI 3rd quartile [23.2– <44] | 0.48 | 0.03–5.04 | |
| Total TI 4th quartile [44– <82] | 0.20 | 0.01–7.40 | Total TI 4th quartile [44– <82] | 0.10 | 0.01–1.14 | |
| Category TI beta-lactam | OR | 95% CI | Category TI fluoroquinolone | OR | 95% CI | |
| Belgium, TI beta-lactam < 3.2 | 1 (reference) | no fluoroquinolone use | ||||
| The Netherlands | 0 | 0–0.03 | ||||
| TI beta-lactam 2nd quartile [3.2– <12.1] | 6.68 | 0.34–350.81 | ||||
| TI beta-lactam 3rd quartile [12.1– <22.7] | 0.47 | 0.01–27.10 | ||||
| TI beta-lactam 4th quartile [22.7– <54] | 0.22 | 0.00–9.93 | ||||
| ESBL-E. coli | CiproR-E. coli | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % MDR A | N | % MDR | ||
| Broiler | Belgium | 523 | 89.7 | 303 | 77.2 |
| The Netherlands | 143 | 68.5 | 301 | 75.9 | |
| Pig | Belgium | 201 | 99.5 | 164 | 73.8 |
| The Netherlands | 16 | 100 | 39 | 100 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Koster, S.; Ringenier, M.; Lammens, C.; Stegeman, A.; Tobias, T.; Velkers, F.; Vernooij, H.; Kluytmans-van den Bergh, M.; Kluytmans, J.; Dewulf, J.; et al. ESBL-Producing, Carbapenem- and Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Escherichia coli in Belgian and Dutch Broiler and Pig Farms: A Cross-Sectional and Cross-Border Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080945
De Koster S, Ringenier M, Lammens C, Stegeman A, Tobias T, Velkers F, Vernooij H, Kluytmans-van den Bergh M, Kluytmans J, Dewulf J, et al. ESBL-Producing, Carbapenem- and Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Escherichia coli in Belgian and Dutch Broiler and Pig Farms: A Cross-Sectional and Cross-Border Study. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(8):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080945
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Koster, Sien, Moniek Ringenier, Christine Lammens, Arjan Stegeman, Tijs Tobias, Francisca Velkers, Hans Vernooij, Marjolein Kluytmans-van den Bergh, Jan Kluytmans, Jeroen Dewulf, and et al. 2021. "ESBL-Producing, Carbapenem- and Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Escherichia coli in Belgian and Dutch Broiler and Pig Farms: A Cross-Sectional and Cross-Border Study" Antibiotics 10, no. 8: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080945
APA StyleDe Koster, S., Ringenier, M., Lammens, C., Stegeman, A., Tobias, T., Velkers, F., Vernooij, H., Kluytmans-van den Bergh, M., Kluytmans, J., Dewulf, J., Goossens, H., & on behalf of the i-4-1-Health Study Group. (2021). ESBL-Producing, Carbapenem- and Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Escherichia coli in Belgian and Dutch Broiler and Pig Farms: A Cross-Sectional and Cross-Border Study. Antibiotics, 10(8), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080945







