The Antimicrobial Properties of Nanotitania Extract and Its Role in Inhibiting the Growth of Klebsiella pneumonia and Haemophilus influenza
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanoparticle Extraction Preparation
2.2. Antibacterial Activity Evaluation
2.3. Toxicology Properties of TiO2
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodgin, K.E.; Moss, M. The epidemiology of sepsis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, A.; Mandrell, R.E.; Gibson, B.W.; Apicella, M.A. The lipooligosaccharides of pathogenic gram-negative bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1996, 22, 139–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyavathy, K.; Madhusudhan, B.K.I. Review on clinical diseases caused by klebsiella. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.-I.; Kim, S.H.; Bang, J.W.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, E.C.; Oh, M.-D.; Choe, K.-W. Community-acquired versus nosocomial Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia: Clinical features, treatment outcomes, and clinical implication of antimicrobial resistance. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2006, 21, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whittaker, R.; Economopoulou, A.; Dias, J.G.; Bancroft, E.; Ramliden, M.; Celentano, L.P. Epidemiology of invasive Haemophilus influenza disease, Europe 2007–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, D.F.; Myers, A.L. Changing epidemiology of Haemophilus influenza in children. Infect. Dis. Clin. 2018, 32, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harun, M.A.; Noor, N.F.M.; Yusoff, M.E.; Abas, R.; Alam, M.K. The result of modified hydrothermal nanotitania extract to the Escherichia coli growth. Bangladesh J. Med. Sci. 2020, 19, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, M.; Hara, K.; Kudo, J. Bactericidal actions of a silver ion solution on Escherichia coli, studied by energy-filtering transmission electron microscopy and proteomic analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7589–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yemmireddy, V.K.; Hung, Y.-C. Selection of photocatalytic bactericidal titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles for food safety applications. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, H.; Mukifza, A.; Yusof, S.; Ongkudon, C.; Farid, E.M. Effect of acid concentration and time on synthesizing the titanium dioxide from synthetic rutile waste. Int. J. Recent Res. Phys. Chem. Sci. 2017, 3, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Harun, M.; Yusof, S.; Awang, H. Experimental analysis of titanium dioxide synthesis from synthetic rutile waste using a moderate acid concentration and temperature. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2017, 132, 833–835. [Google Scholar]
- Mukifza, A.; Awang, H.; Yusof, S. Synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide using a caustic hydrothermal with moderate molarity and ratio from synthetic rutile waste. Eur. J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 4, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Jimmy, M.J.; Harun, A.M.; Rahman, M.Y.A.; Ludin, N.A. Comparative study of dye sensitized solar cell utilizing seaweed and rose Bengal sensitizer: Influence of dye concentration. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 3219–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.G.; Harun, A.M.; Rahman, M.Y.A. Dye sensitized solar cell utilizing Degaussa P25 and anatese TiO2 films: Comparative study of photovoltaic performance: Effect of N719 dye concentration. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.F.M.; Harun, A.M.; Yusof, S.; Yusoff, M.E.; Mohamad, S. Effects of modified hydrothermal nanotitania on the viability of Staphylococcus aureus. Arch. Orofac. Sci. 2018, 13, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Harun, A.M.; Ghani, N.B.A.; Noor, N.F.M.; Abas, R.; Alam, M.K. Mutagenic properties of modified hydrothermal nanotitania extract. Bangladesh J. Med. Sci. 2020, 19, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, A.M.; Noor, N.F.M.; Shaari, R.; Ying, L.X.; Yusoff, M.E.; Alam, M.K. The toxicology properties of modified hydrothermal nanotitania extraction. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.F.M.; Yusoff, M.E.; Abdul Rahman, M.A.; Alam, M.K.; Harun, A.M. The Disinfectant Effect of Modified Hydrothermal Nanotitania Extract on Candida albicans. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6617645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. Biomedical applications of nano-titania in theranostics and photodynamic therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandamalla, D.; Lingabathula, H.; Yellu, N. Nano Titanium Induces Cytotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Human Lung Cells. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2017, 7, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Dolmans, D.E.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; He, S.; Seare, W.J.; Almutairi, A. Review of the progress toward achieving heat confinement- the holy grail of photothermal therapy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 080901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Mo, A.; Peng, Q. Nanomaterials-Based Photothermal Therapy and Its Potentials in Antibacterial Treatment. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, G.; Yu, J.C.; Wong, P.K. Advances in photocatalytic disinfection of bacteria: Development of photocatalysts and mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein-Al-Ali, S.H.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Hussein, M.Z.; Geilich, B.M.; Webster, T.J. Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of an ampicillin-conjugated magnetic nanoantibiotic for medical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3801–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chhabilal, R.; Bupendra, J.; Schindra, K.R.; Gobinda, G.; Ramesh, P.P. Understanding Mechanism of Photocatalytic Microbial Decontamination of Environmental Wastewater. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, Y.H.; Ng, A.M.; Xu, X.; Shen, Z.; Gethings, L.A.; Wong, M.T.; Chan, C.M.N.; Guo, M.Y.; Ng, Y.H.; Djurišić, A.B.; et al. Mechanisms of antibacterial activity of MgO: Non-ROS mediated toxicity of MgO nanoparticles towards Escherichia coli. Small 2014, 10, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Method for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2006, Approved standard—Eighth Edition; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2006.
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Analysis. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jesline, A.; John, N.P.; Narayanan, P.; Vani, C.; Murugan, S. Antimicrobial activity of zinc and titanium dioxide nanoparticles against biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefatshe, K.; Muiva, C.M.; Kebaabetswe, L.P. Extraction of nanocellulose and in-situ casting of ZnO/cellulose nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharfudeen, B.F.J.M.; Latheef, A.F.A.; Ambrose, R.V. Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles and investigation of antimicrobial activities against human pathogens. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 9, 1604. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, G. Potent antibacterial activities of Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite powders synthesized by a one-pot sol− gel method. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2905–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedziora, A.; Speruda, M.; Krzyzewska, E.; Rybka, J.; Lukowiak, A.; Bugla-Ploskonska, G. Similarities and differences between silver ions and silver in nanoforms as antibacterial agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abed, A.S.; Al-Khafaji, H.K.; AL-Hamdani, A.H. Detection of Serotype Gene of Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolated from Different Clinical Cases of Hospitalized Infections in Al-Diwaniya city. Al Qadisiyah Med. J. 2016, 12, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Sahly, H.; Podschun, R.; Ullmann, U. Klebsiella infections in the immunocompromised host. Biol. Pathol. Innate Immun. Mech. 2002, 479, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Codo, A.C.; Saraiva, A.C.; Dos Santos, L.L.; Visconde, M.F.; Gales, A.C.; Zamboni, D.S.; Medeiros, A.I. Inhibition of inflammasome activation by a clinical strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae impairs efferocytosis and leads to bacterial dissemination. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, W.M. Bacterial adhesion: Seen any good biofilms lately? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramalingam, B.; Parandhaman, T.; Das, S.K. Antibacterial effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on surface ultrastructure and nanomechanical properties of gram-negative bacteria viz. Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Appl. Mater. 2016, 8, 4963–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donia, D.; Carbone, M. Fate of the nanoparticles in environmental cycles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusy, R.P.; Whitley, J.Q. Thermal and mechanical characteristics of stainless steel, titanium-molybdenum, and nickel-titanium archwires. Am. J. Orthod. 2007, 131, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, M.-J.; Shim, E.; Kho, E.H.; Park, K.J.; Jung, J.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, B.; Lee, K.-H.; Cho, D.-L.; Bai, D.-H.; et al. Surface modification of orthodontic wires with photocatalytic titanium oxide for its anti-adherent and antibacterial properties. Angle Orthod. 2007, 77, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
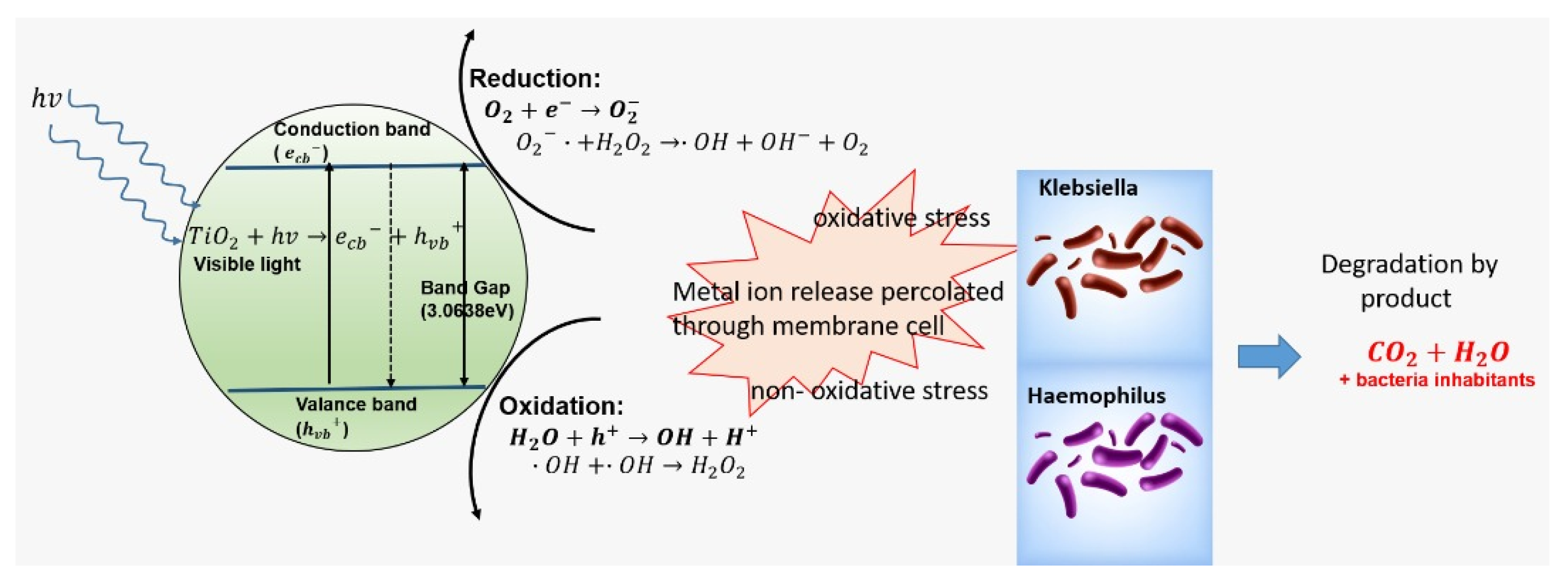
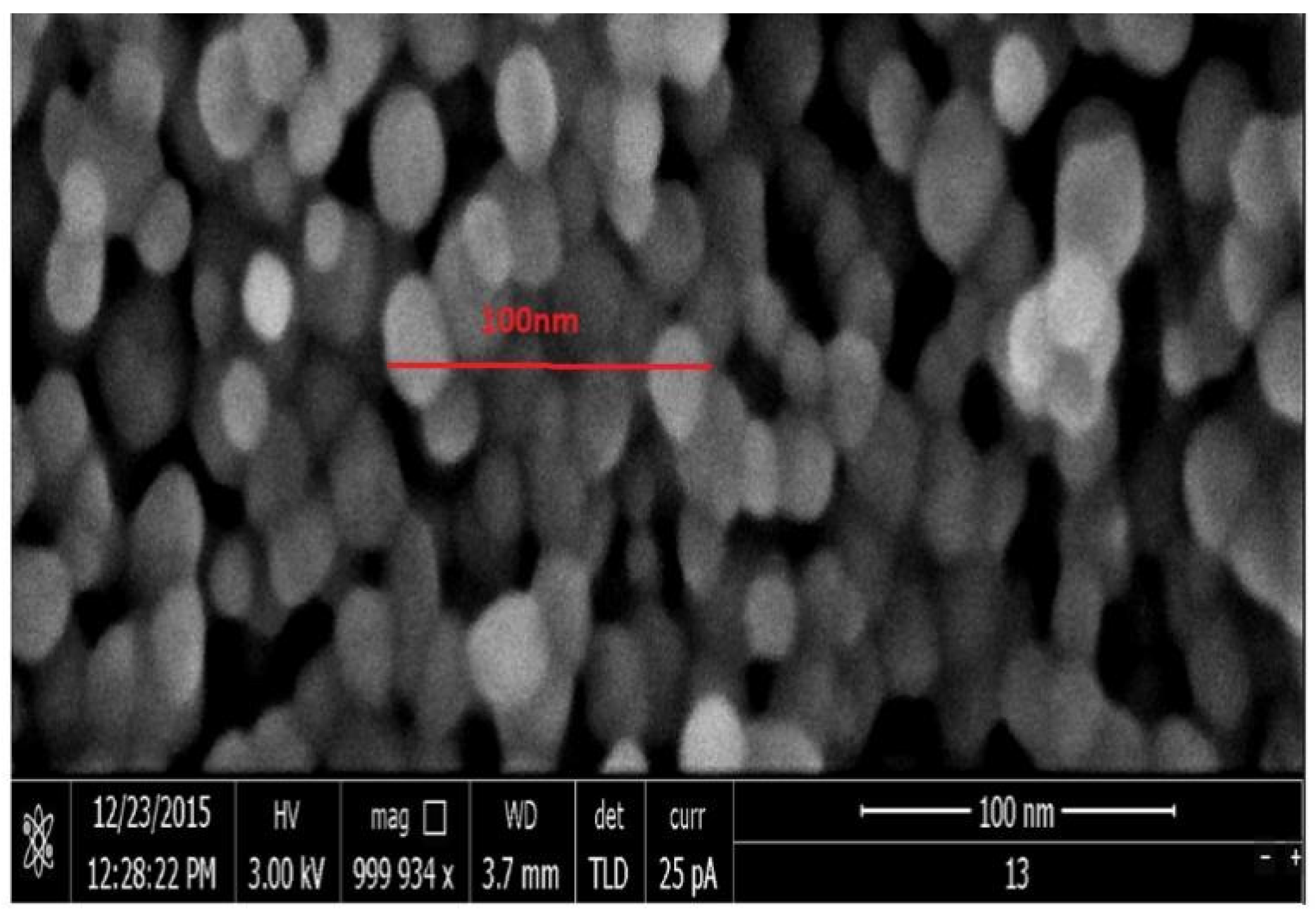

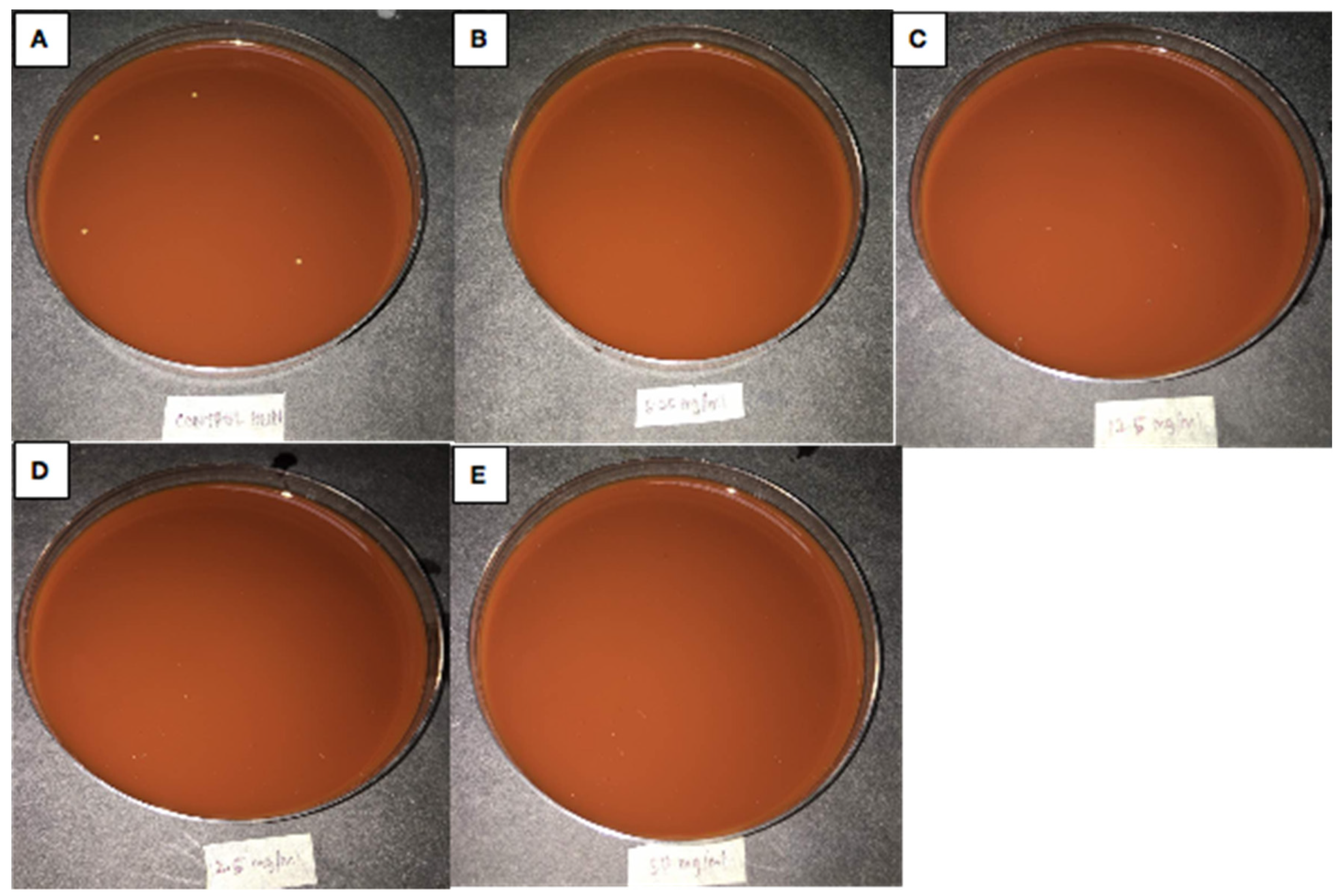

| Nanoparticles Extract Concentrations | Haemophilus influenza | Klebsiella pneumonia |
|---|---|---|
| 150 mg/mL + 0.03% silver + bacteria | No growth | No growth |
| 25 mg/mL + 0.03% silver + bacteria | No growth | No growth |
| 12.5 mg/mL + 0.03% silver + bacteria | No growth | Growth |
| 6.25 mg/mL + 0.03% silver + bacteria | No growth | Growth |
| Bacterial only (Negative Control) | Growth | Growth |
| Test Tube | Dilution (Ratio) | Sample Strength (mg/mL) | MIC | MBC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | ||||
| 1 | 1:1 | 50 | T | N | N | N |
| 2 | 1:3 | 25 | T | G | G | G |
| 3 | 1:7 | 12.5 | T | G | G | G |
| 4 | 1:15 | 6.25 | T | G | G | G |
| 5 | Positive control | T | G | G | G | |
| 6 | Negative control | C | N | N | N | |
| Test inoculum size | 3.90 × 106 CFU/mL | |||||
| Test tube 5: Purity check | Pure strain | |||||
| Test tube 5: Viable count | 4.10 × 104 CFU/mL | |||||
| Test tube 6: Medium sterility | Clear and sterile | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harun, A.M.; Noor, N.F.M.; Zaid, A.; Yusoff, M.E.; Shaari, R.; Affandi, N.D.N.; Fadil, F.; Rahman, M.A.A.; Alam, M.K. The Antimicrobial Properties of Nanotitania Extract and Its Role in Inhibiting the Growth of Klebsiella pneumonia and Haemophilus influenza. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080961
Harun AM, Noor NFM, Zaid A, Yusoff ME, Shaari R, Affandi NDN, Fadil F, Rahman MAA, Alam MK. The Antimicrobial Properties of Nanotitania Extract and Its Role in Inhibiting the Growth of Klebsiella pneumonia and Haemophilus influenza. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(8):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080961
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarun, Ahmad Mukifza, Nor Farid Mohd Noor, Awatief Zaid, Mohamad Ezany Yusoff, Ramizu Shaari, Nor Dalila Nor Affandi, Fatirah Fadil, Mohd Azizi Abdul Rahman, and Mohammad Khursheed Alam. 2021. "The Antimicrobial Properties of Nanotitania Extract and Its Role in Inhibiting the Growth of Klebsiella pneumonia and Haemophilus influenza" Antibiotics 10, no. 8: 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080961
APA StyleHarun, A. M., Noor, N. F. M., Zaid, A., Yusoff, M. E., Shaari, R., Affandi, N. D. N., Fadil, F., Rahman, M. A. A., & Alam, M. K. (2021). The Antimicrobial Properties of Nanotitania Extract and Its Role in Inhibiting the Growth of Klebsiella pneumonia and Haemophilus influenza. Antibiotics, 10(8), 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10080961








