Efficacies of Colistin–Carbapenem versus Colistin–Tigecycline in Critically Ill Patients with CR-GNB-Associated Pneumonia: A Multicenter Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population and Setting
2.2. Data Collection of Baseline Characteristics
2.3. Diagnosis of Pneumonia and Microbiological Tests
2.4. Therapeutic Regimens
2.5. Outcomes and Nephrotoxicity Evaluations
2.6. Propensity-Score Matching Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics and Disease Severities before and after PS Matching
3.2. Therapeutic Efficacy
3.3. Nephrotoxicity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viderman, D.; Brotfain, E.; Khamzina, Y.; Kapanova, G.; Zhumadilov, A.; Poddighe, D. Bacterial resistance in the intensive care unit of developing countries: Report from a tertiary hospital in Kazakhstan. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 17, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phu, V.D.; Wertheim, H.F.; Larsson, M.; Nadjm, B.; Dinh, Q.D.; Nilsson, L.E.; Rydell, U.; Le, T.T.; Trinh, S.H.; Pham, H.M.; et al. Burden of Hospital Acquired Infections and Antimicrobial Use in Vietnamese Adult Intensive Care Units. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievert, D.M.; Ricks, P.; Edwards, J.R.; Schneider, A.; Patel, J.; Srinivasan, A.; Kallen, A.; Limbago, B.; Fridkin, S. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: Summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2009–2010. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2013, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperaki, E.T.; Tzouvelekis, L.S.; Miriagou, V.; Daikos, G.L. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: In pursuit of an effective treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnacho-Montero, J.; Dimopoulos, G.; Poulakou, G.; Akova, M.; Cisneros, J.M.; De Waele, J.; Petrosillo, N.; Seifert, H.; Timsit, J.F.; Vila, J.; et al. Task force on management and prevention of Acinetobacter baumannii infections in the ICU. Intensiv. Care Med. 2015, 41, 2057–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonell, A.; Azarrafiy, R.; Huong, V.T.L.; Viet, T.L.; Phu, V.D.; Dat, V.Q.; Wertheim, H.; van Doorn, H.R.; Lewycka, S.; Nadjm, B. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Ventilator-associated Pneumonia in Adults in Asia: An Analysis of National Income Level on Incidence and Etiology. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly-Guillou, M.L. Clinical impact and pathogenicity of Acinetobacter. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuon, F.F.; Rocha, J.L.; Merlini, A.B. Combined therapy for multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infection--is there evidence outside the laboratory? J. Med Microbiol. 2015, 64, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnacho-Montero, J.; Amaya-Villar, R.; Ferrándiz-Millón, C.; Díaz-Martín, A.; López-Sánchez, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Pizarraya, A. Optimum treatment strategies for carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii bacteremia. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopirala, M.M.; Mangino, J.E.; Gebreyes, W.A.; Biller, B.; Bannerman, T.; Balada-Llasat, J.M.; Pancholi, P. Synergy testing by Etest, microdilution checkerboard, and time-kill methods for pan-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4678–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.H.; Wang, J.T.; Li, S.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Cheng, A.; Chen, Y.C.; Chang, S.C. Comparative in vitro antimicrobial susceptibilities and synergistic activities of antimicrobial combinations against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter species: Acinetobacter baumannii versus Acinetobacter genospecies 3 and 13TU. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, B.; Doi, Y.; Bonomo, R.A.; Paterson, D.L. New Treatment Options against Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01110–e01118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; Ko, Y.; Eom, J.S. Colistin Plus Carbapenem versus Colistin Monotherapy in the Treatment of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3925–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNair, C.R.; Stokes, J.M.; Carfrae, L.A.; Fiebig-Comyn, A.A.; Coombes, B.K.; Mulvey, M.R.; Brown, E.D. Overcoming mcr-1 mediated colistin resistance with colistin in combination with other antibiotics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, A.; Schmidt, S.; Ma, B.; Schiefelbein, L.; Rand, K.H.; Burkhardt, O.; Derendorf, H. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tigecycline. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 48, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, J.E., Jr.; Golden, J.A.; Kelly, M.G.; Zurlinden, E. Steady-state serum and intrapulmonary pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tigecycline. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Yang, S.; Noh, H.; Chung, E.K.; Lee, J.I. Antimicrobials for the treatment of drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia in critically ill patients: A systemic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zusman, O.; Altunin, S.; Koppel, F.; Dishon Benattar, Y.; Gedik, H.; Paul, M. Polymyxin monotherapy or in combination against carbapenem-resistant bacteria: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kengkla, K.; Kongpakwattana, K.; Saokaew, S.; Apisarnthanarak, A.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Comparative efficacy and safety of treatment options for MDR and XDR Acinetobacter baumannii infections: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardakas, K.Z.; Mavroudis, A.D.; Georgiou, M.; Falagas, M.E. Intravenous colistin combination antimicrobial treatment vs. monotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.Y.; Peng, C.K.; Sheu, C.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Chan, M.C.; Wang, S.H.; Chen, C.M.; Shen, Y.C.; Zheng, Z.R.; Lin, Y.T.; et al. Efficacy of adjunctive nebulized colistin in critically ill patients with nosocomial carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacterial pneumonia: A multi-centre observational study. Clin. Microbiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katip, W.; Uitrakul, S.; Oberdorfer, P. The effectiveness and nephrotoxicity of loading dose colistin combined with or without meropenem for the treatment of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 97, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.; Daikos, G.L.; Durante-Mangoni, E.; Yahav, D.; Carmeli, Y.; Benattar, Y.D.; Skiada, A.; Andini, R.; Eliakim-Raz, N.; Nutman, A.; et al. Colistin alone versus colistin plus meropenem for treatment of severe infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaari, A.; Pham, T.; Mnif, B.; Chtara, K.; Medhioub, F.; Baccouche, N.; Bahloul, M.; Hammami, A.; Bouaziz, M. Colistin-tigecycline versus colistin-imipenem-cilastatin combinations for the treatment of Acinetobacter baumannii ventilator-acquired pneumonia: A prognosis study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 2018–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khawcharoenporn, T.; Pruetpongpun, N.; Tiamsak, P.; Rutchanawech, S.; Mundy, L.M.; Apisarnthanarak, A. Colistin-based treatment for extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 43, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Cai, Y. Efficacy and safety of tigecycline in treatment of pneumonia caused by MDR Acinetobacter baumannii: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 3423–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
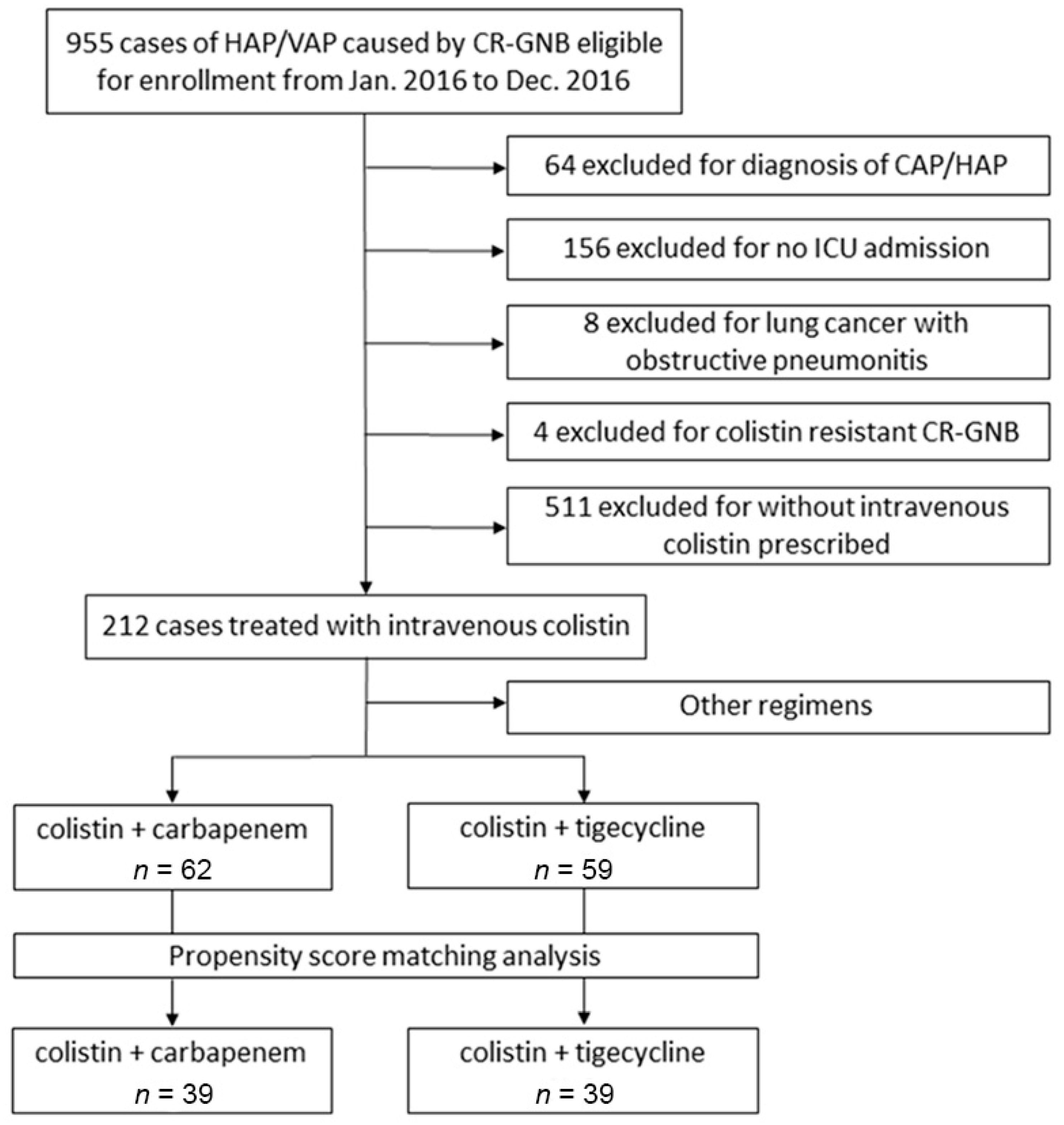
| Colistin + Carbapenem (n = 62) | Colistin + Tigecycline (n = 59) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, M (SD) | 66.63 (18.07) | 69.24 (12.62) | 0.357 |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.868 | ||
| Female | 24 (38.7) | 21 (35.6) | |
| Male | 38 (61.3) | 38 (64.4) | |
| Height, M (SD) | 163.44 (9.98) | 161.68 (8.74) | 0.330 |
| Weight, M (SD) | 60.44 (13.11) | 63.20 (16.21) | 0.336 |
| BMI, M (SD) | 22.48 (3.63) | 24.07 (5.46) | 0.075 |
| Smoking | 23 (37.7) | 23 (39.7) | 0.976 |
| Alcohol consumption | 13 (21.7) | 7 (11.9) | 0.236 |
| Pathogen, n (%) | 0.102 | ||
| CR-Pseudo | 3 (4.8) | 3 (5.1) | |
| CRAB | 57 (91.9) | 48 (81.4) | |
| CRKP | 2 (3.2) | 8 (13.6) | |
| Pneumonia types, n (%) | 0.006 | ||
| HAP | 11 (17.7) | 25 (42.4) | |
| VAP | 51 (82.3) | 34 (57.6) | |
| ICU types, n (%) | 0.649 | ||
| Medical ICU | 44 (71.0) | 45 (76.3) | |
| Surgical ICU | 18 (29.0) | 14 (23.7) | |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Lung cancer, n (%) | 6 (9.7) | 2 (3.4) | 0.274 |
| Malignancy | 10 (16.1) | 6 (10.2) | 0.485 |
| Liver disease | 6 (9.7) | 8 (13.6) | 0.702 |
| Heart failure | 4 (6.5) | 13 (22.0) | 0.028 |
| Hypertension | 29 (46.8) | 32 (54.2) | 0.523 |
| Stroke | 9 (14.5) | 7 (11.9) | 0.871 |
| Degenerative brain disease | 7 (11.3) | 4 (6.8) | 0.585 |
| Renal insufficiency | 11 (17.7) | 16 (27.1) | 0.308 |
| Lung disease | 7 (11.3) | 18 (30.5) | 0.017 |
| Diabetes | 14 (22.6) | 28 (47.5) | 0.007 |
| Autoimmune disease | 3 (4.8) | 5 (8.5) | 0.484 |
| Coadministered antibiotics | |||
| Inhaled colistin, n (%) | 26 (41.9) | 21 (35.6) | 0.597 |
| Sulbactam | 8 (12.9) | 8 (13.6) | 1.000 |
| Amikacin | 1 (1.6) | 1 (1.7) | 1.000 |
| Disease severity | |||
| APACHE II score, M (SD) | 22.74 (8.93) | 21.70 (8.13) | 0.396 |
| SOFA score (ICU admission date), M (SD) | 8.18 (3.76) | 8.71 (3.82) | 0.543 |
| SOFA score (pneumonia index date), M (SD) | 8.34 (3.45) | 8.00 (3.71) | 0.508 |
| Septic shock | 10 (16.1) | 13 (22.0) | 0.551 |
| Invasive ventilator | 52 (83.9) | 56 (94.9) | 0.095 |
| PF ratio, M (SD) | 268.62 (130.44) | 267.46 (113.51) | 0.907 |
| Dialysis (HD + CVVH) Lab data analysis | 14 (22.6) | 7 (11.9) | 0.188 |
| Leukocyte, M (SD) | 12,784.52 (8319.27) | 15,487.63 (8722.18) | 0.027 |
| Neutrophil, M (SD) | 10,670.78 (6904.97) | 12,784.51 (7195.77) | 0.031 |
| C-reactive protein, M (SD) | 15.08 (29.77) | 11.90 (9.19) | 0.974 |
| Albumin, M (SD) | 2.61 (0.61) | 2.51 (0.55) | 0.188 |
| Creatinine, M (SD) | 2.10 (1.79) | 2.06 (1.81) | 0.989 |
| Colistin + Carbapenem (n = 39) | Colistin + Tigecycline (n = 39) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, M (SD) | 71.72 (17.94) | 68.00 (14.05) | 0.304 |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.245 | ||
| Female | 18 (46.2) | 12 (30.8) | |
| Male | 21 (53.8) | 27 (69.2) | |
| Height, M (SD) | 162.03 (9.63) | 162.94 (8.98) | 0.687 |
| Weight, M (SD) | 58.25 (12.09) | 64.44 (15.64) | 0.075 |
| BMI, M (SD) | 22.10 (3.64) | 24.10 (4.82) | 0.061 |
| Smoking | 13 (33.3) | 16 (42.1) | 0.576 |
| Alcohol consumption | 8 (20.5) | 6 (15.4) | 0.768 |
| Pathogen, n (%) | 0.588 | ||
| CR-Pseudo | 1 (2.6) | 3 (7.7) | |
| CRAB | 36 (92.3) | 33 (84.6) | |
| CRKP | 2 (5.1) | 3 (7.7) | |
| Pneumonia types, n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| HAP | 11 (28.2) | 12 (30.8) | |
| VAP | 28 (71.8) | 27 (69.2) | |
| ICU types, n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| Medical ICU | 29 (74.4) | 28 (71.8) | |
| Surgical ICU | 10 (25.6) | 11 (28.2) | |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Lung cancer, n (%) | 2 (5.1) | 2 (5.1) | 1.000 |
| Malignancy | 5 (12.8) | 3 (7.7) | 0.711 |
| Liver disease | 4 (10.3) | 5 (12.8) | 1.000 |
| Heart failure | 4 (10.3) | 6 (15.4) | 0.735 |
| Hypertension | 21 (53.8) | 19 (48.7) | 0.821 |
| Stroke | 8 (20.5) | 6 (15.4) | 0.768 |
| Degenerative brain disease | 6 (15.4) | 4 (10.3) | 0.735 |
| Renal insufficiency | 11 (28.2) | 11 (28.2) | 1.000 |
| Lung disease | 7 (17.9) | 8 (20.5) | 1.000 |
| Diabetes | 14 (35.9) | 10 (25.6) | 0.462 |
| Autoimmune disease | 3 (7.7) | 4 (10.3) | 1.000 |
| Coadministered antibiotics | |||
| Inhaled colistin, n (%) | 16 (41.0) | 13 (33.3) | 0.639 |
| Sulbactam | 5 (12.8) | 7 (17.9) | 0.754 |
| Amikacin | 1 (2.60) | 1 (2.6) | 1.000 |
| Disease severity | |||
| APACHE II score, M (SD) | 22.72 (9.58) | 20.19 (7.69) | 0.216 |
| SOFA score (ICU admission date), M (SD) | 8.54 (3.70) | 8.21 (4.40) | 0.718 |
| SOFA score (pneumonia index date), M (SD) | 8.38 (3.45) | 8.10 (4.04) | 0.741 |
| Septic shock | 5 (12.8) | 7 (17.9) | 0.754 |
| Invasive ventilator | 31 (79.5) | 36 (92.3) | 0.193 |
| PF ratio, M (SD) | 245.12 (123.90) | 266.68 (109.21) | 0.439 |
| Dialysis (HD + CVVH) Lab data analysis | 8 (20.5) | 5 (12.8) | 0.543 |
| Leukocyte, M (SD) | 12,022.82 (7664.57) | 14,000.77 (7233.81) | 0.245 |
| Neutrophil, M (SD) | 10,028.23 (6385.35) | 11,547.83 (6035.16) | 0.262 |
| C-reactive protein, M (SD) | 16.97 (36.13) | 11.51 (9.35) | 0.411 |
| Albumin, M (SD) | 2.73 (0.60) | 2.51 (0.57) | 0.107 |
| Creatinine, M (SD) | 2.04 (1.90) | 1.90 (1.86) | 0.740 |
| Colistin + Carbapenem (n = 39) | Colistin + Tigecycline (n = 39) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
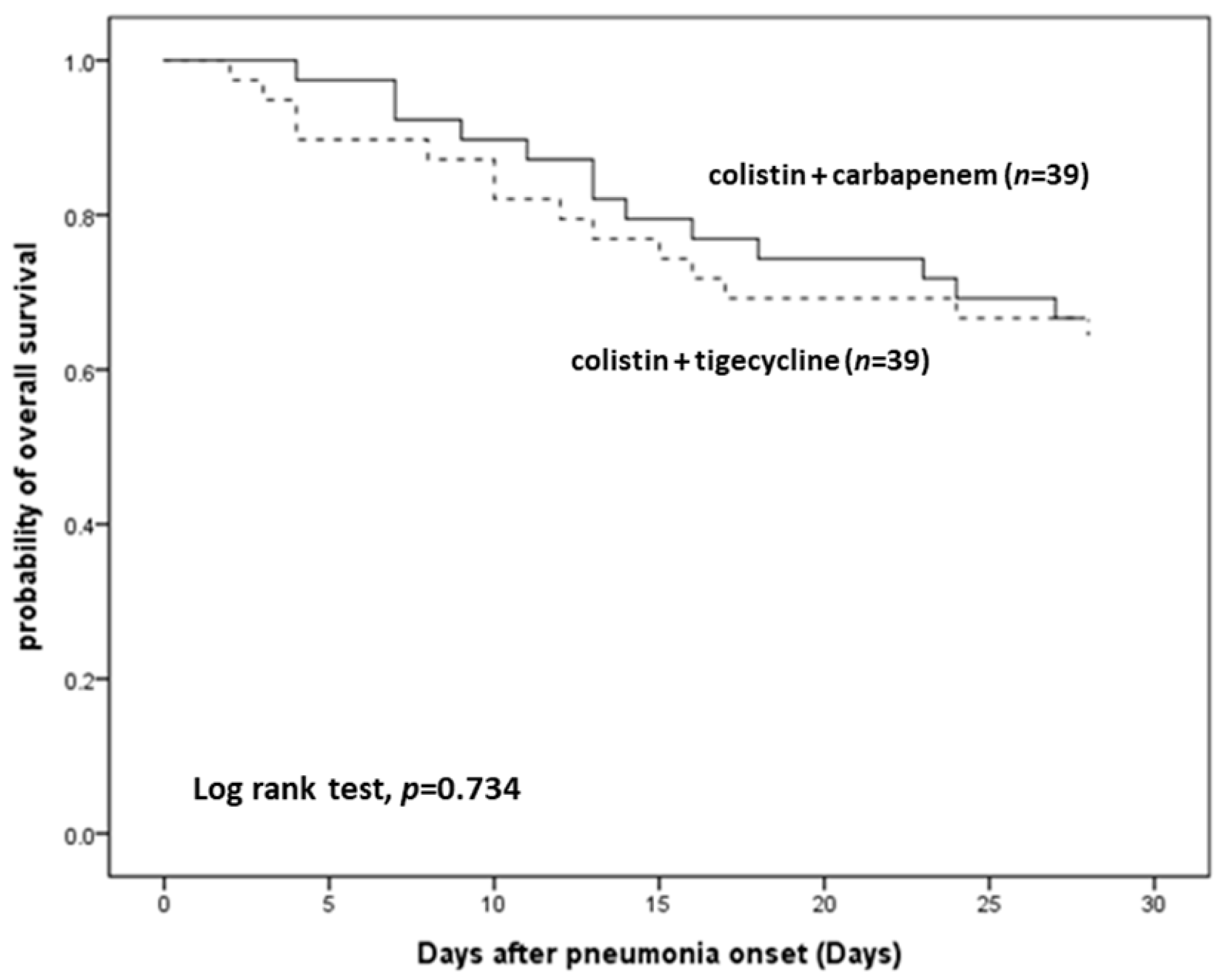
| Mortality (since pneumonia onset) | |||
| Day 7, n (%) | 3 (7.7) | 4 (10.3) | 1.000 |
| Day 14, n (%) | 8 (20.5) | 9 (23.1) | 1.000 |
| Day 28, n (%) | 13 (33.3) | 14 (35.9) | 1.000 |
| In-hospital mortality, n (%) | 20 (51.3) | 16 (41.0) | 0.496 |
| Favorable clinical outcomes | |||
| Day 7 | 20 (51.3) | 19 (48.7) | 1.000 |
| Day 14 | 21 (53.8) | 20 (51.3) | 1.000 |
| Day 28 | 18 (46.2) | 22 (56.4) | 0.497 |
| Microbiological eradication | |||
| Day 7 | 5 (25.0) | 3 (15.8) | 0.695 |
| Day 14 | 13 (46.4) | 7 (33.3) | 0.529 |
| Day 28 | 18 (60.0) | 12 (57.1) | 1.000 |
| Length of hospital stay (days), M (R) | 62 (14–284) (n = 19) | 55 (27–134) (n = 23) | 0.390 a |
| Length of ICU stay (days), M (R) | 26 (9–95) (n = 19) | 21 (7–101) (n = 23) | 0.487 a |
| 28-day ventilator weaning | 10 (55.6) (n = 18) | 10 (43.5) (n = 23) | 0.651 |
| Acute kidney injury | 15 (53.6) | 16 (50.0) | 0.986 |
| 28-Day All-Cause Mortality a | Favorable Clinical Outcomes on Day 14 b | Microbiological Eradication Day 14 b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aHR (95% CI) | p Value | aOR (95% CI) | p Value | aOR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Colistin + tigecycline (vs. colistin + carbapenem) | 1.15 (0.53–2.49) | 0.722 | 0.79 (0.31–2.01) | 0.626 | 0.60 (0.18–1.94) | 0.388 |
| Age | 0.98 (0.96–1.00) | 0.110 | 1.01 (0.98–1.04) | 0.751 | 1.01 (0.97–1.04) | 0.654 |
| Male | 0.69 (0.32–1.52) | 0.359 | 2.44 (0.94–6.35) | 0.069 | 0.64 (0.20–2.05) | 0.449 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-H.; Yang, K.-Y.; Sheu, C.-C.; Chen, W.-C.; Chan, M.-C.; Feng, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-M.; Wu, B.-R.; Zheng, Z.-R.; Chou, Y.-C.; et al. Efficacies of Colistin–Carbapenem versus Colistin–Tigecycline in Critically Ill Patients with CR-GNB-Associated Pneumonia: A Multicenter Observational Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091081
Wang S-H, Yang K-Y, Sheu C-C, Chen W-C, Chan M-C, Feng J-Y, Chen C-M, Wu B-R, Zheng Z-R, Chou Y-C, et al. Efficacies of Colistin–Carbapenem versus Colistin–Tigecycline in Critically Ill Patients with CR-GNB-Associated Pneumonia: A Multicenter Observational Study. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(9):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091081
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Sheng-Huei, Kuang-Yao Yang, Chau-Chyun Sheu, Wei-Cheng Chen, Ming-Cheng Chan, Jia-Yih Feng, Chia-Min Chen, Biing-Ru Wu, Zhe-Rong Zheng, Yu-Ching Chou, and et al. 2021. "Efficacies of Colistin–Carbapenem versus Colistin–Tigecycline in Critically Ill Patients with CR-GNB-Associated Pneumonia: A Multicenter Observational Study" Antibiotics 10, no. 9: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091081
APA StyleWang, S.-H., Yang, K.-Y., Sheu, C.-C., Chen, W.-C., Chan, M.-C., Feng, J.-Y., Chen, C.-M., Wu, B.-R., Zheng, Z.-R., Chou, Y.-C., Peng, C.-K., & on behalf of the T-CARE (Taiwan Critical Care Infection) Group. (2021). Efficacies of Colistin–Carbapenem versus Colistin–Tigecycline in Critically Ill Patients with CR-GNB-Associated Pneumonia: A Multicenter Observational Study. Antibiotics, 10(9), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091081






