Polyethylenimine Increases Antibacterial Efficiency of Chlorophyllin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
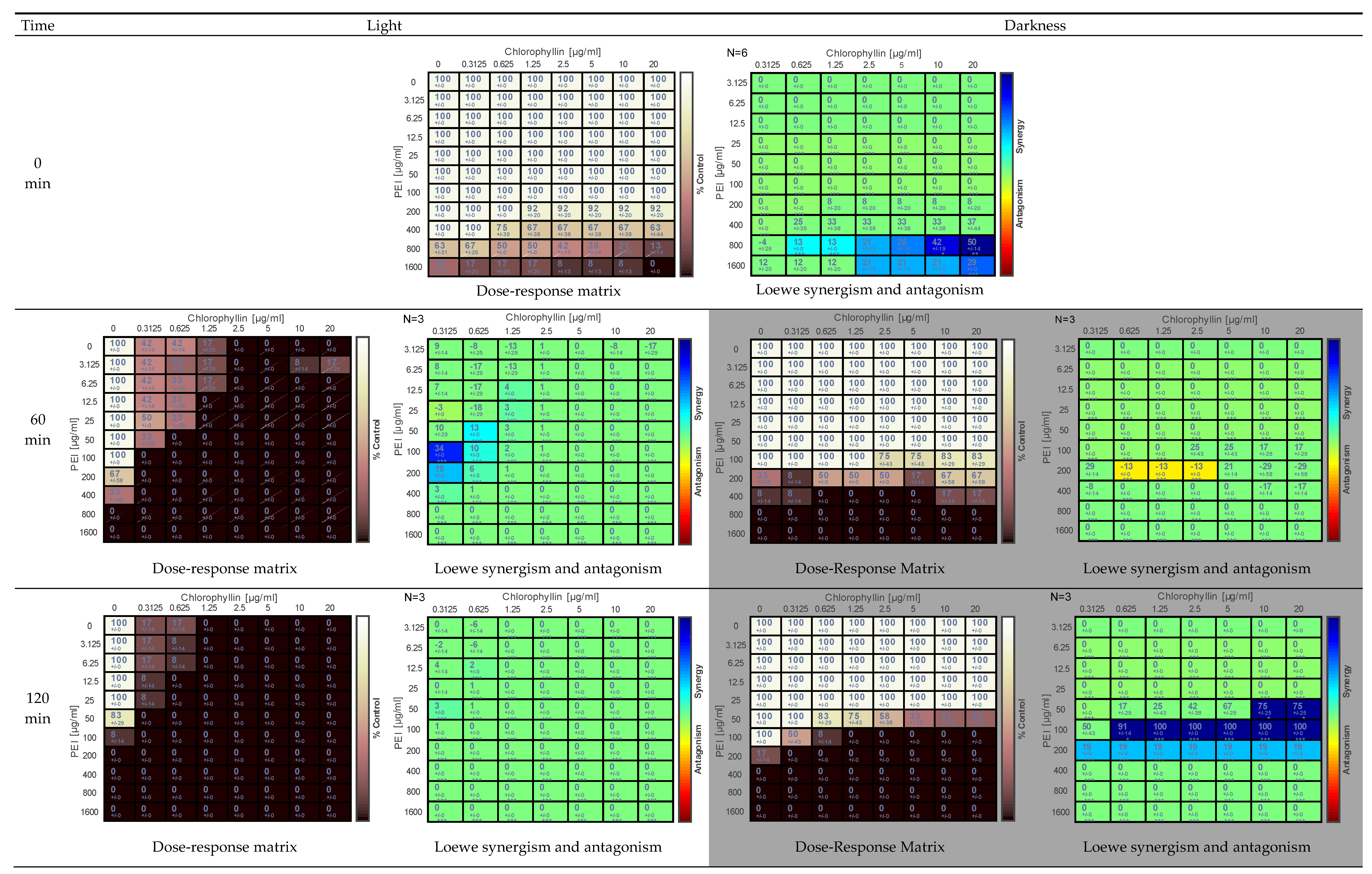
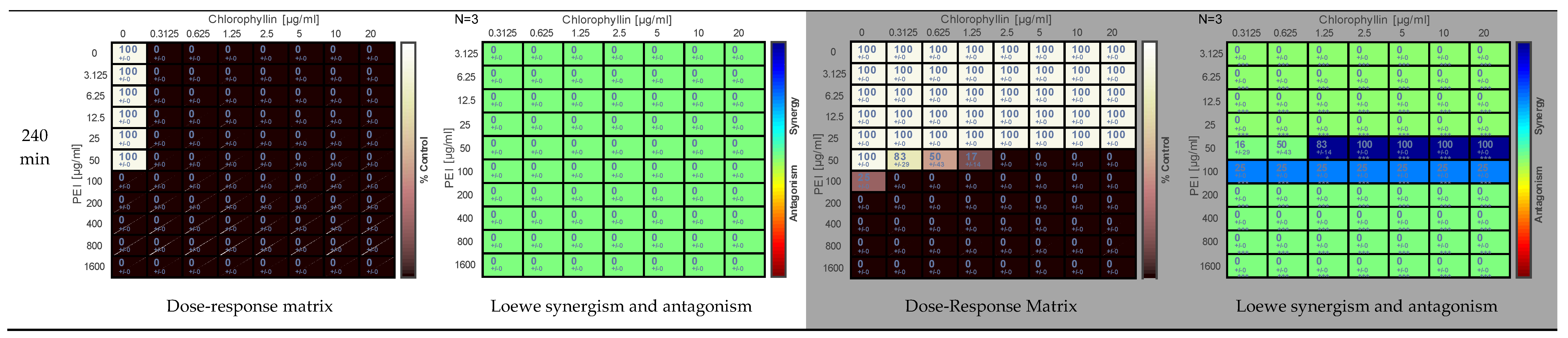
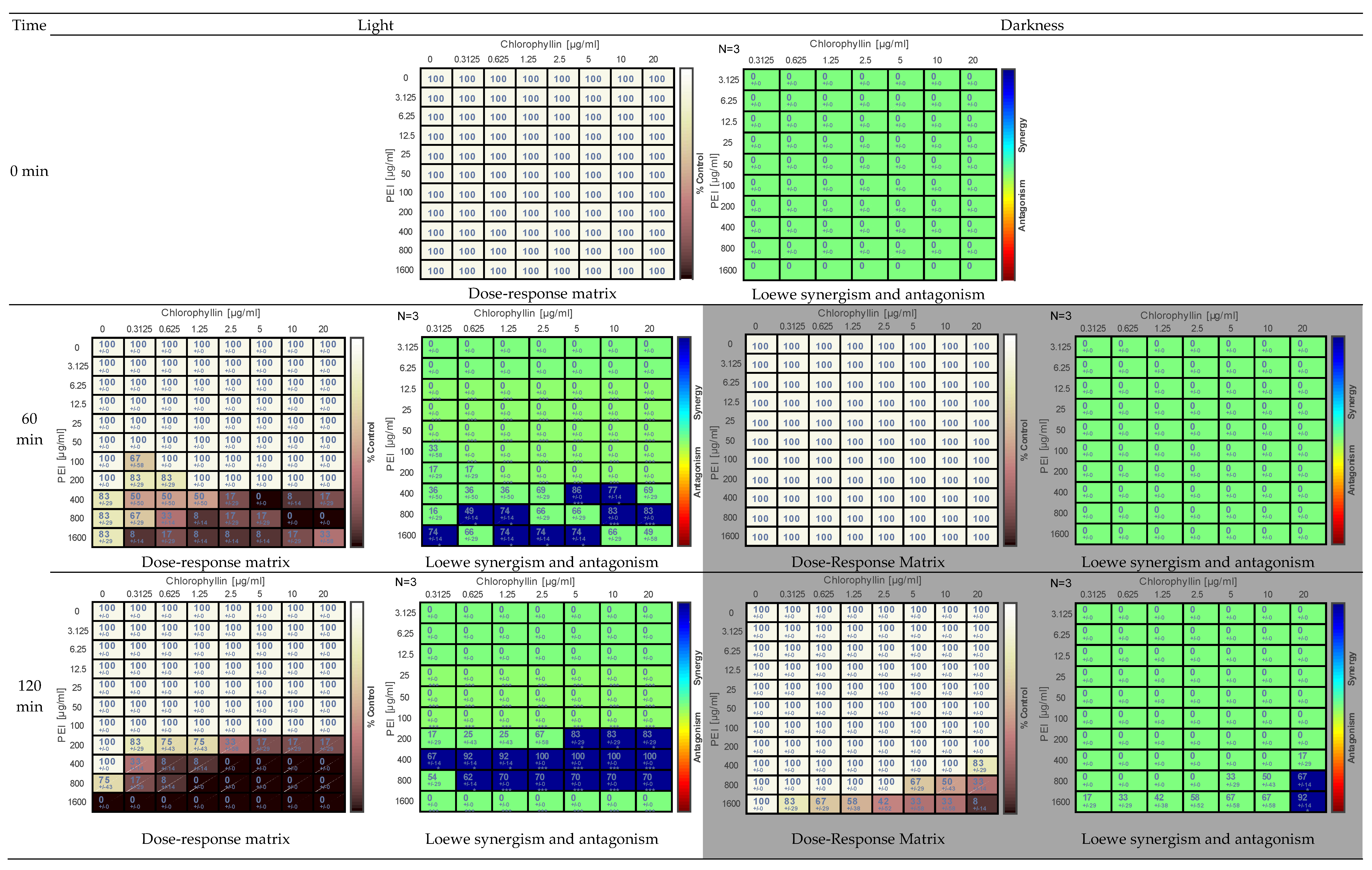
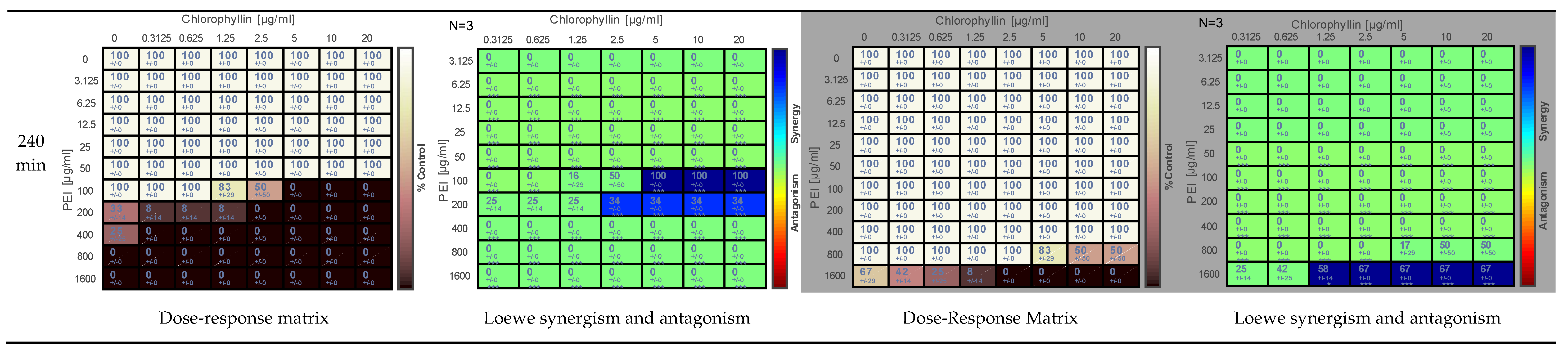
2.1. Effect of PEI and Chlorophyllin on Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
2.2. Effects of PEI and Chlorophyllin on Escherichia coli DH5α
2.3. Effect of PEI and Chlorophyllin on Escherichia coli RB791
2.4. Effect of PEI and Chlorophyllin on Bacillus subtilis 168
2.5. Determination of the Effect of PEI and Chlorophyllin Related to Cell Density
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Preparation of Chlorophyllin
4.3. Determination of Minimum Bactericidal Effects of PEI and Chlorophyllin Combinations
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Determination of PEI/Chlorophyllin Effects on Cell Density
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adedeji, W. The Treasure Called Antibiotics. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2016, 14, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- WHO Advisory Group on Integrated Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine: Ranking of Medically Important Antimicrobials for Risk Management of Antimicrobial Resistance due to Non-Human Use, 5th Revision 2016; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-151222-0.
- Ventola, C.L. The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Frieri, M.; Kumar, K.; Boutin, A. Antibiotic resistance. J. Infect. Public Health 2017, 10, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allan, A.C.; Fluhr, R. Two distinct sources of elicited reactive oxygen species in tobacco epidermal cells. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 1559–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajneesh; Pathak, J.; Chatterjee, A.; Singh, S.; Sinha, R. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Cyanobacteria Using the Oxidant-sensing Probe 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein Diacetate (DCFH-DA). Bio-Protocol 2017, 7, e2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieplik, F.; Deng, D.; Crielaard, W.; Buchalla, W.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Maisch, T. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy—What we know and what we don’t. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vatansever, F.; de Melo, W.C.; Avci, P.; Vecchio, D.; Sadasivam, M.; Gupta, A.; Chandran, R.; Karimi, M.; Parizotto, N.A.; Yin, R.; et al. Antimicrobial strategies centered around reactive oxygen species—Bactericidal antibiotics, photodynamic therapy, and beyond. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 955–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krüger, M.; Richter, P.; Strauch, S.M.; Nasir, A.; Burkovski, A.; Antunes, C.A.; Meißgeier, T.; Schlücker, E.; Schwab, S.; Lebert, M. What an Escherichia coli Mutant Can Teach Us About the Antibacterial Effect of Chlorophyllin. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richter, P.; Krüger, M.; Prasad, B.; Gastiger, S.; Bodenschatz, M.; Wieder, F.; Burkovski, A.; Geißdörfer, W.; Lebert, M.; Strauch, S.M. Using Colistin as a Trojan Horse: Inactivation of Gram-Negative Bacteria with Chlorophyllin. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hensley, K.; Robinson, K.A.; Gabbita, S.P.; Salsman, S.; Floyd, R.A. Reactive oxygen species, cell signaling, and cell injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, R.; Fedoroff, N. Stress response, cell death and signalling: The many faces of reactive oxygen species. Physiol. Plant. 2003, 119, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, P.; Cai, L.; Iqbal, Z.; Huang, M. Rapid killing of bacteria by a new type of photosensitizer. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 4691–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, S.; Wu, M.; Kenry, K.; Huang, Z.; Lee, C.-S.; Liu, B. Membrane-Anchoring Photosensitizer with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics for Combating Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.-P.; Schmidl, J.; Hilbig, R.; Oberle, M.; Wedekind, H.; Richter, P. Fighting fish parasites with photodynamically active chlorophyllin. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohllebe, S.; Ulbrich, C.; Grimm, D.; Pietsch, J.; Erzinger, G.; Richter, R.; Lebert, M.; Richter, P.R.; Häder, D.-P. Photodynamic Treatment of Chaoborus crystallinus Larvae with Chlorophyllin Induces Necrosis and Apoptosis. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 87, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohllebe, S.; Richter, P.; Häder, D.-P. Chlorophyllin for the control of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (Fouquet). Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchovec, I.; Lukseviciūtė, V.; Kokstaite, R.; Labeikyte, D.; Kaziukonyte, L.; Luksiene, Z. Inactivation of Gram (−) bacteria Salmonella enterica by chlorophyllin-based photosensitization: Mechanism of action and new strategies to enhance the inactivation efficiency. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 172, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustov, A.V.; Belykh, D.V.; Smirnova, N.L.; Venediktov, E.A.; Kudayarova, T.V.; Kruchin, S.O.; Khudyaeva, I.S.; Berezin, D.B. Synthesis and investigation of water-soluble chlorophyll pigments for antimicrobial photodynamic therapy. Dye. Pigment. 2018, 149, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Tan, L.; Li, H.; Chen, B.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ou, J. Photodynamic inactivation of planktonic Staphylococcus aureus by sodium magnesium chlorophyllin and its effect on the storage quality of lettuce. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2021, 20, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, A.; Cattaneo, D. Dosing Colistin Properly: Let’s Save “Our Last Resort Old Drug!”. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spapen, H.; Jacobs, R.; Van Gorp, V.; Troubleyn, J.; Honoré, P.M. Renal and neurological side effects of colistin in critically ill patients. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2011, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, J.H.; Harper, M.; Harrison, P.; Hale, J.D.; Vinogradov, E.; Seemann, T.; Henry, R.; Crane, B.; St. Michael, F.; Cox, A.D.; et al. Colistin Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Is Mediated by Complete Loss of Lipopolysaccharide Production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4971–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yemul, O.; Imae, T. Synthesis and characterization of poly(ethyleneimine) dendrimers. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2008, 286, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roest, S.; van der Mei, H.C.; Loontjens, T.J.; Busscher, H.J. Charge properties and bacterial contact-killing of hyperbranched polyurea-polyethyleneimine coatings with various degrees of alkylation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victorelli, F.D.; Calixto, G.M.F.; Dos Santos Ramos, M.A.; Bauab, T.M.; Chorilli, M. Metronidazole-Loaded Polyethyleneimine and Chitosan-Based Liquid Crystalline System for Treatment of Staphylococcal Skin Infections. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, I.M.; Alakomi, H.-L.; Latva-Kala, K.; Koski, P. Polyethyleneimine is an effective permeabilizer of Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helander, I.M.; Latva-Kala, K.; Lounatmaa, K. Permeabilizing action of polyethyleneimine on Salmonella typhimurium involves disruption of the outer membrane and interactions with lipopolysaccharide. Microbiology 1998, 144, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alakomi, H.-L. Weakening of the Gram-Negative Bacterial Outer Membrane: A Tool for Increasing Microbiological Safety; VTT: Espoo, Finland, 2007; ISBN 9513870154. [Google Scholar]
- Boland, W.; Hoever, F.-P.; Krüger, B.-W. Application of Molecular Modelling Techniques to Pheromones of the Marine Brown Algae Cutleria multifida and Ectocarpus siliculosus (Phaeophyceae). Metalloproteins as Chemoreceptors? Z. Nat. C 1989, 44, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caires, C.S.A.; Leal, C.R.B.; Ramos, C.A.N.; Bogo, D.; Lima, A.R.; Arruda, E.J.; Oliveira, S.L.; Caires, A.R.L.; Nascimento, V.A. Photoinactivation effect of eosin methylene blue and chlorophyllin sodium-copper against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellamare, B.M.; Fini, P.; Agostiano, A.; Sortino, S.; Cosma, P. Identification of Ros Produced by Photodynamic Activity of Chlorophyll/Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes. Photochem. Photobiol. 2013, 89, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.-C.; Jen, J.-F.; Tsai, T.-H. Hydroxyl radical in living systems and its separation methods. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 781, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.B.; Boff, J.M. Chemistry and Reaction of Singlet Oxygen in Foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2002, 1, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumova, K.; Cosa, G. Chapter 1: Overview of Reactive Oxygen Species. In Singlet Oxygen; Nonell, S., Flors, C., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 1–21. ISBN 978-1-78262-038-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bahulekar, R.; Ayyangar, N.; Ponrathnam, S. Polyethyleneimine in immobilization of biocatalysts. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1991, 13, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Li, H.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, R.; Walsh, T.R.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y. Novel Plasmid-Mediated Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-3 in Escherichia coli. mBio 2017, 8, e00543-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azevedo, M.M.; Ramalho, P.; Silva, A.P.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rodrigues, A.G. Polyethyleneimine and polyethyleneimine-based nanoparticles: Novel bacterial and yeast biofilm inhibitors. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudovin-Farber, I.; Golenser, J.; Beyth, N.; Weiss, E.I.; Domb, A.J. Quaternary Ammonium Polyethyleneimine: Antibacterial Activity. J. Nanomater. 2010, 2010, 826343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyth, N.; Yudovin-Farber, I.; Perez-Davidi, M.; Domb, A.J.; Weiss, E.I. Polyethyleneimine nanoparticles incorporated into resin composite cause cell death and trigger biofilm stress in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22038–22043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abramovitz, I.; Wisblech, D.; Zaltsman, N.; Weiss, E.I.; Beyth, N. Intratubular Antibacterial Effect of Polyethyleneimine Nanoparticles: An Ex Vivo Study in Human Teeth. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 980529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foxley, M.A.; Friedline, A.W.; Jensen, J.M.; Nimmo, S.L.; Scull, E.M.; King, J.B.; Strange, S.; Xiao, M.T.; Smith, B.E.; Thomas, K.J., III; et al. Efficacy of ampicillin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus restored through synergy with branched poly(ethylenimine). J. Antibiot. 2016, 69, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farha, M.A.; Leung, A.; Sewell, E.W.; D’Elia, M.A.; Allison, S.E.; Ejim, L.; Pereira, P.M.; Pinho, M.G.; Wright, G.D.; Brown, E.D. Inhibition of WTA Synthesis Blocks the Cooperative Action of PBPs and Sensitizes MRSA to β-Lactams. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 10 µg mL−1 Chlorophyllin + PEI Concentration [µg mL−1] | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 0 | 10 µg mL−1 Chlorophyllin + PEI Concentrations [µg mL−1] | 800 | 600 | 400 | 200 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Illumination | Dark Incubation | ||||||||||
| 0 min | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 0 min | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 60 min | 33 | 67 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 60 min | 33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 120 min | 17 | 33 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 120 min | 17 | 17 | 50 | 50 | 100 |
| 180 min | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 180 min | 0 | 33 | 33 | 100 | 100 |
| 240 min | 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 240 min | 0 | 50 | 67 | 100 | 100 |
| Light | Initial Cell Densities (OD600) Inactivated by PEI-Chlorophyllin Concentrations (µg mL−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHL→ PEI↓ | 0 | 1.25 | 10 | 30 |
| 1.95 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. |
| 3.91 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | 0.0014 |
| 7.81 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | 0.0057 |
| 15.63 | n.e. | n.e. | 0.0004 | 0.0114 |
| 31.25 | n.e. | n.e. | 0.0057 | 0.0114 |
| 62.50 | n.e. | 0.0007 | 0.0228 | 0.1825 |
| 125.00 | n.e. | 0.0057 | 0.0913 | 0.7300 |
| 250.00 | 0.0007 | 0.1813 | 0.3650 | 0.7300 |
| Dark | Initial Cell Densities (OD600) Inactivated by PEI-Chlorophyllin Concentrations (µg mL−1) | |||
| CHL→ PEI↓ | 0 | 1.25 | 10 | 30 |
| 1.95 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. |
| 3.91 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. |
| 7.81 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. |
| 15.63 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. |
| 31.25 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. |
| 62.50 | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. | n.e. |
| 125.00 | n.e. | n.e. | 0.0004 | 0.0004 |
| 250.00 | n.e. | n.e. | 0.0014 | 0.0014 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akif, F.A.; Mahmoud, M.; Prasad, B.; Richter, P.; Azizullah, A.; Qasim, M.; Anees, M.; Krüger, M.; Gastiger, S.; Burkovski, A.; et al. Polyethylenimine Increases Antibacterial Efficiency of Chlorophyllin. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101371
Akif FA, Mahmoud M, Prasad B, Richter P, Azizullah A, Qasim M, Anees M, Krüger M, Gastiger S, Burkovski A, et al. Polyethylenimine Increases Antibacterial Efficiency of Chlorophyllin. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(10):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101371
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkif, Faheem Ahmad, Mona Mahmoud, Binod Prasad, Peter Richter, Azizullah Azizullah, Muhammad Qasim, Muhammad Anees, Marcus Krüger, Susanne Gastiger, Andreas Burkovski, and et al. 2022. "Polyethylenimine Increases Antibacterial Efficiency of Chlorophyllin" Antibiotics 11, no. 10: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101371
APA StyleAkif, F. A., Mahmoud, M., Prasad, B., Richter, P., Azizullah, A., Qasim, M., Anees, M., Krüger, M., Gastiger, S., Burkovski, A., Strauch, S. M., & Lebert, M. (2022). Polyethylenimine Increases Antibacterial Efficiency of Chlorophyllin. Antibiotics, 11(10), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101371










