Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Nebulized Colistimethate Sodium Using Two Different Types of Nebulizers in Critically Ill Patients with Ventilator-Associated Respiratory Infections
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
Safety
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Study Procedures
4.3. Colistin Measurement Assay in Plasma and BAL Fluid
4.3.1. Instrumentation
4.3.2. Plasma and BAL Fluid Assay
4.3.3. Urea Plasma and BAL Assay
4.3.4. PK Analysis
4.4. Safety
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Protocol Approval and Ethical Considerations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalil, A.C.; Metersky, M.L.; Klompas, M.; Muscedere, J.; Sweeney, D.A.; Palmer, L.B.; Napolitano, L.M.; O’Grady, N.P.; Bartlett, J.G.; Carratalà, J.; et al. Management of Adults With Hospital-acquired and Ventilator-associated Pneumonia: 2016 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e61–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rello, J.; Solé-Lleonart, C.; Rouby, J.J.; Chastre, J.; Blot, S.; Poulakou, G.; Luyt, C.E.; Riera, J.; Palmer, L.B.; Pereira, J.M.; et al. Use of nebulized antimicrobials for the treatment of respiratory infections in invasively mechanically ventilated adults: A position paper from the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niederman, M.S.; Alder, J.; Bassetti, M.; Boateng, F.; Cao, B.; Corkery, K.; Dhand, R.; Kaye, K.S.; Lawatscheck, R.; McLeroth, P.; et al. Inhaled amikacin adjunctive to intravenous standard-of-care antibiotics in mechanically ventilated patients with Gram-negative pneumonia (INHALE): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3, superiority trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollef, M.H.; Ricard, J.-D.; Roux, D.; Francois, B.; Ischaki, E.; Rozgonyi, Z.; Boulain, T.; Ivanyi, Z.; János, G.; Garot, D.; et al. A Randomized Trial of the Amikacin Fosfomycin Inhalation System for the Adjunctive Therapy of Gram-Negative Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Chest 2017, 151, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.S.; Barone, A.A.; Penço, J.; Santos, M.V.; Marinho, I.S.; Arruda, E.A.; Manrique, E.I.; Costa, S.F. Intravenous colistin as therapy for nosocomial infections caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kasiakou, S.K. Colistin: The revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michalopoulos, A.; Kasiakou, S.K.; Mastora, Z.; Rellos, K.; Kapaskelis, A.M.; Falagas, M.E. Aerosolized colistin for the treatment of nosocomial pneumonia due to multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in patients without cystic fibrosis. Crit. Care 2005, 9, R53–R59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rattanaumpawan, P.; Lorsutthitham, J.; Ungprasert, P.; Angkasekwinai, N.; Thamlikitkul, V. Randomized controlled trial of nebulized colistimethate sodium as adjunctive therapy of ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by Gram-negative bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 2645–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdellatif, S.; Trifi, A.; Daly, F.; Mahjoub, K.; Nasri, R.; Lakhal, S. Ben Efficacy and toxicity of aerosolised colistin in ventilator-associated pneumonia: A prospective, randomised trial. Ann. Intensive Care 2016, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valachis, A.; Samonis, G.; Kofteridis, D.P. The role of aerosolized colistin in the treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, B.T.; Pogue, J.M.; Zavascki, A.P.; Paul, M.; Daikos, G.L.; Forrest, A.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Viscoli, C.; Giamarellou, H.; Karaiskos, I.; et al. International Consensus Guidelines for the Optimal Use of the Polymyxins: Endorsed by the American College of Clinical Pharmacy (ACCP), European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDS. Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 10–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solé-Lleonart, C.; Roberts, J.A.; Chastre, J.; Poulakou, G.; Palmer, L.B.; Blot, S.; Felton, T.; Bassetti, M.; Luyt, C.E.; Pereira, J.M.; et al. Global survey on nebulization of antimicrobial agents in mechanically ventilated patients: A call for international guidelines. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Athanassa, Z.E.; Markantonis, S.L.; Fousteri, M.-Z.F.; Myrianthefs, P.M.; Boutzouka, E.G.; Tsakris, A.; Baltopoulos, G.J. Pharmacokinetics of inhaled colistimethate sodium (CMS) in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson, M.; Jacobs, M.; Grégoire, N.; Gobin, P.; Marchand, S.; Couet, W.; Mimoz, O. Comparison of Intrapulmonary and Systemic Pharmacokinetics of Colistin Methanesulfonate (CMS) and Colistin after Aerosol Delivery and Intravenous Administration of CMS in Critically Ill Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 7331–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boisson, M.; Grégoire, N.; Cormier, M.; Gobin, P.; Marchand, S.; Couet, W.; Mimoz, O. Pharmacokinetics of nebulized colistin methanesulfonate in critically ill patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkoufa, A.; Sou, T.; Karaiskos, I.; Routsi, C.; Lin, Y.W.; Psichogiou, M.; Zakynthinos, S.; Giamarellou, H.; Li, J.; Friberg, L.E. Pulmonary and systemic pharmacokinetics of colistin methanesulfonate (CMS) and formed colistin following nebulisation of CMS among patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 59, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Filho, V.C.; Alcoforado, L.; Rattes, C.; Paiva, D.N.; Brandão, S.C.S.; Fink, J.B.; Dornelas de Andrade, A. A mesh nebulizer is more effective than jet nebulizer to nebulize bronchodilators during non-invasive ventilation of subjects with COPD: A randomized controlled trial with radiolabeled aerosols. Respir. Med. 2019, 153, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Moon, S.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Yoon, Y.S.; Gu, N.; Lim, C.Y.; Park, B.J.; Nam, K.C. Comparison of salbutamol delivery efficiency for jet versus mesh nebulizer using mice. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, J.; Alp, E.; Koulenti, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ehrmann, S.; Blot, S.; Bassetti, M.; Conway-Morris, A.; Reina, R.; Teran, E.; et al. Nebulization of antimicrobial agents in mechanically ventilated adults in 2017: An international cross-sectional survey. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoints Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. 2022. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Forrest, A.; Garonzik, S.M.; Thamlikitkul, V.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Paterson, D.L.; Li, J.; Silveira, F.P.; Nation, R.L. Pharmacokinetic/Toxicodynamic Analysis of Colistin-Associated Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01367-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, J.P.; Sorlí, L.; Luque, S.; Benito, N.; Segura, C.; Campillo, N.; Montero, M.; Esteve, E.; Mirelis, B.; Pomar, V.; et al. Validation of a colistin plasma concentration breakpoint as a predictor of nephrotoxicity in patients treated with colistin methanesulfonate. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsala, M.; Vourli, S.; Georgiou, P.C.; Pournaras, S.; Tsakris, A.; Daikos, G.L.; Mouton, J.W.; Meletiadis, J. Exploring colistin pharmacodynamics against Klebsiella pneumoniae: A need to revise current susceptibility breakpoints. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergen, P.J.; Landersdorfer, C.B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Lee, H.J.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of “old” polymyxins: What is new? Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 74, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polemis, M.; Mandilara, G.; Pappa, O.; Argyropoulou, A.; Perivolioti, E.; Koudoumnakis, N.; Pournaras, S.; Vasilakopoulou, A.; Vourli, S.; Katsifa, H.; et al. COVID-19 and Antimicrobial Resistance: Data from the Greek Electronic System for the Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance—WHONET-Greece (January 2018–March 2021). Life 2021, 11, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouby, J.-J.; Zhu, Y.; Torres, A.; Rello, J.; Monsel, A. Aerosolized polymyxins for ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by extensive drug resistant Gram negative bacteria: Class, dose and manner should remain the trifecta. Ann. Intensive Care 2022, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-L.; Fink, J.B.; Ge, H. Aerosol delivery via invasive ventilation: A narrative review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Girardi, C.; Zhang, M.; Bouhemad, B.; Louchahi, K.; Petitjean, O.; Wallet, F.; Becquemin, M.-H.; Le Naour, G.; Marquette, C.-H.; et al. Nebulized and intravenous colistin in experimental pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrentraut, S.F.; Muenster, S.; Kreyer, S.; Theuerkauf, N.U.; Bode, C.; Steinhagen, F.; Ehrentraut, H.; Schewe, J.C.; Weber, M.; Putensen, C.; et al. Extensive therapeutic drug monitoring of colistin in critically Ill patients reveals undetected risks. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, E.T.; Guppy, M.; Straus, S.E.; Bell, K.J.L.; Glasziou, P. Rate of normal lung function decline in ageing adults: A systematic review of prospective cohort studies. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouby, J.J.; Sole-Lleonart, C.; Rello, J.; Monsel, A.; Constantin, J.-M.; Bouglé, A.; Blot, S.; Poulakou, G.; Pontikis, K.; Kyriakoudi, A.; et al. Ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: Understanding nebulization of aminoglycosides and colistin. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsel, A.; Torres, A.; Zhu, Y.; Pugin, J.; Rello, J.; Rouby, J.-J.; European Investigators Network for Nebulized Antibiotics in Ventilator-associated Pneumonia (ENAVAP). Nebulized antibiotics for ventilator-associated pneumonia: Methodological framework for future multicenter randomized controlled trials. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 34, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouby, J.J.; Monsel, A.; Leone, M.; Mimoz, O.; Laterre, P.F.; Pugin, J. The IASIS, INHALE and VAPORISE trials. Reasons for a triple failure: Study design, aminoglycosides dosing and technique of nebulisation. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2020, 39, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.R.; Honeybourne, D.; Wise, R. Pulmonary disposition of antimicrobial agents: Methodological considerations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Milne, R.W.; Nation, R.L.; Turnidge, J.D.; Smeaton, T.C.; Coulthard, K. Use of high-performance liquid chromatography to study the pharmacokinetics of colistin sulfate in rats following intravenous administration. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Markou, N.; Markantonis, S.L.; Dimitrakis, E.; Panidis, D.; Boutzouka, E.; Karatzas, S.; Rafailidis, P.; Apostolakos, H.; Baltopoulos, G. Colistin serum concentrations after intravenous administration in critically ill patients with serious multidrug-resistant, gram-negative bacilli infections: A prospective, open-label, uncontrolled study. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratjen, F.; Rietschel, E.; Kasel, D.; Schwiertz, R.; Starke, K.; Beier, H.; van Koningsbruggen, S.; Grasemann, H. Pharmacokinetics of inhaled colistin in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyriakoudi, A.; Valsami, G.; Pontikis, K.; Avgeropoulou, S.; Neroutsos, E.; Christodoulou, E.; Moraitou, E.; Markantonis, S.; Dekoumetzidis, A.; Koutsoukou, A. Colistin Concentration in Epithelial Lining Fluid (ELF), Following High-Dose Colistimethate Sodium (CMS) Nebulization, Using Two Different Nebulizers. In A59. Clinical Diagnosis, Prediction and Outcomes of Lung Infections; American Thoracic Society: New York, NY, USA, 2020; p. A2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
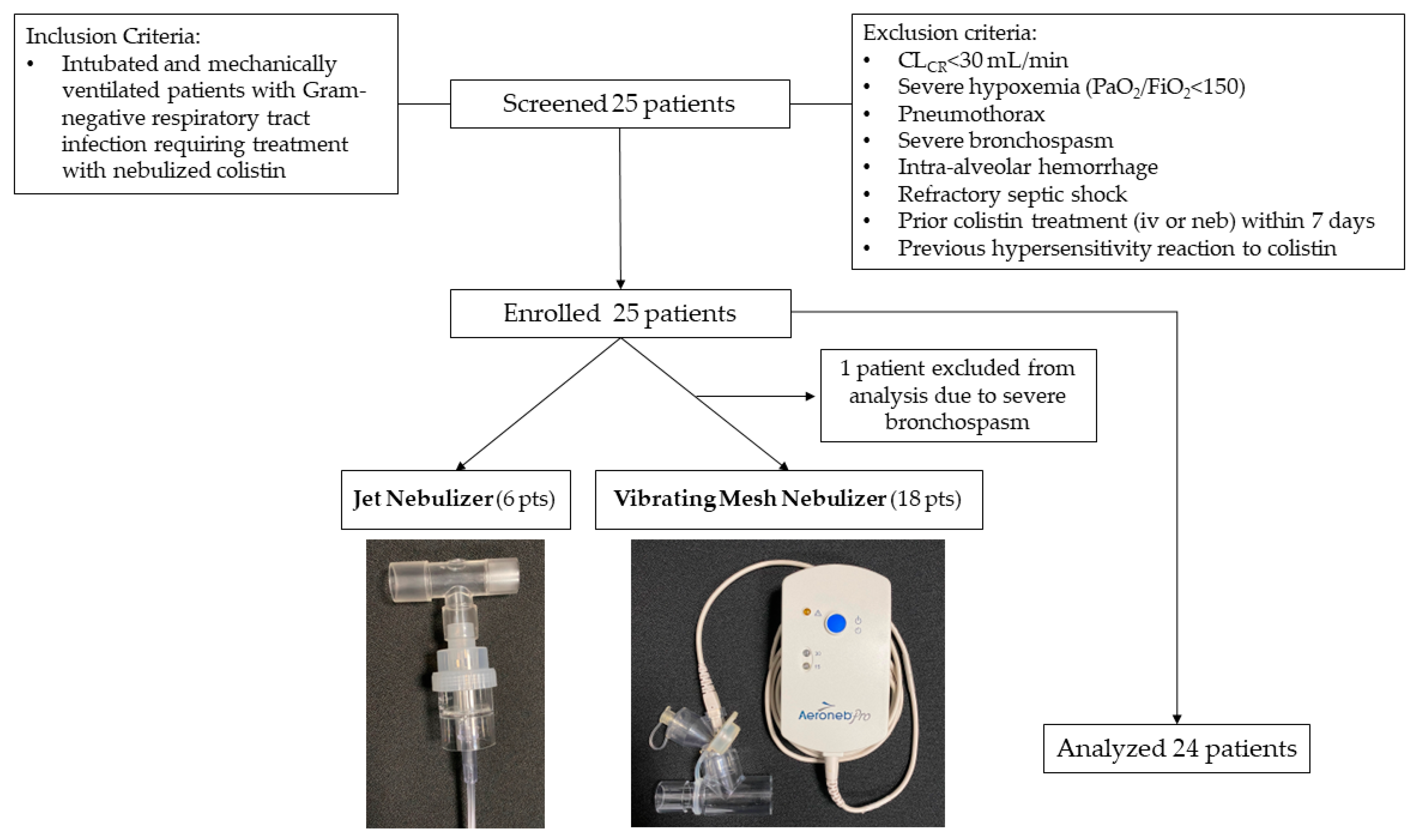
| Characteristic | VMN (n = 18) | JN (n = 6) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median age in years (IQR) | 69.5 (56.8–83.0) | 57.5 (55.5–67.3) | |
| Female gender, n (%) | 5 (27.8) | 1 (16.7) | |
| Caucasian race, n (%) | 18 (100) | 6 (100) | |
| Mean admission APACHE II (SD) | 21.4 (6.3) | 18.2 (6.0) | |
| Type of infection (%) | VAP | 11 (61.1%) | 3 (50%) |
| VAT | 7 (38.9%) | 3 (50%) | |
| Isolated pathogen (%) | A.baumannii | 11 (61.1%) | 3 (50%) |
| K.pneumoniae | 2 (11.1%) | ||
| Both | 2 (11.1%) | ||
| Culture negative | 3 (16.7%) | 3 (50%) | |
| Median creatinine clearance, mL/min (IQR) | 53.0 (40–65.5) | 86 (67.5–122.0) | |
| Mean PaO2/FiO2 (SD) | 258.7 (88.0) | 190.3 (68.1) | |
| PK/PD parameter | ELF | Plasma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VMN | JN | p Value | VMN | JN | p Value | |
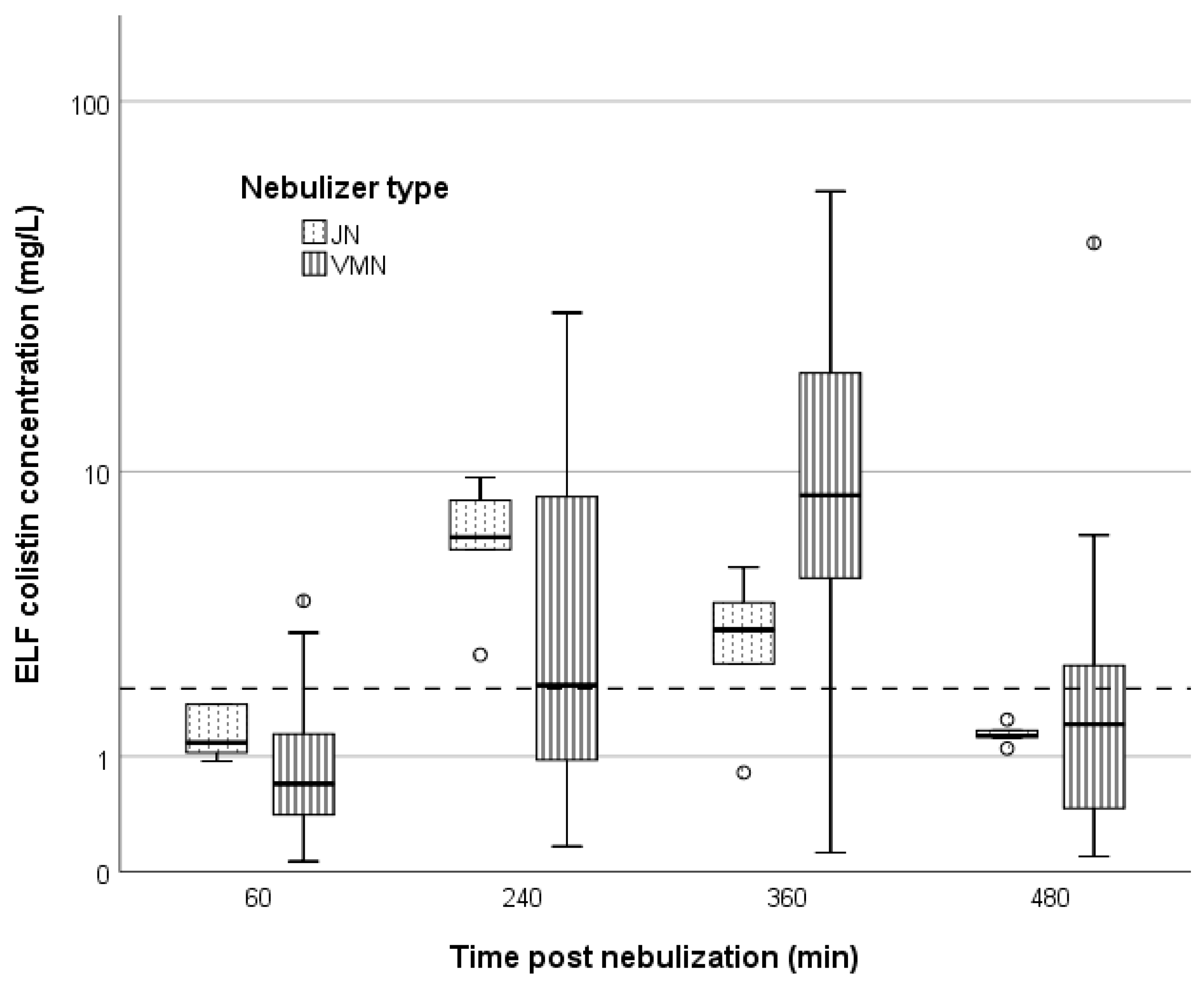
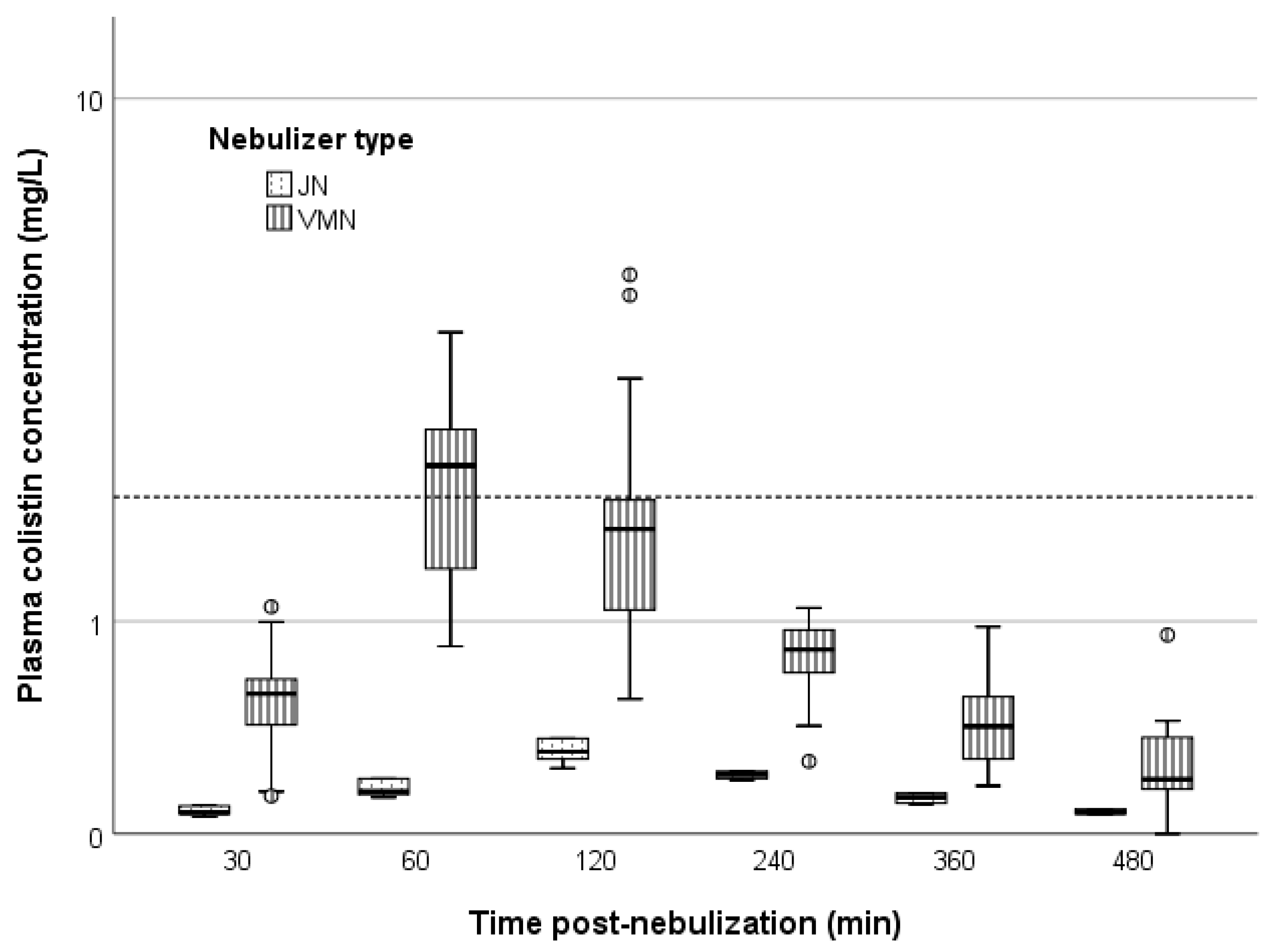
| AUC0–8 h, mg/L∙h | 28.7 (15.1–68.1) | 30.5 (26.0–36.8) | 0.871 | 7.5 (5.5–8.8) | 1.3 (1.3–6.4) | 0.039 |
| AUC0–24, mg/L∙h | 86.2 (46.0–185.9) | 91.5 (78.1–110.3) | 0.871 | 22.45 (±9.1) | 4.0 (3.8–19.3) | 0.039 |
| Ccolistin over 2 mg/L | ||||||
| 30 min, % | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 60 min, % | 16.7 | 16.7 | 1.0 | 61.1 | 16.7 | 0.155 |
| 120 min, % | 22.2 | 16.7 | 1.0 | |||
| 240 min, % | 50 | 100 | 0.052 | 5.6 | 16.7 | 0.446 |
| 360 min, % | 88.9 | 83.3 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 480 min, % | 41.2 | 0 | 0.124 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ccolistin over 4 mg/L | ||||||
| 60 min, % | 5.6 | 16.7 | 0.446 | |||
| 240 min, % | 27.8 | 83.3 | 0.050 | |||
| 360 min, % | 83.3 | 33.3 | 0.038 | |||
| 480 min, % | 17.6 | 0 | 0.539 | |||
| Cmax, mg/L | 10.4 (4.7–22.6) | 7.4 (6.2–10.3) | 0.549 | 2.6 (2.0–3.5) | 0.3 (0.3–1.6) | 0.016 |
| Cmin, mg/L | 0.4 (0.1–0.8) | 1.1 (0.9–1.2) | 0.006 | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | 0.1 (0.1–0.2) | 0.016 |
| Tmax, h | 6.5 (6.3–6.6) | 4.3 (3.5–4.3) | 0.003 | 1.5 (1.4–1.7) | 2.2 (2.1–2.2) | 0.013 |
| Volume of distribution/ fraction of dose absorbed (L) | 1.7 (0.8–5.2) | 4.5 (3.5–5.1) | 0.141 | 22.8 (16.8–33.0) | 129.8 (95.6–151.9) | 0.016 |
| Clearance/fraction of dose absorbed (L/h) | 1.4 (0.8–3.6) | 1.8 (1.5–2.1) | 0.779 | 7.3 (6.0–9.1) | 37.6 (23.2–39.9) | 0.016 |
| Mean T1/2, h (SD) | - | - | 2.4 (1.1) | 2.4 (0.5) | ||
| Mean ELF/Plasma ratio (SD) | 5.5 (13.2) | 4.8 (1.4) | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kyriakoudi, A.; Pontikis, K.; Valsami, G.; Avgeropoulou, S.; Neroutsos, E.; Christodoulou, E.; Moraitou, E.; Markantonis, S.L.; Dokoumetzidis, A.; Rello, J.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Nebulized Colistimethate Sodium Using Two Different Types of Nebulizers in Critically Ill Patients with Ventilator-Associated Respiratory Infections. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111528
Kyriakoudi A, Pontikis K, Valsami G, Avgeropoulou S, Neroutsos E, Christodoulou E, Moraitou E, Markantonis SL, Dokoumetzidis A, Rello J, et al. Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Nebulized Colistimethate Sodium Using Two Different Types of Nebulizers in Critically Ill Patients with Ventilator-Associated Respiratory Infections. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111528
Chicago/Turabian StyleKyriakoudi, Anna, Konstantinos Pontikis, Georgia Valsami, Stavrina Avgeropoulou, Efthymios Neroutsos, Eirini Christodoulou, Eleni Moraitou, Sophia L. Markantonis, Aristides Dokoumetzidis, Jordi Rello, and et al. 2022. "Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Nebulized Colistimethate Sodium Using Two Different Types of Nebulizers in Critically Ill Patients with Ventilator-Associated Respiratory Infections" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111528
APA StyleKyriakoudi, A., Pontikis, K., Valsami, G., Avgeropoulou, S., Neroutsos, E., Christodoulou, E., Moraitou, E., Markantonis, S. L., Dokoumetzidis, A., Rello, J., & Koutsoukou, A. (2022). Pharmacokinetic Characteristics of Nebulized Colistimethate Sodium Using Two Different Types of Nebulizers in Critically Ill Patients with Ventilator-Associated Respiratory Infections. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111528






