Genomic Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 Strain Coproducing KPC-2 and CTX-M-14 Isolated from Poultry in the Brazilian Amazon Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
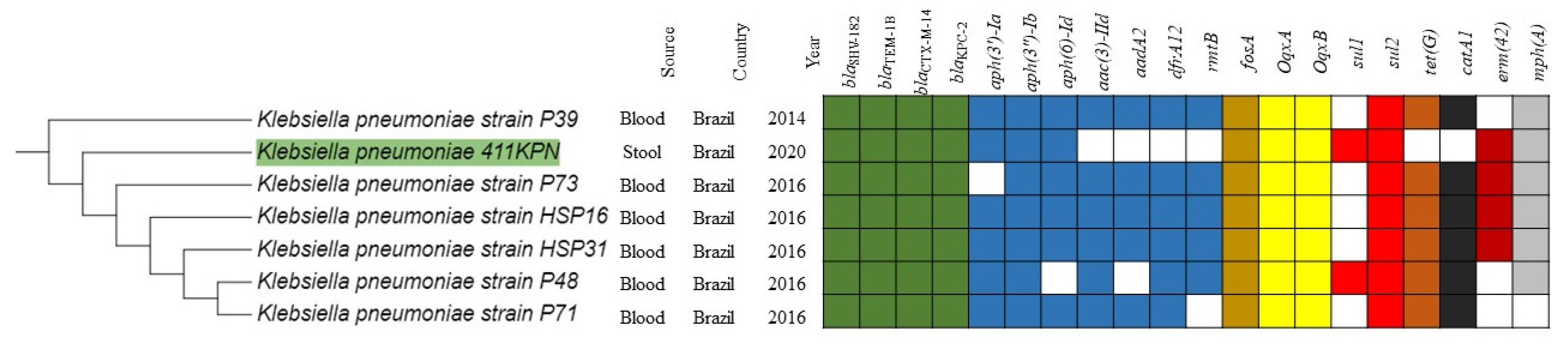
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Strain
3.2. In Vitro Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3.3. Analysis of Hypermucoviscous Phenotype
3.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing and In Silico Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Remschmidt, C.; Schneider, S.; Meyer, E.; Schroeren-Boersch, B.; Gastmeier, P.; Schwab, F. Surveillance of Antibiotic Use and Resistance in Intensive Care Units (SARI). Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Global dissemination of Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, genetic context, treatment options, and detection methods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordmann, P.; Dortet, L.; Poirel, L. Carbapenem resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: Here is the storm! Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordmann, P.; Naas, T.; Poirel, L. Global spread of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Epidemiology and Diagnostics of Carbapenem Resistance in Gram-negative Bacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, S.S.; Harnod, D.; Hsueh, P.R. Global Threat of Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 15, 823684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopotsa, K.; Osei Sekyere, J.; Mbelle, N.M. Plasmid evolution in carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: A review. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1457, 61–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, Z. Antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in food animals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 18377–18384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.; Fang, C.; Lai, S.; Chang, S.; Wang, J. Genetic Determinants of Capsular Serotype K1 of Klebsiella pneumoniae Causing Primary Pyogenic Liver Abscess. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.R.; Lin, T.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Chou, H.C.; Wang, J.T. The role of Klebsiella pneumoniae rmpA in capsular polysaccharide synthesis and virulence revisited. Microbiology 2011, 157, 3446–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Liu, J.W.; Su, L.H.; Chien, C.C.; Li, C.C.; Yang, K.D. Hypermucoviscosity associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated invasive syndrome: A prospective cross-sectional study in Taiwan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Sun, S.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Sun, Y. The pathogenicity of rmpA or aerobactin-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae in infected mice. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 4344–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrey, D.O.; Dantas, P.P.; Martins, W.B.S.; de Carvalho, F.M.; Almeida, L.G.P.; Sands, K.; Portal, E.; Sauser, J.; Cayô, R.; Nicolas, M.F.; et al. An Emerging Clone, Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase 2-Producing K. pneumoniae Sequence Type 16, Associated With High Mortality Rates in a CC258-Endemic Setting. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, C.A.M.; Pereira, P.S.; Rocha-de-Souza, C.M.; Silveira, M.C.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D.; Asensi, M.D. Population Structure of KPC-2-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Surveillance Rectal Swabs in Brazil. Microb. Drug. Resist. 2020, 26, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, H.; Cardoso, B.; Esposito, F.; de Lima, A.V.; Sampaio, J.L.M.; Lincopan, N. Small IncQ1 Plasmid Encoding KPC-2 Expands to Invasive Nontyphoidal Salmonella. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0155221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitout, J.D.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, a Key Pathogen Set for Global Nosocomial Dominance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5873–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.N.; Curiao, T.; Ferreira, J.C.; Longo, J.M.; Clímaco, E.C.; Martinez, R.; Bellissimo-Rodrigues, F.; Basile-Filho, A.; Evaristo, M.A.; Del Peloso, P.F.; et al. Dissemination of blaKPC-2 by the spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal complex 258 clones (ST258, ST11, ST437) and plasmids (IncFII, IncN, IncL/M) among Enterobacteriaceae species in Brazil. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3579–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szijártó, V.; Guachalla, L.M.; Hartl, K.; Varga, C.; Badarau, A.; Mirkina, I.; Visram, Z.C.; Stulik, L.; Power, C.A.; Nagy, E.; et al. Endotoxin neutralization by an O-antigen specific monoclonal antibody: A potential novel therapeutic approach against Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258. Virulence 2017, 8, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Deng, B.; Liao, W.; Wang, P.; Chen, P.; Wei, J. High rate of multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from human and animal origin. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.L.; Cheung, Y.Y.; Lo, W.U.; Li, Z.; Chow, K.H.; Lin, C.H.; Chan, J.F.W.; Cheng, V.C.C. Molecular characterization of an atypical IncX3 plasmid pKPC-NY79 carrying blaKPC-2 in a Klebsiella pneumoniae. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.R.; Ginn, A.N.; Wiklendt, A.M.; Ellem, J.; Wong, J.S.; Ingram, P.; Guy, S.; Garner, S.; Iredell, J.R. Emergence of blaKPC carbapenemase genes in Australia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakopoulos, A.; van der Goot, J.; Bossers, A.; Betts, J.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Kant, A.; Smith, H.; Ceccarelli, D.; Mevius, D. Genomic and functional characterisation of IncX3 plasmids encoding blaSHV -12 in Escherichia coli from human and animal origin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.G.; Murphy, C.N.; Sippy, J.; Johnson, T.J.; Clegg, S. Type 3 fimbriae and biofilm formation are regulated by the transcriptional regulators MrkHI in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanukollu, U.; Bieler, S.; Hull, S.; Hull, R. Contribution of the traT gene to serum resistance among clinical isolates of Enterobacteriaceae. J. Med. Microbiol. 1985, 19, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, A.; Manning, P.A.; Timmis, K.N. Plasmid-determined resistance to serum bactericidal activity: A major outer membrane protein, the traT gene product, is responsible for plasmid-specified serum resistance in Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1980, 28, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.M.; Valiatti, T.B.; Santos, F.F.; Silveira, A.C.O.; Guimarães, A.P.C.; Gerber, A.L.; Souza, C.O.; Corsi, D.C.; Brasiliense, D.M.; Castelo-Branco, D.S.C.M.; et al. Exploring the Bacteriome and Resistome of Humans and Food-Producing Animals in Brazil. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0056522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.T.; Chuang, Y.P.; Shun, C.T.; Chang, S.C.; Wang, J.T. A Novel Virulence Gene in Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Causing Primary Liver Abscess and Septic Metastatic Complications. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, E.E.; Kampanya, N.; Lu, J.; Nordberg, E.K.; Karur, H.R.; Shukla, M.; Soneja, J.; Tian, Y.; Xue, T.; Yoo, H.; et al. PATRIC: The VBI PathoSystems Resource Integration Center. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL): An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antimicrobials | MIC | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Aztreonam | 128 μg/mL | R |
| Ceftriaxone | >256 μg/mL | R |
| Ceftazidime | 64 μg/mL | R |
| Cefepime | >256 μg/mL | R |
| Ertapenem | 256 μg/mL | R |
| Imipenem | 64 μg/mL | R |
| Meropenem | 64 μg/mL | R |
| Ciprofloxacin | >64 μg/mL | R |
| Levofloxacin | 32 μg/mL | R |
| Gentamicin | 64 μg/mL | R |
| Amikacin | 4 μg/mL | S |
| Colistin | 0.5 μg/mL | S |
| Polymyxin B | <0.25 μg/mL | S |
| Plasmid Identification | Coverage | Identity | Accession Number | Species | Source of Infection | Year | Geographical Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pKP64477d | 100% | 100% | MF150120.1 | K. pneumoniae | Urine | 2014 | Brazil |
| pKP13D | 99% | 100% | CP003997.1 | K. pneumoniae | Blood | 2009 | Brazil |
| pk89 | 99% | 99.85% | MK264770.1 | K. pneumoniae | Rectal Swab | 2015 | Brazil |
| pk1194a | 100% | 99.99% | KX756453.1 | K. pneumoniae | Catheter Tip | 2011 | Brazil |
| EC037P1 | 99% | 99.99% | KU963389.1 | E. coli | NI | 2016 | Brazil |
| strain KP30835 plasmid unnamed5 | 100% | 99.96% | CP027700.1 | K. pneumoniae | Pneumonia | 2015 | United States |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valiatti, T.B.; Cayô, R.; Santos, F.F.; Bessa-Neto, F.O.; Brandão Silva, R.G.; Veiga, R.; de Nazaré Miranda Bahia, M.; Guerra, L.M.G.D.; Pignatari, A.C.C.; de Oliveira Souza, C.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 Strain Coproducing KPC-2 and CTX-M-14 Isolated from Poultry in the Brazilian Amazon Region. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121835
Valiatti TB, Cayô R, Santos FF, Bessa-Neto FO, Brandão Silva RG, Veiga R, de Nazaré Miranda Bahia M, Guerra LMGD, Pignatari ACC, de Oliveira Souza C, et al. Genomic Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 Strain Coproducing KPC-2 and CTX-M-14 Isolated from Poultry in the Brazilian Amazon Region. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(12):1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121835
Chicago/Turabian StyleValiatti, Tiago Barcelos, Rodrigo Cayô, Fernanda Fernandes Santos, Francisco Ozório Bessa-Neto, Ramon Giovani Brandão Silva, Ruanita Veiga, Márcia de Nazaré Miranda Bahia, Lívia Maria Guimarães Dutra Guerra, Antônio Carlos Campos Pignatari, Cintya de Oliveira Souza, and et al. 2022. "Genomic Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 Strain Coproducing KPC-2 and CTX-M-14 Isolated from Poultry in the Brazilian Amazon Region" Antibiotics 11, no. 12: 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121835
APA StyleValiatti, T. B., Cayô, R., Santos, F. F., Bessa-Neto, F. O., Brandão Silva, R. G., Veiga, R., de Nazaré Miranda Bahia, M., Guerra, L. M. G. D., Pignatari, A. C. C., de Oliveira Souza, C., Brasiliense, D. M., & Gales, A. C., on behalf of the Guarani Network. (2022). Genomic Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258 Strain Coproducing KPC-2 and CTX-M-14 Isolated from Poultry in the Brazilian Amazon Region. Antibiotics, 11(12), 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11121835







