Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Derived from LL-37
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peptide Synthesis
2.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
2.3. Biofilm Susceptibility Assay
2.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.5. SEM
2.6. Cytoxicity
2.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.8. Cytokine and Inflammation Assays
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Structural Characterization of Peptides
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity against S. Gordonii
3.3. Biofilm Inhibition
3.4. SEM
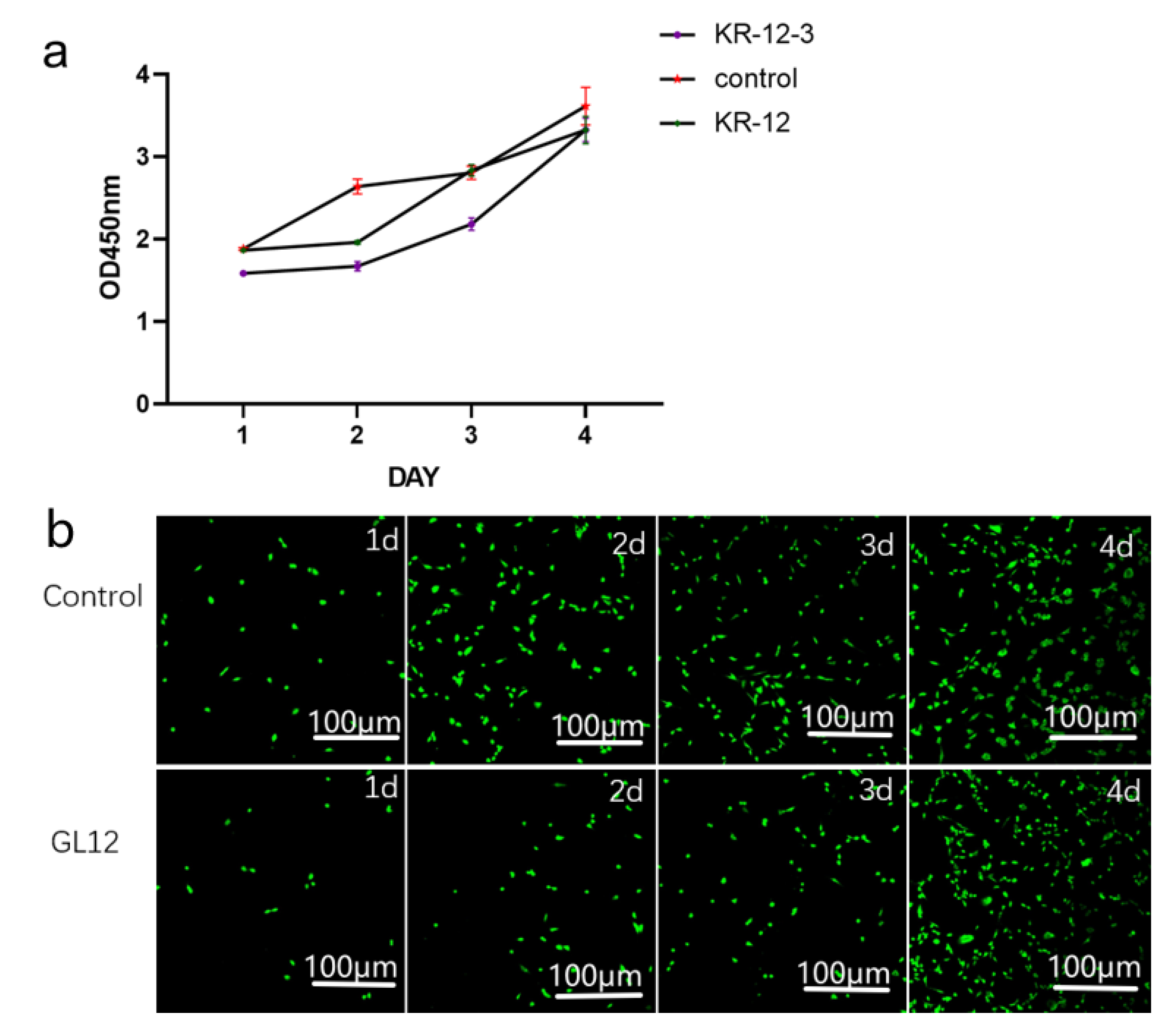
3.5. Effects of the KR-12-3 Peptide on S. gordonii Surface Adhesion Protein sspA/sspB Gene Expression
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.7. Effect of KR-12-3 and KR-12 on IL-6 and IL-8 Production/Gene Expression in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, N.P.; Berglundh, T.; Working Group 4 of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology. Periimplant diseases: Where are we now?—Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38 (Suppl. S11), 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanz, M.; Chapple, I.L.; Working Group 4 of the VIII European Workshop on Periodontology. Clinical research on peri-implant diseases: Consensus report of Working Group 4. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39 (Suppl. S12), 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jepsen, S.; Berglundh, T.; Genco, R.; Aass, A.M.; Demirel, K.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; Giovannoli, J.L.; Goldstein, M.; Lambert, F.; et al. Primary prevention of peri-implantitis: Managing peri-implant mucositis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42 (Suppl. S16), S152–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindhe, J.; Meyle, J.; Group D of the European Workshop on Periodontology. Peri-implant diseases: Consensus Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kilian, M.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Hannig, M.; Marsh, P.D.; Meuric, V.; Pedersen, A.M.L.; Tonetti, M.S.; Wade, W.G.; Zaura, E. The oral microbiome—An update for oral healthcare professionals. Br. Dent. J. 2016, 221, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, M.; Beighton, D.; Curtis, M.A.; Cury, J.A.; Dige, I.; Dommisch, H.; Ellwood, R.; Giacaman, R.A.; Herrera, D.; Herzberg, M.C.; et al. Role of microbial biofilms in the maintenance of oral health and in the development of dental caries and periodontal diseases. Consensus report of group 1 of the Joint EFP/ORCA workshop on the boundaries between caries and periodontal disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44 (Suppl. S18), S5–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Martin, I.; Doolittle-Hall, J.; Teles, R.P.; Patel, M.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E.; Teles, F.R.F. Exploring the microbiome of healthy and diseased peri-implant sites using Illumina sequencing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rams, T.E.; Degener, J.E.; van Winkelhoff, A.J. Antibiotic resistance in human peri-implantitis microbiota. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, J.G.S.; Bertolini, M.; Thompson, A.; Barao, V.A.R.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A. Biofilm interactions between Candida albicans and mitis group streptococci in a titanium-mucosal interface model. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02950-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafaurie, G.I.; Sabogal, M.A.; Castillo, D.M.; Rincón, M.V.; Gómez, L.A.; Lesmes, Y.A.; Chambrone, L. Microbiome and Microbial Biofilm Profiles of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1066–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, P.L.; Otazu, I.B.; Balduino, A.; de Mello, W.; Barboza, E.P.; Duarte, M.E. Identification of periodontal pathogens in healthy periimplant sites. Implant Dent. 2011, 20, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgerton, M.; Lo, S.E.; Scannapieco, F.A. Experimental salivary pellicles formed on titanium surfaces mediate adhesion of streptococci. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1996, 11, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Greber, K.E.; Dawgul, M. Antimicrobial Peptides Under Clinical Trials. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 17, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczulla, A.R.; Bals, R. Antimicrobial Peptides: Current Status and Therapeutic Potential. Drugs 2003, 63, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.; Migonney, V.; Falentin-Daudre, C. Review of silicone surface modification techniques and coatings for antibacterial/antimicrobial applications to improve breast implant surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2020, 121, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouly, I.; López, S.; Ruff, R.R.; Strauss, F.J. Efficacy of growth factors for the treatment of peri-implant diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 2141–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corra, M.G.; Pimentel, S.P.; Ribeiro, F.V.; Cirano, F.R.; Casati, M.Z. Host response and peri-implantitis. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33, e066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L. Peri-implantitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45 (Suppl. S20), S246–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Lakshmaiah, J.; Biswajit, N.; Yingxia, Z.; Fangyu, W.; Chunfeng, W.; Zarena, D.; Lushnikova, T.; Xiuqing, W. Design of Antimicrobial Peptides: Progress Made with Human Cathelicidin LL-37. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1117, 215–240. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.T.; Huang, Y.W.; Zhu, L.; Weltman, R. Prevalences of peri-implantitis and peri-implant mucositis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2017, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Takeshita, T. The oral microbiome and human health. J. Oral 2017, 59, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Yan, L.; Cao, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhou, X. The oral microbiome diversity and its relation to human diseases. Folia Microbiol. 2014, 60, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubovics, N.S.; Kolenbrander, P.E. The road to ruin: The formation of disease-associated oral biofilms. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joycharat, N.; Thammavong, S.; Limsuwan, S.; Homlaead, S.; Subhadhirasakul, S. Antibacterial substance from Albizia myriophylla wood against cariogenic Streptococcus mutans. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2013, 36, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, J.; Miao, W.J.; Chen, A. Resveratrol Attenuates Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-Induced Inhibition of Osteoblast Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2018, 24, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, M.; Tanabe, N.; Manaka, S.; Naito, M.; Sekino, J.; Takayama, T.; Takayuki, K.; Torigoe, G.; Shunichiro, K.; Tsukune, N.; et al. LIPUS suppressed LPS-induced IL-1α through the inhibition of NF-κB nuclear translocation via AT1-PLCβ pathway in MC3T3-E1 cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 3337–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.H.; Wang, H.L. Breaking the wave of peri-implantitis. Periodontology 2000, 2020, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derks, J.; Tomasi, C. Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, S158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Polyzois, I. Treatment of pathologic peri-implant pockets. Periodontology 2018, 76, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, T.; Osorio, M.T.; Vallecillo-Rivas, M.; Toledano-Osorio, M.; Rodríguez-Archilla, A.; Toledano, R.; Osorio, R. Efficacy of local antibiotic therapy in the treatment of peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2021, 113, 103790. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Zhentan, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhongming, W.; Xinge, Z.; Yanan, W.; Yuting, L.; Chaoxing, L.; Yanxia, J. Bioconjugated nanoparticles for attachment and penetration into pathogenic bacteria. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 10328–10337. [Google Scholar]
- Smeets, R.; Stadlinger, B.; Schwarz, F.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.; Jung, O.; Precht, C.; Kloss, F.; Gröbe, A.; Heiland, M.; Ebker, T. Impact of Dental Implant Surface Modifications on Osseointegration. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6285620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chouirfa, H.; Bouloussa, H.; Migonney, V.; Falentin-Daudré, C. Review of titanium surface modification techniques and coatings for antibacterial applications. Acta Biomater. 2018, 83, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harawaza, K.; Cousins, B.; Roach, P.; Fernandez, A. Modification of the surface nanotopography of implant devices: A translational perspective. Mater. Today Biol. 2021, 12, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorsa, T.; Bacigalupo, J. Host-Modulation Therapy and Chair-Side Diagnostics in the Treatment of Peri-Implantitis. Biosensors 2020, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziel, J.; Bryzek, D.; Sroka, A.; Maresz, K.; Glowczyk, I.; Bielecka, E.; Kantyka, T.; Pyrc, K.; Svoboda, P.; Pohl, J.; et al. Citrullination alters immunomodulatory function of LL-37 essential for prevention of endotoxin-induced sepsis. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5363–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Megumi, I.; Toshi, H.; Takeshi, I. Effect of the Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37 on Gene Expression of Chemokines and 29 Toll-like Receptor-Associated Proteins in Human Gingival Fibroblasts Under Stimulation with Porphyromonas gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Su, D.; Li, L.; Cai, H.; Hu, K. Anti-inflammatory effects of Aureusidin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via suppressing NF-κB and activating ROS- and MAPKs-dependent Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 387, 114846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucki, R.; Leszczyńska, K.; Namiot, A.; Sokoowski, W. Cathelicidin LL-37: A Multitask Antimicrobial Peptide. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2010, 58, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahar, B.; Madonna, S.; Das, A.; Albanesi, C.; Girolomoni, G. Immunomodulatory Role of the Antimicrobial LL-37 Peptide in Autoimmune Diseases and Viral Infections. Vaccines 2020, 8, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabisiak, A.; Murawska, N.; Fichna, J. LL-37: Cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide with pleiotropic activity. Pharmacol. Rep. Pract. 2016, 68, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari, A.; Flach, T.L.; Shi, Y.; Mydlarski, P.R. Toll-like receptors: Role in dermatological disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 437246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, S.; Gao, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Du, L.J.; Jun, L.; Ying-Ying, L.; Jun-Xiu, L.; Li-Chun, Z.; et al. Procyanidin A1 Alleviates Inflammatory Response induced by LPS through NF-κB, MAPK, and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways in RAW264.7 cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Diao, P.; Shu, X.; Li, L.; Xiong, L. Quercetin and Quercitrin Attenuates the Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells: In Vitro Assessment and a Theoretical Model. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7039802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Hirata, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Minamoto, S.; Aono, A.; Nishimoto, N.; Kajita, T.; Taga, T.; Yoshizaki, K.; et al. Structure and function of a new STAT-induced STAT inhibitor. Nature 1997, 387, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi-Tezuka, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Fukada, T.; Ohtani, T.; Yamanaka, Y.; Nishida, K.; Nakajima, K.; Hibi, M.; Hirano, T. Gab1 Acts as an Adapter Molecule Linking the Cytokine Receptor gp130 to ERK Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 4109–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Q. The cytokine network involved in the host immune response to periodontitis. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2019, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roebuck, K.A. Regulation of Interleukin-8 Gene Expression. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1999, 19, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| sspA-F | 5′-TCCTGACAAACCTGAGACACC-3′ |
| sspA-R | 5′-TTTAACTTTCAGAGCTTAGTTGCTTTC-3′ |
| sspB-F | 5′-TCCTGACAAACCTGAGACACC-3′ |
| sspB-R | 5′-CATCAAAGATGAAACAAGTCTAAGC-3′ |
| 16S rRNA-F | 5′-AAGCAACGCGAAGAACCTTA-3′ |
| 16S rRNA-R | 5′-GTCTCGCTAGAGTGCCCAAC-3′ |
| GAPDH-F | 5′-GTTGTCTCCTGCGACTTCA-3′ |
| GAPDH-R | 5′-GCCCCTCCTGTTATTATGG-3′ |
| IL-6-F | 5′-CTGCAAGAGACTTCCATCCAG-3′ |
| IL-6-R | 5′-AGTGGTATAGACAGGTCTGTTGG-3′ |
| IL-8-F | 5′-GACTTCCAAGCTGGCTGTTG-3′ |
| IL-8-R | 5′-GGGTGGAAAGGTGTGGAATG-3′ |
| Peptide | %Hydrophobic Residues | Net Positive Charge | μH (Relative) | PI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR-12 | 41.67 | 4 | 0.782 | 12.20 |
| KR-12-3 | 50 | 6 | 0.893 | 11.87 |
| Peptide | MIC (µg/mL) | MBC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| KR-12-3 | 156.25 | 312.5 |
| KR-12 | >2500 | >2500 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuo, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Derived from LL-37. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060754
Zhuo H, Zhang X, Li M, Zhang Q, Wang Y. Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Derived from LL-37. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(6):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060754
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuo, Haiwei, Xi Zhang, Maogen Li, Qian Zhang, and Yonglan Wang. 2022. "Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Derived from LL-37" Antibiotics 11, no. 6: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060754
APA StyleZhuo, H., Zhang, X., Li, M., Zhang, Q., & Wang, Y. (2022). Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Derived from LL-37. Antibiotics, 11(6), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060754





