Chemotherapeutic Strategies with Valnemulin, Tilmicosin, and Tulathromycin to Control Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Infection in Pigs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantification of IgG in Swine Serum over Time
2.2. Detection and Quantification of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae by qPCR in Nasal Swab
2.3. Assessment of Health Indicators
2.3.1. Cough Examination
2.3.2. Mortality
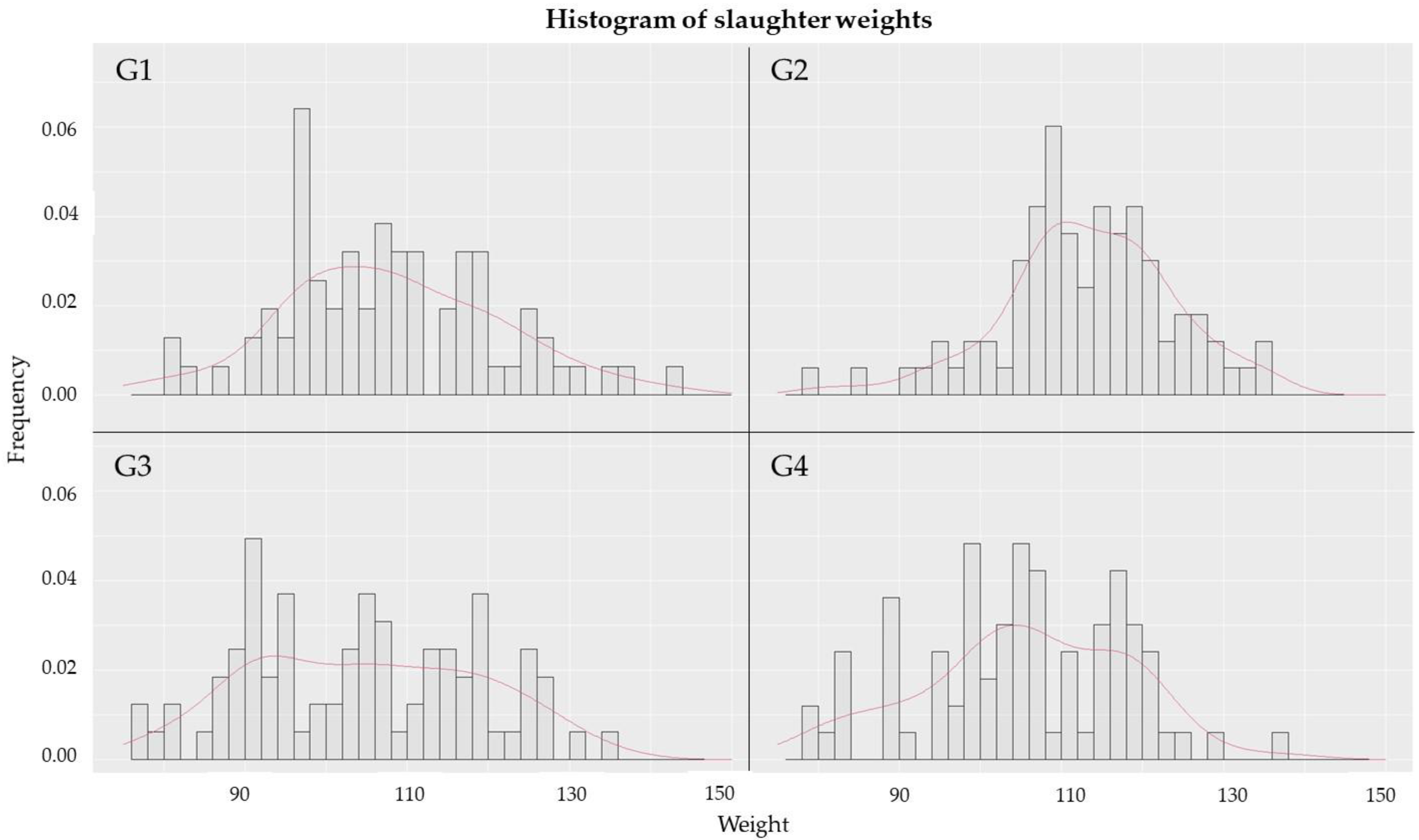
2.4. Evaluation of Performance Indicators
2.5. Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Quantification in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid and Lung Tissue Samples by qPCR
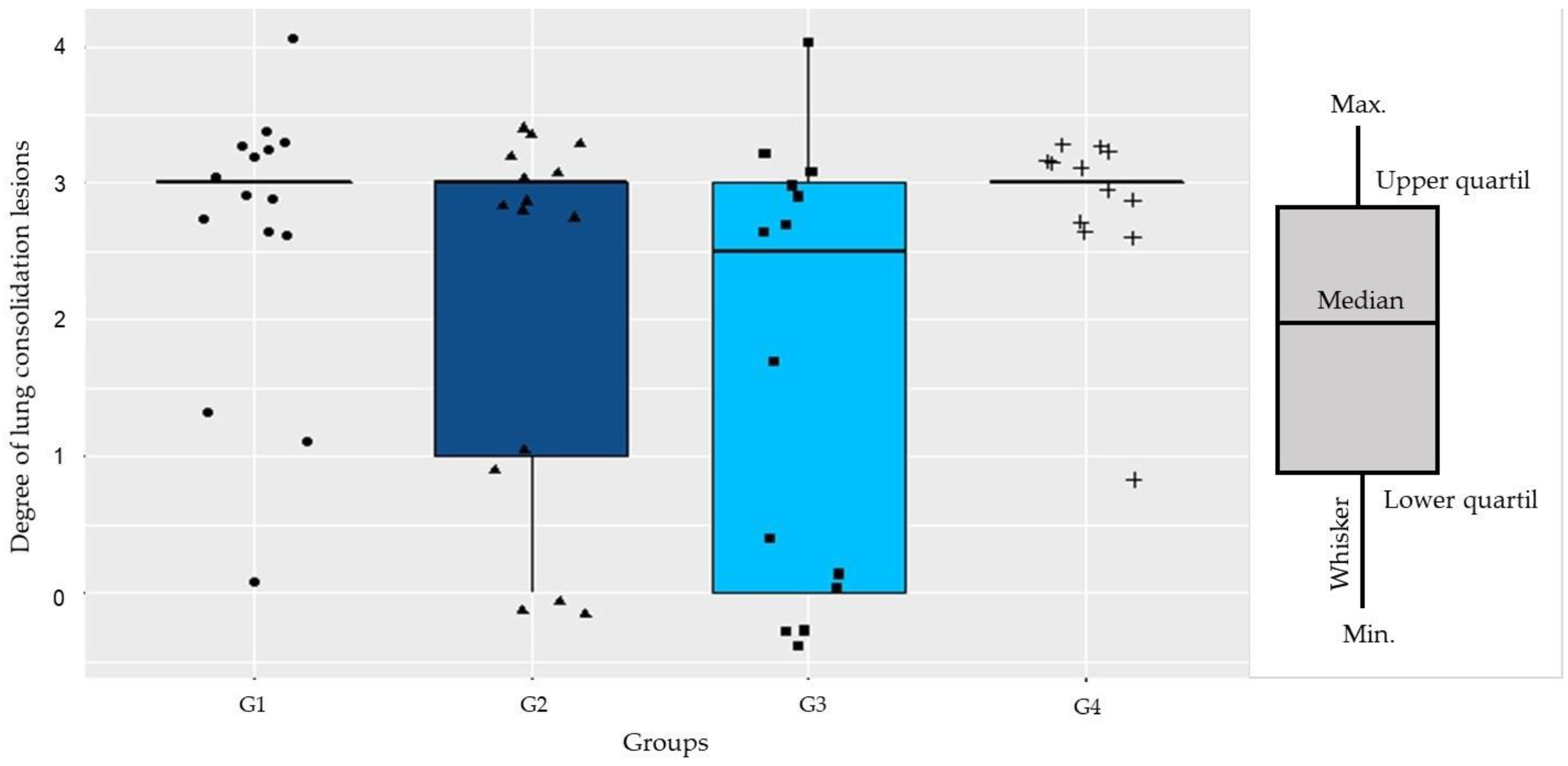
2.6. Lung Injuries Examination
Determination of the Pneumonia Index
2.7. Histopathological Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Study Farm
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Collection of Blood Serum Samples
4.4. Cough Index
4.5. Zootechnical Performance
4.6. Mortality
4.7. Slaughter of Animals, Lung Evaluation, and Sample Collection
4.8. Detection and Quantification of Antibodies by ELISA
4.9. DNA Extraction and cPCR Performance for the Gapdh Gene
4.10. Detection and Quantification of M. hyopneumoniae by qPCR
5. Statistical Analysis
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pieters, M.; Maes, D. Mycoplasmosis. In Diseases of Swine; Zimmerman, J.J., Karriker, L.A., Ramirez, A., Schwartz, K.J., Stevenson, G.W., Zhang, J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 863–883. ISBN 9781119350903. [Google Scholar]
- Holst, S.; Yeske, P.; Pieters, M. Elimination of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae from breed-to-wean farms: A review of current protocols with emphasis on herd closure and medication. J. Swine Health Prod. 2015, 23, 321–330. Available online: https://www.aasv.org/jshap/issues/v23n6/v23n6p321.pdf/ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Maes, D.; Segales, J.; Meyns, T.; Sibyl, M.; Pieters, M.; Haesebrouck, F. Control of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infections in pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 126, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stärk, K.D.C. Epidemiological Investigation of the influence of environmental risk factors on respiratory diseases in swine—A literature review. Vet. J. 2000, 159, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fano, E.; Pijoan, C.; Dee, S. Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae prevalence at weaning as a predictor of the group’s subsequent Mycoplasma status. In Allen D. Leman Swine Conference; University of Minnesota Digital Conservancy: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2005; pp. 109–113. Available online: https://conservancy.umn.edu/handle/11299/142894 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- European Medicines Agency. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 30 European Countries in 2015: Trends from 2010 to 2015: Seventh ESVAC Report; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; 184p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallarés, F.J.; Lasa, C.; Roozen, M.; Ramis, G. Use of Tylvalosin in the control of Porcine Enzootic Pneumonia. Vet. Rec. Open 2015, 2, e000079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xia, X.; Gu, X.; Shen, X.; Yang, H.; Ding, H. The PK/PD integration and resistance of Tilmicosin against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Pathogens 2020, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Feng, H.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y.; Yu, L.; Deng, X. Valnemulin downregulates nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2, and cytokine production via inhibition of NF-Κ B and MAPK activity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutsch, R.G.; Hart, F.J.; Rooney, K.A.; Weigel, D.J.; Kilgore, W.R.; Skogerboe, T.L. Efficacy of Tulathromycin injectable solution for the treatment of naturally occurring swine respiratory disease. Vet. Ther. 2005, 6, 214–224. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16094568/ (accessed on 20 June 2022). [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calsamiglia, M.; Pijoan, C.; Bosch, G.J. Profiling Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in farms using serology and a Nested-PCR technique. J. Swine Health Prod. 1999, 7, 263–268. Available online: https://www.aasv.org/jshap/issues/v7n6/v7n6p263.pdf/ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Pieters, M.; Pijoan, C. Detection pattern of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae DNA in nasal swabs. In Proceedings of the International Pig Veterinary Society Congress, Copenhagen, Denmark, 16–19 July 2006; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuti, K.L.; de Barcellos, D.E.S.N.; Lara, A.C.; Kunrath, C.F.; Pieters, M. Detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in naturally infected gilts over time. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 203, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozen, M.; Marco, E. Overview of eradications of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae with Tylvalosin (Aivlosin®) in sows in Europe. In Proceedings of the 6th European Symposium of Porcine Health Management, Sorrento, Italy, 7–9 May 2014; p. 229. [Google Scholar]
- Fablet, C.; Marois, C.; Kobisch, M.; Madec, F.; Rose, N. Estimation of the sensitivity of four sampling methods for Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae detection in live pigs using a Bayesian approach. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fano, E.; Pijoan, C.; Dee, S.; Deen, J. Effect of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae colonization at weaning on disease severity in growing pigs. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2007, 71, 195–200. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1899865/ (accessed on 20 June 2022). [PubMed]
- Pieters, M.; Pijoan, C.; Fano, E.; Dee, S. An assessment of the duration of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection in an experimentally infected population of pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, F.A.M.; Sonalio, K.; Almeida, H.M.S.; Ferraz, M.E.S.; Storino, G.Y.; de Souza, M.R.; André, M.R.; de Oliveira, L.G. Porcine hemothropic Mycoplasmas infection associated with productive impact in intensive pig production. Porc. Health Manag. 2020, 6, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Van Brussel, L.; Saunders, G.; Runnels, P.; Taylor, L.; Fredrickson, D.; Salt, J. Vaccination of piglets up to 1 week of age with a single-dose Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccine induces protective immunity within 2 weeks against virulent challenge in the presence of maternally derived antibodies. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maes, D.; Boyen, F.; Devriendt, B.; Kuhnert, P.; Summerfield, A.; Haesebrouck, F. Perspectives for improvement of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccines in pigs. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandrick, M.; Theis, K.; Molitor, T.W. Maternal immunity enhances Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccination induced cell-mediated immune responses in piglets. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, P.; Ziesenitz, V.C.; Curtis, N.; Ritz, N. The immunomodulatory effects of macrolides—A systematic review of the underlying mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nau, R.; Sörgel, F.; Eiffert, H. Penetration of drugs through the blood-cerebrospinal fluid/blood-brain barrier for treatment of central nervous system infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 858–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeRosa, D.C.; Veenhuizen, M.F.; Bade, D.J.; Shryock, T.R. In Vitro susceptibility of porcine respiratory pathogens to Tilmicosin. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2000, 12, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burch, D.G.S. Antimicrobial Drug Use in Swine. In Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary Medicine; Giguère, S., Prescott, J.F., Dowling, P.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013; pp. 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMEA European Medicines Agency. Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products- Valnemulin–Summary Report, EMEA/MRL/339/98-FINAL. May 1998; 6p. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/mrl-report/valnemulin-summary-report-committee-veterinary-medicinal-products_en.pdf/ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Gorniak, S.L. Agentes antimicrobianos. In Farmacologia Aplicada à Medicina Veterinária, 6th ed.; Spinosa, H.S., Gorniak, S.L., Bernardi, M.M., Eds.; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2017; 972p, ISBN 9788527730808. [Google Scholar]
- Hirose, F.; Neto, J.S. Utilização de medicação via água de bebida na suinocultura: Aspectos práticos e econômicos. Simpósio Brasil Sul de Suinocultura. In Proceedings of the V Brasil Sul Simpósio de Suinocultura and the IV Brasil Sul Pig Fair, 14–16 August 2012; Embrapa Suínos e Aves: Concordia, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rostagno, H.S. Tabelas Brasileiras para Aves e Suínos—Composição de Alimentos e Exigências Nutricionais, 3rd ed.; UFV/DZO: Viçosa, Brazil, 2011; 252p, Available online: https://centrodepesquisasavicolas.files.wordpress.com/2011/02/tabelas-brasileiras-2011.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Sobestiansky, J.; Wentz, I.; Silveira, P.R.S.; Sesti, L.A.C. Suinocultura Intensiva. Produção: Manejo e Saúde do Rebanho, 1st ed.; Embrapa: Brasilia, Brazil, 1998; p. 388. ISBN 978-8573830361. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez, A.; Karriker, L.A. Herd evaluation. In Diseases of Swine; Zimmerman, J.J., Karriker, L.A., Ramirez, A., Schwartz, K.J., Stevenson, G.W., Zhang, J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 3–16. ISBN 9781119350903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portaria nº 711/95—Normas Técnicas para Instalações e Equipamentos para Abate e Industrialização de Suínos; Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento (MAPA): Brasília, Brazil, 1995; 98p. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/inspecao/produtos-animal/empresario/arquivos/Portaria_711.1995.pdf/view/ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Piffer, I.A.; Brito, J.R.F. Descrição de um Modelo para Avaliação e Quantificação de Lesões Pulmonares de Suínos e Formulação de um Índice para Classificação de Rebanhos; EMBRAPA/CNPSA: Concórdia, Brazil, 1991; 16p, Available online: https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/item/42227/1/documento-23.pdf/ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Brito, J.R.; Piffer, I.A.; Sobestiansky, J.; Brito, M.A.V. Vacinação com Bordetella bronchiseptica e Pasteurella multocida, associada a alterações do manejo, no controle da rinite atrófica dos suínos. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec 1993, 45, 183–191. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, P.R.; Bahnson, P.B.; Grass, J.J.; Marsh, W.E.; Dial, G.D. Comparison of methods for measurement of Enzootic Pneumonia lesions in pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kuramae-Izioka, E.E. A rapid, easy and high yield protocol for total genomic DNA isolation of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Fusarium oxysporum. Rev. Univ. Estadual. Mar. 1997, 19, 683–689. Available online: https://periodicos.uem.br/ojs/index.php/RevUNIMAR/article/view/4550/ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Birkenheuer, A.J.; Levy, M.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Development and Evaluation of a Seminested PCR for Detection and Differentiation of Babesia Gibsoni (Asian Genotype) and B. Canis DNA in Canine Blood Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4172–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fourour, S.; Fablet, C.; Tocqueville, V.; Dorenlor, V.; Eono, F.; Eveno, E.; Kempf, I.; Marois - Créhan, C. A new multiplex real-time TaqMan® PCR for quantification of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, M. Hyorhinis and M. Flocculare: Exploratory epidemiological investigations to research Mycoplasmal association in Enzootic Pneumonia-like lesions in slaughtered pigs. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, H.M.S.; Mechler-Dreibi, M.L.; Sonálio, K.; Ferraz, M.E.S.; Storino, G.Y.; Barbosa, F.O.; Maes, D.; Montassier, H.J.; de Oliveira, L.G. Cytokine expression and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae burden in the development of lung lesions in experimentally inoculated pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.D. The R Project in Statistical Computing. MSOR Connections. MSOR Connect. Newsl. LTSN Maths Stats OR Netw. 2001, 1, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- De Mendiburu, M.F. Agricolae: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research’ R Package Version 2019, 1–2. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/agricolae/agricolae.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Soft. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Su, Y.-S.; Yajima, M.; Hill, J.; Pittau, M.G.; Kerman, J.; Zheng, T.; Dorie, V. Package ‘Arm’. R Top. Doc. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/arm/index.html (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Lenth, R.; Lenth, M.R. Package ‘Lsmeans’. Am. Stat. 2018, 34, 216–221. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lsmeans/lsmeans.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA; Available online: https://socialsciences.mcmaster.ca/jfox/Books/Companion/ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Gross, J.; Ligges, U. Nortest: Tests for Normality. R Package Version 1.0-4. 2015. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nortest (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Ripley, B.; Venables, B.; Bates, D.M.; Hornik, K.; Gebhardt, A.; Firth, D.; Ripley, M. Package ‘Mass’. Cran r No. 538, 113–120. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/MASS/ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Wickham, M.H. Package ‘ggplot2’: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics. Package Version 3.3.3. 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggplot2 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
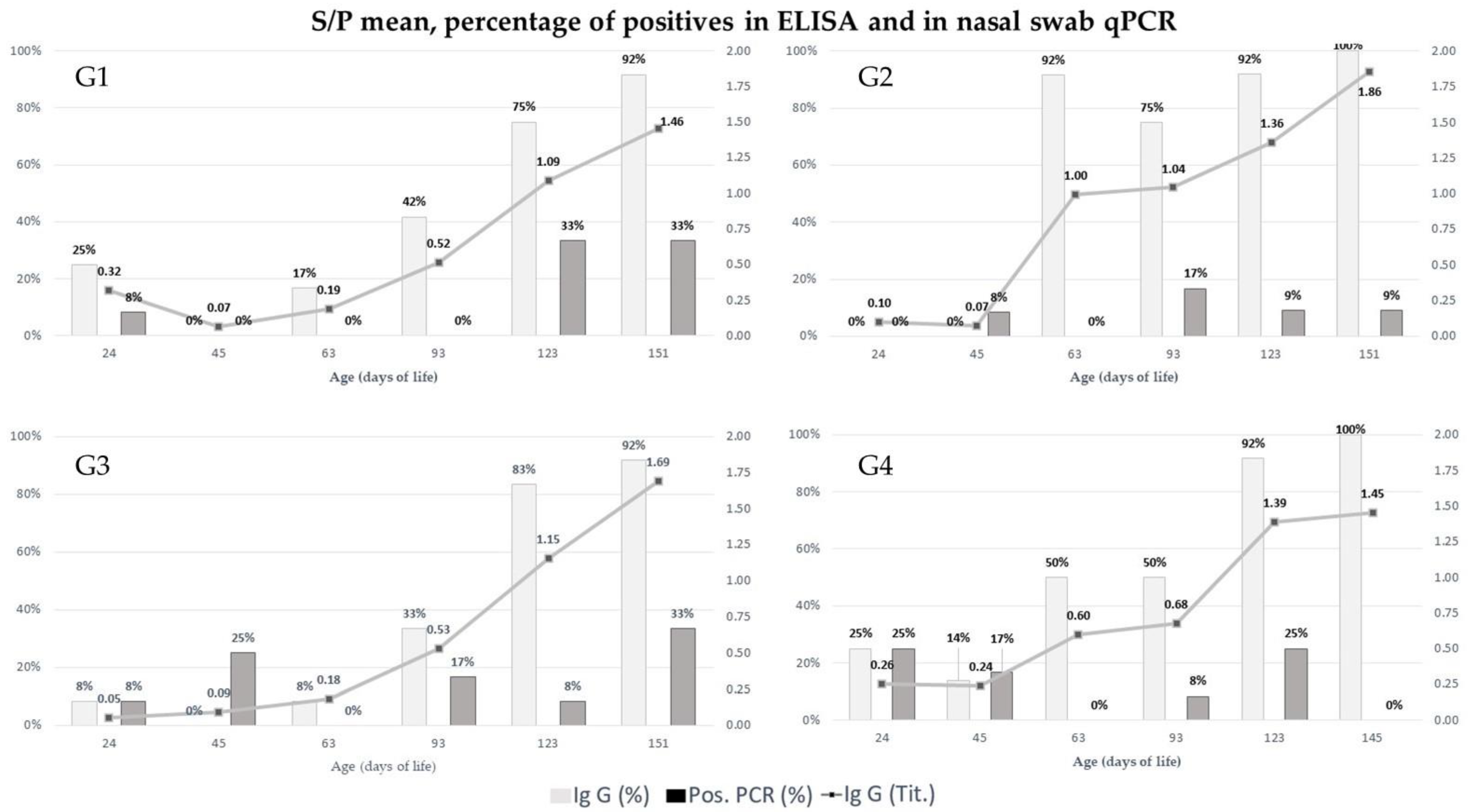

| Points | Group | Mean * | Median Standard Error | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 (24 days) | G1 | 0.32 a | 0.14 | 2.35 × 10−1 |
| G2 | 0.10 a | 0.04 | ||
| G3 | 0.05 a | 0.04 | ||
| G4 | 0.26 a | 0.14 | ||
| T2 (45 days) | G1 | 0.07 a | 0.03 | 2.7 × 10−1 |
| G2 | 0.07 a | 0.02 | ||
| G3 | 0.09 a | 0.03 | ||
| G4 | 0.24 a | 0.13 | ||
| T3 (63 days) | G1 | 0.19 b | 0.05 | 2.3 × 10−5 |
| G2 | 0.10 a | 0.15 | ||
| G3 | 0.18 b | 0.05 | ||
| G4 | 0.60 ab | 0.18 | ||
| T4 (93 days) | G1 | 0.52 a | 0.17 | 1.5 × 10−1 |
| G2 | 1.04 a | 0.19 | ||
| G3 | 0.53 a | 0.19 | ||
| G4 | 0.68 a | 0.16 | ||
| T5 (123 days) | G1 | 1.09 a | 0.22 | 6.4 × 10−1 |
| G2 | 1.36 a | 0.22 | ||
| G3 | 1.15 a | 0.19 | ||
| G4 | 1.39 a | 0.15 | ||
| T6 (151 days) | G1 | 1.46 a | 0.21 | 2.9 × 10−1 |
| G2 | 1.86 a | 0.11 | ||
| G3 | 1.69 a | 0.20 | ||
| G4 | 1.45 a | 0.14 |
| Points | Group | Mean * | Standard Error | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 (weight at 25 days) | G1 | 6.20 b | 0.17 | 1 × 10−5 |
| G2 | 7.05 a | 0.14 | ||
| G3 | 6.01 b | 0.14 | ||
| G4 | 6.47 b | 0.14 | ||
| T2 (weight at 63 days) | G1 | 20.64 b | 0.42 | 7 × 10−6 |
| G2 | 22.42 a | 0.40 | ||
| G3 | 20.66 b | 0.48 | ||
| G4 | 23.35 a | 0.43 | ||
| T3 (G1, G2 and G3 weight at 151 days, G4 weight at 145 days) | G1 | 107.18 b | 1.50 | 8 × 10−5 |
| G2 | 113.33 a | 1.28 | ||
| G3 | 104.95 b | 1.47 | ||
| G4 | 103.42 b | 1.86 | ||
| T3 (G4 estimated weight at 151 days) | G1 | 107.18 ab | 1.50 | 8 × 10−3 |
| G2 | 113.33 a | 1.28 | ||
| G3 | 104.95 b | 1.47 | ||
| G4 | 108.29 ab | 2.34 |
| ADWG (kg) | Group | Mean * | Standard Error | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nursery | G1 | 0.39 b | 0.01 | 4 × 10−6 |
| G2 | 0.41 b | 0.01 | ||
| G3 | 0.39 b | 0.01 | ||
| G4 | 0.45 a | 0.01 | ||
| Finishing | G1 | 1.01 b | 0.01 | 3 × 10−3 |
| G2 | 1.07 a | 0.01 | ||
| G3 | 0.99 b | 0.01 | ||
| G4 | 1.01 b | 0.01 | ||
| Between 25d and 151d, considering the G4 up to 145d | G1 | 0.82 b | 0.01 | |
| G2 | 0.87 a | 0.01 | 1 × 10−2 | |
| G3 | 0.81 b | 0.01 | ||
| G4 | 0.84 ab | 0.01 |
| Food Conversion (FC) (kg) | Group | Mean * | Standard Error | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nursery | G1 | 2.01 a | 0.05 | 5 × 10−9 |
| G2 | 1.76 b | 0.05 | ||
| G3 | 2.11 a | 0.06 | ||
| G4 | 1.69 b | 0.04 | ||
| Finishing | G1 | 2.12 a | 0.03 | 4 × 10−2 |
| G2 | 2.02 b | 0.03 | ||
| G3 | 2.12 ab | 0.03 | ||
| G4 | 2.03 ab | 0.03 | ||
| Between 25d and 151d, considering the G4 up to 145d | G1 | 2.12 a | 0.03 | 3 × 10−4 |
| G2 | 1.97 b | 0.02 | ||
| G3 | 2.14 a | 0.03 | ||
| G4 | 1.97 b | 0.03 |
| Molecular Quantification of M. hyopneumoniae in Lung | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Mean * | Standard Error | p Value |
| G1 | 1.34 × 105 a | 4.84 × 104 | 4 × 10−2 |
| G2 | 6.74 × 104 ab | 2.90 × 104 | |
| G3 | 3.15 × 104 b | 9.72 × 103 | |
| G4 | 2.41 × 104 b | 1.06 × 104 | |
| Molecular Quantification of M. hyopneumoniae in BALF | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Mean * | Standard Error | p Value |
| G1 | 2.32 × 106 a | 9.33 × 105 | 4 × 10−1 |
| G2 | 5.67 × 106 a | 2.23 × 106 | |
| G3 | 3.57 × 106 a | 1.05 × 106 | |
| G4 | 3.33 × 106 a | 9.55 × 105 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stingelin, G.M.; Mechler-Dreibi, M.L.; Storino, G.Y.; Sonalio, K.; Almeida, H.M.d.S.; Petri, F.A.M.; de Oliveira, L.G. Chemotherapeutic Strategies with Valnemulin, Tilmicosin, and Tulathromycin to Control Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Infection in Pigs. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070893
Stingelin GM, Mechler-Dreibi ML, Storino GY, Sonalio K, Almeida HMdS, Petri FAM, de Oliveira LG. Chemotherapeutic Strategies with Valnemulin, Tilmicosin, and Tulathromycin to Control Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Infection in Pigs. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(7):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070893
Chicago/Turabian StyleStingelin, Giovani Marco, Marina Lopes Mechler-Dreibi, Gabriel Yuri Storino, Karina Sonalio, Henrique Meiroz de Souza Almeida, Fernando Antônio Moreira Petri, and Luís Guilherme de Oliveira. 2022. "Chemotherapeutic Strategies with Valnemulin, Tilmicosin, and Tulathromycin to Control Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Infection in Pigs" Antibiotics 11, no. 7: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070893
APA StyleStingelin, G. M., Mechler-Dreibi, M. L., Storino, G. Y., Sonalio, K., Almeida, H. M. d. S., Petri, F. A. M., & de Oliveira, L. G. (2022). Chemotherapeutic Strategies with Valnemulin, Tilmicosin, and Tulathromycin to Control Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Infection in Pigs. Antibiotics, 11(7), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11070893









