Pharmacodynamics of Flucloxacillin in a Neutropenic Murine Thigh Infection Model: A Piece of the Puzzle towards Evidence-Based Dosing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pharmacokinetics
2.2. Plasma Protein Binding
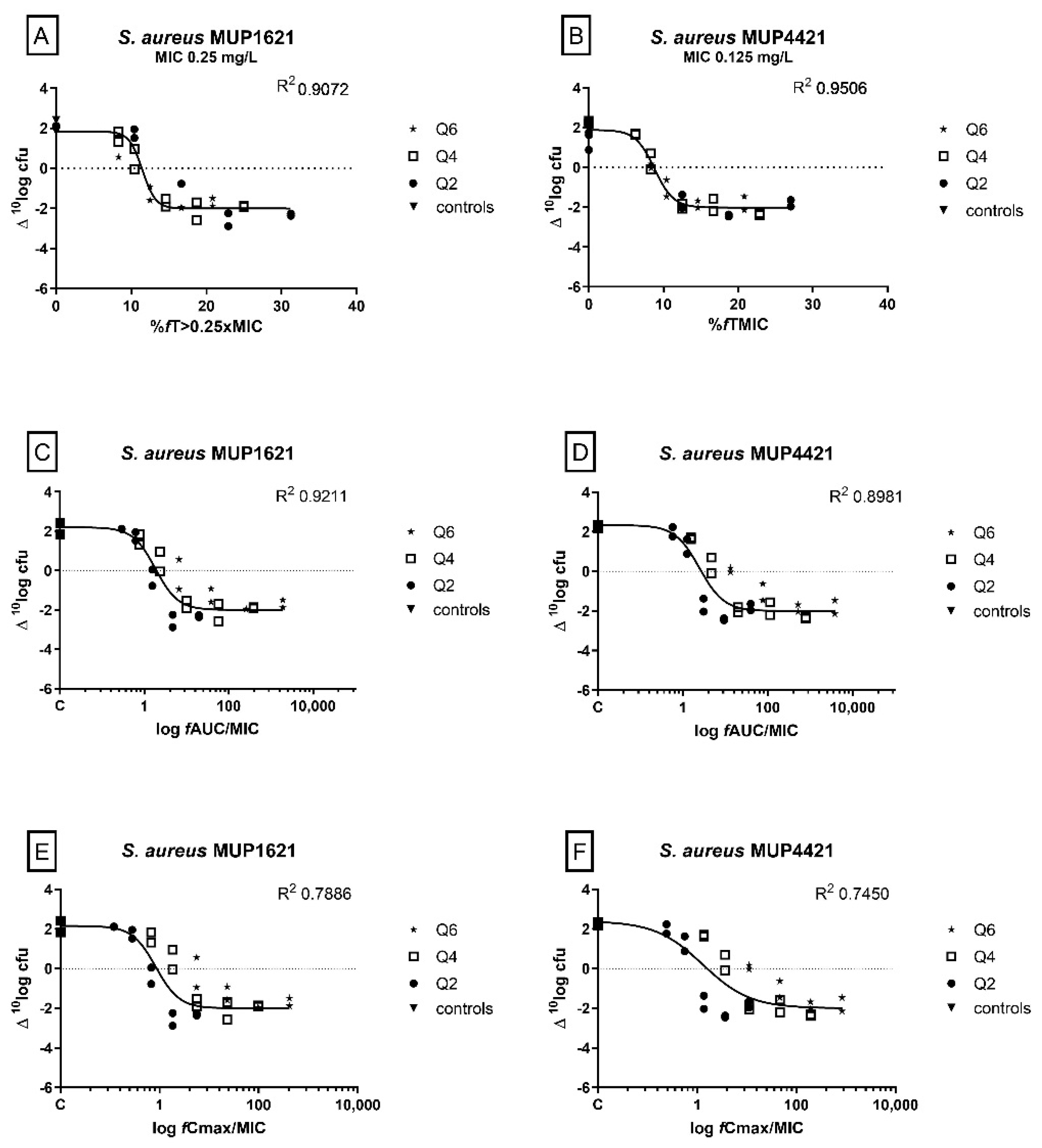
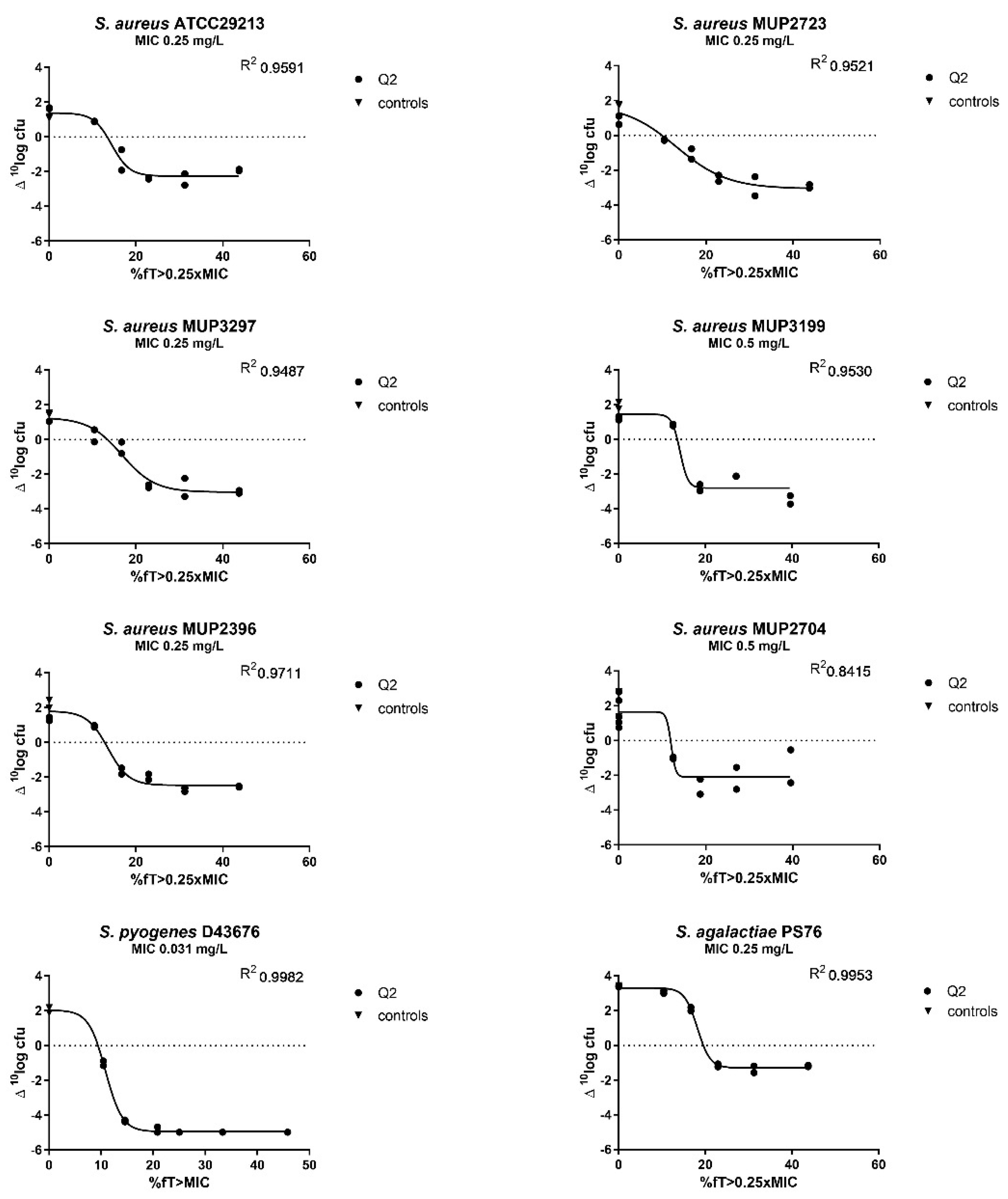
2.3. Determination of the PK/PD Index and the Magnitude of the Index Correlated with Efficacy
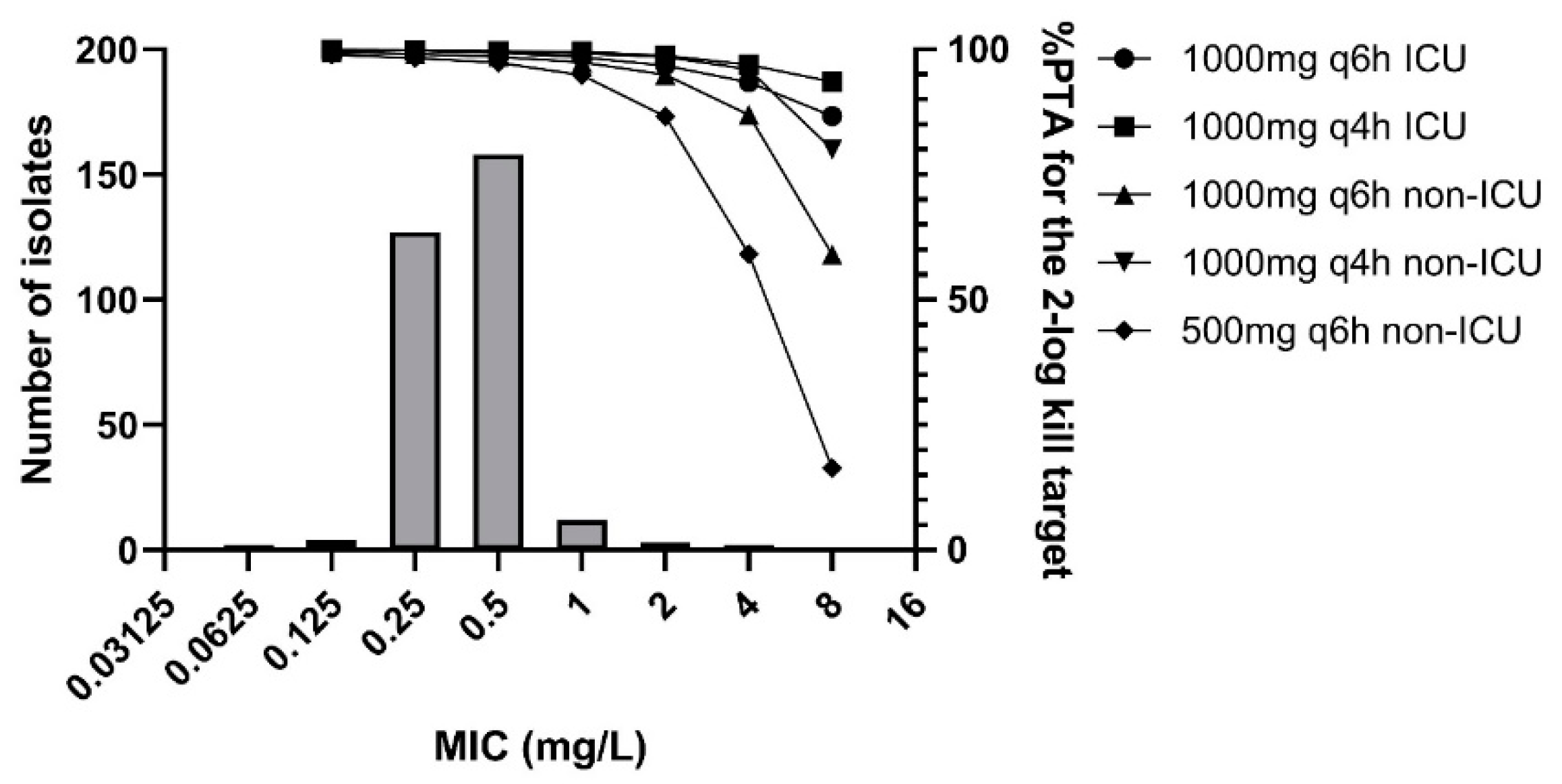
2.4. MIC Distribution
2.5. Monte Carlo Simulations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacteria, Media, and Antibiotics for Animal Experiments
4.2. Animals
4.3. Thigh and Lung Infection Model in Neutropenic Mice
4.4. Measurement of Flucloxacillin Concentrations in Plasma
4.5. Flucloxacillin Pharmacokinetics in Mice
4.6. Pharmacodynamic and Statistical Analysis
4.7. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC) and Wild-Type Distribution
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craig, W.A. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters: Rationale for antibacterial dosing of mice and men. Clin. Infect Dis. 1998, 26, 1–10; quiz 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouton, J.W.; Punt, N.; Vinks, A.A. Concentration-effect relationship of ceftazidime explains why the time above the MIC is 40 percent for a static effect in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3449–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, A.E.; Punt, N.; Mouton, J.W. Optimal exposures of ceftazidime predict the probability of microbiological and clinical outcome in the treatment of nosocomial pneumonia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EUCAST Steering Committee. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters, version 12.0; EUCAST Steering Committee: Växjö, Sweden, 2022; Available online: https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- EUCAST Steering Committee. MIC Distributions and the Setting of Epidemiological Cutoff (ECOFF) Values; EUCAST SOP: Växjö, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, G.; Briscoe, S.; McWhinney, B.; Ally, M.; Ungerer, J.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A. Therapeutic drug monitoring of beta-lactam antibiotics in the critically ill: Direct measurement of unbound drug concentrations to achieve appropriate drug exposures. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 3087–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallenburg, E.; Ter Heine, R.; de Lange, D.W.; van Leeuwen, H.; Schouten, J.A.; Ten Oever, J.; Kolwijck, E.; Burger, D.M.; Pickkers, P.; Gieling, E.M.; et al. High unbound flucloxacillin fraction in critically ill patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 3220–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, S.; van Berlo, I.; Ten Oever, J.; Jansman, F.; Ter Heine, R. Population pharmacokinetic modelling of total and unbound flucloxacillin in non-critically ill patients to devise a rational continuous dosing regimen. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, S.; Rehm, S.; Guertler, N.; Hinic, V.; Drager, S.; Bassetti, S.; Rentsch, K.M.; Sendi, P.; Osthoff, M. Probability of pharmacological target attainment with flucloxacillin in Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection: A prospective cohort study of unbound plasma and individual MICs. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; McDonald, C.; McWhinney, B.; Ungerer, J.P.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A. Low flucloxacillin concentrations in a patient with central nervous system infection: The need for plasma and cerebrospinal fluid drug monitoring in the ICU. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boast, A.; Carr, J.; Curtis, N.; Daley, A.J.; Gwee, A. Effective CSF concentrations achieved with continuous-infusion flucloxacillin in a child. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 1535–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlier, M.; Roberts, J.A.; Stove, V.; Verstraete, A.G.; Lipman, J.; de Waele, J.J. A Simulation Study Reveals Lack of Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Target Attainment in De-escalated Antibiotic Therapy in Critically Ill Patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4689–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin, P.K.L.; Drennan, P.G.; Gardiner, S.J.; Zhang, M.; Dalton, S.C.; Chambers, S.T.; Begg, E.J. Total flucloxacillin plasma concentrations poorly reflect unbound concentrations in hospitalized patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2311–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulldemolins, M.; Roberts, J.A.; Wallis, S.C.; Rello, J.; Lipman, J. Flucloxacillin dosing in critically ill patients with hypoalbuminaemia: Special emphasis on unbound pharmacokinetics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, G.; Briscoe, S.; Adnan, S.; McWhinney, B.; Ungerer, J.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A. Protein binding of beta-lactam antibiotics in critically ill patients: Can we successfully predict unbound concentrations? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 6165–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Wart, S.A.; Ambrose, P.G.; Rubino, C.M.; Khariton, T.; Riccobene, T.A.; Friedland, H.D.; Critchley, I.A.; Bhavnani, S.M. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic target attainment analyses to evaluate in vitro susceptibility test interpretive criteria for ceftaroline against Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacGowan, A.P.; Noel, A.R.; Tomaselli, S.; Bowker, K.E. Pharmacodynamics of ceftaroline against Staphylococcus aureus studied in an in vitro pharmacokinetic model of infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2451–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craig, W.A.; Andes, D.R. In vivo pharmacodynamics of ceftobiprole against multiple bacterial pathogens in murine thigh and lung infection models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3492–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugihara, K.; Sugihara, C.; Matsushita, Y.; Yamamura, N.; Uemori, M.; Tokumitsu, A.; Inoue, H.; Kakuta, M.; Namba, E.; Nasu, H.; et al. In vivo pharmacodynamic activity of tomopenem (formerly CS-023) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a murine thigh infection model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5298–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacGowan, A.P.; Noel, A.; Tomaselli, S.; Elliott, H.; Bowker, K. Pharmacodynamics of razupenem (PZ601) studied in an in vitro pharmacokinetic model of infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sy, S.K.B.; Zhuang, L.; Sy, S.; Derendorf, H. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Ceftazidime-Avibactam Combination: A Model-Informed Strategy for its Clinical Development. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Aziz, M.H.; Brady, K.; Cotta, M.O.; Roberts, J.A. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Antibiotics: Defining the Therapeutic Range. Ther. Drug Monit. 2022, 44, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, S.J.; Drennan, P.G.; Begg, R.; Zhang, M.; Green, J.K.; Isenman, H.L.; Everts, R.J.; Chambers, S.T.; Begg, E.J. In healthy volunteers, taking flucloxacillin with food does not compromise effective plasma concentrations in most circumstances. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landersdorfer, C.B.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; Kinzig-Schippers, M.; Bulitta, J.B.; Holzgrabe, U.; Drusano, G.L.; Sorgel, F. Population pharmacokinetics at two dose levels and pharmacodynamic profiling of flucloxacillin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adam, D.; Koeppe, P.; Heilmann, H.D. Pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin and flucloxacillin following the simultaneous intravenous administration of 4 g and 1 g, respectively. Infection 1983, 11, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergan, T.; Engeset, A.; Olszewski, W.; Ostby, N.; Solberg, R. Extravascular penetration of highly protein-bound flucloxacillin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1986, 30, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gath, J.; Charles, B.; Sampson, J.; Smithurst, B. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of flucloxacillin in elderly hospitalized patients. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 35, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Ferrero, M.M.; Vree, T.B.; Van Ewijk-Beneken Kolmer, E.W.; Slooff, T.J. Relationship between plasma and bone concentrations of cefuroxime and flucloxacillin. Three different parenteral administrations compared in 30 arthroplasties. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1994, 15, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.; Bluhm, G.; Ehrnebo, M.; Herngren, L.; Jacobson, B. Pharmacokinetics and distribution of flucloxacillin in pacemaker patients. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1985, 27, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, U.; Schmidt-Eisenlohr, E.; Schlosser, V.; Spillner, G.; Schindler, M.; Daschner, F.D. Concentrations of flucloxacillin in heart valves and subcutaneous and muscle tissues of patients undergoing open-heart surgery. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 930–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Union. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulla, A.; Bahmany, S.; Wijma, R.A.; van der Nagel, B.C.H.; Koch, B.C.P. Simultaneous determination of nine beta-lactam antibiotics in human plasma by an ultrafast hydrophilic-interaction chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1060, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytic Method Validation. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm368107.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2021).
| Model | Bootstrap | 95% Percentiles | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Estimate | Rel. SE (%) | Median | 2.5% | 97.5% |
| Ka (h−1) | 9.78 | 28 | 9.59 | 6.09 | 19.48 |
| V (L) | 0.511 | 17 | 0.51 | 0.31 | 0.70 |
| KM (mg/L) | 7.51 | 18 | 7.36 | 3.99 | 10.67 |
| Vmax (mg/h) | 98.8 | 4 | 98.34 | 45.65 | 131.45 |
| Variability on KM (%) | 41.2 | 60 | 40.7 | 4.1 | 69.5 |
| Additive error (mg/L) | 0.0477 | 4 | 0.048 | 0.047 | 0.049 |
| Proportional error (%) | 42.5 | 16 | 40.0 | 22.4 | 56.8 |
| Isolates | Stasis | 1-log Kill | 2-log Kill |
|---|---|---|---|
| %fT > 0.25xMIC | |||
| S. aureus ATCC29213 | 13.38 | 15.71 | 19.73 |
| S. aureus MUP4421 | 13.77 | 15.29 | 19.18 |
| S. aureus MUP1621 | 11.42 | 12.41 | 30.60 |
| S. aureus MUP2723 | 9.92 | 14.90 | 20.64 |
| S. aureus MUP3297 | 13.44 | 17.20 | 22.21 |
| S. aureus MUP3199 | 13.53 | 14.41 | 15.47 |
| S. aureus MUP2396 | 12.79 | 15.10 | 18.58 |
| S. aureus SA2704 | 11.91 | 12.50 | 13.95 |
| S. aureus-average | 12.52 | 14.69 | 20.05 |
| S. aureus-median | 13.09 | 15.00 | 19.46 |
| S. aureus-SD | 1.34 | 1.60 | 5.04 |
| S. agalactiae | 19.55 | 22.13 | n.a. |
| %fT > MIC | |||
| S. pyogenes | 9.39 | 10.41 | 11.34 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roelofsen, E.E.; de Winter, B.C.M.; van der Spek, H.; Snijders, S.; Koch, B.C.P.; van den Berg, S.; Muller, A.E. Pharmacodynamics of Flucloxacillin in a Neutropenic Murine Thigh Infection Model: A Piece of the Puzzle towards Evidence-Based Dosing. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11081049
Roelofsen EE, de Winter BCM, van der Spek H, Snijders S, Koch BCP, van den Berg S, Muller AE. Pharmacodynamics of Flucloxacillin in a Neutropenic Murine Thigh Infection Model: A Piece of the Puzzle towards Evidence-Based Dosing. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(8):1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11081049
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoelofsen, Eveline E., Brenda C. M. de Winter, Heleen van der Spek, Susan Snijders, Birgit C. P. Koch, Sanne van den Berg, and Anouk E. Muller. 2022. "Pharmacodynamics of Flucloxacillin in a Neutropenic Murine Thigh Infection Model: A Piece of the Puzzle towards Evidence-Based Dosing" Antibiotics 11, no. 8: 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11081049
APA StyleRoelofsen, E. E., de Winter, B. C. M., van der Spek, H., Snijders, S., Koch, B. C. P., van den Berg, S., & Muller, A. E. (2022). Pharmacodynamics of Flucloxacillin in a Neutropenic Murine Thigh Infection Model: A Piece of the Puzzle towards Evidence-Based Dosing. Antibiotics, 11(8), 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11081049






