Antibiotic Resistance Profiling and Phylogenicity of Uropathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infections
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Review Statement
2.2. Specimen Collection and Study Duration
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Specimen Processing
2.5. Identification of Isolates
2.6. Molecular Identification of Isolates
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis of Isolates
2.8. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
2.9. Kirby–Bauer Disk Diffusion Method
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
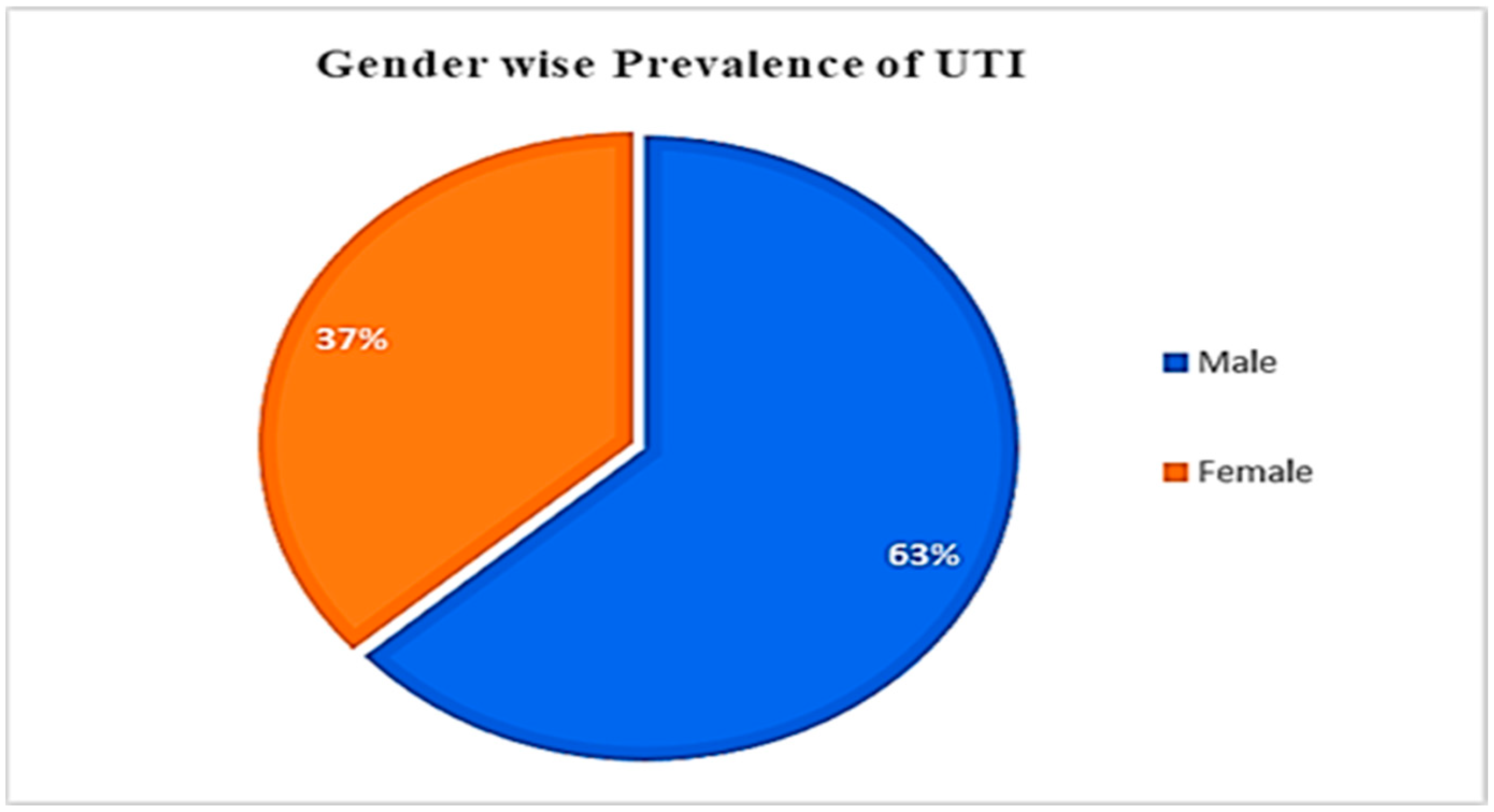
3.1. UTI Prevalence, concerning Gender and Age
3.2. Morphological and Biochemical Identification of Uropathogens
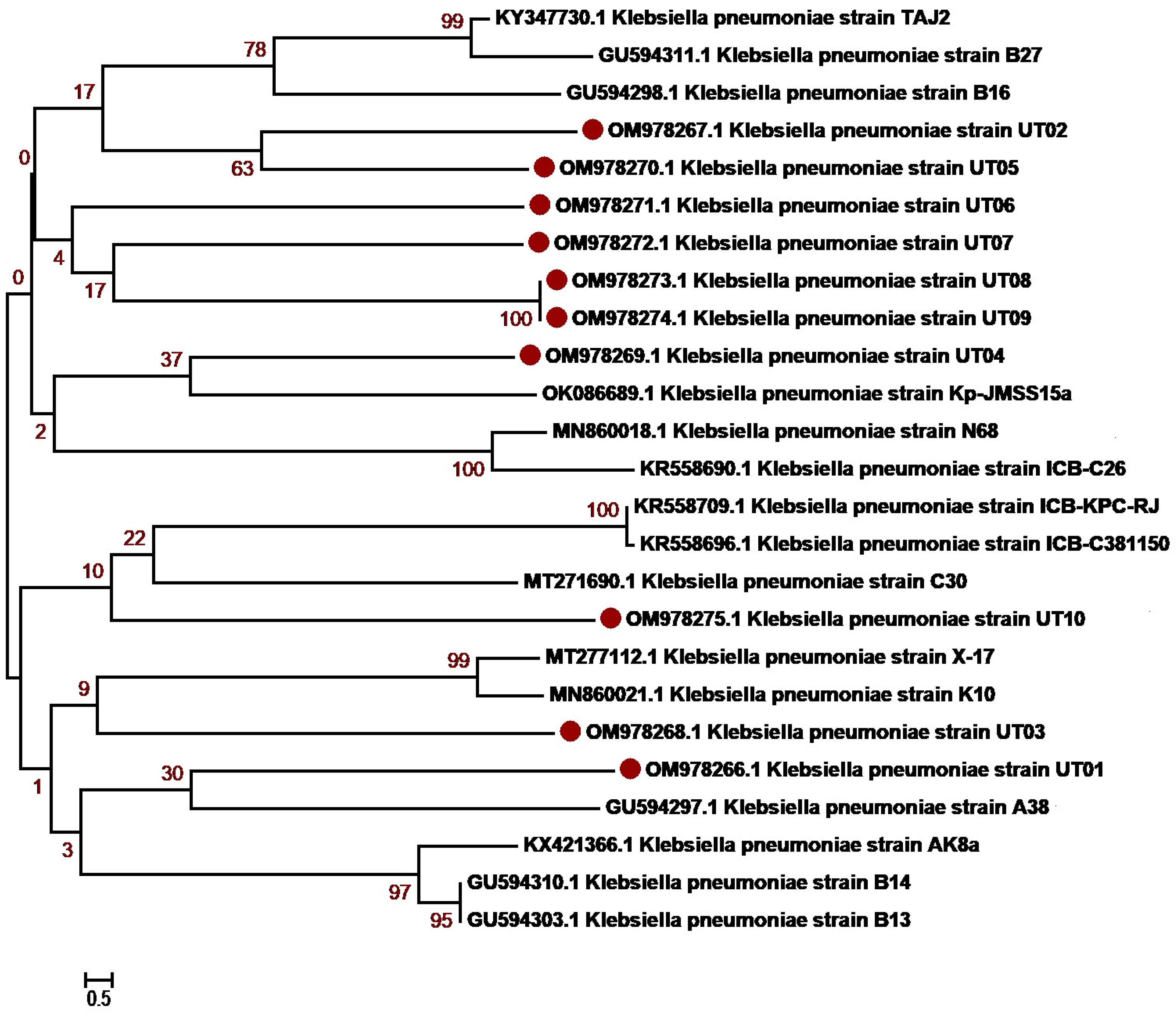
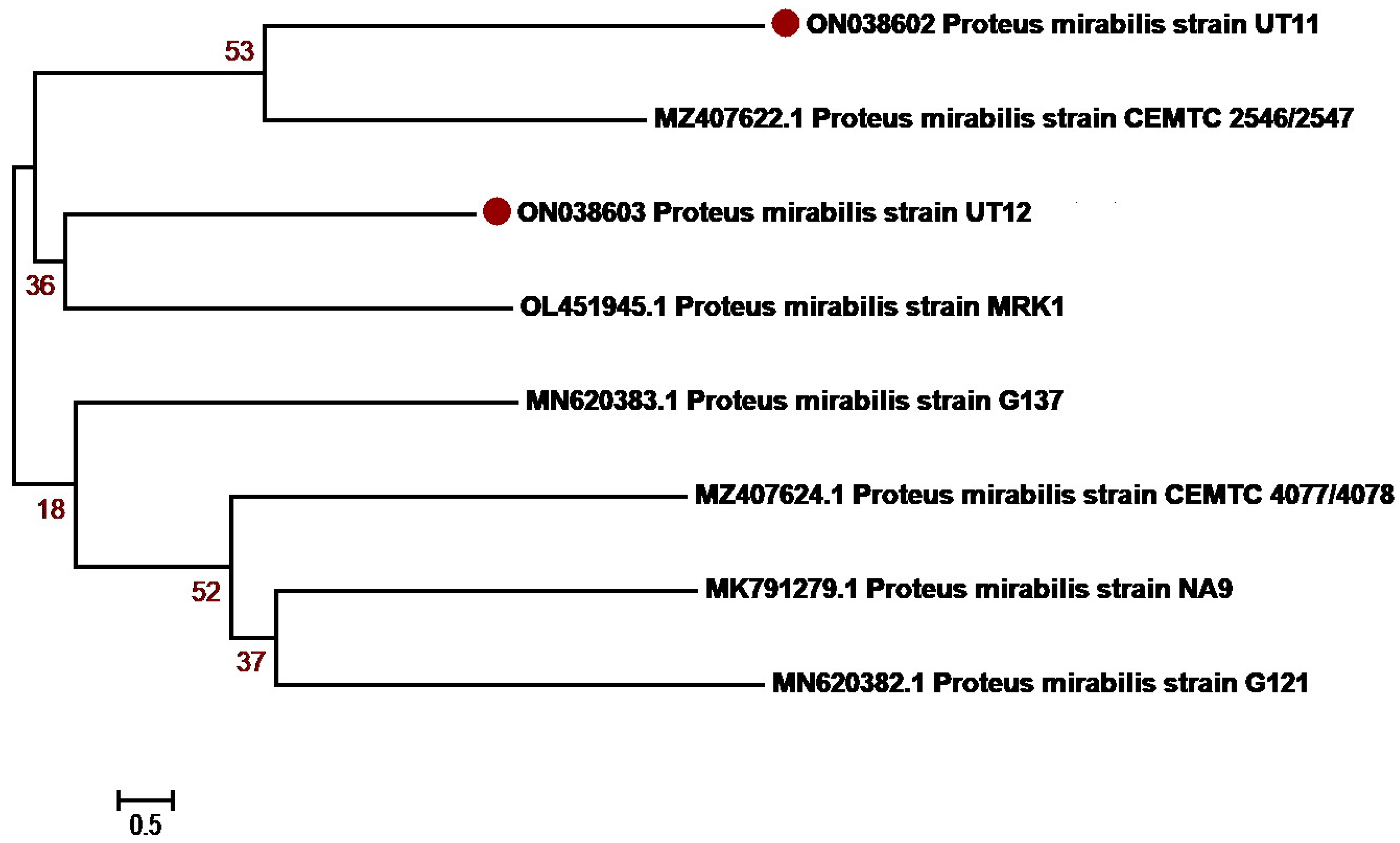
3.3. Molecular Identification and Phylogenetic Network Analysis of Uropathogens
3.4. Bacterial Isolates from UTI Patients
3.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Uropathogenic Bacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olin, S.J.; Bartges, J.W. Urinary Tract Infections: Treatment/Comparative Therapeutics. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2015, 45, 721–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Penfield, N.W.; Trautner, B.W.; Jump, R.L.P. Urinary Tract Infection and Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Older Adults. Infect. Dis. Clin. 2017, 31, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, C.-Y.; Yang, H.-Y.; Hsiao, M.-C.; Hung, P.-H.; Wang, M.-C. Risk Factors for Development of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Urinary Tract Infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, M.; Narasimhappa, S.; Madhura, N.S. Urinary Tract Infection in Chronic Kidney Disease Population: A Clinical Observational Study. Cureus 2021, 13, e12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhang, J.-F.; Kuo, H.-C. Recent Advances in Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection from Pathogenesis and Biomarkers to Prevention. Tzu-Chi Med. J. 2017, 29, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, K.; Hooton, T.M.; Stamm, W.E. Increasing Antimicrobial Resistance and the Management of Uncomplicated Community-Acquired Urinary Tract Infections. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 135, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minardi, D.; d’Anzeo, G.; Cantoro, D.; Conti, A.; Muzzonigro, G. Urinary Tract Infections in Women: Etiology and Treatment Options. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2011, 4, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, P.; Behzadi, E.; Pawlak-Adamska, E.A. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) or Genital Tract Infections (GTIs)? It’s the Diagnostics That Count. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2019, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sabih, A.; Leslie, S.W. Complicated Urinary Tract Infections; StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Walker, J.N.; Caparon, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary Tract Infections: Epidemiology, Mechanisms of Infection and Treatment Options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demilie, T.; Beyene, G.; Tsegaye, W.; Melaku, S. Urinary Tract Infection among Pregnant Women in Felege Hiwot Referral Hospital, Bahir Dar, North West Ethiopia: Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors. East Afr. J. Public Health 2013, 10, 561–570. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaria, Z.Z.; Al-Rumaihi, S.; Al-Absi, R.S.; Farah, H.; Elamin, M.; Nader, R.; Bouabidi, S.; Suleiman, S.E.; Nasr, S.; Al-Asmakh, M. Physiological Changes and Interactions between Microbiome and the Host During Pregnancy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 124, 824925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonko, I.O.; Ijandipe, L.A.; Ilusanya, A.O.; Donbraye-Emmanuel, O.B.; Ejembi, J.; Udeze, A.O.; Egun, O.C.; Fowotade, A.; Nkang, A.O. Detection of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) among Pregnant Women in Oluyoro Catholic Hospital, Ibadan, South-Western Nigeria. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2010, 6, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, H.Z.; Ziad, A.H.M.; Ali, S.K.; Adam, I. Epidemiology of Urinary Tract Infections and Antibiotics Sensitivity among Pregnant Women at Khartoum North Hospital. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2011, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najar, M.S.; Saldanha, C.L.; Banday, K.A. Approach to Urinary Tract Infections. Indian J. Nephrol. 2009, 19, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbschat, A.; Obermüller, N.; Paulus, P.; Reissig, M.; Hadji, P.; Hofmann, R.; Geiger, H.; Gauer, S. Upper and Lower Urinary Tract Infections Can Be Detected Early but Not Be Discriminated by Urinary NGAL in Adults. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mnif, M.F.; Kamoun, M.; Kacem, F.H.; Bouaziz, Z.; Charfi, N.; Mnif, F.; Naceur, B.B.; Rekik, N.; Abid, M. Complicated Urinary Tract Infections Associated with Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 442–445. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, E.A.; Mak, R.H. Urinary Tract Infection in Pediatrics: An Overview. J. Pediatr. Rio. J. 2020, 96, 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Sihra, N.; Goodman, A.; Zakri, R.; Sahai, A.; Malde, S. Nonantibiotic Prevention and Management of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 750–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chardavoyne, P.C.; Kasmire, K.E. Appropriateness of Antibiotic Prescriptions for Urinary Tract Infections. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 21, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshikhudo, P.; Nnzeru, R.; Ntushelo, K.; Mudau, F. Bacterial Species Identification Getting Easier. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 5975–5982. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Qian, P.-Y. Sensitivity and Correlation of Hypervariable Regions in 16S RRNA Genes in Phylogenetic Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing for Bacterial Identification in the Diagnostic Laboratory: Pluses, Perils, and Pitfalls. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2761–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Steinberg, K.M.; Larson, D.E.; Wilson, R.K.; Mardis, E.R. The Next-Generation Sequencing Revolution and Its Impact on Genomics. Cell 2013, 155, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlar, K.; Kupkova, K.; Provaznik, I. Bioinformatics Strategies for Taxonomy Independent Binning and Visualization of Sequences in Shotgun Metagenomics. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmat, U.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Malik, A. Rising Prevalence of Multidrug-Resistant Uropathogenic Bacteria from Urinary Tract Infections in Pregnant Women. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2021, 16, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, P.; Bharadwaj, A.; Srivastava, R.K. Molecular Detection and Identification of Bacteria in Urine Samples of Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Pregnant Women by 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 15, e101136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezatofighi, S.E.; Mirzarazi, M.; Salehi, M. Virulence Genes and Phylogenetic Groups of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolates from Patients with Urinary Tract Infection and Uninfected Control Subjects: A Case-Control Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.C.C.; Andrade, N.L.; Ferdous, M.; Chlebowicz, M.A.; Santos, C.C.; Correal, J.C.D.; LoTen Foe, J.R.; Rosa, A.C.P.; Damasco, P.V.; Friedrich, A.W. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Escherichia Coli Isolates from Urine Samples of Hospitalized Patients in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.L.; Gaido, L. Laboratory Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections in Adult Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, M.J.; Matsen, J.M. Evidence against the Practicality and Cost-Effectiveness of a Gram-Positive Coccal Selective Plate for Routine Urine Cultures. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1981, 14, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, R.; Dogan, H.S.; Hoebeke, P.; Kočvara, R.; Nijman, R.J.M.; Radmayr, C.; Tekgül, S. Urinary Tract Infections in Children: EAU/ESPU Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaleque, M.; Akter, S.; Akhter, H.; Khan, S.I.; Begum, A. Analysis of Diarrheagenic Potential of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolates in Dhaka, Bangladesh. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2017, 11, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S Ribosomal DNA Amplification for Phylogenetic Study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The Neighbor-Joining Method: A New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for Inferring Very Large Phylogenies by Using the Neighbor-Joining Method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI-M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st Edition, CLSI Document m100. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2022. Available online: https://clsi.org/media/z2uhcbmv/m100ed31_sample.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Bauer, A.W.; Kirby, W.M.M.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing by a Standardized Single Disk Method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Lucy, I.B. Conventional Methods, and Future Trends in Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashef, N.; Djavid, G.E.; Shahbazi, S. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of Community-Acquired Uropathogens in Tehran, Iran. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2010, 4, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, D.; Saxena, R.S. Distribution and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Bacterial Pathogens Causing Urinary Tract Infection in Urban Community of Meerut City, India. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 749629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, H.E.; Jugo, M.B.; Macan, A.; Visser, M.; Hidalgo, M.; Maccallini, G.C. Frequency and Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Urinary Pathogens in Male Outpatients in Argentina. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taye, S.; Getachew, M.; Desalegn, Z.; Biratu, A.; Mubashir, K. Bacterial Profile, Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern and Associated Factors among Pregnant Women with Urinary Tract Infection in Goba and Sinana Woredas, Bale Zone, Southeast Ethiopia. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Bashir, K.; Idrees, M.; Ullah, A.; Hassan, N.; Khan, S.; Nasir, B.; Nadeem, T.; Ahsan, H.; Khan, M.I.; et al. Phylogenetic Analysis and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile of Uropathogens. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Qu, S.; Wang, H.; Yi, F. Disease Burden and Long-Term Trends of Urinary Tract Infections: A Worldwide Report. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 888205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.Y.; Rocheleau, C.M.; Howley, M.M.; Chiu, S.K.; Arnold, K.E.; Ailes, E.C.; National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Characteristics of Women with Urinary Tract Infection in Pregnancy. J. Women’s Health 2021, 30, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, L.; Jacob, L.; AlAwadhi, R.; Yahya, L.O.; Catroon, K.M.; Soundararajan, L.P.; Wani, S.; Alabadla, S.; Hussein, Y.A.; Yahya, L. Urinary Tract Infection in Pregnancy and Its Effects on Maternal and Perinatal Outcome: A Retrospective Study. Cureus 2022, 14, e21500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Khan, S.N.; Ali, N.; Rehman, M.U.; Ali, I. Prevalence and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Uropathogens in Outpatients at a Tertiary Care Hospital. New Microbes New Infect. 2020, 36, 100716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicar, E.K.; Acquah, S.E.K.; Wallana, W.; Kuugbee, E.D.; Osbutey, E.K.; Aidoo, A.; Acheampong, E.; Mensah, G.I. Urinary Tract Infection and Associated Factors among Pregnant Women Receiving Antenatal Care at a Primary Health Care Facility in the Northern Region of Ghana. Int. J. Microbiol. 2023, 2023, 3727265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Emergency: Women and Girls Living in Pakistan Flood Zone Suffering from Urinary Tract Infections and Reproductive Complications in Part Due to Lack of Clean Water, Sanitation and Hygiene—WaterAid. 2022. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/pakistan/climate-emergency-women-and-girls-living-pakistan-flood-zone-suffering-urinary-tract-infections-and-reproductive-complications-part-due-lack-clean-water-sanitation-and-hygiene-wateraid (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Azhar, A.; Amir, F.; Shakeel, A.; Ali, S.H. A Rising Threat of Urinary Tract Infections among the Flood-Affected Women of Pakistan: Challenges and Recommendations. Med. Confl. Surviv. 2023, 39, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humayun, T.; Iqbal, A. The Culture and Sensitivity Pattern of Urinary Tract Infections in Females of Reproductive Age Group. Ann. Pak. Inst. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Jian, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; He, L. Staphylococcus Aureus ST1 Promotes Persistent Urinary Tract Infection by Highly Expressing the Urease. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1101754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, A.; Giske, C.G.; Ternhag, A. The Relative Importance of Staphylococcus Saprophyticus as a Urinary Tract Pathogen: Distribution of Bacteria among Urinary Samples Analysed during 1 Year at a Major S Wedish Laboratory. Apmis 2013, 121, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, H.; Takahashi, S.; Ishikawa, K.; Yasuda, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Uehara, S.; Hamasuna, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Minamitani, S.; Watanabe, A. Nationwide Surveillance of Bacterial Pathogens from Patients with Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis Conducted by the Japanese Surveillance Committee during 2009 and 2010: Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Saprophyticus. J. Infect. Chemother. 2013, 19, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raz, R.; Colodner, R.; Kunin, C.M. Who Are You—Staphylococcus Saprophyticus? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Hasan, F.; Hussain, S.; Shah, A.A. Prevalence of Multi Drug Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii in the Clinical Samples from Tertiary Care Hospital in Islamabad, Pakistan. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 29, 1253. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Alnour, T.M.S.; Shakurfo, O.M.; Aburass, M.M. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern of Bacterial Strains Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infection in Messalata Central Hospital, Libya. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.A.; kamil Alhameedawi, A.; Muhamad, S.M.S.G.; Taha, Z. Prevalence of Multi-Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Children with Urinary Tract Infection from Baghdad, Iraq. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2022, 50, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, T.; Mekonnen, Y.; Ayenew, Z.; Fentaw, S.; Biazin, H. Bacterial Uropathogens and Burden of Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern in Urine Specimens Referred to Ethiopian Public Health Institute. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfa, T.; Baye, Y.; Sisay, M.; Amare, F.; Gashaw, T. Bacterial Uropathogens and Susceptibility Testing among Patients Diagnosed with Urinary Tract Infections at Hiwot Fana Specialized University Hospital, Eastern Ethiopia. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 20503121211001160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; El-Gamal, M.S.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Salem, S.S. Isolation, Identification and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Urinary Tract Infection Bacterial Isolates. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2021, 10, 2820–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, W.S.; Ziganshina, E.E.; Shagimardanova, E.I.; Gogoleva, N.E.; Ziganshin, A.M. Comparison of Intestinal Bacterial and Fungal Communities across Various Xylophagous Beetle Larvae (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.S.; Das, A.P. Molecular Identification of Multi Drug Resistant Bacteria from Urinary Tract Infected Urine Samples. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 98, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerurkar, A.; Solanky, P.; Naik, S.S. Bacterial Pathogens in Urinary Tract Infection and Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern. J. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 21, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, D.A.; Wasim, S.; Abdullah, F.E. Antibiotic Resistance Pattern of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated from Urine Samples of Urinary Tract Infections Patients in Karachi, Pakistan. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 31, 341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Age Group | Male | Patient % | Female | Patient % | Total | Total % | p = Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5–15 | 8 | 15.09 | 12 | 13.04 | 20 | 13.79 | 0.114 |
| 16–25 | 9 | 16.98 | 20 | 21.74 | 29 | 20 | |
| 26–35 | 5 | 9.43 | 22 | 23.91 | 27 | 18.62 | |
| 36–45 | 11 | 20.75 | 9 | 9.78 | 20 | 13.79 | |
| 46–55 | 4 | 7.55 | 11 | 11.96 | 15 | 10.34 | |
| 56–65 | 12 | 22.64 | 11 | 11.96 | 23 | 15.86 | |
| 66–75 | 4 | 7.55 | 7 | 7.61 | 11 | 7.59 | |
| Total | 53 | 36.55 | 92 | 63.45 | 145 | 100 |
| No. of Isolates | Bacteria | Colony | Gram Staining | Catalase | Coagulase | Oxidase | Sulfide | Indole | Motility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33 | K. pneumoniae | Yellow to whitish | −ve | +ve | −ve | −ve | −ve | −ve | −ve |
| 23 | E. coli | Yellow opacity | −ve | +ve | −ve | −ve | −ve | +ve | +ve |
| 09 | P. aeruginosa | yellow, green to blue | −ve | +ve | −ve | +ve | −ve | −ve | +ve |
| 08 | S. aureus | Pale Yellow | +ve | +ve | +ve | −ve | −ve | −ve | −ve |
| 06 | P. mirabilis | Pale or colorless | −ve | +ve | −ve | −ve | +ve | −ve | +ve |
| 04 | S. saprophyticus | Cream to white colonies | +ve | +ve | −ve | −ve | +ve | −ve | −ve |
| S. No. | Bacteria | No. of Isolates | NCBI Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | K. pneumoniae | 10 | OM978266-OM978275 |
| 2 | E. coli | 10 | OM967345-OM967349, OM977110-OM977114 |
| 3 | P. aeruginosa | 05 | ON038592-ON038596 |
| 4 | S. aureus | 05 | ON038597-ON038601 |
| 5 | P. mirabilis | 02 | ON038602-ON038603 |
| S No. | Name of Pathogen | No. of Isolates | Percentage | Male | Female | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Percentage | Positive | Percentage | ||||
| 1 | K. pneumonia | 33 | 39.76 | 11 | 40.74 | 22 | 39.28 |
| 2 | E. coli | 23 | 27.71 | 6 | 22.22 | 17 | 30.35 |
| 3 | P. aeruginosa | 9 | 10.84 | 4 | 14.80 | 5 | 8.92 |
| 4 | Proetus mirabilis | 6 | 7.23 | 2 | 7.40 | 4 | 7.14 |
| 5 | S. aureus | 8 | 9.64 | 3 | 11.11 | 5 | 8.92 |
| 6 | S. saprophyticus | 4 | 4.82 | 1 | 3.70 | 3 | 5.35 |
| Antibiotics | Character | Gram-Negative Bacteria | Gram-Positive Bacteria | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K. pneumoniae | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | P. mirabilis | S. aureus | S. saprophyticus | ||
| Ciprofloxacin | Susceptibility | 6% | 0% | 22.20% | 33.30% | 50% | 25% |
| Resistance | 94% | 100% | 77.80% | 77.80% | 50% | 75% | |
| Cefuroxime | Susceptibility | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | - | - |
| Resistance | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | - | - | |
| Gentamicin | Susceptibility | 9% | 26% | 11.10% | 0% | 50% | 50% |
| Resistance | 91% | 74% | 91.90% | 100% | 50% | 50% | |
| Clindamycin | Susceptibility | - | - | - | - | 0% | 0% |
| Resistance | - | - | - | - | 100% | 100% | |
| Cefotaxime | Susceptibility | 33.30% | 43.40% | 0% | 0% | - | - |
| Resistance | 66.70% | 56.60% | 100% | 100% | - | - | |
| Fosfomycin | Susceptibility | 78.70% | 78.20% | 22.20% | 100% | 75% | 50% |
| Resistance | 21.30% | 22.80% | 77.80% | 0% | 25% | 50% | |
| Tazobactam | Susceptibility | 57.50% | 56.50% | 66.60% | 50% | - | - |
| Resistance | 42.50% | 43.50% | 33.40% | 50% | - | - | |
| Penicillin G | Susceptibility | - | - | - | - | 37.50% | 50% |
| Resistance | - | - | - | - | 37.50% | 50% | |
| Imipenem | Susceptibility | 100% | 100% | 77.70% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Resistance | 0% | 0% | 22.30% | 0% | 0% | 0% | |
| Cephradine | Susceptibility | - | - | - | - | 12.50% | 50% |
| Resistance | - | - | - | - | 87.50% | 50% | |
| Meropenem | Susceptibility | 69.60% | 74% | 44.40% | 83.40% | 87.50% | 75% |
| Resistance | 30.40% | 26% | 55.60% | 16.60% | 12.50% | 25% | |
| Nitrofurantoin | Susceptibility | 42.40% | 78.20% | 0% | 33.30% | - | - |
| Resistance | 57.60% | 21.80% | 100% | 66.70% | - | - | |
| Lincomycin | Susceptibility | - | - | - | - | 0% | 0% |
| Resistance | - | - | - | - | 100% | 100% | |
| Amikacin | Susceptibility | 48.40% | 43.40% | 88.80% | 50% | 75% | 50% |
| Resistance | 51.60% | 56.60% | 11.20% | 50% | 25% | 50% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.A.; Rahman, A.U.; Khan, B.; Al-Mijalli, S.H.; Alswat, A.S.; Amin, A.; Eid, R.A.; Zaki, M.S.A.; Butt, S.; Ahmad, J.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance Profiling and Phylogenicity of Uropathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infections. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101508
Khan MA, Rahman AU, Khan B, Al-Mijalli SH, Alswat AS, Amin A, Eid RA, Zaki MSA, Butt S, Ahmad J, et al. Antibiotic Resistance Profiling and Phylogenicity of Uropathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infections. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(10):1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101508
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Muhammad Ajmal, Atta Ur Rahman, Bakhtawar Khan, Samiah Hamad Al-Mijalli, Amal S. Alswat, Aftab Amin, Refaat A. Eid, Mohamed Samir A. Zaki, Sadia Butt, Jamshaid Ahmad, and et al. 2023. "Antibiotic Resistance Profiling and Phylogenicity of Uropathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infections" Antibiotics 12, no. 10: 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101508
APA StyleKhan, M. A., Rahman, A. U., Khan, B., Al-Mijalli, S. H., Alswat, A. S., Amin, A., Eid, R. A., Zaki, M. S. A., Butt, S., Ahmad, J., Fayad, E., & Ullah, A. (2023). Antibiotic Resistance Profiling and Phylogenicity of Uropathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infections. Antibiotics, 12(10), 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101508







