Complementary Activities of Host Defence Peptides and Antibiotics in Combating Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria
Abstract
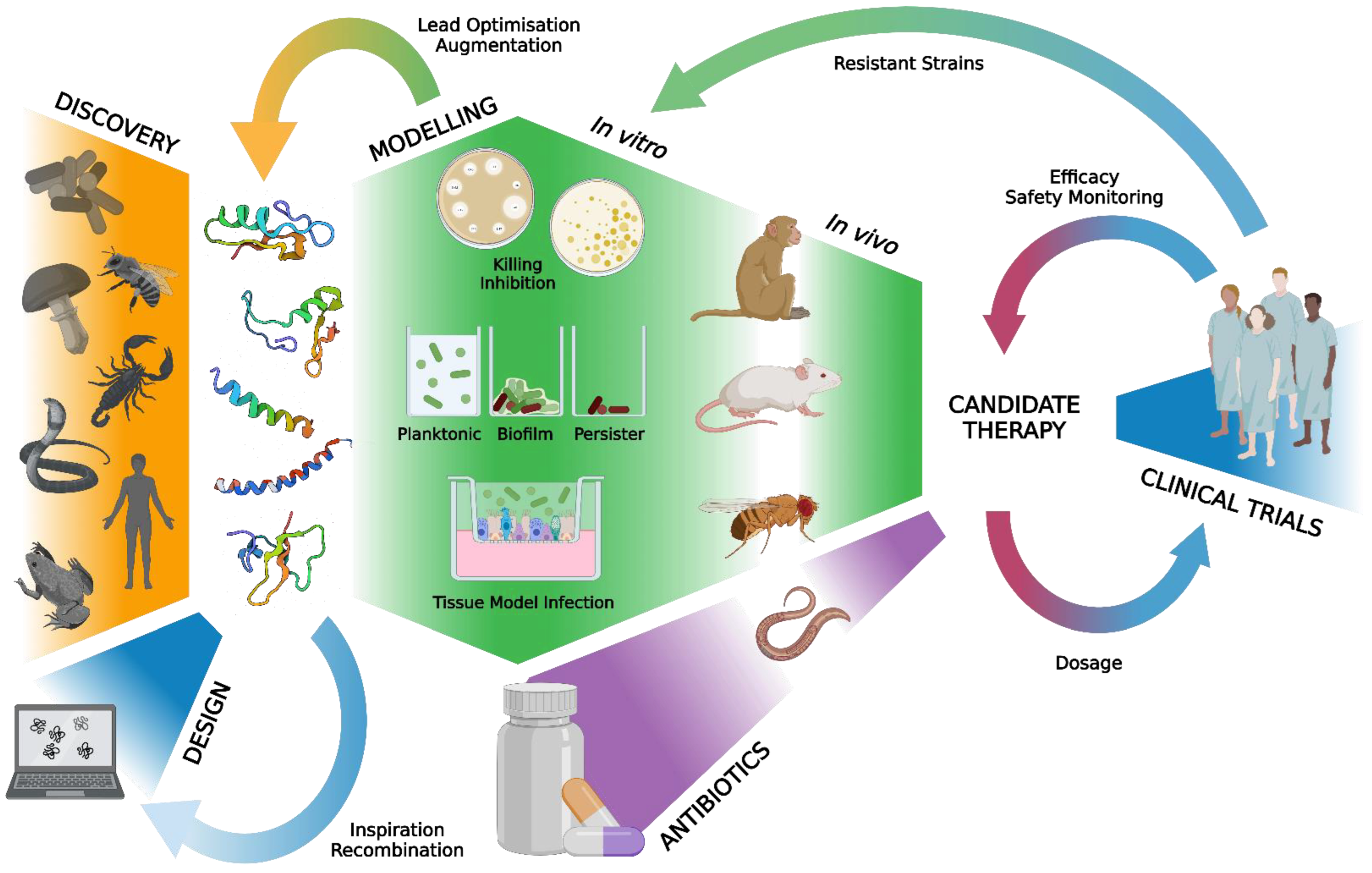
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.4. Data Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial HDPs
3.2. Fungal HDPs
3.3. Plant HDPs
3.4. Invertebrate HDPs
3.5. Vertebrate HDPs
3.6. De Novo HDPs
| Kingdom: Bacteria Phylum | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Bacillota | Bacillus subtilis | p138c | Efm Efs Sa | Efm Efs Sa | Sa | Efm Efs Sa | [34] | ||||||||||||
| Efm Efs | |||||||||||||||||||
| Brevibacillus sp. | Laterosporulin10 | Mt | [35] | ||||||||||||||||
| Enterococcus durans | Durancin 61A | Sa | Efm Str | [36] | |||||||||||||||
| Cd Ec Str | Cd Sa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Efm | Ec | ||||||||||||||||||
| Enterococcus faecium | L12 | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | [37] | ||||||||||||
| Lactococcus lactis | Nisin | Efm Efs | Efm Efs | Efm Efs Sa | [38] | ||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Bacteria Phylum | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Bacillota | Lactococcus lactis | Nisin | Nisin Z | Pf | Pf | Pf | Pf | Pf | Pf | Pf | [39] | ||||||||
| Lacticin 3147 | Cs Ec | [40] | |||||||||||||||||
| Efm Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bc | |||||||||||||||||||
| ST | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ltnα/β | Ec | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ec | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pediococcus spp. | Pediocin PA-1/AcH | Pf | Pf | Pf | Pf | Pf | Pf | Pf | [39] | ||||||||||
| Campylobacterota | Helicobacter pylori | HP (2–20) | Pa | Pa | [41,42] | ||||||||||||||
| HP (4–16) | LHP7 | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | [43] | |||||||||||
| Pseudomonadota | Achromobacter spp. | Cyclic Dipeptides | Bs Efm Kp Pa Pm Pv Sa Se Sf ST | [44] | |||||||||||||||
| Bs Efm Kp Pa Pm Pv Sa Se Sf ST | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Fungi Division | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Ascomycota | Pseudoplectania nigrella | Plectasin | Ec | Ec | [45] | ||||||||||||||
| Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | [43] | |||||||||||||
| LHP7 | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | |||||||||||||
| Plectasin NZ2114 | Efs | Efs | Efs | [46] | |||||||||||||||
| Efs | Efs | ||||||||||||||||||
| Plantae Order | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ericales | Impatiens balsamina | Ib-AMP4 | Efs | Efs | [49] | ||||||||||||||
| Kp | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fabales | Pisum sativum | NuriPep 1653 | Ab | [50] | |||||||||||||||
| Animalia Phylum Order | |||||||||||||||||||
| Annelida Sedentaria | Arenicola marina | Arenicin-1 | Ec Efm Pa Sa Se | Ec Efm Pa Sa Se | Ec Pa Sa Se | [53] | |||||||||||||
| Efm | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ec Pa Sa | Ec Pa Sa | Pa Sa | Sa | Ec Pa Sa | Ec Pa Sa | Ec Sa | Ec | Ec Pa Sa | [54] | ||||||||||
| Ec Pa | Pa Sa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ec | Pa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Arthropoda Hymenoptera | Apis mellifera | Melittin | Ab Pa | Pa | Ab | Ab | [55] | ||||||||||||
| Hecate | Sa | [56] | |||||||||||||||||
| MelitAP-27 | Pa | Sa | Pa Sa | Sa | Sa | [57] | |||||||||||||
| Sa | Pa | Pa | |||||||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa Sa | Sa | Sa | ||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Arthropoda Hymenoptera | Apis mellifera | Melittin | CM11 | Ab Ec Sa | Pa | Ab Kp | Ec Sa | Sa | [58] | ||||||||||
| Kp Pa | Ab Ec Kp ST | Ab Ec Kp Pa Sa | Ab Kp ST | ||||||||||||||||
| Hemiptera | Podisus maculiventris | Linear Thanatin | Ec | [59] | |||||||||||||||
| Coleoptera | Copris tripartitus | Coprisin | Efm Pa | Ec Efm Pa Sa Sm | Ec Efm Pa Sa Sm | [60] | |||||||||||||
| Ec Sa Sm | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ec Efm Pa Sa Sm | Ec Efm Pa Sa Sm | Ec Efm Pa Sa Sm | |||||||||||||||||
| Arachnida | Androctonus amoeruxi | AamAP1 | A3 | Sa | Efm Sa | Sa | Sa | [61] | |||||||||||
| Efm Sa | Sa | Efm Sa | Efm Sa | ||||||||||||||||
| Heterometrus petersii | Hp1404 | Sa | [62] | ||||||||||||||||
| Mesobuthus martensii Karsch | BmKn-22 | Pa | [63] | ||||||||||||||||
| Insecta | Hyalophora cecropia | Cecropin A | CAMA-syn | Efs | [65] | ||||||||||||||
| Efs | |||||||||||||||||||
| CM11 | Ab Ec Sa | Pa | Ab Kp | Ec Sa | Sa | [58] | |||||||||||||
| Kp Pa | Ab Ec Kp ST | Ab Ec Kp Pa Sa | Ab Kp ST | ||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Arthropoda Insecta | Aedes aegypti | Cecropin A2 | Pa | [64] | |||||||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Anoplius samariensis | Anoplin | Ec Kp Pa | Ec Kp Pa | [66] | |||||||||||||||
| Anoplin/-RW Dimers | Sa | Ec | [67] | ||||||||||||||||
| FA-anoplin | Ec | Ec Sa | Ec Sa | Sa | [68] | ||||||||||||||
| Sa | Ec | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ec Kp Pa | Ec Kp Pa | [66] | |||||||||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| FA-anoplin Dimers | Ec Kp Pa | Ec Kp Pa | |||||||||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Calliphora vicina | Alloferon-1 | ZL-2 | Ec Kp Pa Sa Se | Ec Pa Se | Ec Kp Pa Sa Se | [69] | |||||||||||||
| Kp Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Vespula lewisii | Mastoparan | Transportan-10 | Efm Efs Sa | [70] | |||||||||||||||
| Xiphosura | Tachypleus gigas | Tachyplesin III | Pa | [71] | |||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Chordata Cypriniformes | Culter alburnus | LEAP-2 | Vh Vp | [73] | |||||||||||||||
| As Ah Va Vc Vh Vp Vv Vs | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ah | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pleuronectiformes | Pleuronectes americanus | Pleurocidin-1 | Ca Ec Pa Sa | Ca Ec Efm Pa Sa | Ca Ec Efm Pa Sa | [72] | |||||||||||||
| Efm | |||||||||||||||||||
| Amphibia | Rana catesbeiana | Ranalexin | Sa Se | [74] | |||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | [75] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Rana chensinensis | Brevinin-2CE | Ec Sa | Ec Sa | Sa | Ec | Ec | [76] | ||||||||||||
| Sa | Sa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Rana temporaria | Temporin G | Sa | [77] | ||||||||||||||||
| Xenopus laevis | Magainin 2 | Efm Efs Sa Mc | [78] | ||||||||||||||||
| CAMA-syn | Efs | [65] | |||||||||||||||||
| Efs | |||||||||||||||||||
| Squamata | Ophiophagus hannah | OH-CATH30 | Pa | Pa | Pa | [79] | |||||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Galliformes | Gallus domesticus | Fowlicidin-3 | Pa | Pa | [100] | ||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Chordata Artiodactyla | Bos taurus | Bactenecin | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | [91] | ||||||||
| Pa | Pa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | |||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | Pa | |||||||||||||||||
| IDR-1018 | Ab Ec Kp Pa | Pa Sa | Ab Pa Sa ST | Pa Sa | [105] | ||||||||||||||
| Ab Ec Kp ST | Ac Ec Kp ST | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sa ST | Ec Kp | Pa | |||||||||||||||||
| Ec Kp | Ab Sa ST | ||||||||||||||||||
| DP7 | Sa | Ab Ec Pa Sa | Pa Sa | Ab Ec Sa | Ab Pa Sa | [106] | |||||||||||||
| Ab Ec Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ab Ec | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pa | Ec | ||||||||||||||||||
| Indolicidin | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | [91] | ||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | |||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Omiganan | Ec Sa | Sa | Sa | Ab | Ab Pa Sa | [107] | |||||||||||||
| Ab Pa | Ab Ec Pa | Ec | |||||||||||||||||
| Ab Pa | Pa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ec | Sa | Ec | |||||||||||||||||
| LHP7 | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | [43] | ||||||||||||
| Ovis aries | Novicidin | Ec Ecl Kp | Ec Ecl Kp | [45] | |||||||||||||||
| Ec Ecl Kp | Ec Ecl Kp | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Chordata Artiodactyla | Capra hircus | Bactenecin | Ab Kp Pa Sa | Ab Sa | Ab Ml Sa | Ec Kp Pa Sa | Sa | Ab Ec Ml Sa | Ec | [93] | |||||||||
| Ab Ml Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ab Ec Kp Ml Sa | Ec Kp Pa | Ab Ec Kp Pa Sa | Ab Ec Kp Pa | Ab Ml Sa | |||||||||||||||
| Ab | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sus domesticus | Protegrin-1 | Ab Ec Kp Ml Pa | Ab Sa | Kp | Kp Pa | Ab Ml Sa | Ab Ec Ml Sa | Ec Ml Sa | |||||||||||
| Ab Ec Ml Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | Ec Kp Pa | Pa | Ab Ec Sa | Ec Kp Pa Sa | Ab | ||||||||||||||
| Ab | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rodentia | Mus musculus | CRAMP | Bc Bs Ec Ml Pp Sa ST Ye | [104] | |||||||||||||||
| ST | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | [95] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ubiquicidin | ZnO@ PEP-MPA | Bs Ec Sa | Sa | [112] | |||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Chordata Primates | Homo sapiens | Cathelicidin | Ab Kp Pa | [84] | |||||||||||||||
| Efs | Efs | [85] | |||||||||||||||||
| Sa | [86] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Efm Efs | Efm Efs | Efm Efs | [87] | ||||||||||||||||
| Sa | [88] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Efm | [89] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | [95] | |||||||||||||||
| Pa Sa Str | [90] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | Pa | [98] | ||||||||||||||||
| Sa | [99] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Se | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa Se | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | [100] | |||||||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | Pa | [101] | ||||||||||||||||
| Pa Sa | [97] | ||||||||||||||||||
| ST | ST | ST | ST | [92] | |||||||||||||||
| Sa | [94] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Chordata Primates | Homo sapiens | Cathelicidin | Ec | Ec | Ec | Ec Pa | Ec Pa | Ec | [96] | ||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | Pa | Ec Pa | Pa | |||||||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | [91] | |||||||||||
| Ml | Ab Ml | Ml | Ab Ec Ml | Ec Ml | [93] | ||||||||||||||
| Ab Ec | Ec | Ab | Ab | ||||||||||||||||
| LL-13/-17 | Sa | [88] | |||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| FK-13-a1/-a7 | Pa Sa | [97] | |||||||||||||||||
| FK-16 | Pa | [103] | |||||||||||||||||
| KR-12-a5 | Pa | Pa | Pa | [98] | |||||||||||||||
| SAAP-148 | Sa | [102] | |||||||||||||||||
| Ab Ec | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ec Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | [99] | ||||||||||||
| Sa Se | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | Sa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| SAAP-276 | Sa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Chordata Primates | Homo sapiens | α-MSH | Ana-10 | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | [111] | |||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | Sa | Sa | Sa | ||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| CXCL14 | CXCL14-C17 a1-3 | Pa | Pa | Pa | [101] | ||||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | Pa | |||||||||||||||||
| tPMP | Efm | [89] | |||||||||||||||||
| RP-1 | Efm | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | Sa | [95] | |||||||||||||||||
| hNP-1 | Efm | [89] | |||||||||||||||||
| Sa | Sa | [95] | |||||||||||||||||
| Ec | Sa | [109] | |||||||||||||||||
| Ml | Ab Ml Sa | Ab Ml Sa | Ab Ec Ml | Sa | [93] | ||||||||||||||
| Ab Ec Sa | Ec | Sa | Ab Ec Ml | ||||||||||||||||
| hNP-4 | Ab Ml Sa | Ab Ml Sa | Ab Ml | Ab Ml | Ml Sa | ||||||||||||||
| Sa | Sa | Ab | |||||||||||||||||
| hBD-1 | Ec | Sa | [109] | ||||||||||||||||
| hBD-2 | Ml | Ab Ml | Ab Ml | Ab Ml | Ab | [93] | |||||||||||||
| Ab | Ml | ||||||||||||||||||
| hPAB-beta | Sa | Sa | Sa | [110] | |||||||||||||||
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | |||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Chordata Primates | Homo sapiens | hBD-3 | Ec | Sa | [109] | ||||||||||||||
| Ab Ec Ml | Ec Ml Sa | Ab Ml Sa | Ab Ec Ml Sa | Sa | [93] | ||||||||||||||
| Ec Ml | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | Ab | Ab | |||||||||||||||||
| Thrombocidin-1 | TC84 | Sa | [99] | ||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Galanin | Transportan-10 | Efm Efs Sa | [70] | ||||||||||||||||
| De novo Class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Peptides | M33 | Ec Pa | [113] | ||||||||||||||||
| Ab Kp | Ab Kp Pa | Ab Kp Pa | Ab Kp | Ab | [114] | ||||||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | Kp | |||||||||||||||||
| UP-5 | Pa | Sa | Pa | Pa Sa | Pa | [115] | |||||||||||||
| Sa | Pa | Sa | Sa | ||||||||||||||||
| M(LLKK)2M | Mb Ms | [116] | |||||||||||||||||
| Mt | |||||||||||||||||||
| ASU014 | Sa | [117] | |||||||||||||||||
| Sa | |||||||||||||||||||
| B2088 | Kp Pa | Kp Pa | Pa | Kp Pa | Pa | Pa | [118] | ||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | Pa | |||||||||||||||||
| ARV1502 | Ec | Bp | [119] | ||||||||||||||||
| A3-APO | Ab | Kp | |||||||||||||||||
| Kp | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kp | Kp | ||||||||||||||||||
| De novo Class | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | ||||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Peptides | WLBU2 | Ab Kp | Ab Kp | Ab Kp | Ab Kp | [120] | |||||||||||||
| HHC-53 | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | [91] | ||||||||||
| Pa | |||||||||||||||||||
| LOP1-5 | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | Pa | |||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | Pa | |||||||||||||||||
| D-enantiomers | DJK-5/-6 | Ab Ec Kp Pa ST | Ab Ec Kp Pa ST | Ec Pa | Pa | [122] | |||||||||||||
| Ab Kp ST | Ab Ec Kp ST | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ab Kp | Ab | Ec | Pa ST | ||||||||||||||||
| Kp | Kp | Kp | [123] | ||||||||||||||||
| Kp | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kp | Kp | Kp | |||||||||||||||||
| Kp | |||||||||||||||||||
| D-RR4 | Ab Pa | [124] | |||||||||||||||||
| Peptidomimetic | Ec Kp Pa | Ec Kp Pa | Kp | [125] | |||||||||||||||
| Antibiotic conjugates | Polybasic Peptide-Levofloxacin | Ec Kp Pa | [126] | ||||||||||||||||
| kW-OBn | Ec Pa Sa Se | [127] | |||||||||||||||||
| De novo Class | Peptide | Derivative | Antibiotic Class | ||||||||||||||||
| AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Oth. | Ref. | |||||
| Antibiotic conjugates | P5 | Pa | [128] | ||||||||||||||||
| P14LRR | Ab Efm Kp Pa Sa Se | [129] | |||||||||||||||||
| Lipidated peptides | BA250-C10 | Pa | Pa | [131] | |||||||||||||||
| Pa | Pa | ||||||||||||||||||
3.7. Summary of Studies into Combinatory Activities of HDPs and Antibiotics against AMR Bacteria
4. Discussion
4.1. Prokaryote HDPs
4.2. HDPs from Plants and Fungi
4.3. HDPs from Invertebrates
4.4. HDPs from Vertebrates
4.5. De Novo HDPs
4.6. Summary of Studies into Combinatory Activities of HDPs and Antibiotics against AMR Bacteria
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. In Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; Wellcome Trust: London, UK, 2016; pp. 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Theuretzbacher, U.; Outterson, K.; Engel, A.; Karlén, A. The Global Preclinical Antibacterial Pipeline. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 18, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, M.A.; Brown, E.D. Drug Repurposing for Antimicrobial Discovery. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, J.M.; Yang, K.; Swanson, K.; Jin, W.; Cubillos-Ruiz, A.; Donghia, N.M.; MacNair, C.R.; French, S.; Carfrae, L.A.; Bloom-Ackerman, Z.; et al. A Deep Learning Approach to Antibiotic Discovery. Cell 2020, 180, 688–702.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.-X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of Plasmid-Mediated Colistin Resistance Mechanism MCR-1 in Animals and Human Beings in China: A Microbiological and Molecular Biological Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mookherjee, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Davidson, D.J. Antimicrobial Host Defence Peptides: Functions and Clinical Potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, B.; Reiling, S.; Zarena, D.; Wang, G. Host Defense Antimicrobial Peptides as Antibiotics: Design and Application Strategies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 38, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbalakshmi, C.; Sitaram, N. Mechanism of Antimicrobial Action of Indolicidin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 160, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardirossian, M.; Grzela, R.; Giglione, C.; Meinnel, T.; Gennaro, R.; Mergaert, P.; Scocchi, M. The Host Antimicrobial Peptide Bac71-35 Binds to Bacterial Ribosomal Proteins and Inhibits Protein Synthesis. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Hafeez, A.; Jiang, X.; Bergen, P.J.; Zhu, Y. Antimicrobial Peptides: An Update on Classifications and Databases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DRAMP Database. Available online: http://dramp.cpu-bioinfor.org/browse/ClinicalTrialsData.php (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Niyonsaba, F.; Someya, A.; Hirata, M.; Ogawa, H.; Nagaoka, I. Evaluation of the Effects of Peptide Antibiotics Human β-Defensins-1/-2 and LL-37 on Histamine Release and Prostaglandin D2 Production from Mast Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Niyonsoba, F.; Ushio, H.; Hara, M.; Yokoi, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Saito, H.; Nagaoka, I.; Ikeda, S.; Okumura, K.; et al. Antimicrobial Peptides Human β-Defensin (hBD)-3 and hBD-4 Activate Mast Cells and Increase Skin Vascular Permeability. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, D.; Miyasaki, K.T.; Lehrer, R.I. Sensitivity of Actinobacillus Actinomycetemcomitans and Capnocytophaga spp. to the Bactericidal Action of LL-37: A Cathelicidin Found in Human Leukocytes and Epithelium. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 15, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisetta, G.; Di Luca, M.; Esin, S.; Florio, W.; Brancatisano, F.L.; Bottai, D.; Campa, M.; Batoni, G. Evaluation of the Inhibitory Effects of Human Serum Components on Bactericidal Activity of Human Beta Defensin 3. Peptides 2008, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieprawska-Lupa, M.; Mydel, P.; Krawczyk, K.; Wójcik, K.; Puklo, M.; Lupa, B.; Suder, P.; Silberring, J.; Reed, M.; Pohl, J.; et al. Degradation of Human Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37 by Staphylococcus Aureus-Derived Proteinases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4673–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Schauber, J.; Coda, A.; Lin, H.; Dorschner, R.A.; Schechter, N.M.; Bonnart, C.; Descargues, P.; Hovnanian, A.; Gallo, R.L. Kallikrein-mediated Proteolysis Regulates the Antimicrobial Effects of Cathelicidins in Skin. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2068–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, C.C.; Greene, C.M.; Smith, S.G.; Levine, R.L.; McCray, P.B.; O’Neill, S.; McElvaney, N.G. Inactivation of Human β-Defensins 2 and 3 by Elastolytic Cathepsins. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gent, M.E.; Ali, M.; Nibbering, P.H.; Kłodzińska, S.N. Current Advances in Lipid and Polymeric Antimicrobial Peptide Delivery Systems and Coatings for the Prevention and Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlongo, J.T.; Waddad, A.Y.; Albericio, F.; de la Torre, B.G. Antimicrobial Peptide Synergies for Fighting Infectious Diseases. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2300472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, R.; Kawano, K.; Yamaoka, Y.; Taniguchi, A.; Yano, Y.; Takasu, K.; Matsuzaki, K. Development of Antimicrobial Peptide–Antibiotic Conjugates to Improve the Outer Membrane Permeability of Antibiotics against Gram-Negative Bacteria. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 2339–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etebu, E.; Arikekpar, I. Antibiotics: Classification and Mechanisms of Action with Emphasis on Molecular Perspectives. Int. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Res. 2016, 4, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Trimble, M.J.; Mlynárčik, P.; Kolář, M.; Hancock, R.E.W. Polymyxin: Alternative Mechanisms of Action and Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, A.; Teimouri, H.; Kolomeisky, A.B. Predicting Antimicrobial Activity for Untested Peptide-Based Drugs Using Collaborative Filtering and Link Prediction. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 3697–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berti, A.; Rose, W.; Nizet, V.; Sakoulas, G. Antibiotics and Innate Immunity: A Cooperative Effort toward the Successful Treatment of Infections. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hao, W.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, J.; Deng, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Antimicrobial Peptides, Conventional Antibiotics, and Their Synergistic Utility for the Treatment of Drug-Resistant Infections. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1377–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doern, C.D. When Does 2 plus 2 Equal 5? A Review of Antimicrobial Synergy Testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4124–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogart, S. SankeyMATIC. A Sankey Diagram Builder for Everyone. 2020. Available online: http://sankeymatic.com (accessed on 25 September 2023).
- Wang, G. Chapter One—Unifying the Classification of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Antimicrobial Peptide Database. In Antimicrobial Peptides; Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 663, pp. 1–18. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- Dubos, R.J. Studies on a Bactericidal Agent Extracted from a Soil Bacillus: I. Preparation of the Agent. Its Activity in Vitro. J. Exp. Med. 1939, 70, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubos, R.J. Studies on a Bactericidal Agent Extracted from a Soil Bacillus: II. Protective Effect of the Bactericidal Agent against Experimental Pieuococcus Infections in Mice. J. Exp. Med. 1939, 70, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, R.; Fernandez, B.; Lacroix, C.; Fliss, I. Anti-Infective Properties of Bacteriocins: An Update. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2947–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, S.; Choi, Y.H.Y.S.; Choi, Y.H.Y.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Cho, S.S.; Yoo, J.C.; Suh, J.W. Antimicrobial Peptide from Bacillus Subtilis CSB138: Characterization, Killing Kinetics, and Synergistic Potency. Int. Microbiol. 2017, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baindara, P.; Singh, N.; Ranjan, M.; Nallabelli, N.; Chaudhry, V.; Pathania, G.L.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, A.; Patil, P.B.; Korpole, S. Laterosporulin10: A Novel Defensin like Class IId Bacteriocin from Brevibacillus sp. Strain SKDU10 with Inhibitory Activity against Microbial Pathogens. Microbiology 2016, 162, 1286–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanchi, H.; Hammami, R.; Gingras, H.; Kourda, R.; Michel, G.; Bergeron, M.G.; Ben Hamida, J.; Ouellette, M.; Fliss, I. Inhibition of MRSA and of Clostridium Difficile by Durancin 61A: Synergy with Bacteriocins and Antibiotics. Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Dai, X.; Li, Y.X.; Wei, R.; An, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Effects of the Antimicrobial Peptide L12 against Multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3337–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumfitt, W.; Salton, M.R.J.; Hamilton-Miller, J.M.T. Nisin, Alone and Combined with Peptidoglycan-Modulating Antibiotics: Activity against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghmouchi, K.; Le Lay, C.; Baah, J.; Drider, D.; Le, C.; Baah, J.; Drider, D. Antibiotic and Antimicrobial Peptide Combinations: Synergistic Inhibition of Pseudomonas Fluorescens and Antibiotic-Resistant Variants. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, L.A.; Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. The Two Peptide Lantibiotic Lacticin 3147 Acts Synergistically with Polymyxin to Inhibit Gram Negative Bacteria. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.Y.; Park, S.N.S.C.; Park, S.N.S.C.; Park, J.Y.; Park, Y.H.Y.; Hahm, J.S.; Hahm, K.S. Antibiotic Activity and Synergistic Effect of Antimicrobial Peptide against Pathogens from a Patient with Gallstones. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 321, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Hahm, J.; Hahm, K.K. Antibiotic Activity of Antimicrobial Peptide against Pseudomonads Isolated from a Patient with Gallstones. Protein Pept. Lett. 2006, 13, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, D.; Teng, D.; Wang, X.; Mao, R.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, W.; Wang, J. Design, Expression and Characterization of the Hybrid Antimicrobial Peptide LHP7, Connected by a Flexible Linker, against Staphylococcus and Streptococcus. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, I.; Kumar, S.N.; Sreerag, R.S.; Nath, V.S.; Mohandas, C. Purification and Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Arginine Derived Cyclic Dipeptides, from Achromobacter Sp. Associated with a Rhabditid Entomopathogenic Nematode against Major Clinically Relevant Biofilm Forming Wound Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soren, O.; Brinch, K.S.; Patel, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Coates, A.; Hu, Y. Antimicrobial Peptide Novicidin Synergizes with Rifampin, Ceftriaxone, and Ceftazidime against Antibiotic-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae In Vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6233–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breidenstein, E.B.M.; Courvalin, P.; Meziane-Cherif, D. Antimicrobial Activity of Plectasin NZ2114 in Combination with Cell Wall Targeting Antibiotics against VanA-Type Enterococcus Faecalis. Microb. Drug Resist. 2015, 21, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaee, H.; Neira Peralta, N.L.; Carvalhais, L.C.; Dennis, P.G.; Schenk, P.M. Plant-Produced Bacteriocins Inhibit Plant Pathogens and Confer Disease Resistance in Tomato. New Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Ali, Z.; Tehseen, M.; Haney, E.F.; Pantoja-Angles, A.; Alshehri, S.; Wang, T.; Clancy, G.J.; Ayach, M.; Hauser, C.; et al. Efficient in Planta Production of Amidated Antimicrobial Peptides That Are Active against Drug-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Reichling, J.; Wink, M. Antibacterial Activity of the Recombinant Antimicrobial Peptide Ib-AMP4 from Impatiens Balsamina and Its Synergy with Other Antimicrobial Agents against Drug Resistant Bacteria. Pharmazie 2013, 68, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, N.M.; Zorgani, A.; Jalowicki, G.; Kerr, A.; Khaldi, N.; Martins, M. Unlocking NuriPep 1653 From Common Pea Protein: A Potent Antimicrobial Peptide to Tackle a Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, B.; Hoffmann, J. The Host Defense of Drosophila Melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 697–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, M.A.; Dostálová, A.; Ceroni, C.; Poidevin, M.; Kondo, S.; Lemaitre, B. Synergy and Remarkable Specificity of Antimicrobial Peptides in Vivo Using a Systematic Knockout Approach. eLife 2019, 8, e44341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Lee, D.G. Synergistic Effect of Antimicrobial Peptide Arenicin-1 in Combination with Antibiotics against Pathogenic Bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolosov, I.A.; Kalashnikov, A.A.; Panteleev, P.V.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Analysis of Synergistic Effects of Antimicrobial Peptide Arenicin-1 and Conventional Antibiotics. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 162, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, R.; Hakemi-Vala, M.; Pashaie, F.; Bevalian, P.; Hashemi, A.; Bagheri, K.P. Highly Synergistic Effects of Melittin with Conventional Antibiotics against Multidrug-Resistant Isolates of Acinetobacter Baumannii and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 25, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinkova, P.; Splichal, Z.; Jimenez, A.M.J.; Haddad, Y.; Mazumdar, A.; Sur, V.P.; Milosavljevic, V.; Kopel, P.; Buchtelova, H.; Guran, R.; et al. Novel Vancomycin–Peptide Conjugate as Potent Antibacterial Agent against Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaaytah, A.; Alnaamneh, A.; Abualhaijaa, A.; Alshari’, N.; Al-Balas, Q. In Vitro Synergistic Activities of the Hybrid Antimicrobial Peptide MelitAP-27 in Combination with Conventional Antibiotics against Planktonic and Biofilm Forming Bacteria. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2016, 22, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, J.; Barjini, K.; Moghaddam, M.; Asadi, A. In Vitro Synergistic Effect of the CM11 Antimicrobial Peptide in Combination with Common Antibiotics against Clinical Isolates of Six Species of Multidrug-Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria. Protein Pept. Lett. 2015, 22, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Fan, H.; Lu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J. Linear Thanatin Is an Effective Antimicrobial Peptide against Colistin-Resistant Escherichia coli in Vitro. Adv. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.S.H.J.; Hong, J.; Lee, D.G.; Hwang, J.H.J.S.; Hwang, J.H.J.S.; Choi, H.; Lee, E.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.G. Synergistic Effect and Antibiofilm Activity between the Antimicrobial Peptide Coprisin and Conventional Antibiotics against Opportunistic Bacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 66, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaaytah, A.; Farajallah, A.; Abualhaijaa, A.; Al-Balas, Q. A3, A Scorpion Venom Derived Peptide Analogue with Potent Antimicrobial and Potential Antibiofilm Activity against Clinical Isolates of Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Positive Bacteria. Molecules 2018, 23, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Meng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, L.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Z. Hp1404, a New Antimicrobial Peptide from the Scorpion Heterometrus Petersii. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teerapo, K.; Roytrakul, S.; Sistayanarain, A.; Kunthalert, D.; Id, D.K. A Scorpion Venom Peptide Derivative BmKn-22 with Potent Antibiofilm Activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Tharmalingam, N.; Liu, Q.; Jayamani, E.; Kim, W.; Fuchs, B.B.; Zhang, R.; Vilcinskas, A.; Mylonakis, E. Synergistic Efficacy of Aedes Aegypti Antimicrobial Peptide Cecropin A2 and Tetracycline against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.W.; Shin, S.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y. Antibacterial Activity and Synergism of the Hybrid Antimicrobial Peptide, CAMA-Syn. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2009, 30, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Liu, T.; Gou, S.; He, Y.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J.; et al. Design and Synthesis of New N-Terminal Fatty Acid Modified-Antimicrobial Peptide Analogues with Potent in Vitro Biological Activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.B.; Huang, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, B.B.; Gou, S.; Zhong, C.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, J.; Wang, R. Design of Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Dimer Analogues with Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity in Vitro and in Vivo by Intermolecular Triazole Bridge Strategy. Peptides 2017, 88, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, N.; Zhong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Gou, S.; Chang, L.; Bao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, J. Effect of N-Methylated and Fatty Acid Conjugation on Analogs of Antimicrobial Peptide Anoplin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Wu, G.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S. ZL-2, a Cathelicidin-Derived Antimicrobial Peptide, Has a Broad Antimicrobial Activity against Gram-Positive Bacteria and Gram-Negative Bacteria in Vitro and in Vivo. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2015, 38, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruczyński, J.; Rusiecka, I.; Turecka, K.; Kozłowska, A.; Alenowicz, M.; Gągało, I.; Kawiak, A.; Rekowski, P.; Waleron, K.; Kocić, I. Transportan 10 Improves the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Vancomycin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirioni, O.; Ghiselli, R.; Silvestri, C.; Kamysz, W.; Orlando, F.; Mocchegiani, F.; Di Matteo, F.; Riva, A.; Łukasiak, J.; Scalise, G.; et al. Efficacy of Tachyplesin III, Colistin, and Imipenem against a Multiresistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Strain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Lee, D.G. Antimicrobial Peptide Pleurocidin Synergizes with Antibiotics through Hydroxyl Radical Formation and Membrane Damage, and Exerts Antibiofilm Activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Cheng, H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Xiong, F.; Xu, W.; Wei, L. Anti-Infective Effects of a Fish-Derived Antimicrobial Peptide against Drug-Resistant Bacteria and Its Synergistic Effects With Antibiotic. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 602412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbois, A.P.; Gemmell, C.G.; Coote, P.J. In Vivo Efficacy of the Antimicrobial Peptide Ranalexin in Combination with the Endopeptidase Lysostaphin against Wound and Systemic Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) Infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P.; Sattar, A.; Graham, S.; Warn, P.A.; Coote, P.J.; House, W.; Park, M.S.; North, L.S.; Manchester, M. MRSA Decolonization of Cotton Rat Nares by a Combination Treatment Comprising Lysostaphin and the Antimicrobial Peptide Ranalexin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Hao, J. In Vitro Synergistic Activities of Antimicrobial Peptide Brevinin-2CE with Five Kinds of Antibiotics against Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Isolates. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casciaro, B.; Loffredo, M.R.; Cappiello, F.; Fabiano, G.; Torrini, L.; Mangoni, M.L. The Antimicrobial Peptide Temporin G: Anti-Biofilm, Anti-Persister Activities, and Potentiator Effect of Tobramycin Efficacy against Staphylococcus Aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnusch, C.J.; Pieters, R.J.; Breukink, E. Enhanced Membrane Pore Formation through High-Affinity Targeted Antimicrobial Peptides. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.A.; Liu, J.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Lee, W.H.; Zhang, Y. Therapeutic Potential of the Antimicrobial Peptide Oh-Cath30 for Antibiotic-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Keratitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3144–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patocka, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Klimova, B.; Wu, Q.; Kuca, K. Antimicrobial Peptides: Amphibian Host Defense Peptides. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 5924–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, E.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Cardoso, M.H.; Santos, N.C.; Franco, O.L.; Cândido, E.S. Snake Venom Cathelicidins as Natural Antimicrobial Peptides. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, F.P.; Gallo, R.L.; Nizet, V. Differing Effects of Exogenous or Endogenous Cathelicidin on Macrophage Toll-like Receptor Signaling. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2009, 87, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nell, M.J.; Tjabringa, G.S.; Wafelman, A.R.; Verrijk, R.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Grote, J.J. Development of Novel LL-37 Derived Antimicrobial Peptides with LPS and LTA Neutralizing and Antimicrobial Activities for Therapeutic Application. Peptides 2006, 27, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Nonejuie, P.; Munguia, J.; Hollands, A.; Olson, J.; Dam, Q.; Kumaraswamy, M.; Rivera, H.; Corriden, R.; Rohde, M.; et al. Azithromycin Synergizes with Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides to Exert Bactericidal and Therapeutic Activity Against Highly Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoulas, G.; Nonejuie, P.; Nizet, V.; Pogliano, J.; Crum-Cianflone, N.; Haddad, F. Treatment of High-Level Gentamicin-Resistant Enterococcus Faecalis Endocarditis with Daptomycin plus Ceftaroline. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4042–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoulas, G.; Moise, P.A.; Casapao, A.M.; Nonejuie, P.; Olson, J.; Okumura, C.Y.M.M.; Rybak, M.J.; Kullar, R.; Dhand, A.; Rose, W.E.; et al. Antimicrobial Salvage Therapy for Persistent Staphylococcal Bacteremia Using Daptomycin plus Ceftaroline. Clin. Ther. 2014, 36, 1317–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.R.; Barber, K.E.; Raut, A.; Rybak, M.J. β-Lactams Enhance Daptomycin Activity against Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus Faecalis and Enterococcus Faecium in in Vitro Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2842–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurko, J.F.; Galega, R.S.; Li, C.; Lee, G.C.; Lee, G.C. Evaluation of LL-37 Antimicrobial Peptide Derivatives Alone and in Combination with Vancomycin against S. Aureus. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakoulas, G.; Bayer, A.S.; Pogliano, J.; Tsuji, B.T.; Yang, S.J.; Mishra, N.N.; Nizet, V.; Yeaman, M.R.; Moise, P.A. Ampicillin Enhances Daptomycin- and Cationic Host Defense Peptide-Mediated Killing of Ampicillin- and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus Faecium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.E.; Dubois, A.V.; Ingram, R.J.; Weldon, S.; Taggart, C.C.; Elborn, J.S.; Tunney, M.M. Activity of Innate Antimicrobial Peptides and Ivacaftor against Clinical Cystic Fibrosis Respiratory Pathogens. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruden, S.; Rieder, A.; Chis Ster, I.; Schwartz, T.; Mikut, R.; Hilpert, K. Synergy Pattern of Short Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides Against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoulas, G.; Kumaraswamy, M.; Kousha, A.; Nizet, V. Interaction of Antibiotics with Innate Host Defense Factors against Salmonella Enterica Serotype Newport. mSphere 2017, 2, e00410-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharkova, M.S.; Orlov, D.S.; Golubeva, O.Y.; Chakchir, O.B.; Eliseev, I.E.; Grinchuk, T.M.; Shamova, O.V. Application of Antimicrobial Peptides of the Innate Immune System in Combination with Conventional Antibiotics—A Novel Way to Combat Antibiotic Resistance? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friberg, C.; Haaber, J.K.; Vestergaard, M.; Fait, A.; Perrot, V.; Levin, B.R.; Ingmer, H. Human Antimicrobial Peptide, LL-37, Induces Non-Inheritable Reduced Susceptibility to Vancomycin in Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakoulas, G.; Okumura, C.Y.; Thienphrapa, W.; Olson, J.; Nonejuie, P.; Dam, Q.; Dhand, A.; Pogliano, J.; Yeaman, M.R.; Hensler, M.E.; et al. Nafcillin Enhances Innate Immune-Mediated Killing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridyard, K.E.; Elsawy, M.; Mattrasingh, D.; Klein, D.; Strehmel, J.; Beaulieu, C.; Wong, A.; Overhage, J. Synergy between Human Peptide LL-37 and Polymyxin B against Planktonic and Biofilm Cells of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, G.; Kim, E.Y.; Shin, S.Y. LL-37-Derived Membrane-Active FK-13 Analogs Possessing Cell Selectivity, Anti-Biofilm Activity and Synergy with Chloramphenicol and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Rajasekaran, G.; Shin, S.Y. LL-37-Derived Short Antimicrobial Peptide KR-12-A5 and Its D-Amino Acid Substituted Analogs with Cell Selectivity, Anti-Biofilm Activity, Synergistic Effect with Conventional Antibiotics, and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppen, B.C.; Mulder, P.P.G.G.; de Boer, L.; Riool, M.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Zaat, S.A.J.J. Synergistic Microbicidal Effect of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides and Teicoplanin against Planktonic and Biofilm-Encased Staphylococcus Aureus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, G.; Shin, S.Y. Fowlicidin-3 Analog with Improved Cell Selectivity Synthesized by Shifting a PXXP Motif from the N-Terminus to a Central Position. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2018, 39, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, G.; Dinesh Kumar, S.; Nam, J.; Jeon, D.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.W.; Park, I.S.; Shin, S.Y. Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Chemokine CXCL14-Derived Antimicrobial Peptide and Its Analogs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gent, M.E.; van der Reijden, T.J.K.; Lennard, P.R.; de Visser, A.W.; Schonkeren-Ravensbergen, B.; Dolezal, N.; Cordfunke, R.A.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Nibbering, P.H. Synergism between the Synthetic Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Peptide (SAAP)-148 and Halicin. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, I.; Said, D.G.; Nubile, M.; Mastropasqua, L.; Dua, H.S. Cathelicidin-Derived Synthetic Peptide Improves Therapeutic Potential of Vancomycin Against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.M.; Briers, Y.; Lamberigts, C.; Steenackers, H.; Robijns, S.; Landuyt, B.; Vanderleyden, J.; Schoofs, L.; Lavigne, R.; Luyten, W.; et al. Evaluation of the Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of Novel CRAMP-Vancomycin Conjugates with Diverse Linkers. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 7477–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reffuveille, F.; De La Fuente-Núñez, C.; Mansour, S.; Hancock, R.E.W. A Broad-Spectrum Antibiofilm Peptide Enhances Antibiotic Action against Bacterial Biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5363–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Fan, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, R.; Yang, L. Synergistic Effects of Antimicrobial Peptide DP7 Combined with Antibiotics against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinchik, E.; Dugourd, D.; Algara, T.; Pasetka, C.; Friedland, H.D. Antimicrobial and Antifungal Activities of a Novel Cationic Antimicrobial Peptide, Omiganan, in Experimental Skin Colonisation Models. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duits, L.A.; Ravensbergen, B.; Rademaker, M.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Nibbering, P.H. Expression of β-Defensin 1 and 2 mRNA by Human Monocytes, Macrophages and Dendritic Cells. Immunology 2002, 106, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolatchiev, A. Antibacterial Activity of Human Defensins against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, W.; Rao, X. A Recombinant Antimicrobial Peptide Inhibits the Growth of Oxacillin-Induced l-Forms of Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumtaz, S.; Behera, S.; Joshi, S.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Efficacy and Toxicity Studies of Novel α-MSH Analogues with Antibiofilm Action and β-Lactam Resensitization Potential against MRSA. ACS Infect. Dis. 2022, 8, 2480–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Chen, D.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y. Versatile Antimicrobial Peptide-Based ZnO Quantum Dots for Invivo Bacteria Diagnosis and Treatment with High Specificity. Biomaterials 2015, 53, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccherini, F.; Falciani, C.; Onori, M.; Scali, S.; Pollini, S.; Rossolini, G.M.; Bracci, L.; Pini, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Levofloxacin-M33 Peptide Conjugation or Combination. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, S.; Brunetti, J.; Sennati, S.; Rossolini, G.M.; Bracci, L.; Pini, A.; Falciani, C. Synergistic Activity Profile of an Antimicrobial Peptide against Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Strains of Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens. J. Pept. Sci. 2017, 23, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaaytah, A.; Qaoud, M.T.; Mohammed, G.K.; Abualhaijaa, A.; Knappe, D.; Hoffmann, R.; Al-Balas, Q. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity of UP-5, an Ultrashort Antimicrobial Peptide Designed Using Only Arginine and Biphenylalanine. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khara, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Ke, X.Y.; Liu, S.; Newton, S.M.; Langford, P.R.; Yang, Y.Y.; Ee, P.L.R. Anti-Mycobacterial Activities of Synthetic Cationic α-Helical Peptides and Their Synergism with Rifampicin. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2032–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainson, J.C.; Daly, S.M.; Triplett, K.; Johnston, S.A.; Hall, P.R.; Diehnelt, C.W. Synthetic Antibacterial Peptide Exhibits Synergy with Oxacillin against MRSA. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshminarayanan, R.; Tan, W.X.; Aung, T.T.; Goh, E.T.L.; Muruganantham, N.; Li, J.; Chang, J.Y.T.; Dikshit, N.; Saraswathi, P.; Lim, R.R.; et al. Branched Peptide, B2088, Disrupts the Supramolecular Organization of Lipopolysaccharides and Sensitizes the Gram-Negative Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otvos, L., Jr.; Ostorhazi, E.; Szabo, D.; Zumbrun, S.D.; Miller, L.L.; Halasohoris, S.A.; Desai, P.D.; Veldt, S.M.I.I.; Kraus, C.N. Synergy Between Proline-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides and Small Molecule Antibiotics Against Selected Gram-Negative Pathogens in Vitro and in Vivo. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedan, S.; Shubair, Z.; Almaaytah, A. Synergism of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptide WLBU2 with Antibacterial Agents against Biofilms of Multi-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii and Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shai, Y.; Oren, Z. From “Carpet” Mechanism to de-Novo Designed Diastereomeric Cell-Selective Antimicrobial Peptides. Peptides 2001, 22, 1629–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente-Núñez, C.; Reffuveille, F.; Mansour, S.C.; Reckseidler-Zenteno, S.L.; Hernández, D.; Brackman, G.; Coenye, T.; Hancock, R.E.W. D-Enantiomeric Peptides That Eradicate Wild-Type and Multidrug-Resistant Biofilms and Protect against Lethal Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infections. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.M.; De La Fuente-Núñez, C.; Baquir, B.; Faria-Junior, C.; Franco, O.L.; Hancock, R.E.W. Antibiofilm Peptides Increase the Susceptibility of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Clinical Isolates to β-Lactam Antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3906–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.F.; Brezden, A.; Mohammad, H.; Chmielewski, J.; Seleem, M.N. A Short D-Enantiomeric Antimicrobial Peptide with Potent Immunomodulatory and Antibiofilm Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Acinetobacter Baumannii. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.R.; Jana, B.; Hansen, A.M.; Nielsen, H.M.; Franzyk, H.; Guardabassi, L. Repurposing Azithromycin and Rifampicin against Gram-Negative Pathogens by Combination with Peptidomimetics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, L.; Domalaon, R.; Brizuela, M.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Polybasic Peptide-Levofloxacin Conjugates Potentiate Fluoroquinolones and Other Classes of Antibiotics against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Amphiphilic Lysine-Ligated Neomycin B Conjugates. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.; Gonçalves, S.; Felício, M.R.; Maturana, P.; Santos, N.C.; Semorile, L.; Hollmann, A.; Maffía, P.C. Synergistic and Antibiofilm Activity of the Antimicrobial Peptide P5 against Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.F.; Brezden, A.; Mohammad, H.; Chmielewski, J.; Seleem, M.N. Targeting Biofilms and Persisters of ESKAPE Pathogens with P14KanS, a Kanamycin Peptide Conjugate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menacho-Melgar, R.; Decker, J.S.; Hennigan, J.N.; Lynch, M.D. A Review of Lipidation in the Development of Advanced Protein and Peptide Therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gier, M.G.; Bauke Albada, H.; Josten, M.; Willems, R.; Leavis, H.; Van Mansveld, R.; Paganelli, F.L.; Dekker, B.; Lammers, J.W.J.; Sahl, H.G.; et al. Synergistic Activity of a Short Lipidated Antimicrobial Peptide (lipoAMP) and Colistin or Tobramycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, T.W.; Schofield, W.B.; Barry, N.A.; Putnam, E.E.; Rundell, E.A.; Trent, M.S.; Degnan, P.H.; Booth, C.J.; Yu, H.; Goodman, A.L. Antimicrobial Peptide Resistance Mediates Resilience of Prominent Gut Commensals during Inflammation. Science 2015, 347, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, K.F.; Herzberg, M.C. Antimicrobial Peptides: Defending the Mucosal Epithelial Barrier. Front. Oral Health 2022, 3, 958480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, C.; Franco, O.L. Advances in the Use of Plants as Potential Biofactories in the Production of Antimicrobial Peptides. Pept. Sci. 2023, 115, e24290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, W.; Lehmbeck, J. Heterologous Expression and Protein Secretion in Filamentous Fungi. In Advances in Fungal Biotechnology for Industry, Agriculture, and Medicine; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 201–219. ISBN 978-1-4419-8859-1. [Google Scholar]
- Needham, A.J.; Kibart, M.; Crossley, H.; Ingham, P.W.; Foster, S.J. Drosophila Melanogaster as a Model Host for Staphylococcus Aureus Infection. Microbiology 2004, 150, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apidianakis, Y.; Rahme, L.G. Drosophila Melanogaster as a Model Host for Studying Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| (A) | Gram-Negative | Total | (B) | Gram-Positive | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acinetobacter baumannii | 20 | Bacillus cereus | 1 | |||
| 50 | 1 | |||||
| 14 | Bacillus subtilis | 1 | ||||
| 7 | 3 | |||||
| Aeromonas hydrophila | 2 | Cutibacterium acnes | 3 | |||
| Aeromonas sobria | 1 | Clostridium dificile | 2 | |||
| Burkholderia pseudomallei | 1 | Enterococcus faecium | 10 | |||
| Cronobacter sakazakii | 1 | 11 | ||||
| Enterobacter cloacae | 2 | 2 | ||||
| 2 | 3 | |||||
| Escherichia coli | 43 | 13 | ||||
| 57 | Enterococcus faecalis | 5 | ||||
| 12 | 10 | |||||
| 1 | 3 | |||||
| 11 | 2 | |||||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 31 | 6 | ||||
| 24 | Mycobacterium bovis | 1 | ||||
| 12 | Micrococcus luteus | 7 | ||||
| 11 | 28 | |||||
| Moraxella catarrhalis | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 80 | Mycobacterium smegmatis | 1 | |||
| 83 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 1 | ||||
| 31 | 1 | |||||
| 24 | Staphylococcus aureus | 65 | ||||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | 14 | 90 | ||||
| Pseudomonas mirabilis | 1 | 25 | ||||
| 1 | 7 | |||||
| Pseudomonas putida | 1 | 42 | ||||
| Pseudomonas vulgaris | 1 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 7 | |||
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium | 6 | 1 | ||||
| 11 | 4 | |||||
| 2 | Staphylococcus faecalis | 1 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | |||||
| 3 | Streptococcus mutans | 2 | ||||
| Vibrio anguillarum | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Vibrio cholerae | 1 | 3 | ||||
| Vibro harveyi | 1 | Streptococcus spp. | 1 | |||
| 1 | 1 | |||||
| Vibro parahaemolyticus | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 1 | ||||||
| Vibrio splendidus | 1 | |||||
| Vibrio vulnificus | 1 | |||||
| Yersinia enterocolitica | 1 |
| FICI Assessment | AG | AM | CP | CS | FQ | GP | ML | PC | PG | PM | PP | RF | TC | Other | Total |
| Synergy | 36 | 23 | 14 | 25 | 33 | 16 | 32 | 47 | 1 | 25 | 0 | 32 | 8 | 12 | 304 |
| Additive | 48 | 14 | 26 | 22 | 59 | 28 | 27 | 43 | 0 | 34 | 0 | 40 | 14 | 16 | 371 |
| Indifferent | 18 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 7 | 13 | 2 | 26 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 106 |
| Antagonistic | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 14 |
| Not Assessed | 17 | 10 | 6 | 10 | 7 | 33 | 4 | 41 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 147 |
| Total | 119 | 55 | 47 | 64 | 109 | 91 | 65 | 157 | 2 | 75 | 5 | 79 | 30 | 44 | 942 |
| Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Order | Origin Species | Peptide | Derivative | Clinical Use | Clinical Trial Phase | DRAMP ID |
| Amphibia | Xenopus laevis | Magainin 2 | Pexiganan | Diabetic foot ulcer infection | III Failed | 18057 |
| Artiodactyla | Bos taurus | Bactenecin | IDR-1 | Immuno-compromised infection | I | 18178 |
| Bactenecin, Indolicidin | IMX942 | Nosocomial infection, chemotherapeutic-induced neutropenia | II | 18152 | ||
| Indolicidin | Omiganan | Rosacea, atopic dermatitis, acne vulgaris, genital warts | III | 18160 | ||
| Sus domesticus | Protegrin-1 | Pneumonia peritoneal infection | - | 18073 | ||
| Iseganan | Ventilator-associated pneumonia, opportunistic infection during radiotherapy | III Failed | 18059 | |||
| Murepavadin | Nosocomial and ventilator-associated pneumonia | III Suspended | 20774 | |||
| Primates | Homo sapiens | Cathelicidin | Venous leg ulcers | I–II | 18084 | |
| AMP60.4Ac | Chronic suppurative otitis media | II | 18161 | |||
| Defensin | Brilacidin | Acute bacterial skin infection | IIb | 18158 | ||
| α-MSH | CZEN-002 | Gram-positive and -negative bacterial and fungal infection | IIb | 18083 | ||
| Modimelanotide | Sepsis, acute post-surgical kidney injury | II | 18164 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lennard, P.R.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Nibbering, P.H. Complementary Activities of Host Defence Peptides and Antibiotics in Combating Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101518
Lennard PR, Hiemstra PS, Nibbering PH. Complementary Activities of Host Defence Peptides and Antibiotics in Combating Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(10):1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101518
Chicago/Turabian StyleLennard, Patrick R., Pieter S. Hiemstra, and Peter H. Nibbering. 2023. "Complementary Activities of Host Defence Peptides and Antibiotics in Combating Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria" Antibiotics 12, no. 10: 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101518
APA StyleLennard, P. R., Hiemstra, P. S., & Nibbering, P. H. (2023). Complementary Activities of Host Defence Peptides and Antibiotics in Combating Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria. Antibiotics, 12(10), 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12101518








