Bioactive Compounds from the Mushroom-Forming Fungus Chlorophyllum molybdites
Abstract
1. Introduction
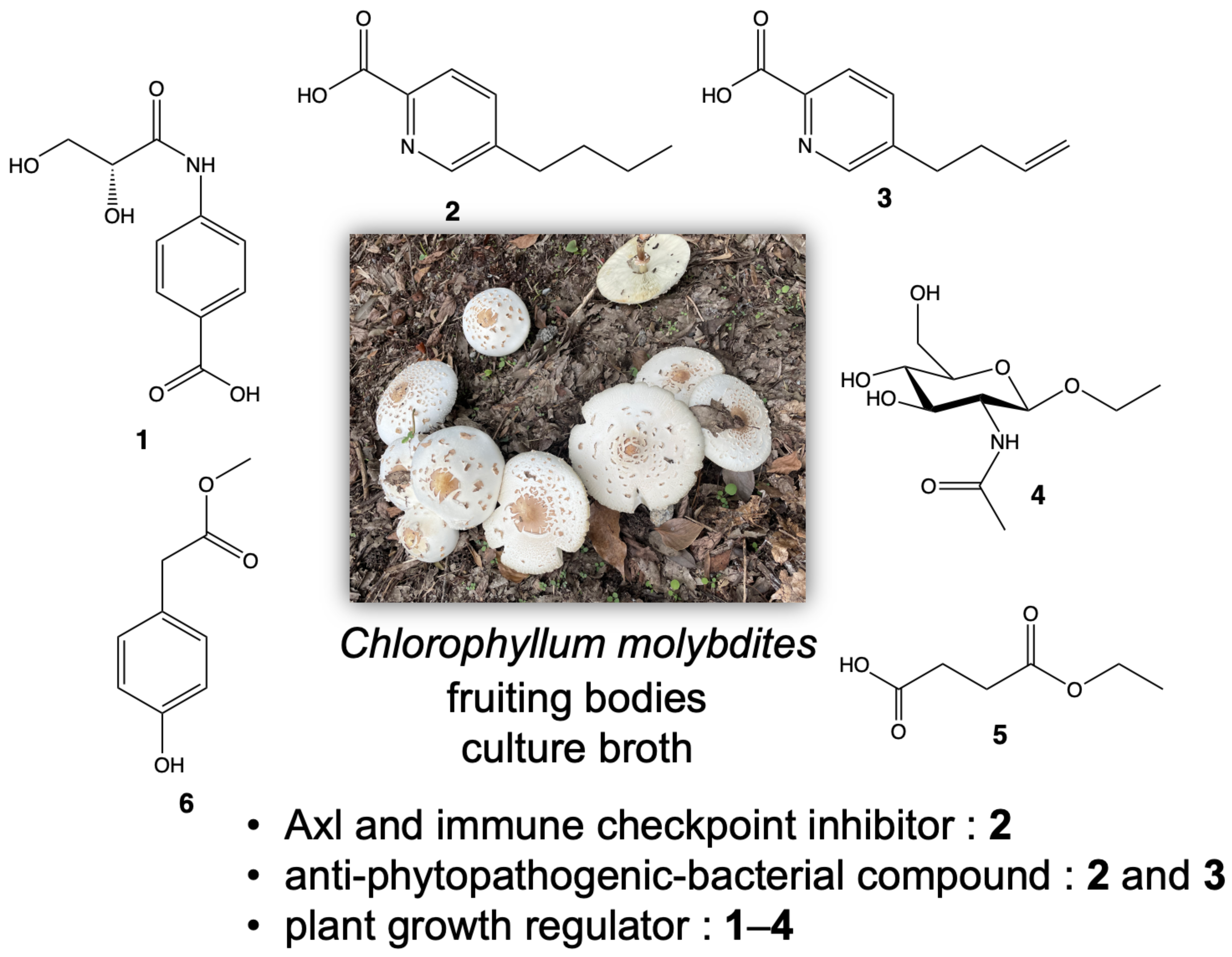
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Axl and Immune Checkpoint Molecule Assay [35]
3.5. Antibacterial Assay [40]
3.6. Plant-Growth-Regulating Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chugh, R.M.; Mittal, P.; Mp, N.; Arora, T.; Bhattacharya, T.; Chopra, H.; Cavalu, S.; Gautam, R.K. Fungal Mushrooms: A Natural Compound With Therapeutic Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 925387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kawagishi, H. Plant growth regulators from mushrooms. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, M. The Fungi: 1, 2, 3…5.1 Million Species? Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassert, J.F.H.; Monaghan, M.T. Phylogenomic insights into the early diversification of fungi. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 3628–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargano, M.L.; Van Griensven, L.J.L.D.; Isikhuemhen, O.S.; Lindequist, U.; Venturella, G.; Wasser, S.P.; Zervakis, G.I. Medicinal mushrooms: Valuable biological resources of high exploitation potential. Plant Biosyst. 2017, 151, 548–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rajhi, A.M.H.; Alawlaqi, M.M.; Abdel Ghany, T.M.; Moawad, H. Amanita sp. from Subtropical Region of Saudi Arabia as a Source of Chitinase Enzyme and its Antifungal Activity. BioRersources 2023, 18, 2928–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.M.; Younis, A.M.; Abdelgany, T.M.; Abdelbary, S. Trends in Assessment of Ganoderma lucidum Methanol extract Against MRSA Infection In Vitro and In Vivo with Nutrition Support. J. Adv. Pharm. Res. 2022, 6, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, H. Chemical studies on bioactive compounds related to higher fungi. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- Park, H.J. Current uses of mushrooms in cancer treatment and their anticancer mechanisms. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10502–10516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.-S.; Guo, J.-J.; Bao, J.-L.; Li, X.-W.; Chen, X.-P.; Lu, J.-J.; Wang, Y.-T. Anti-cancer properties of triterpenoids isolated from Ganoderma lucidum-A review. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2013, 22, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boh, B.; Berovic, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhi-Bin, L. Ganoderma lucidum and its pharmaceutically active compounds. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 2007, 13, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, T.P.; Chanda, W.; Padhiar, A.A.; Batool, S.; LiQun, S.; Zhong, M.; Huang, M. A preclinical evaluation of the antitumor activities of edible and medicinal mushrooms: A molecular insight. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawagishi, H.; Kanao, T.; Inagaki, R.; Mizuno, T.; Shimura, K.; Ito, H.; Hagiwara, T.; Nakamura, T. Formolysis of a potent antitumor (1-6)-β-d-glucan-protein complex from Agaricus blazei fruiting bodies and antitumor activity of the resulting products. Carbohydr. Polym. 1990, 12, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsayal, U.A.; Abdurahman, E.M.; Abubakar, M.S.; Musa, K.Y.; Ambali, S.F.; Jahun, M.B. Fungi as a potential source of antimalarial agents. Niger. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 8, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Bala, N.; Aitken, E.; Fechner, N.; Cusack, A.; Steadman, K.J. Evaluation of antibacterial activity of Australian basidiomycetous macrofungi using a high-throughput 96-well plate assay. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Ikuta, M.; Arihara, S.; Matsumura, E.; Katayama, S. Two new steroidal derivatives from the fruit body of Chlorophyllum molybdites. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1030–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, T.; Inoue, H.; Kusano, G.; Oshima, Y. Lepiotins A and B, new alkaloids from the mushrooms, Macrolepiota neomastoidea and Chlorophyllum molybdites. Heterocycles 1998, 47, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Tokumitsu, N.; Saikawa, Y.; Nakata, M.; Asano, J.; Miyairi, K.; Okuno, T.; Konno, K.; Hashimoto, K. Molybdophyllysin, a toxic metalloendopeptidase from the tropical toadstool, Chlorophyllum molybdites. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6583–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Umehara, K.; Dohra, H.; Murata, T.; Usui, T.; Kawagishi, H. Purification, characterization, and sugar binding specificity of an N-glycolylneuraminic acid-specific lectin from the mushroom Chlorophyllum molybdites. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 53048–53055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.N. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.; Pelosof, L.; Lemery, S.; Gong, Y.; Goldberg, K.B.; Farrell, A.T.; Keegan, P.; Veeraraghavan, J.; Wei, G.; Blumenthal, G.M. Systematic Review of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Oncology: From Personalized Medicine to Public Health. Oncologist 2021, 26, e1786–e1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, X. Study and analysis of antitumor resistance mechanism of PD1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blocker. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 8086–8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Peng, D.; Chen, Z.; Sehdev, V.; Belkhiri, A. ABL regulation by AXL promotes cisplatin resistance in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 73, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Greger, J.; Shi, H.; Liu, Y.; Greshock, J.; Annan, R.; Halsey, W.; Sathe, G.M.; Martin, A.M.; Gilmer, T.M. Novel mechanism of lapatinib resistance in HER2-positive breast tumor cells: Activation of AXL. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6871–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meer, J.H.; Van der Poll, T.; Van’t Veer, C. TAM receptors, Gas6, and protein S: Roles in inflammation and hemostasis. Blood 2014, 123, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berclaz, G.; Altermatt, H.J.; Rohrbach, V.; Kieffer, I.; Dreher, E.; Andres, A.C. Estrogen dependent expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase axl in normal and malignant human breast. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Kim, P.S. A high-affinity human PD-1/PD-L2 complex informs avenues for small-molecule immune checkpoint drug discovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24500–24506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, K.M.; Grudnik, P.; Magiera, K.; Dömling, A.; Dubin, G.; Holak, T.A. Structural biology of the immune checkpoint receptor PD-1 and its ligands PD-L1/PD-L2. Structure 2017, 25, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Ota, K.; Kawahara, A.; Hattori, S.; Iwama, E.; Harada, T. Association of PD-L1 overexpression with activating EGFR mutations in surgically resected nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2014, 25, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colavito, S.A. AXL as a target in breast cancer therapy. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 5291952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aehnlich, P.; Powell, R.M.; Peeters, M.J.W.; Rahbech, A.; Thor Straten, P. TAM receptor inhibition-implications for cancer and the immune system. Cancers 2021, 13, 1195–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, S.H.; Brunton, V.G.; Unciti-Broceta, A. AXL inhibitors in cancer: A medicinal chemistry perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3593–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodajima, M.; Choi, J.H.; Kondo, M.; CN, D.A.-G.; Toda, M.; Yasuma, T.; Gabazza, E.C.; Miwa, Y.; Shoda, C.; Lee, D.; et al. Axl, immune checkpoint molecules and HIF inhibitors from the culture broth of Lepista luscina. Molecules 2022, 27, 8925–8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crous, P.W.; Rossman, A.Y.; Aime, M.C.; Allen, W.C.; Burgess, T.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Castlebury, L.A. Names of Phytopathogenic Fungi: A Practical Guide. Phytopathology 2021, 111, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghany, T.M. Fungal leaf spot of maize: Pathogen isolation, identification and host biochemical characterization. Mycopath 2012, 10, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Abd EL-Ghany, T.M.; Eman, W. EI-Taher; EI-Sheikh, H.H. Efficacy of fungal Rust Disease on Willow Plant in Egypt. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2009, 3, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar]
- Riyaz, M.; Shah, R.A.; Sivasankaran, K. Pesticide Residues: Impacts on Fauna and the Environment. In Biodegradation Technology of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants; InterchOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Ogura, Y.; Kobori, H.; Choi, J.-H.; Hirai, H.; Takikawa, Y.; Kawagishi, H. Anti-phytopathogenic bacterial fatty acids from the mycelia of the edible mushroom Agaricus blazei. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2022, 86, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couch, H.B. Diseases of Turfgrasses, 3rd ed.; Krieger: Malabar, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchinson, A. Fairy chemicals. Nature 2014, 505, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, H. Are fairy chemicals a new family of plant hormones? Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B 2019, 95, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Miwa, Y.; Wu, J.; Shoda, C.; Jeong, H.; Kawagishi, H.; Tsubota, K.; Kurihara, T. A Fairy Chemical Suppresses Retinal Angiogenesis as a HIF Inhibitor. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoshima, H.; Ito, S.; Ibuki, R.; Kawagishi, H. Potential of Fairy Chemicals as Functional Cosmetic Ingredients: Effect of 2-Aza-8-Oxohypoxanthine on Skin Lightness. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2022, 24, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, C.; Yasuma, T.; D’Alessandro-Gabazza, C.N.; Toda, M.; Fridman D’Alessandro, V.; Inoue, R.; Fujimoto, H.; Kobori, H.; Tharavecharak, S.; Takeshita, A.; et al. The Fairy Chemical Imidazole-4-carboxamide Inhibits the Expression of Axl, PD-L1, and PD-L2 and Improves Response to Cisplatin in Melanoma. Cells 2022, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A.; Gimpel, J.; Lohmar, E. Über enzymanalog gebaute Polymere, III. Zur Synthese von polymerisierbaren D-Glycerinsäurederivaten. Chem. Ber. 1974, 107, 3364–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, R.; Evidente, A.; Cutignano, A.; Vurro, M.; Zonno, M.C.; Bottalico, A. Fusaric and 9,10-dehydrofusaric acids and their methyl esters from Fusarium nygamai. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.; Zilliken, F. Novel growth faxtors for Lactobacillus bifidus var pennsylvanicus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1965, 110, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, H. Trametes versicolor (L.) mushrooms liquefaction in supercritical solvents: Effects of operating conditions on product yields and chromatographic characterization. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 131, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklingf, F.; Malaisse-Lagaew, F.; Malaisse, W.J. Insulinotropic action of novel succinic acid esters. Pharmacol. Res. 1996, 33, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödecke, J.; König, W.A. Odorous compounds from the fungus Gloeophyllum odoratum. Flavour Fragr. J. 2000, 15, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Li, W.; Wang, J. A novel and other bioactive seondary metabolites from a marine fungus Penicillium oxalicum 0312F1. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérombelon, M.C.M. Potato diseases caused by soft rot erwinias: An overview of pathogenesis. Plant Pathol. 2002, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowski, R.; Pérombelon, M.C.M.; van Veen, J.A.; van der Wolf, J.M. Control of blackleg and tuber soft rot of potato caused by Pectobacterium and Dickeya species: A review. Plant Pathol. 2011, 60, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, E.; Park, T.H.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Ryu, S.; Oh, C.S.; Rhee, S.; Kim, D.H.; Park, B.S.; Heu, S. Characterization of a new bacteriocin, Carocin D, from Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum Pcc21. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7541–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, I.K.; Bell, K.S.; Holeva, M.C.; Birch, P.R.J. Soft rot erwiniae: From genes to genomes. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2003, 4, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, J.; Genin, S.; Magori, S.; Citovsky, V.; Sriariyanum, M.; Ronald, P.; Dow, M.; Verdier, V.; Beer, S.V.; Machado, M.A.; et al. Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, M.; Macdonald, J.; Liu, P.; Weselowski, B.; Yuan, Z.C. Clavibacter michiganensis ssp. michiganensis: Bacterial canker of tomato, molecular interactions and disease management. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 2036–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.J.; Graves Gillaspie, A., Jr.; Vidaver, A.K.; Harris, R.W. Clavibacter: A new genus containing some phytopathogenic coryneform bacteria, Including Clavibacter xyli subsp. xyli sp. nov., subsp. nov. and Clavibacter xyli subsp. cynodontis subsp. nov., Pathogens that cause ratoon stunting disease of sugarcane and bermudagrass stunting disease. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1984, 34, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartemann, K.H.; Kirchner, O.; Engermann, J.; Gräfen, I.; Eichenlaub, R.; Burger, A. Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis: First steps in the understanding of virulence of a Gram-positive phytopathogenic bacterium. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 106, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Ohata, K. New bacterial diseases of rice (brown stripe and grain rot). Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 1956, 21, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Mondal, K.K.; Ghoshal, T.; Kulshreshtha, A.; Sreenayana, B.; Amrutha Lakshmi, M.; Mrutyunjaya, S.; Rashmi, E.R.; Kalaivanan, N.S.; Mani, C. Genetic and pathogenic diversity analysis of Burkholderia glumae strains from Indian hot spot regions causing bacterial panicle blight of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Trop Plant Pathol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
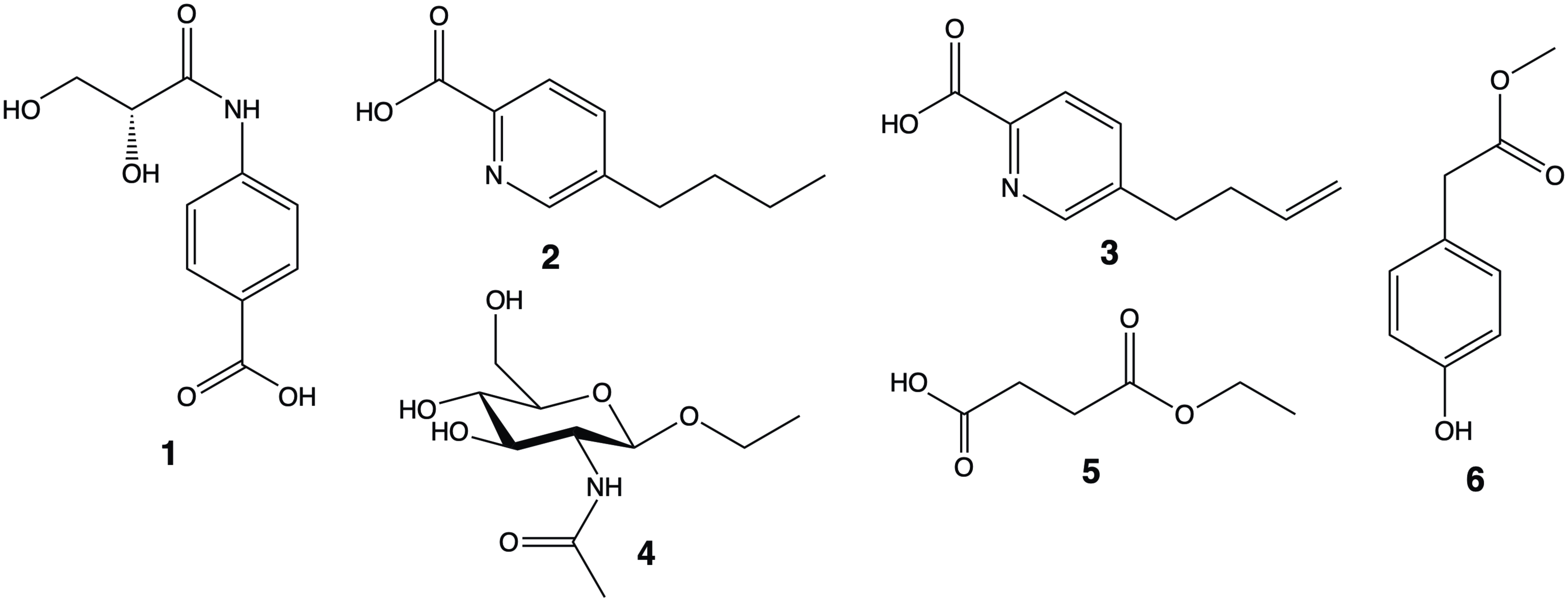
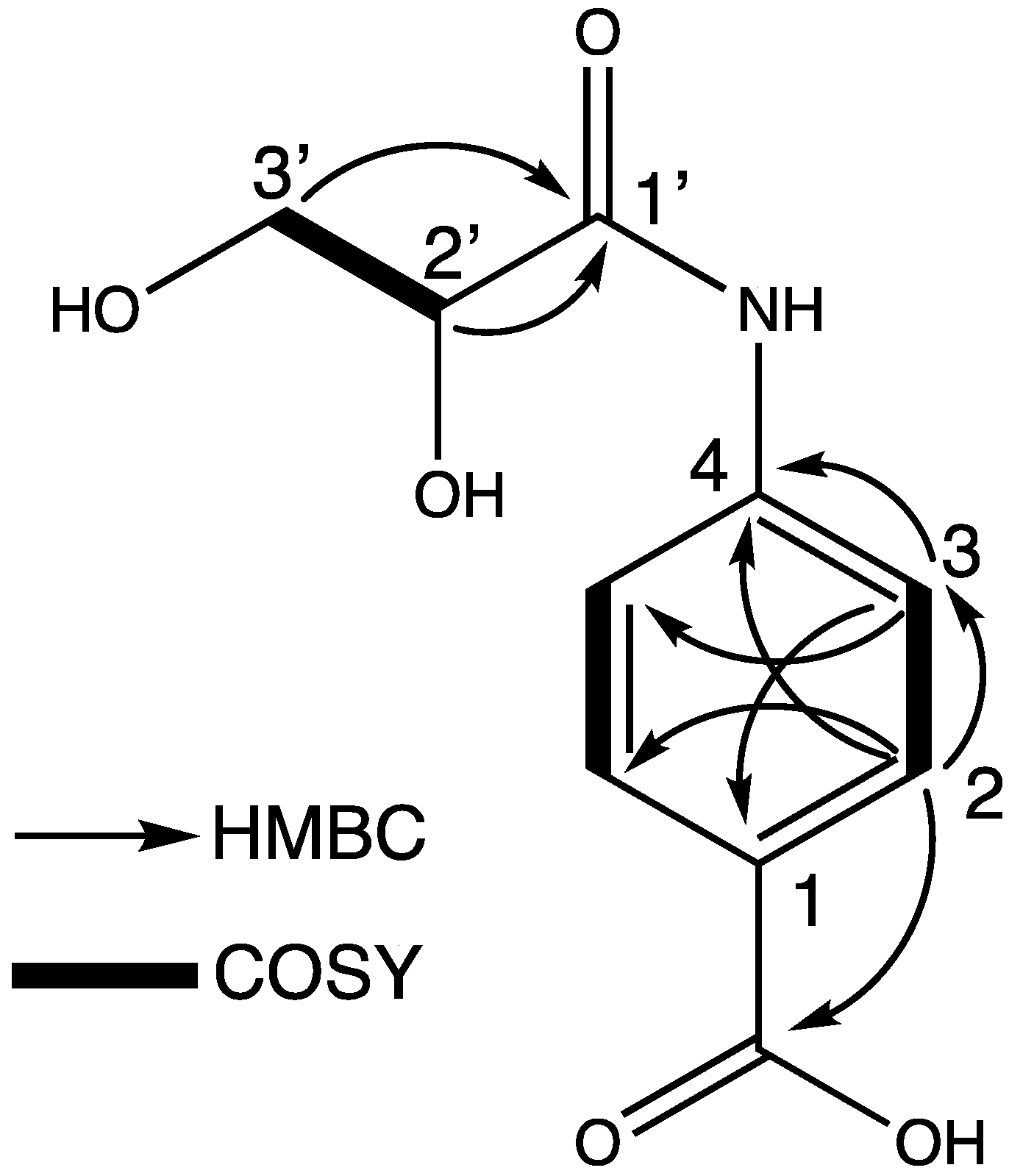
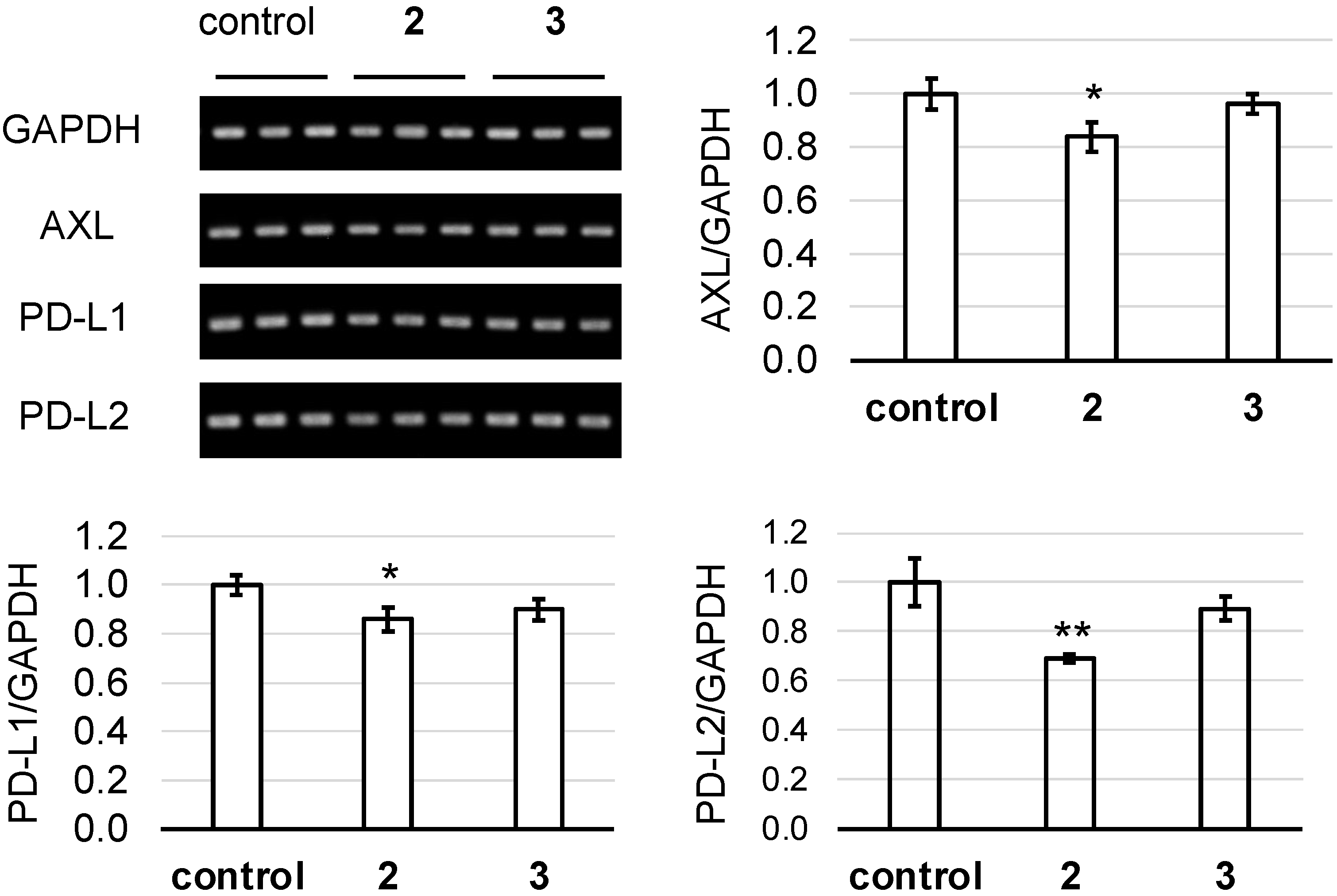

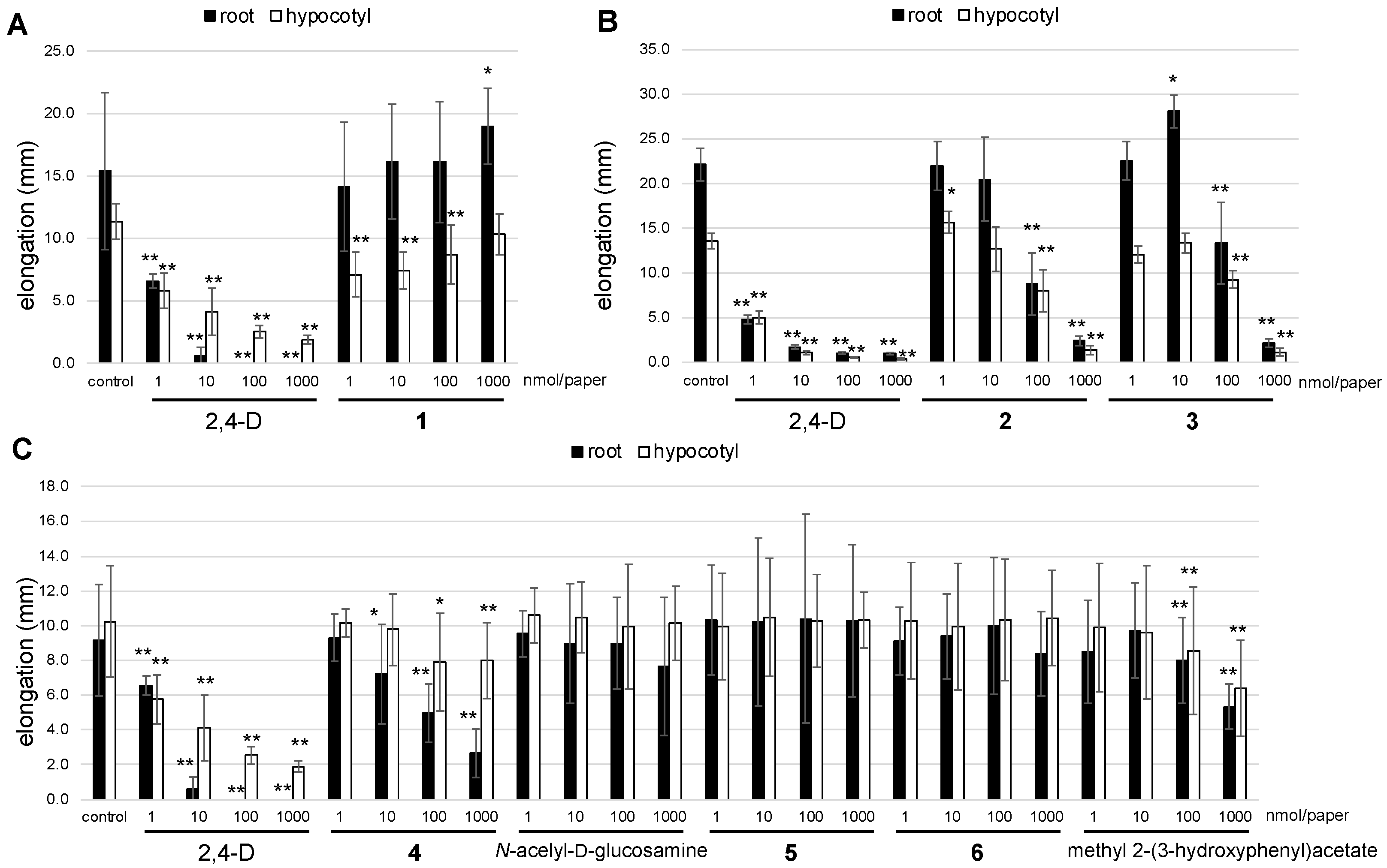
| Position | δH (J inHz) | δc |
|---|---|---|
| 1-COOH | − | 171.0 |
| 1 | − | 129.5 |
| 2, 6 | 7.96 (d, 8.4) | 131.6 |
| 3, 5 | 7.71 (d, 8.4) | 120.4 |
| 4 | − | 142.7 |
| 1′ | – | 173.6 |
| 2′ | 4.20 (dd, 4.6, 3.7) | 74.6 |
| 3′ | 3.80 (dd, 11.6, 4.6) 3.83 (dd, 11.6, 3.7) | 65.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Ohura, T.; Ogura, R.; Wang, J.; Choi, J.-H.; Kobori, H.; D’Alessandro-Gabazza, C.N.; Toda, M.; Yasuma, T.; Gabazza, E.C.; et al. Bioactive Compounds from the Mushroom-Forming Fungus Chlorophyllum molybdites. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030596
Wu J, Ohura T, Ogura R, Wang J, Choi J-H, Kobori H, D’Alessandro-Gabazza CN, Toda M, Yasuma T, Gabazza EC, et al. Bioactive Compounds from the Mushroom-Forming Fungus Chlorophyllum molybdites. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(3):596. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030596
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jing, Takeru Ohura, Ryuhei Ogura, Junhong Wang, Jae-Hoon Choi, Hajime Kobori, Corina N. D’Alessandro-Gabazza, Masaaki Toda, Taro Yasuma, Esteban C. Gabazza, and et al. 2023. "Bioactive Compounds from the Mushroom-Forming Fungus Chlorophyllum molybdites" Antibiotics 12, no. 3: 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030596
APA StyleWu, J., Ohura, T., Ogura, R., Wang, J., Choi, J.-H., Kobori, H., D’Alessandro-Gabazza, C. N., Toda, M., Yasuma, T., Gabazza, E. C., Takikawa, Y., Hirai, H., & Kawagishi, H. (2023). Bioactive Compounds from the Mushroom-Forming Fungus Chlorophyllum molybdites. Antibiotics, 12(3), 596. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030596









