Inhibition of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Efflux Pumps by Using Staphylococcus aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synergistic Activity of EPI/Antimicrobial Combinations
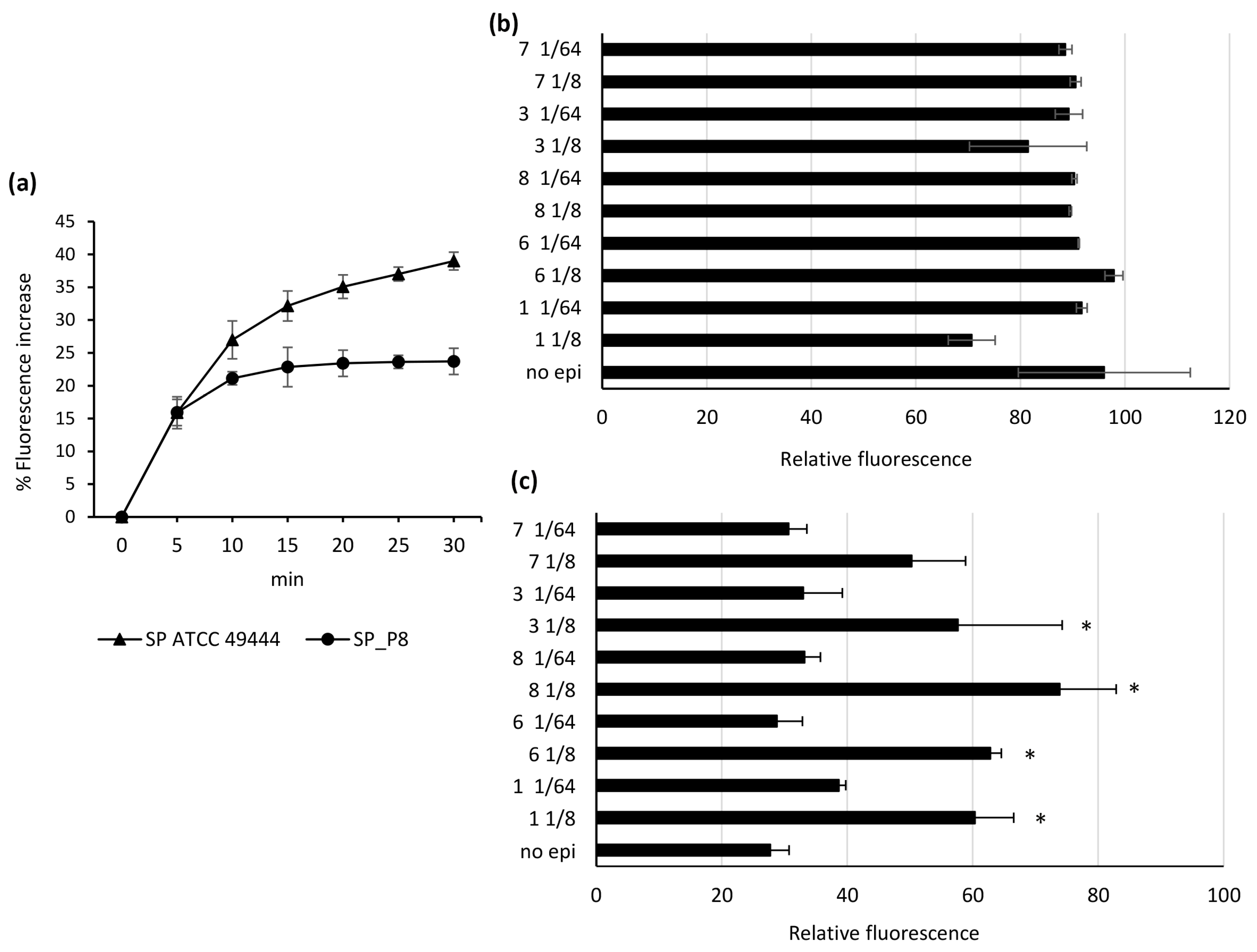
2.2. Comparative Inhibition of EtBr Efflux
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Efflux Pump Inhibitors
4.3. MIC Determination
4.4. Sinergy Studies
4.5. Fluorometric Tests
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miethke, M.; Pieroni, M.; Weber, T.; Brönstrup, M.; Hammann, P.; Halby, L.; Arimondo, P.B.; Glaser, P.; Aigle, B.; Bode, H.B.; et al. Towards the sustainable discovery and development of new antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 726–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Amaral, L.; Couto, I. Multidrug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: An update. Open Microbiol. J. 2013, 7, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampacci, E.; Marenzoni, M.L.; Cannalire, R.; Pietrella, D.; Sabatini, S.; Giovagnoli, S.; Felicetti, T.; Pepe, M.; Passamonti, F. Ethidium bromide exposure unmasks an antibiotic efflux system in Rhodococcus equi. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampacci, E.; Felicetti, T.; Pietrella, D.; Sabatini, S.; Passamonti, F. Drug efflux transporters in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: In silico prediction and characterization of resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 3283–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papkou, A.; Hedge, J.; Kapel, N.; Young, B.; MacLean, R.C. Efflux pump activity potentiates the evolution of antibiotic resistance across S. aureus isolates. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.H.; Hao, Z.H.; Liu, P.L.; Liu, M.M.; Zhao, L.L.; Zhao, X. Increased expression of efflux pump NorA drives the rapid evolutionary trajectory from tolerance to resistance against ciprofloxacin in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0059422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brawley, D.N.; Sauer, D.B.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Koide, A.; Jedhe, G.S.; Suwatthee, T.; Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Arora, P.S.; et al. Structural basis for inhibition of the drug efflux pump NorA from Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernicchi, G.; Felicetti, T.; Sabatini, S. Microbial efflux pump inhibitors: A journey around quinoline and indole derivatives. Molecules 2021, 26, 6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamut, A.; Peterlin Mašič, L.; Kikelj, D.; Tomašič, T. Efflux pump inhibitors of clinically relevant multidrug resistant bacteria. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2460–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, K.L.C.; de Aquino, T.M.; Mendonça Junior, F.J.B. An update on Staphylococcus aureus Nora efflux pump inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 2168–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicetti, T.; Machado, D.; Cannalire, R.; Astolfi, A.; Massari, S.; Tabarrini, O.; Manfroni, G.; Barreca, M.L.; Cecchetti, V.; Viveiros, M.; et al. Modifications on c6 and c7 positions of 3-phenylquinolone efflux pump inhibitors led to potent and safe antimycobacterial treatment adjuvants. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 982–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Animal Health and Welfare (AHAW); Nielsen, S.S.; Bicout, D.J.; Calistri, P.; Canali, E.; Drewe, J.A.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Gonzales Rojas, J.L.; Gortazar Schmidt, C.; Herskin, M.; et al. Assessment of animal diseases caused by bacteria resistant to antimicrobials: Dogs and cats. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06680. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bannoehr, J.; Guardabassi, L. Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in the dog: Taxonomy, diagnostics, ecology, epidemiology and pathogenicity. Vet. Dermatol. 2012, 23, 253-e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.A.; Helbig, K.J. The Complex Diseases of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Canines: Where to Next? Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoPinto, A.J.; Mohammed, H.O.; Ledbetter, E.C. Prevalence and risk factors for isolation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus in dogs with keratitis. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2015, 18, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Walker, M.; Rousseau, J.; Weese, J.S. Characterization of the biofilm forming ability of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarbrough, M.L.; Lainhart, W.; Burnham, C.A. Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of human clinical isolates of Staphylococcus intermedius group. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01788-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhooshan, S.; Negi, V.; Khatri, P.K. Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: An undocumented, emerging pathogen in humans. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2020, 15, Doc32. [Google Scholar]
- Cester, C.C.; Toutain, P.L. A comprehensive model for enrofloxacin to ciprofloxacin transformation and disposition in dog. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Abrantes, P.; Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Couto, I. Occurrence and variability of the efflux pump gene norA across the Staphylococcus genus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, S.; Gosetto, F.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; Kaatz, G.W.; Patel, D.; Cecchetti, V. Evolution from a natural flavones nucleus to obtain 2-(4-propoxyphenyl)quinoline derivatives as potent inhibitors of the S. aureus NorA efflux pump. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 5722–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, S.; Gosetto, F.; Iraci, N.; Barreca, M.L.; Massari, S.; Sancineto, L.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; Dimovska, M.; Kaatz, G.W.; et al. Re-evolution of the 2-phenylquinolines: Ligand-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a potent new class of Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors to combat antimicrobial resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4975–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felicetti, T.; Cannalire, R.; Pietrella, D.; Latacz, G.; Lubelska, A.; Manfroni, G.; Barreca, M.L.; Massari, S.; Tabarrini, O.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; et al. 2-phenylquinoline S. aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors: Evaluation of the importance of methoxy group introduction. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7827–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felicetti, T.; Mangiaterra, G.; Cannalire, R.; Cedraro, N.; Pietrella, D.; Astolfi, A.; Massari, S.; Tabarrini, O.; Manfroni, G.; Barreca, M.L.; et al. C-2 phenyl replacements to obtain potent quinoline-based Staphylococcus aureus NorA inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, S.; Gosetto, F.; Serritella, S.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; Iraci, N.; Brincat, J.P.; Carosati, E.; Villarini, M.; Kaatz, G.W.; et al. Pyrazolo[4,3-c][1,2]Benzothiazines 5,5-Dioxide: A promising new class of Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3568–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, A.; Felicetti, T.; Iraci, N.; Manfroni, G.; Massari, S.; Pietrella, D.; Tabarrini, O.; Kaatz, G.W.; Barreca, M.L.; Sabatini, S.; et al. Pharmacophore-based repositioning of approved drugs as novel Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannalire, R.; Mangiaterra, G.; Felicetti, T.; Astolfi, A.; Cedraro, N.; Massari, S.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; Vaiasicca, S.; Barreca, M.L.; et al. Structural modifications of the quinolin-4-yloxy core to obtain new Staphylococcus aureus NorA inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedraro, N.; Cannalire, R.; Astolfi, A.; Mangiaterra, G.; Felicetti, T.; Vaiasicca, S.; Cernicchi, G.; Massari, S.; Manfroni, G.; Tabarrini, O.; et al. From quinoline to quinazoline-based S. aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors by coupling a focused scaffold hopping approach and a pharmacophore search. ChemMedChem. 2021, 16, 3044–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, E.M.; Trampari, E.; Siasat, P.; Gaya, M.S.; Alav, I.; Webber, M.A.; Blair, J.M.A. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance revisited. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Wieczorek, K.; Dec, M.; Nowaczek, A.; Osek, J. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria—A review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, M.; Shaaban, A.; Rahman, K.M. Antibiotic resistance breakers: Current approaches and future directions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 43, 490–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMatar, M.; Albarri, O.; Makky, E.A.; Köksal, F. Efflux pump inhibitors: New updates. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2475067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! an update from the infectious diseases society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D. Antibiotic resistance breakers: Can repurposed drugs fill the antibiotic discovery void? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, V.K.; Pathania, R. Efflux pump inhibitors for bacterial pathogens: From bench to bedside. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 129–145. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, S.S.; Falcão, C.; Viveiros, M.; Machado, D.; Martins, M.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Amaral, L.; Couto, I. Exploring the contribution of efflux on the resistance to fluoroquinolones in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Bhattacharyya, M.; Pfannenstiel, D.M.; Nandi, A.K.; Hwang, Y.; Ho, K.; Harshey, R.M. Efflux-linked accelerated evolution of antibiotic resistance at a population edge. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 4368–4385.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, A.M.; El Meouche, I.; Dunlop, M.J. Mapping the role of AcrAB-TolC efflux pumps in the evolution of antibiotic resistance reveals near-MIC treatments facilitate resistance acquisition. mSphere 2020, 5, e01056-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, I.; Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Martins, M.; Amaral, L. Efflux-mediated response of Staphylococcus aureus exposed to ethidium bromide. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 11th ed.; CLSI Standard M07; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, S.K.; Moellering, R.C.; Eliopoulos, G.M. Antimicrobial combinations. In Antibiotics in Laboratory Medicine, 5th ed.; Lorian, V., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 365–440. [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz, G.W.; Seo, S.M.; O’Brien, L.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Foster, T.J. Evidence for the existence of a multidrug efflux transporter distinct from NorA in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1404–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
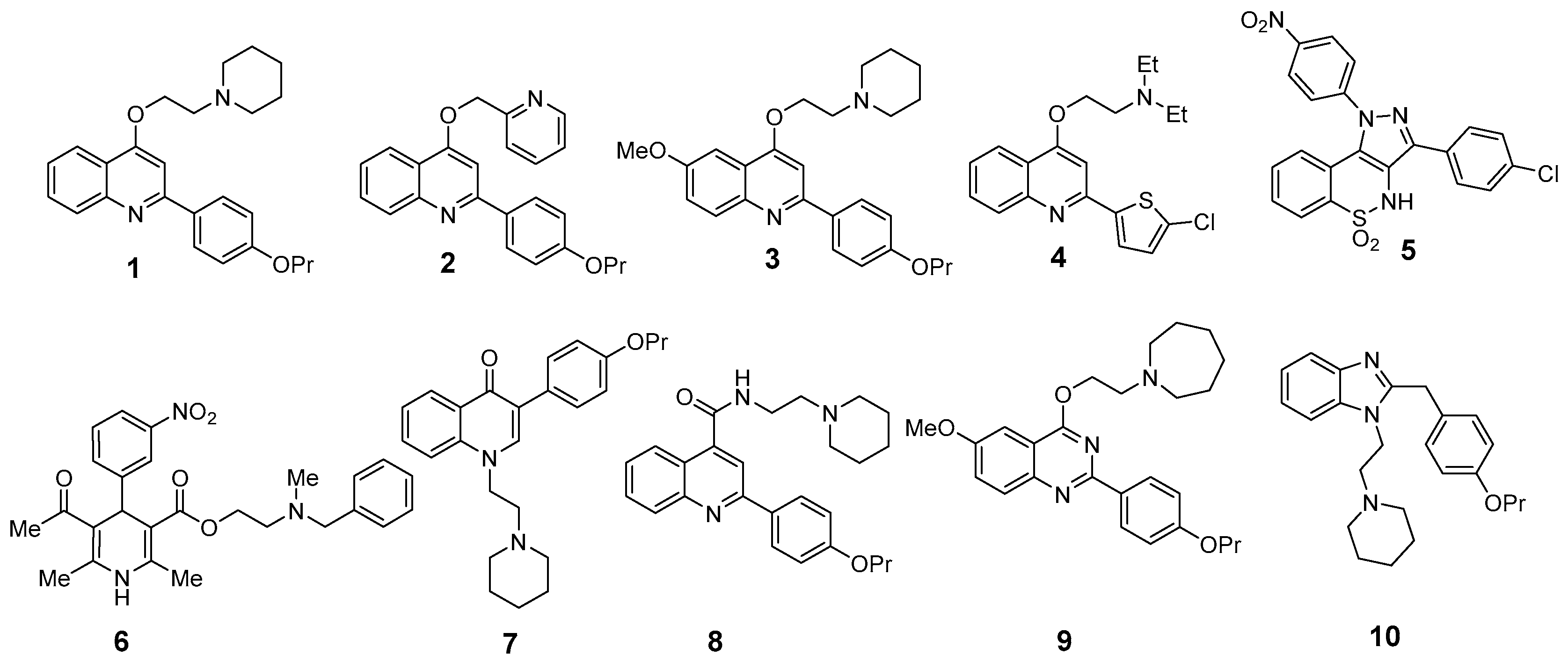
| MIC (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compound | SP ATCC 49444 | SP_P8 |
| 1 | >100 | >100 |
| 2 | >100 | >100 |
| 3 | 50 | 50 |
| 4 | 25 | 25 |
| 5 | 6.25 | 6.25 |
| 6 | >100 | >100 |
| 7 | >100 | >100 |
| 8 | >100 | >100 |
| 9 | >100 | >100 |
| 10 | >100 | >100 |
| EtBr | 0.5 | 32 |
| CIP | ≤0.125 | 8 |
| GEN | 0.25 | 1 |
| CHX | 1 | 4 |
| MIC in mg/L (MF) * | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPI (mg/L) | GEN | CHX | CIP | EtBr | EPI | GEN | CHX | CIP | EtBr |
| No EPI | 1 | 4 | 8 | 32 | No EPI | 1 | 4 | 8 | 32 |
| 1 1/4 (50) | 0.125 (8) | 0.5 (8) | 0.125 (64) | 0.5 (64) | 2 1/4 (50) | 0.125 (8) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) |
| 1 1/8 (25) | 0.125 (8) | 0.5 (8) | 0.125 (64) | 0.5 (64) | 2 1/8 (25) | 0.25 (4) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) |
| 1 1/16 (12.5) | 0.25 (4) | 1 (4) | 0.25 (32) | 0.5 (64) | 2 1/16 (12.5) | 0.25 (4) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) |
| 1 1/32 (6.25) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 2 (16) | 2 1/32 (6.25) | 0.25 (4) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) |
| 1 1/64 (3.13) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 4 (8) | 2 1/64 (3.13) | 0.5 (2) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) |
| 1 1/128 (1.57) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 8 (4) | 2 1/128 (1.57) | 0.5 (2) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 32 (-) |
| 3 1/4 (12.5) | 0.25 (4) | 0.5 (8) | 0.25 (32) | 0.5 (64) | 4 1/4 (6.25) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 0.25 (32) | 0.5 (64) |
| 3 1/8 (6.25) | 0.25 (4) | 1 (4) | 0.5 (16) | 1 (32) | 4 1/8 (3.13) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 0.5 (16) | 2 (16) |
| 3 1/16 (3.13) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 4 (8) | 4 1/16 (1.57) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 (4) | 8 (4) |
| 3 1/32 (1.57) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 (4) | 8 (4) | 4 1/32 (0.78) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 4 (2) | 16 (2) |
| 3 1/64 (0.78) | 0.5 (2) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 32 (-) | 4 1/64 (0.39) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 4 (2) | 16 (2) |
| 3 1/128 (0.39) | 0.5 (2) | 4 (-) | 4 (2) | 32 (-) | 4 1/128 (0.20) | 1 (-) | 4 (-) | 8 (-) | 32 (-) |
| 5 1/4 (1.57) | 0.25 (4) | 1 (4) | 0.5 (16) | 4 (8) | 6 1/4 (50) | 0.125 (8) | 1 (4) | 0.25 (32) | 0.5 (64) |
| 5 1/8 (0.78) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 2 (4) | 8 (4) | 6 1/8 (25) | 0.125 (8) | 1 (4) | 0.25 (32) | 0.5 (64) |
| 5 1/16 (0.39) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) | 6 1/16 (12.5) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 0.5 (16) | 1 (32) |
| 5 1/32 (0.20) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) | 6 1/32 (6.25) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 8 (4) |
| 5 1/64 (0.10) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) | 6 1/64 (3.13) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 16 (2) |
| 5 1/128 (0.05) | 1 (-) | 4 (-) | 4 (2) | 32 (-) | 6 1/128 (1.57) | 1 (-) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 32 (-) |
| 7 1/4 (50) | 0.25 (4) | 1 (4) | 0.25 (32) | 0.5 (64) | 8 1/4 (50) | 0.25 (4) | 0.5 (8) | 0.25 (32) | 0.5 (64) |
| 7 1/8 (25) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 0.25 (32) | 2 (16) | 8 1/8 (25) | 0.25 (4) | 0.5 (8) | 0.25 (32) | 0.5 (64) |
| 7 1/16 (12.5) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 0.5 (16) | 8 (4) | 8 1/16 (12.5) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 0.25 (32) | 2 (16) |
| 7 1/32 (6.25) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 16 (2) | 8 1/32 (6.25) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 0.5 (16) | 8 (4) |
| 7 1/64 (3.13) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 16 (2) | 8 1/64 (3.13) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 16 (2) |
| 7 1/128 (1.57) | 1 (-) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 32 (-) | 8 1/128 (1.57) | 0.5 (2) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 32 (-) |
| 9 1/4 (50) | 0.25 (4) | 4 (-) | 0.5 (16) | 2 (16) | 10 1/4 (50) | 0.25 (4) | 1 (4) | 0.5 (16) | 8 (4) |
| 9 1/8 (25) | 0.25 (4) | 4 (-) | 1 (8) | 2 (16) | 10 1/8 (25) | 0.25 (4) | 1 (4) | 0.5 (16) | 8 (4) |
| 9 1/16 (12.5) | 0.25 (4) | 4 (-) | 1 (8) | 2 (16) | 10 1/16 (12.5) | 0.25 (4) | 2 (2) | 0.5 (16) | 8 (4) |
| 9 1/32 (6.25) | 0.25 (4) | 4 (-) | 1 (8) | 4 (8) | 10 1/32 (6.25) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 1 (8) | 16 (2) |
| 9 1/64 (3.13) | 0.5 (2) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 8 (4) | 10 1/64 (3.13) | 0.5 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) |
| 9 1/128 (1.57) | 0.5 (2) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 16 (2) | 10 1/128 (1.57) | 1 (-) | 4 (-) | 2 (4) | 32 (-) |
| MIC (mg/L) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GEN | CHX | CIP | EtBr | |||||
| EPI | SP 49444 | SP P8 | SP 49444 | SP P8 | SP 49444 | SP P8 | SP 49444 | SP P8 |
| 1 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.56 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.08 |
| 2 | 2.00 | 0.28 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.26 | 2.00 | 0.51 |
| 3 | 2.00 | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.38 | 2.00 | 0.16 | 0.50 | 0.16 |
| 4 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 2.00 | 0.53 | 2.00 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.19 |
| 5 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 2.00 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 0.28 | 2.00 | 0.38 |
| 6 | 0.50 | 0.31 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 2.00 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.09 |
| 7 | 0.50 | 0.31 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 0.19 |
| 8 | 2.00 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 2.00 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.13 |
| 9 | 2.00 | 0.28 | 0.56 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.16 | 0.56 | 0.09 |
| 10 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 2.00 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rampacci, E.; Felicetti, T.; Cernicchi, G.; Stefanetti, V.; Sabatini, S.; Passamonti, F. Inhibition of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Efflux Pumps by Using Staphylococcus aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050806
Rampacci E, Felicetti T, Cernicchi G, Stefanetti V, Sabatini S, Passamonti F. Inhibition of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Efflux Pumps by Using Staphylococcus aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(5):806. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050806
Chicago/Turabian StyleRampacci, Elisa, Tommaso Felicetti, Giada Cernicchi, Valentina Stefanetti, Stefano Sabatini, and Fabrizio Passamonti. 2023. "Inhibition of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Efflux Pumps by Using Staphylococcus aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors" Antibiotics 12, no. 5: 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050806
APA StyleRampacci, E., Felicetti, T., Cernicchi, G., Stefanetti, V., Sabatini, S., & Passamonti, F. (2023). Inhibition of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Efflux Pumps by Using Staphylococcus aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors. Antibiotics, 12(5), 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050806






