Evaluation of Alternative Doxycycline Antibiotic Regimes in an Inhalational Murine Model of Q Fever
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
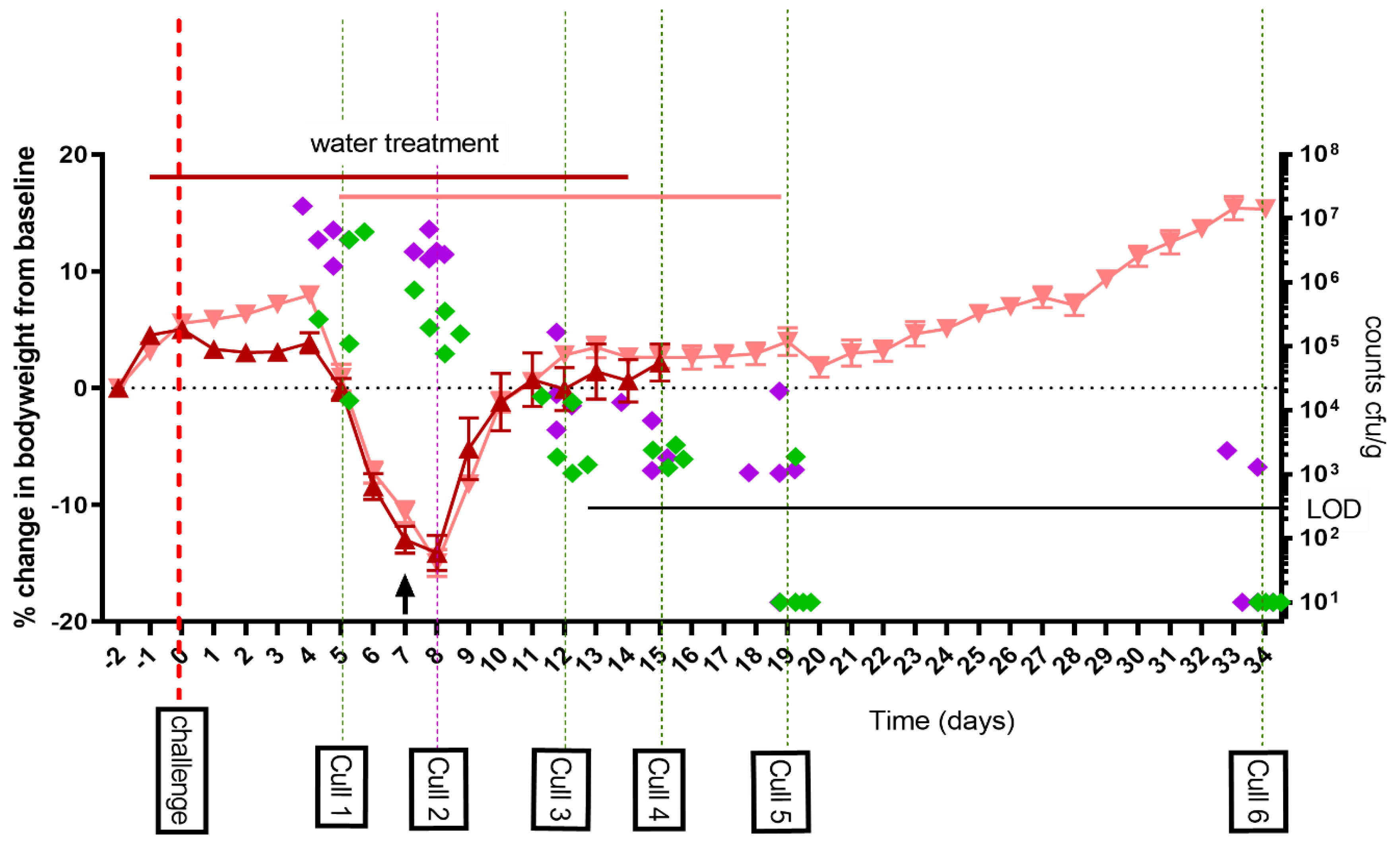
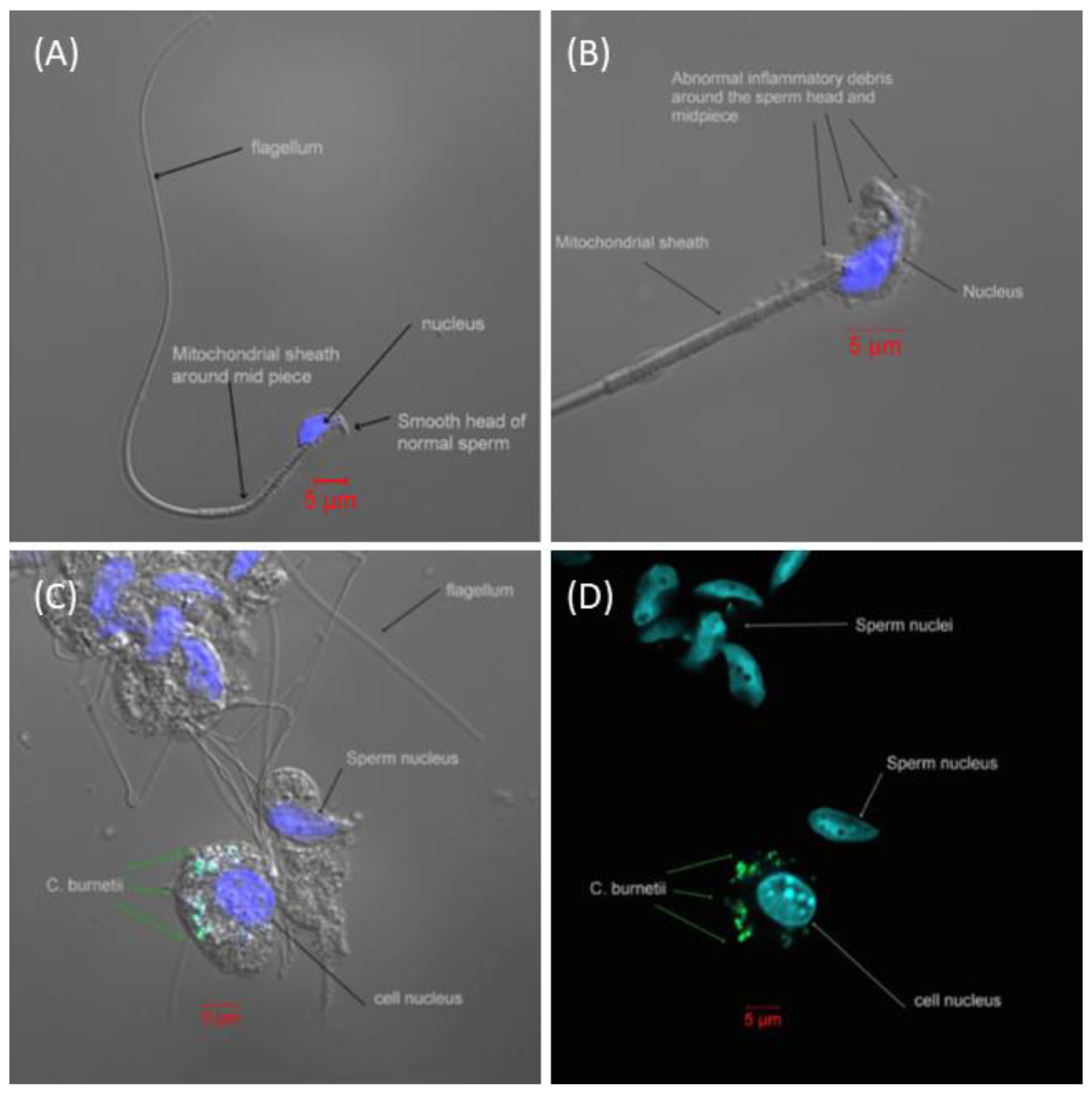
2.1. Dissemination of Bacteria Following Aerosol Challenge in the A/J Mouse Model of Q Fever
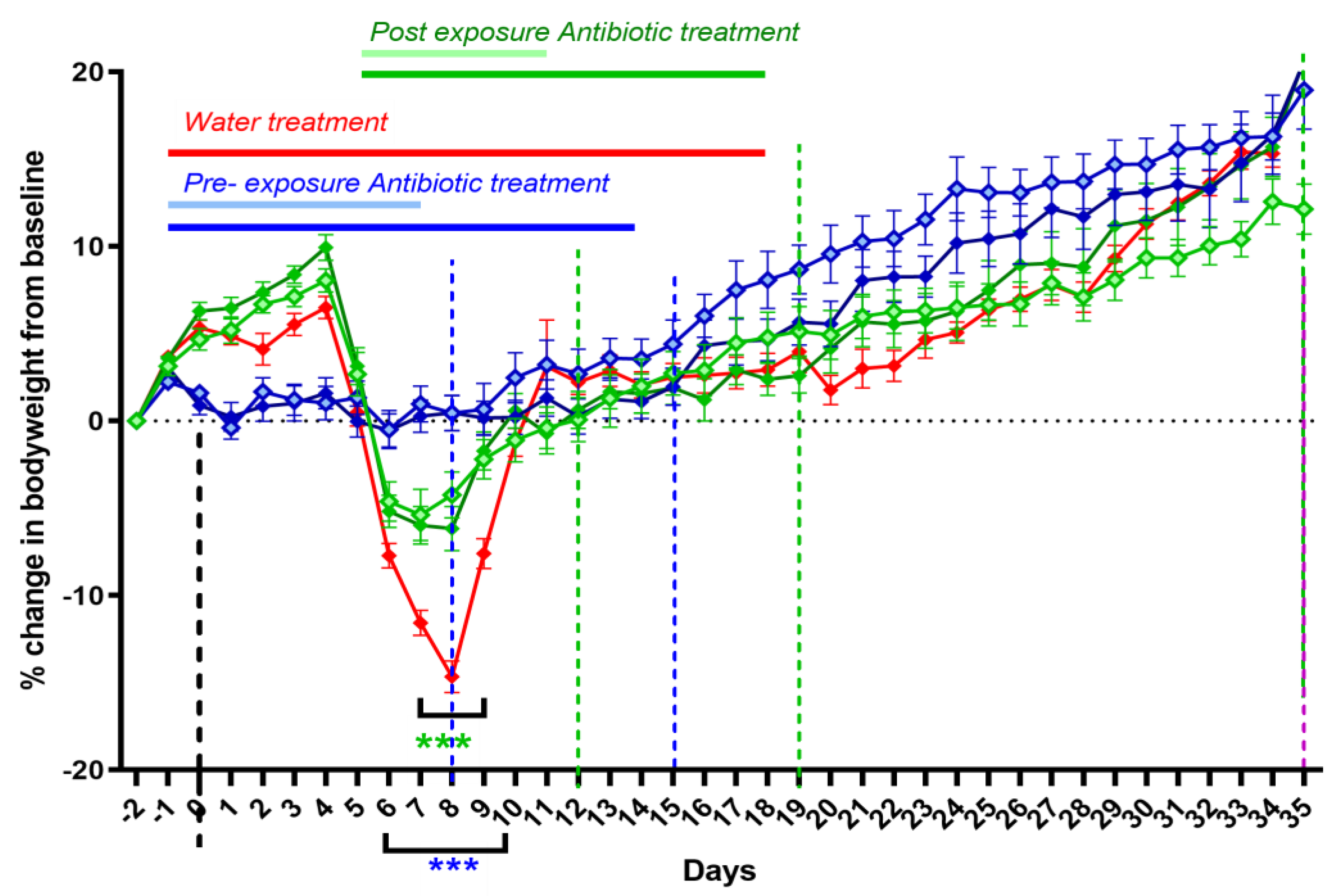
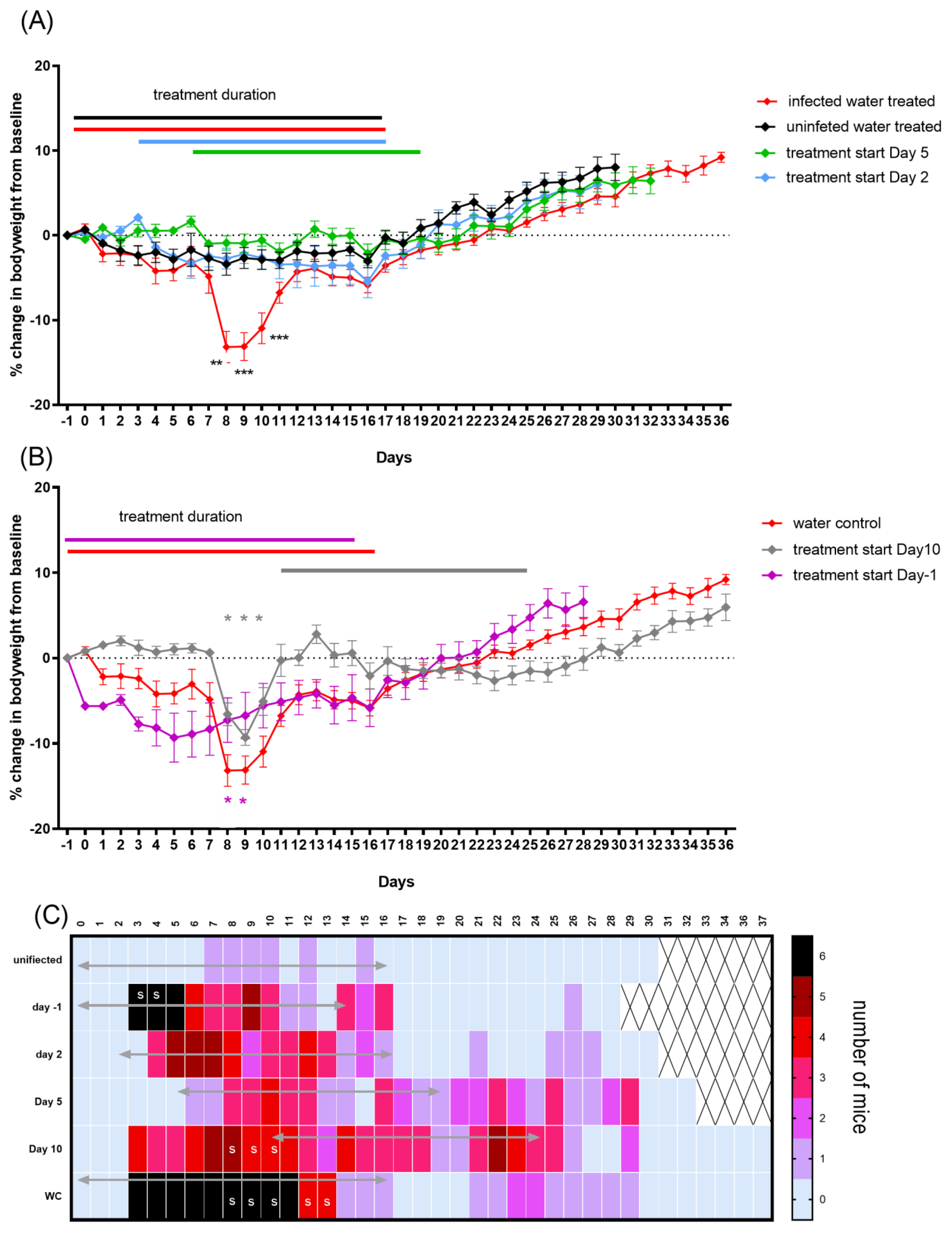
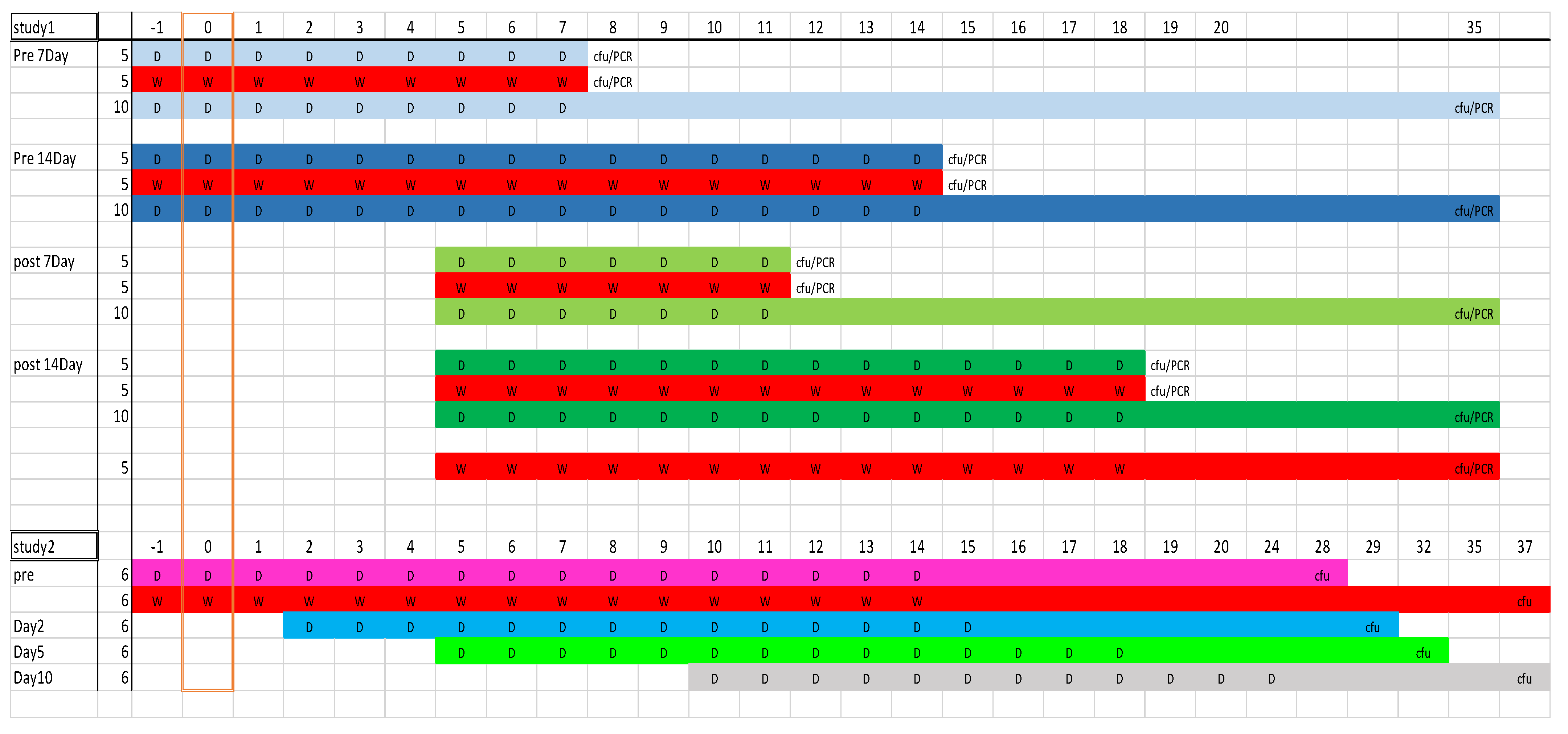
2.2. Evaluation of Alternative Doxycycline Treatment Lengths (7 vs. 14 Days) Initiated Pre- or Post-Challenge in the A/J Mouse Model of Q Fever (Study 1)
2.3. Impact of Initation of Doxycycline Treatment at Different Times Pre- and Post-Challenge on Clinical Signs in the A/J Mouse Model of Q Fever (Study 2)
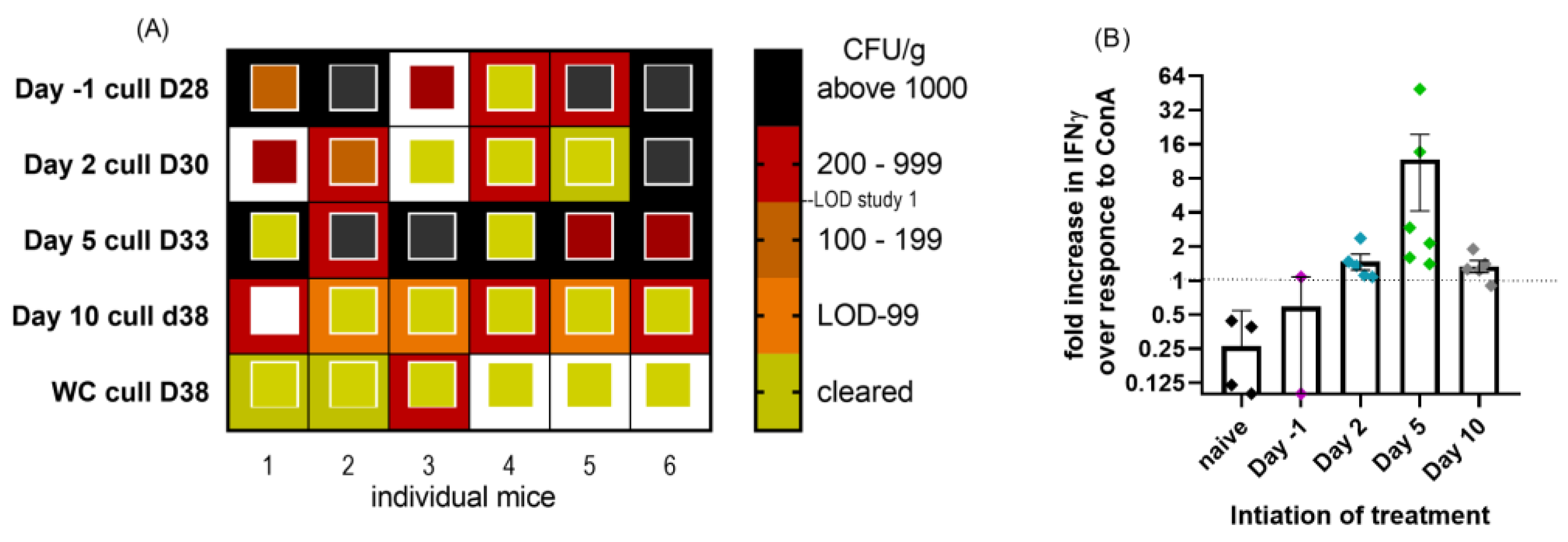
2.4. Impact of Initation of Doxycycline Treatment at Different Times Pre- and Post-Challenge on Bacterial Clearance in a Mouse Model of Q Fever
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joulié, A.; Sidi-Boumedine, K.; Bailly, X.; Gasqui, P.; Barry, S.; Jaffrelo, L.; Poncet, C.; Abrial, D.; Yang, E.; Leblond, A.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Coxiella burnetii in French livestock reveals the existence of three main genotype clusters and suggests species-specific associations as well as regional stability. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 48, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.S.; Trinick, T.R.; Dunbar, J.A.; Hatch, R.; Osborne, J.C.; Brooks, T.J.; Green, A.D. Undifferentiated febrile illnesses amongst British troops in Helmand, Afghanistan. J. R. Army Med. Corps 2011, 157, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delord, M.; Socolovschi, C.; Parola, P. Rickettsioses and Q fever in travelers (2004–2013). Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2014, 12, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.; Bijlmer, H.; Fournier, P.-E.; Graves, S.; Hartzell, J.; Kersh, G.J.; Limonard, G.; Marrie, T.J.; Massung, R.F.; McQuiston, J.H. Diagnosis and management of Q fever—United States, 2013: Recommendations from CDC and the Q Fever Working Group. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. Recomm. Rep. 2013, 62, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, C.J.; Richmond, S.J.; Caul, E.O.; Pearce, N.H.; Silver, I.A. Laboratory outbreak of Q fever acquired from sheep. Lancet 1982, 1, 1004–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.R.; Magill, A.J.; Parise, M.E.; Arguin, P.M. Doxycycline for malaria chemoprophylaxis and treatment: Report from the CDC expert meeting on malaria chemoprophylaxis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampschreur, L.M.; Delsing, C.E.; Groenwold, R.H.; Wegdam-Blans, M.C.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; de Jager-Leclercq, M.G.; Hoepelman, A.I.; van Kasteren, M.E.; Buijs, J.; Renders, N.H.; et al. Chronic Q fever in the Netherlands 5 years after the start of the Q fever epidemic: Results from the Dutch chronic Q fever database. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benenson, A.S.; Tigertt, W.D. Studies on Q fever in man. Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1956, 69, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Marrie, T.J.; Cunning, J.; Durnford, P. Reactivation of Q fever following cardiac surgery. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1992, 11, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, K.R. Animal models of Q fever (Coxiella burnetii). Comp. Med. 2013, 63, 469–476. [Google Scholar]
- Norville, I.H.; Hatch, G.J.; Bewley, K.R.; Atkinson, D.J.; Hamblin, K.A.; Blanchard, J.D.; Armstrong, S.J.; Pitman, J.K.; Rayner, E.; Hall, G.; et al. Efficacy of liposome-encapsulated ciprofloxacin in a murine model of Q fever. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5510–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Hu, X.; Fu, M.; Dai, L.; Yu, Y.; Luo, W.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, Z.; Du, Z.; Zhou, D.; et al. Enhanced protection against Q fever in BALB/c mice elicited by immunization of chloroform-methanol residue of Coxiella burnetii via intratracheal inoculation. Vaccine 2019, 37, 6076–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell-Lodrigue, K.E.; Zhang, G.Q.; McMurray, D.N.; Samuel, J.E. Clinical and pathologic changes in a guinea pig aerosol challenge model of acute Q fever. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6085–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waag, D.M.; Byrne, W.R.; Estep, J.; Gibbs, P.; Pitt, M.L.; Banfield, C.M. Evaluation of cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) and rhesus (Macaca mulatta) monkeys as experimental models of acute Q fever after aerosol exposure to phase-I Coxiella burnetii. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1999, 49, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.; Salguero, F.J.; Hunter, L.; Atkins, T.P. A Novel Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) Model of Human Inhalational Q Fever. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 621635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Pang, W.; Hu, X.T.; Li, J.L.; Yao, Y.G.; Zheng, Y.T. Experimental primates and non-human primate (NHP) models of human diseases in China: Current status and progress. Dongwuxue Yanjiu 2014, 35, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, K.A.; Hartley, M.G.; Armstrong, S.; Bewley, K.R.; Godwin, K.; Rayner, E.; Vipond, J.; Bailey, M.; Atkins, T.P.; Norville, I.H. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Doxycycline, Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, and Co-trimoxazole Using In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Q Fever. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0067321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, K.A. Antibiotic Therapy as Prevention and Treatment of Q Fever. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bernit, E.; Pouget, J.; Janbon, F.; Dutronc, H.; Martinez, P.; Brouqui, P.; Raoult, D. Neurological involvement in acute Q fever: A report of 29 cases and review of the literature. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, A.; Hall, R.; Storm, P.A.; Harris, R.J.; Winslow, W.; Marmion, B.P. Sexually transmitted Q fever. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwis, L.; Balan, K.; Wright, P.; Lever, A.; Carmichael, A. Bone marrow involvement in Q fever—Detection by fluorine-18-labelled fluorodeoxyglucose PET. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmion, B.P.; Storm, P.A.; Ayres, J.G.; Semendric, L.; Mathews, L.; Winslow, W.; Turra, M.; Harris, R.J. Long-term persistence of Coxiella burnetii after acute primary Q fever. QJM 2005, 98, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmion, B.P.; Sukocheva, O.; Storm, P.A.; Lockhart, M.; Turra, M.; Kok, T.; Ayres, J.; Routledge, H.; Graves, S. Q fever: Persistence of antigenic non-viable cell residues of Coxiella burnetii in the host—Implications for post Q fever infection fatigue syndrome and other chronic sequelae. QJM 2009, 102, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechah, Y.; Verneau, J.; Ben Amara, A.; Barry, A.O.; Lépolard, C.; Achard, V.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Textoris, J.; Capo, C.; Ghigo, E.; et al. Persistence of Coxiella burnetii, the agent of Q fever, in murine adipose tissue. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morroy, G.; Keijmel, S.P.; Delsing, C.E.; Bleijenberg, G.; Langendam, M.; Timen, A.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P. Fatigue following Acute Q-Fever: A Systematic Literature Review. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, S.; Golzar, F.; Ayubi, E.; Naghili, B.; Mostafavi, E. Acute Q fever in febrile patients in northwestern of Iran. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melenotte, C.; Lepidi, H.; Nappez, C.; Bechah, Y.; Audoly, G.; Terras, J.; Raoult, D.; Brégeon, F. Mouse Model of Coxiella burnetii Aerosolization. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszewska, D.; Tylewska-Wierzbanowska, S.K. Coxiella burnetii penetration into the reproductive system of male mice, promoting sexual transmission of infection. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4188–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, D.; Lalic, N.; Vukovic, I.; Nale, D.; Micic, S. Sperm Quality and Seminal Biochemical Parameters in Infertile Men with and without Leukocytospermia. Andrology 2018, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, T.F.; Acosta, A.A.; Simmons, K.F.; Swanson, R.J.; Matta, J.F.; Veeck, L.L.; Morshedi, M.; Brugo, S. New method of evaluating sperm morphology with predictive value for human in vitro fertilization. Urology 1987, 30, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, J.G.; Wildman, M.; Groves, J.; Ment, J.; Smith, E.G.; Beattie, J.M. Long-term follow-up of patients from the 1989 Q fever outbreak: No evidence of excess cardiac disease in those with fatigue. QJM Int. J. Med. 2002, 95, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampschreur, L.M.; Dekker, S.; Hagenaars, J.C.; Lestrade, P.J.; Renders, N.H.; de Jager-Leclercq, M.G.; Hermans, M.H.; Groot, C.A.; Groenwold, R.H.; Hoepelman, A.I.; et al. Identification of risk factors for chronic Q fever, The Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukocheva, O.A.; Marmion, B.P.; Storm, P.A.; Lockhart, M.; Turra, M.; Graves, S. Long-term persistence after acute Q fever of non-infective Coxiella burnetii cell components, including antigens. QJM 2010, 103, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersh, G.J. Antimicrobial therapies for Q fever. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigertt, W.D.; Benenson, A.S.; Gochenour, W.S. Airborne Q fever. Bacteriol. Rev. 1961, 25, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Norowitz, T.A.; Weaver, D.; Norowitz, Y.M.; Hammerschlag, M.R.; Joks, R.; Durkin, H.G.; Kohlhoff, S. Doxycycline suppresses Chlamydia pneumoniae induced interferon-gamma responses in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in children with allergic asthma. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florou, D.T.; Mavropoulos, A.; Dardiotis, E.; Tsimourtou, V.; Siokas, V.; Aloizou, A.M.; Liaskos, C.; Tsigalou, C.; Katsiari, C.; Sakkas, L.I.; et al. Tetracyclines Diminish In Vitro IFN-γ and IL-17-Producing Adaptive and Innate Immune Cells in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 739186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, M.; Zhang, G.; Russell-Lodrigue, K.E.; Shive, H.R.; Weeks, B.R.; Samuel, J.E. T cells are essential for bacterial clearance, and gamma interferon, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and B cells are crucial for disease development in Coxiella burnetii infection in mice. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 3245–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoffelen, T.; Herremans, T.; Sprong, T.; Nabuurs-Franssen, M.; van der Meer, J.W.; Joosten, L.A.; Netea, M.G.; Bijlmer, H.A.; van Deuren, M. Immunogenicity of the Q fever skin test. J. Infect. 2014, 69, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, R.J.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Mutters, N.T.; Teunis, P.F. Human dose response relation for airborne exposure to Coxiella burnetii. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampschreur, L.M.; Hagenaars, J.C.; Wielders, C.C.; Elsman, P.; Lestrade, P.J.; Koning, O.H.; Oosterheert, J.J.; Renders, N.H.; Wever, P.C. Screening for Coxiella burnetii seroprevalence in chronic Q fever high-risk groups reveals the magnitude of the Dutch Q fever outbreak. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schaik, E.J.; Chen, C.; Mertens, K.; Weber, M.M.; Samuel, J.E. Molecular pathogenesis of the obligate intracellular bacterium Coxiella burnetii. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, M.G.; Norville, I.H.; Richards, M.I.; Barnes, K.B.; Bewley, K.R.; Vipond, J.; Rayner, E.; Vente, A.; Armstrong, S.J.; Harding, S.V. Finafloxacin, a Novel Fluoroquinolone, Reduces the Clinical Signs of Infection and Pathology in a Mouse Model of Q Fever. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 760698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.R.; Young, S.E. Q-fever endocarditis in England and Wales, 1975–81. Lancet 1982, 2, 1448–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, F.; Riphagen-Dalhuisen, J.; Wijers, N.; Hak, E.; Van der Sande, M.A.; Morroy, G.; Schneeberger, P.M.; Schimmer, B.; Notermans, D.W.; Van der Hoek, W. Antibiotic therapy for acute Q fever in The Netherlands in 2007 and 2008 and its relation to hospitalization. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 139, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartings, J.M.; Roy, C.J. The automated bioaerosol exposure system: Preclinical platform development and a respiratory dosimetry application with nonhuman primates. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2004, 49, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyton, A.C. Measurement of the respiratory volumes of laboratory animals. Am. J. Physiol. 1947, 150, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.J.; Morton, J.D. The respiratory retention of bacterial aerosols: Experiments with radioactive spores. J. Hyg. 1953, 51, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, S.E.; Vallejo-Esquerra, E.; Omsland, A. Use of Axenic Culture Tools to Study Coxiella burnetii. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2018, 50, e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clay, K.A.; Hartley, M.G.; Whelan, A.O.; Bailey, M.S.; Norville, I.H. Evaluation of Alternative Doxycycline Antibiotic Regimes in an Inhalational Murine Model of Q Fever. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050914
Clay KA, Hartley MG, Whelan AO, Bailey MS, Norville IH. Evaluation of Alternative Doxycycline Antibiotic Regimes in an Inhalational Murine Model of Q Fever. Antibiotics. 2023; 12(5):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050914
Chicago/Turabian StyleClay, Kate A., M. Gill Hartley, Adam O. Whelan, Mark S. Bailey, and Isobel H. Norville. 2023. "Evaluation of Alternative Doxycycline Antibiotic Regimes in an Inhalational Murine Model of Q Fever" Antibiotics 12, no. 5: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050914
APA StyleClay, K. A., Hartley, M. G., Whelan, A. O., Bailey, M. S., & Norville, I. H. (2023). Evaluation of Alternative Doxycycline Antibiotic Regimes in an Inhalational Murine Model of Q Fever. Antibiotics, 12(5), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12050914





