Dosage Optimisation of Trimethoprim and Sulfamethoxazole for the Treatment of an Avian Pathogenic Strain of Escherichia coli in Broiler Chickens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To apply data obtained from our previous study [13] involving the determination of PK parameters and antimicrobial efficacy assessment for the single and repeated oral administration of sulfamethoxazole potentiated with trimethoprim using the recommended dosage for poultry and to establish a new experimental dosage of the traditionally used preparation;
- To compare the effects on the survival rate of experimentally infected individuals after treatment with an experimentally designed dose of the sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim combination;
- To compare the efficacy of the experimentally designed dosage of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim with that which is traditionally used.
2. Results
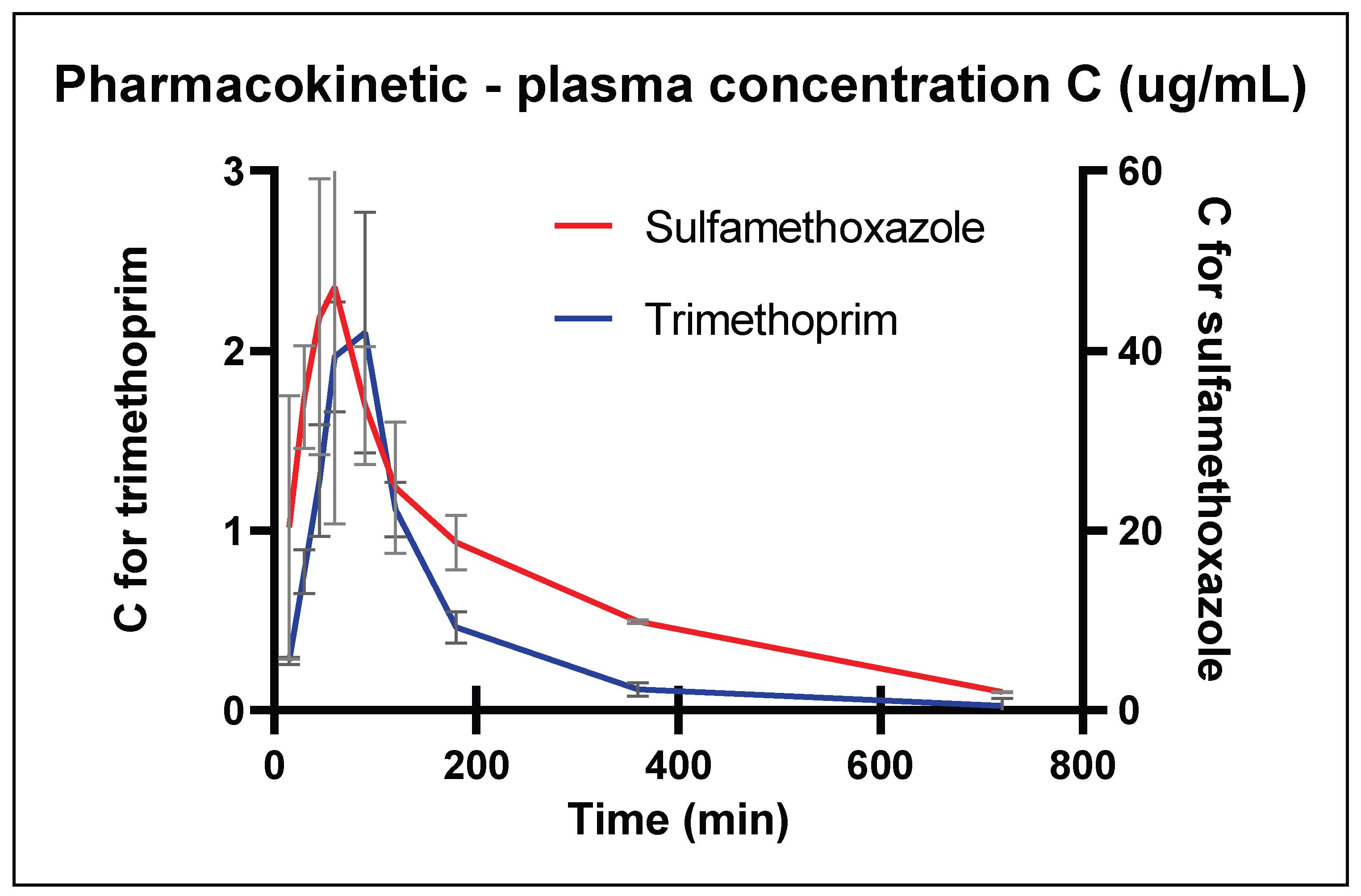
2.1. Validation and Pharmacokinetics
2.2. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Trimethoprim with Sulfamethoxazole
2.3. Animal Experiment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals for Analytical Methods
4.2. Sample Preparation and Analytical Method
4.3. Method Validation and Pharmacokinetic
4.4. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Trimethoprim with Sulfamethoxazole
4.5. Animal Experiment
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nolan, L.K.; Barnes, H.J.; Vaillancourt, J.P.; Abdul-Aziz, T.; Logue, C.M. Colibacillosis. In Diseases of Poultry, 13th ed.; Swayne, D.E., Glisson, J.R., McDouglas, L.R., Nolan, L.K., Suarez, D.L., Nair, V.L., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2013; pp. 751–805. [Google Scholar]
- Sargeant, J.; Bergevin, M.; Churchill, K.; Dawkins, K.; Deb, B.; Dunn, J.; Logue, C.M.; Novy, A.; O’Connor, A.M.; Reist, M.; et al. The efficacy of antibiotics to control collibacillosis in broiler poultry: A systematic review. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2019, 20, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, H.J.; Nolan, J.; Vaillancourt, J.P. Collibacillosis. In Diseases in Poultry, 12th ed.; Saif, I.M., Fadly, A.A., Glisson, J.R., McDougald, L.R., Nolan, L., Swayne, D.E., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2008; pp. 691–732. [Google Scholar]
- Nhung, N.T.; Chansiripornchai, N.; Carrique-Mas, J.J. Antimicrobial resistance in bacterial poultry pathogens: A review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.R. Optimisation of antimicrobial therapy using pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics parameters. Clin. Microbiol. Inf. Dis. 2001, 7, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persoons, D.; Dewulf, J.; Smet, A.; Herman, L.; Heyndrickx, M.; Martel, A.; Catry, B.; Butaye, P.; Haesebrouck, F. Antimicrobial use in belgian broiler production. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 105, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, P.; Sarrazin, S.; Van Gompel, L.; Luiken, R.E.C.; Mevius, D.J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Heedrik, D.J.J.; Dewulf, J.; EFFORD Consortium. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of antimicrobial usage at farm and flock level on 181 broiler farms in nine european countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Categorisation of Antibiotics Used in Animals Promotes Responsible Use to Protect Public and Animal Health. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/categorisation-antibiotics-used-animals-promotes-responsible-use-protect-public-animal-health (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Goetting, V.; Lee, K.A.; Tell, L.A. Pharmacokinetics of veterinary drugs in laying hens and residue in eggs: A review of the literature. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 521–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baert, K.; De Baere, S.; Croubels, S.; De Backer, P. Pharmacokinetics and oral bioavailability of sulfadiazine and trimethoprim in broiler chickens. Vet. Res. Commun. 2003, 27, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumano, H.; Hernandez, L.; Gutierrez, L.; Bernad-Bernad, M.J. Sustained availability of trimethoprim in drinking water to achive higher plasma sulphonamide-trimethoprim antibacterial activity in broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2005, 46, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putecova, K.; Nedbalcova, K.; Bartejsova, I.; Zouharova, M.; Matiaskova, K.; Jeklova, E.; Viskova, M.; Zouzelkova, P.; Jerabek, M.; Stastny, K. Experimental determination of the pharmacokinetic properties of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole combination in the blood serum of broiler chickens. Vet. Med. Czech 2021, 66, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Clinical Breakpoints—Breakpoints and Guidance. Available online: https://eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Harisberger, M.; Gobeli, S.; Hoop, R.; Dewulf, J.; Perretten, V.; Regula, G. Antimicrobial resistance in Swiss laying hens, prevalence and risk factors. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgariglia, E.; Mandolini, N.A.; Napoleoni, M.; Medici, L.; Fraticelli, R.; Conquista, M.; Gianfelici, P.; Staffolani, M.; Fisichella, S.; Capucella, M.; et al. Antibiotic resistance pattern and virulence genes in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) from different breeding systems. Vet. Ital. 2019, 55, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, N.; Käsbohrer, A.; Mayrhofer, S.; Zitz, U.; Hofacre, C.; Domig, K.J. The application of antibiotics in broiler production and the resulting antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli: A global overview. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wormser, G.P.; Keusch, G.T.; Heel, R.C. Co-trimoxazole: Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole. Drugs 1982, 24, 459–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, S.J.; Rosenberger, S.C.; Nolan, L.K. Identification of minimal predictors of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli virulence for use as a rapid diagnostic tool. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bower, C.K.; Daeschel, M.A. Resistance responses of microorganisms in food environments. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 50, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterik, L.H.; Peeters, L.; Mutuku, I.; Goddeeris, B.M.; Butaye, P. Susceptibility of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli from laying hens in Belgium to antibiotics and disinfectants and integron prevalence. Avian Dis. 2014, 58, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, I.K.; Hoyle, A.; Ochoa, G.; Baker-Austin, C.; Taylor, N.G.H. Optimising antibiotic usage to treat bacterial infections. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, F.S.; Lees, P. Antibiotic treatment for animals: Effect on bacterial population and dosage regimen optinalisation. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2000, 14, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goranova, M.; Ochoa, G.; Maier, P.; Hayle, A. Evolutionary optimalisation of antibiotic dosing regiments for bacteria with different levels of resistance. Artif. Intell. Med. 2022, 133, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. One Health. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/one-health (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Mulchandani, R.; Wang, Y.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food-producing animals: 2020 to 2030. PLOS Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0001305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 32019R0006; Regulation (EU) 2019/6 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2018 on Veterinary Medicinal Products and Repealing Directive 2001/82/EC. European Union Regulations: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; pp. L4–L43.
- Eliakim-Raz, N.; Hellerman, M.; Yahav, D.; Cohen, J.; Margalit, I.; Fisher, S.; Zusman, O.; Shaked, H.; Bishara, J. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole versus vancomycin in the treatment of healthcare/ventilator-associated MRSA pneumonia: A case-control study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Queralt, J.; Castells, I. Pharmacokinetics of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim association in hens. Poult. Sci. 1985, 64, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, W.A.; Andes, D. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antibiotics in otitis media. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1996, 15, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, N.; Carr, M.; Balian, S.; Lannin, J.; Kim, Y.; Toth, C.; Jarvis, J. The blood–brain barrier and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic optimization of antibiotics for the treatment of central nervous system infections in adults. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, E.L.; Anderson, J.D.; Lacey, R.W. A reappraisal of the antibacterial action of cotrimoxazole in vitro. J. Clin. Pathol. 1974, 27, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Methoxasol-t—Article 34 Referral—Annex I, II, III. Ref. No. CVMP/458933/08. EC Decision Date 11/01/2008. 2008. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/veterinary/referrals/methoxasol-t#overview-section (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- State Veterinary Administration. Narodni Antibioticky Program. Available online: https://www.svscr.cz/zdravi-zvirat/narodni-antibioticky-program/ (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Gray, P.; Jenner, R.; Norris, J.; Page, S.; Browning, G.; Australian Veterinary Association Ltd.; Animal Medicines Australia. Antimicrobial prescribing guidelines for poultry. Aust. Vet. J. 2021, 99, 181–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. EMEA/CVMP/VICH/591/98 VICH GL 2—Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/vich-gl2-validation-analytical-procedures-methodology-scientific-guideline (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. EMEA/CVMP/VICH/463202/2009 VICH GL 49—Studies to Evaluate the Metabolism and Residue Kinetics of Veterinary Drugs in Food-Producing Animals: Validation of Analytical Methods Used in Residue Depletion Studies. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/vich-gl49-studies-evaluate-metabolism-residue-kinetics-veterinary-drugs-food-producing-animals (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. EMEA/CVMP/EWP/133/1999—Final 2000—Guideline on Conduct of Pharmacokinetic Studies in Target Animal Species. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guidelines-conduct-pharmacokinetic-studies-target-animal-species_en.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. VET01S Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; CLSI Supplement, 5th ed.; Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–216. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. VET01-A4 Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Approved Standard, 4th ed.; Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, S.; Silley, P.; Simjee, S.; Woodford, N.; van Duijkeren, E.; Johnson, A.P.; Gaastra, W. Assessing the antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria obtained from animals. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 141, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedbalcova, K.; Bzdil, J.; Papouskova, A.; Zouharova, M.; Matiaskova, K.; Stastny, K.; Sladecek, V.; Senk, D.; Matej, P.; Stoalr, P. Pathotypes and phenotypic resistance of antimicrobials of Eswcherichia coli isolates from one-day-old chickens. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross Broiler Management Handbook. Aviagen. 2018. Available online: https://aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Broiler/Ross-BroilerHandbook2018-EN.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Ewers, C.; Janssen, T.; Kiessling, S.; Philipp, H.C.; Wieler, L.H. Rapid detection of virulence-associated genes in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Avian Dis. 2005, 49, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.R.; Octavia, S.; Lan, R. Population structure and virulence content of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from outbreaks in Sri Lanka. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papouskova, A.; Masarikova, M.; Valcek, A.; Senk, D.; Cejkova, D.; Jahodarova, E.; Cizek, A. Genomic analysis of Escherichia coli strains isolated from diseased chicken in the Czech Republic. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole Concentrations (mg L−1) | Number of Isolates | % |
|---|---|---|
| >64/1216 | 20 | 17.7 |
| 64/1216 | 2 | 1.8 |
| 32/608 | 0 | 0 |
| 16/304 | 0 | 0 |
| 8/152 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/76 | 0 | 0 |
| 2/38 | 1 | 0.9 |
| 1/19 | 3 | 2.6 |
| ≤0.5/9.5 | 87 | 77.0 |
| Group | Experimentally Infected | Treatment by the Experimental Dosage | Treatment by the Traditional Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | yes | yes | no |
| 2 | yes | no | yes |
| 3 | yes | no | no |
| 4 | no | no | no |
| Day | Activities with Animals |
|---|---|
| 1 | Intake of day-old chicks, divided into 4 groups of n = 10 |
| 19 | Weighing of chickens, experimental infection (groups 1, 2, and 3), initiation of treatment by group (groups 1 and 2) |
| 20 | Continuation of treatment by group (groups 1 and 2), weighing of chickens |
| 21 | Continuation of treatment by group (groups 1 and 2), weighing of chickens |
| 22 | Weighing of chickens |
| 23 | Weighing of chickens |
| 26 | End of experiment |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stastny, K.; Hodkovicova, N.; Jerabek, M.; Petren, M.; Viskova, M.; Papouskova, A.; Bartejsova, I.; Putecova-Tosnerova, K.; Charvatova, M.; Zouharova, M.; et al. Dosage Optimisation of Trimethoprim and Sulfamethoxazole for the Treatment of an Avian Pathogenic Strain of Escherichia coli in Broiler Chickens. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010011
Stastny K, Hodkovicova N, Jerabek M, Petren M, Viskova M, Papouskova A, Bartejsova I, Putecova-Tosnerova K, Charvatova M, Zouharova M, et al. Dosage Optimisation of Trimethoprim and Sulfamethoxazole for the Treatment of an Avian Pathogenic Strain of Escherichia coli in Broiler Chickens. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleStastny, Kamil, Nikola Hodkovicova, Martin Jerabek, Michal Petren, Michaela Viskova, Aneta Papouskova, Iva Bartejsova, Kristina Putecova-Tosnerova, Michaela Charvatova, Monika Zouharova, and et al. 2024. "Dosage Optimisation of Trimethoprim and Sulfamethoxazole for the Treatment of an Avian Pathogenic Strain of Escherichia coli in Broiler Chickens" Antibiotics 13, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010011
APA StyleStastny, K., Hodkovicova, N., Jerabek, M., Petren, M., Viskova, M., Papouskova, A., Bartejsova, I., Putecova-Tosnerova, K., Charvatova, M., Zouharova, M., Matiaskova, K., & Nedbalcova, K. (2024). Dosage Optimisation of Trimethoprim and Sulfamethoxazole for the Treatment of an Avian Pathogenic Strain of Escherichia coli in Broiler Chickens. Antibiotics, 13(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13010011







