Abstract
Background: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a global health concern, affecting approximately two-thirds of the world’s population. Standard first-line treatment regimens often fail, necessitating alternative rescue therapies. Objectives: This review aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of newer treatment regimens in patients who have failed initial H. pylori eradication therapy. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, the Cochrane Library, and Embase. Inclusion criteria were randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published after 2010, involving patients with previous H. pylori treatment failure and interventions with vonoprazan-based therapy, high-dose PPI–amoxicillin dual therapy (HDDT), or rifabutin-containing triple therapy. Results: 10 RCTs were included. HDDT demonstrated high eradication rates (81.3% to 89.2%), particularly when combined with metronidazole (92.6%), although at an increased frequency of adverse events. Vonoprazan-based regimens achieved comparable or higher eradication rates (83.3% to 89.5%) compared to PPI-based therapies, with similar adverse events. Rifabutin-containing triple therapy showed high efficacy (80.7% to 100%), particularly in patients with a history of multiple treatment failures, and it was associated with lower adverse events compared to bismuth-containing regimens. Conclusions: HDDT, vonoprazan-based therapy, and rifabutin-based therapy have proven to be effective and safe rescue regimens for treating H. pylori infection. Additional large-scale randomized studies are needed to determine the optimal doses and durations of these regimens to achieve the highest eradication rate with the lowest incidence of adverse events among patients with refractory H. pylori infections globally.
1. Introduction
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection affects about two-thirds of the population worldwide and leads to significant morbidity and mortality [1,2]. It is the most common cause of peptic ulcer disease and is strongly linked to chronic gastritis and gastric cancer [3,4]. H. pylori is responsible for almost 90% of distal gastric cancers, with the lifetime gastric cancer risk for infected individuals in the range of 1–5% [4,5]. Moreover, it may also exacerbate conditions such as vitamin B12 deficiency, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and non-alcoholic liver disease [6].
H. pylori targets the stomach lining [7] and is adept at surviving in the stomach’s acidic environment by burrowing into the mucous layer, causing inflammation and damage [8,9,10]. The risk factors for H. pylori infection include lower socioeconomic status, poor hygiene, dining at restaurants, alcohol consumption, and smoking [11,12,13]. Additionally, infection may be associated with ethnicity, with Black and Hispanic populations showing higher infection rates compared to Whites [14]. H. pylori infection is typically diagnosed via urea breath tests and stool antigen tests [15]. Eradication therapy is recommended for all infected individuals, with particular emphasis on testing and treating high-risk populations. This approach has been shown to reduce gastric cancer risk, especially in those with a family history of gastric cancer [16,17].
Treatment guidelines generally highlight the importance of achieving eradication on the first attempt to avoid the need for retreatment and the development of antibiotic resistance [18]. Traditional treatment has frequently comprised a combination of antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) [19]. An effective treatment regimen should achieve an eradication rate of over 90% [20]. Recommended first-line therapies for H. pylori infection have included clarithromycin triple therapy, bismuth quadruple therapy, concomitant therapy, and sequential therapy [19,21]. Clarithromycin triple therapy includes the use of a PPI, clarithromycin, and either amoxicillin or metronidazole, administered for 14 days. Bismuth quadruple therapy (BQT) consists of a PPI, bismuth, tetracycline, and nitroimidazole (such as metronidazole or tinidazole), with a treatment duration of 10 to 14 days. Concomitant therapy has included a PPI, clarithromycin, amoxicillin, and nitroimidazole taken for 10 to 14 days. Sequential therapy has offered a two-phase treatment: initially, a PPI and amoxicillin given for five to seven days, followed by a PPI, clarithromycin, and nitroimidazole for an additional five to seven days [19,21].
When initial therapy has failed, bismuth quadruple therapy, levofloxacin salvage regimens, and clarithromycin-containing regimens have been the preferred options based on local antimicrobial resistance rate and patient’s previous exposure to antibiotics [19,22]. However, increased antibiotic resistance and patient nonadherence due to adverse events of medications have made current treatment regimens inadequate to achieve desired outcomes [23]. H. pylori resistance rates were shown to be 21.4% for clarithromycin, 15.8% for levofloxacin, and 38.9% for metronidazole in Europe. The resistance rates in the Asia–Pacific region were shown to be 22% for clarithromycin, 52% for metronidazole, 26% for levofloxacin, 4% for tetracycline, and 4% for amoxicillin [24,25]. Therefore, the search for effective and safe treatment regimens for H. pylori infection in patients who have failed initial therapy has become a high priority.
Newer regimens, such as high-dose PPI–amoxicillin dual therapy (HDDT), vonoprazan-based therapy, and rifabutin-containing triple therapy, offer alternative mechanisms of action and improved acid suppression, providing potential advantages over traditional rescue regimens. Vonoprazan, a potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB), has shown a more profound effect on gastric acid suppression compared to PPIs [26]. Results from clinical trials and meta-analyses have proven the effectiveness and safety of vonoprazan-based therapy as a first-line treatment in treating H. pylori infections [27,28,29], providing evidence for the use of vonoprazan in patients who have failed initial PPI-based therapy. Rifabutin acts by inhibiting the β-subunit of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, resulting in bactericidal activity [30]. Rifabutin-containing triple therapy has also demonstrated high efficacy with few adverse events and high treatment adherence [31]. Furthermore, high-dose PPI combined with amoxicillin dual therapy has also proven to be effective and safe as a non-first-line therapy [32].
This review aims to describe the efficacy and safety of newer treatment regimens for H. pylori infection in patients who have failed first-line therapy and to provide guidance for the use of various therapies in clinical practice.
2. Methods
A literature review was conducted using databases such as PubMed, the Cochrane Library, and Embase on 9 February 2024. The search terms included “Helicobacter pylori”, “H. pylori”, second-line, third-line, fourth-line, rescue, salvage, refractory, and RCT*, random*, “randomized controlled trial*”, intervention, trial* or “clinical trial*”. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) patients with previous treatment failure; (2) interventions involving vonoprazan-based therapy, PPI–amoxicillin dual therapy, or rifabutin-containing therapy; (3) randomized controlled trials; (4) reported results on eradication rate; and (5) published after 2010. Studies conducted in other countries outside the US were also included. Studies such as reviews, meta-analyses, posters, meeting abstracts, and case reports were excluded. Only full-text studies were included.
3. Results
The initial search identified 1010 articles; 313 articles were included in PubMed, 275 in Embase, and 422 in the Cochrane Library. A total of 385 duplicate documents were excluded. After a preliminary screening of the titles or abstracts, 505 papers were excluded. Fifty articles were excluded after a review of the published abstracts. After carefully reading the full texts, an additional 37 articles were excluded. Ultimately, 10 studies were selected for inclusion [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] (Figure 1). Key characteristics of the included studies, the medication regimens, eradication rates, and the adverse events rate can be found in Table 1.
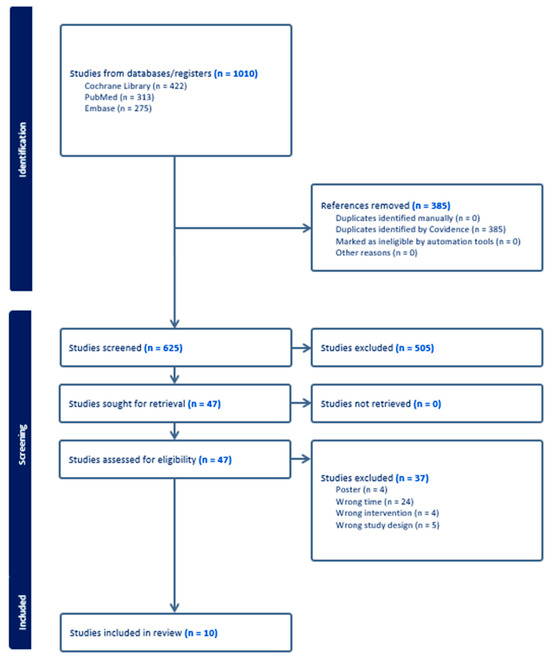
Figure 1.
Study selection flowchart.

Table 1.
Summary of included studies and the efficacy and safety results.
3.1. High-Dose PPI–Amoxicillin Dual Therapy (HDDT)
Five studies explored the efficacy of HDDT compared to other well-established rescue therapies, with some employing modifications to enhance their effectiveness [32,33,34,35,36]. Bi et al. [32] conducted a multicenter, randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of HDDT compared to bismuth-containing quadruple therapy in patients with prior H. pylori treatment failures. The HDDT regimen achieved eradication rates of 75.4% in the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis and 81.3% in the per protocol (PP) analysis. Moreover, patients in the HDDT group experienced significantly fewer adverse events compared to the bismuth-containing quadruple therapy group (11.1% versus 26.8%, p < 0.001). Yang et al. [33] compared HDDT against traditional alternative rescue regimens and found that the HDDT group achieved higher eradication rates (89.3%) compared to sequential therapy (51.8%) and levofloxacin-containing triple therapy (78.6%) in ITT analysis. The overall occurrence of adverse events was similar among all groups. Okimoto et al. [36] observed that the eradication rates were 73.9% in the levofloxacin triple therapy group and 64.0% in the HDDT group in the ITT analysis, with no significant differences in adverse events between the two groups.
Some researchers explored modifications to HDDT to enhance its efficacy [34,35]. Ding et al. [34] found that the addition of metronidazole to HDDT significantly improved eradication rates, reaching 85.8% in ITT and 92.6% in PP analysis, compared to 73.1% and 83.1% for HDDT alone, respectively. However, a higher incidence of adverse events was observed with the metronidazole-containing regimen (23.1% vs. 6.0%, p < 0.001). In contrast, Goh et al. [35] found no significant improvement in eradication rates when bismuth was added to HDDT (80.5% ITT and 82.5% PP) compared to HDDT alone (84.6% ITT and 89.2% PP), with similar adverse effect profiles.
The most frequently reported adverse events for HDDT included nausea, diarrhea, dysgeusia, abdominal pain, flatulence, headache, dizziness, decreased appetite, constipation, fatigue, and skin rash [32,33,34,35,36]. Only a few participants experienced severe adverse events that led to treatment discontinuation. Most adverse events were mild-to-moderate, and patients typically recovered after treatment [32,33,34,35,36].
3.2. Vonoprazan-Based Therapy
Two RCTs reported the efficacy and safety of vonoprazan-based therapy versus PPI-based therapy for patients who had failed first-line therapy [37,38]. Hojo et al. [37] found that the eradication rates in the vonoprazan and PPI groups were 73.9% vs. 82.6% in ITT and 89.5% vs. 86.4% in PP analyses, with no significant differences in the occurrence of adverse events between the groups. Sue et al. [38] noticed that vonoprazan-based therapy achieved higher eradication rates with PP analysis (83.3%) compared to PPI-based therapy (57.1%, p = 0.043), although the differences with ITT analysis were not statistically significant. Both studies reported that adverse events from vonoprazan-based therapy were generally mild-to-moderate, and few participants discontinued treatment. The most common adverse events included nausea, diarrhea, dysgeusia, abdominal discomfort, abdominal bloating, and belching [37,38].
3.3. Rifabutin-Containing Triple Therapy
Three RCTs studied the use of rifabutin as a rescue therapy in patients with previous treatment failures [31,39,40]. Chen et al. [31] compared rifabutin-containing triple therapy (150 mg twice daily) with bismuth quadruple therapy in a large-scale multicenter trial in China. Both therapies demonstrated high eradication rates (89.0% for rifabutin vs. 89.6% for bismuth) in ITT analysis, and the rifabutin group showing significantly lower adverse events (26.4% vs. 54.4%, p < 0.001). Lim et al. [39] evaluated rifabutin-based triple therapy with 30 mg lansoprazole versus 60 mg lansoprazole. The higher dose of lansoprazole achieved eradication rates of 96.3% (ITT) and 100% (PP), significantly higher than the lower-dose group (78.1% ITT, 80.6% PP, p = 0.047). The treatment was well tolerated, with mild adverse effects. Mori et al. [40] assessed 10-day and 14-day rifabutin-based therapies (300 mg once daily) in a small group of Japanese patients and found that the eradication rates were 83.3% and 94.1% in ITT analyses, respectively. However, the incidence of adverse events was high (83.3% to 94.1%) but comparable between the two durations of therapy. Across the three studies, adverse events from rifabutin-containing triple therapy were generally mild and manageable. The most commonly observed adverse events were diarrhea, fever, skin rash, myalgia, and fatigue. The treatments were well tolerated, and all adverse events were reversible [31,39,40].
4. Discussion
This review has described the efficacy and safety of newer treatment regimens for H. pylori eradication in patients who have failed initial therapy. HDDT, vonoprazan-based regimens, and rifabutin-containing triple therapy demonstrated high eradication rates, offering viable options for patients where first-line treatments have failed. HDDT, especially when combined with metronidazole, achieved high eradication rates, albeit with a higher rate of adverse events. Vonoprazan-based therapies showed a comparable or higher eradication rate compared to PPI-based regimens. Rifabutin-containing therapy emerged as a third-line option with high eradication rates and a lower incidence of adverse effects compared to bismuth-containing regimens.
H. pylori infection is a major global health concern. Effective eradication on the first attempt is critical, as failure can lead to increased treatment resistance, requiring the use of more complex treatment regimens and greater healthcare costs [41]. Failure of first-line H. pylori eradication therapy is not uncommon, with global eradication rates often falling below the desired threshold of 90% [42]. Approximately 20% to 30% of patients fail first-line therapy in the US [43]. This failure is primarily driven by increasing antibiotic resistance, poor patient adherence, and suboptimal treatment regimens [23,44]. Treatment of patients after initial therapy failure presents a significant clinical challenge. The need for effective and tolerable rescue regimens is crucial in managing refractory H. pylori infections. The newer regimens explored in this review (HDDT, vonoprazan-based therapies, and rifabutin-containing therapies) address key gaps in the current treatment strategies for H. pylori infection. These regimens offer high eradication rates, and some of them were shown to reduce adverse effects compared to traditional treatments, such as bismuth-containing therapies.
The effectiveness of these newer regimens lies in their ability to overcome the limitations of traditional therapies through enhanced acid suppression, alternative mechanisms of bacterial inhibition, and the strategic use of antibiotics that are less prone to development of resistance. By optimizing the gastric environment and employing antibiotics with distinct mechanisms, these therapies provide a higher likelihood of achieving eradication in patients where standard regimens have failed. An HDDT regimen enhances the efficacy of amoxicillin by maintaining elevated gastric pH levels, which optimizes the antimicrobial activity against H. pylori [45]. Vonoprazan provides more potent and sustained gastric acid suppression than traditional PPIs, creating a more favorable environment for antibiotics to kill H. pylori [46]. Rifabutin targets bacterial RNA polymerase and bypasses common resistance pathways, highlighting its role as a potent salvage therapy [47].
The use of metronidazole and rifabutin in H. pylori rescue therapy, while effective, may present a significant challenge due to elevated adverse events. Metronidazole is known to cause gastrointestinal discomfort, including nausea, metallic taste, and antibiotic-associated diarrhea [48]. The rate of adverse events of metronidazole-containing regimens can be as high as 47.8% [37]. Similarly, rifabutin can cause gastrointestinal disturbances, myalgia, and uveitis [49]. The adverse events of rifabutin appear to be dose-dependent and may vary across populations. A large Chinese study reported significantly lower adverse event rates for rifabutin (150 mg twice daily) compared to bismuth-containing quadruple therapy [31]. Conversely, a small Japanese study observed a high adverse event rate of 94.1% when rifabutin was administered at 300 mg once daily [40]. These findings suggest that a dosage regimen of 150 mg twice daily might be safer while maintaining efficacy.
The occurrence of adverse events can decrease treatment adherence and patient quality of life. The European Registry’s study on H. pylori management found that 1.7% of patients were nonadherent to treatment regimens, with higher rates seen among those prescribed treatment regimens with a longer duration, rescue therapies, and those who experienced adverse events [50]. A recent study found that about 23% of patients experienced at least one adverse event related to H. pylori eradication treatments, such as taste disturbance (7%), diarrhea (7%), nausea (6%), and abdominal pain (3%) [51]. Mitigating adverse events during treatment involves several strategies. Conducting pre-treatment assessments, such as evaluating for history of antibiotics allergies or drug intolerances, can prevent complications from Helicobacter pylori treatment. Clinicians should educate patients about potential adverse effects, such as nausea, diarrhea, dysgeusia, and fatigue, encourage prompt reporting for timely management, and emphasize the importance of medication adherence to prevent antibiotic resistance and treatment failure. Enhanced monitoring and educational interventions, such as telephone follow-up re-education, short-message services, and smart phone applications could be employed as well to enhance the treatment adherence. Evidence shows that enhanced educational interventions have had positive effects on both the H. pylori eradication rate and adherence [52]. Another practical approach is the potential use of probiotics or prebiotics, which may restore the gut microbiota balance and reduce gastrointestinal adverse effects [53,54]. In addition, lowering the dose of metronidazole can reduce the risk of adverse events while maintaining efficacy [55]. Shorter treatment durations, when clinically appropriate, can further decrease cumulative drug exposure and the likelihood of adverse effects. Personalized therapy based on regional resistance profiles may also enhance the optimization of medication regimens to achieve the desired efficacy of antibiotics [56].
Recommendations for treatment
Our recommendations for managing refractory H. pylori infections, addressing patient-specific factors such as prior treatment failures and penicillin allergies, are shown in Figure 2. For patients who have failed clarithromycin-based regimens as an initial therapy, BQT might be recommended as a first-line rescue therapy if the patients have a penicillin allergy. For patients without a penicillin allergy, the treatment regimens could be either HDDT or BQT. Given the lower incidence of adverse events associated with HDDT compared to BQT, HDDT might be the preferred option, as it may result in better tolerability while maintaining high eradication rates. If the first-line rescue therapy fails, vonoprazan-based therapy with metronidazole or levofloxacin-based therapy should be considered as second-line rescue therapies. Third-line rescue treatments may include vonoprazan-based therapy with sitafloxacin or rifabutin-based therapy.
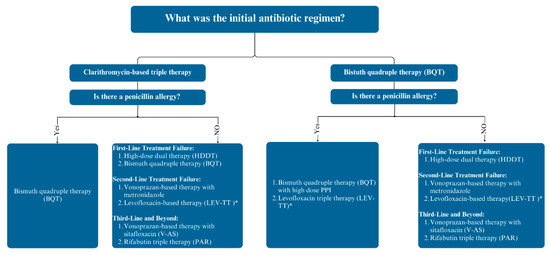
Figure 2.
Approach to antibiotic treatment in patients with persistent Helicobacter pylori infection. Abbreviation: PPI, proton pump inhibitor. * If the local levofloxacin resistance rates were less than 15%.
For patients who have failed BQT as an initial regimen, several next-step treatments are available. For patients with a penicillin allergy, repeating BQT with high-dose PPI or switching to levofloxacin-based triple therapy are effective first-line rescue options. In patients without a penicillin allergy, HDDT should be the preferred treatment for a first-line rescue regimen. For second-line rescue therapies, vonoprazan-based therapy could be used with metronidazole as an option, or levofloxacin-based therapy can be used if needed. Third-line therapies, such as rifabutin-containing triple therapy and vonoprazan-based therapy with sitafloxacin, can be used in those who have not responded to first- and second-line rescue therapies.
Limitations
First, most studies were conducted in China and Japan, which may restrict the applicability of the results to other populations residing in other countries with different antibiotic resistance patterns. These findings do not fully represent the global population due to lack of adequate studies, especially in Western countries. Another limitation is the small sample sizes of most of the included trials. The small sample sizes limit the generalizability of the results and make it difficult to draw robust conclusions. The absence of diverse ethnic and geographic representation in the study populations restricts the relevance of the findings to global clinical practice.
Future research should focus on identifying optimal regimens to mitigate adverse effects, such as the use of lower doses, shorter treatment durations, or combining agents with complementary mechanisms that minimize toxicity while achieving the desired efficacy.
Future research should expand the geographical scope of studies to include diverse populations from various regions with different resistance patterns. This is important, as the current data have largely come from studies conducted in regions like China and Japan. Larger multicenter randomized controlled trials are needed to provide additional robust data on the efficacy and safety of newer regimens. Moreover, future research should focus on thoroughly assessing the safety of different medications by providing detailed reports on adverse events, including their severity, duration, and management strategies. Such comprehensive data will enable clinicians to better anticipate potential adverse effects and implement effective strategies to mitigate them, which, in turn, could enhance patient adherence and improve overall treatment outcomes. Furthermore, future research should evaluate optimal regimens to mitigate adverse effects, such as the use of lower doses of antibiotics, shorter treatment durations, or combined medications with different mechanisms. One possible approach may involve investigating antibiotic combinations that utilize synergistic effects to lower the overall required dose, thereby reducing potential toxicity. For example, dual-therapy regimens involving PPI with amoxicillin may be optimized by adjusting their ratios to achieve efficacy at lower doses. Administration of PPI–amoxicillin dual therapy four times daily has shown greater efficacy and safety compared to other regimens [57]. Shortening the treatment duration might also mitigate adverse events, as longer regimens are associated with higher incidences of adverse effects [58]. Additionally, combining antibiotics with probiotics could reduce the risk of gastrointestinal disturbances while maintaining the desired eradication rates [59]. Future research should also emphasize antibiotic susceptibility testing or genotypic resistance-guided therapy to personalize treatment regimens, including the assessments of their cost-effectiveness among patients [60,61,62]. Additionally, an expansion of global and regional databases of resistance patterns and data regarding clinical efficacy and safety outcomes could guide the location-specific selection of treatments, improving eradication success in diverse populations [63].
5. Conclusions
High-dose PPI and amoxicillin dual therapy, vonoprazan-based therapy, and rifabutin-based therapy have proven to be effective and safe rescue regimens for treating H. pylori infection. These regimens have generally achieved eradication rates exceeding 80%, with some studies reporting rates approaching 90%. The incidence of adverse events associated with these treatments was comparable to or lower than traditional rescue regimens, such as PPI-based triple therapy or bismuth quadruple therapy. Further well-designed large-scale randomized studies are required to determine the optimal doses and durations of various treatment regimens to achieve the highest eradication rate with the lowest incidence of adverse events among patients with refractory H. pylori infections.
Author Contributions
Guarantor: M.C.N. He accepts full responsibility for the work and for performing the study, had access to the data, and controlled the decision to publish. Specific author contributions: L.L. and M.C.N. conceived and drafted the study. L.L. drafted the manuscript. All authors commented on drafts of the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, Y.; Choi, H.; Leung, K.; Jiang, F.; Graham, D.Y.; Leung, W.K. Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection between 1980 and 2022: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, M.; Franceschi, S.; Vignat, J.; Forman, D.; de Martel, C. Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégraud, F.; Bessède, E.; Varon, C. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrift, A.P.; Wenker, T.N.; El-Serag, H.B. Global burden of gastric cancer: Epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsay, F.-W.; Hsu, P.-I. H. pylori infection and extra-gastroduodenal diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.R.; Marshall, B. Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1983, 1, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Survival of Helicobacter pylori in gastric acidic territory. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, P. Helicobacter pylori and inflammation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 4225–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.; Reddy, K.M.; Marsicano, E. Peptic Ulcer Disease and Helicobacter pylori infection. Mo. Med. 2018, 115, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Melese, A.; Genet, C.; Zeleke, B.; Andualem, T. Helicobacter pylori infections in Ethiopia; prevalence and associated factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhaskar, R.S.; Ricardo, I.; Azliyati, A.; Laxminarayan, R.; Amol, B.; Santosh, W.; Boo, K. Assessment of risk factors of Helicobacter pylori infection and peptic ulcer disease. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2013, 5, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Adeloye, D.; Luk, T.T.; Huang, L.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ye, X.; Yi, Q.; Song, P.; Rudan, I. The global prevalence of and factors associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2022, 6, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.; Cantrell, S.; Tang, H.; Epplein, M.; Garman, K.S. Racial Differences in Helicobacter pylori Prevalence in the US: A Systematic Review. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori Infection, Its Laboratory Diagnosis, and Antimicrobial Resistance: A Perspective of Clinical Relevance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 35, e0025821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.-M.; Malfertheiner, P.; Lee, Y.-C.; Sheu, B.-S.; Sugano, K.; Cheng, H.-C.; Yeoh, K.-G.; Hsu, P.-I.; Goh, K.-L.; Mahachai, V.; et al. Screening and eradication of Helicobacter pylori for gastric cancer prevention: The Taipei global consensus. Gut 2020, 69, 2093–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.J.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.-I.; Kook, M.-C.; Park, B.; Joo, J. Family History of Gastric Cancer and Helicobacter pylori Treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, N.; Howden, C.W. Update on the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2020, 18, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Howden, C.W.; Moss, S.F. ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 212–239, Correction in Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Dore, M.P.; Graham, D.Y. Diagnosis and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Liou, J.M.; Schulz, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Hunt, R.H.; Leja, M.; O’Morain, C.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: The Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut, 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, A. H. pylori Infection: ACG Updates Treatment Recommendations. Am. Fam. Physician 2018, 97, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.C.; Iyer, P.G.; Moss, S.F. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Management of Refractory Helicobacter pylori Infection: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megraud, F.; Bruyndonckx, R.; Coenen, S.; Wittkop, L.; Huang, T.D.; Hoebeke, M.; Bénéjat, L.; Lehours, P.; Goossens, H.; Glupczynski, Y. Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics in Europe in 2018 and its relationship to antibiotic consumption in the community. Gut 2021, 70, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.-C.; El-Omar, E.M.; Kuo, Y.-T.; Wu, J.-Y.; Chen, M.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; Fang, Y.-J.; Leow, A.H.R.; Lu, H.; Lin, J.-T.; et al. Primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori in the Asia-Pacific region between 1990 and 2022: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echizen, H. The First-in-Class Potassium-Competitive Acid Blocker, Vonoprazan Fumarate: Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 55, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Nahata, M.C. Vonoprazan With Amoxicillin or Amoxicillin and Clarithromycin for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Ann. Pharmacother. 2023, 57, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Tsai, F.-P.; Chen, M.-J.; Yang, H.-Y.; Wu, M.-S.; Liou, J.-M. Vonoprazan-based versus proton pump inhibitor-based therapy in Helicobacter pylori eradication: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Gut 2023, 73, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, A.; Guo, N.; Li, F.; Nahata, M.C. Vonoprazan-based therapies versus PPI-based therapies in patients with H. pylori infection: Systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Helicobacter 2024, 29, e13094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borraccino, A.V.; Celiberto, F.; Pricci, M.; Girardi, B.; Iannone, A.; Rendina, M.; Ierardi, E.; Di Leo, A.; Losurdo, G. Rifabutin as salvage therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: Cornerstones and novelties. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 6356–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Xu, P.; Han, Y.; Lu, H. Rifabutin-Containing Triple Therapy Versus Bismuth Quadruple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Rescue Treatment: A Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 228, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Lyu, T.; Han, S.; Lin, T.; Li, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of high-dose esomeprazole-amoxicillin dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori rescue treatment: A multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-C.; Lin, C.-J.; Wang, H.-L.; Chen, J.-D.; Kao, J.Y.; Shun, C.-T.; Lu, C.-W.; Lin, B.-R.; Shieh, M.-J.; Chang, M.-C.; et al. High-dose Dual Therapy Is Superior to Standard First-line or Rescue Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 13, 895–905.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.N.; Luo, L.S.; Zhang, W.; Liang, X.; Lu, H. A randomized superiority clinical trial: Metronidazole improved the efficacy of high-dose dual therapy in Helicobacter pylori rescue treatment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.; Chang, J.; Leow, A.H. High-dose proton pump inhibitor and amoxicillin dual therapy with or without bismuth for 14 days as rescue therapies after Helicobacter pylori treatment failure. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimoto, K.; Arai, M.; Saito, K.; Minemura, S.; Maruoka, D.; Matsumura, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Katsuno, T.; Ishii, C.; Murata, S.; et al. Efficacy of Levofloxacin Based Triple and High-Dose PPI-Amoxicillin Dual Eradication Therapy for Helicobacter pylori after Failures of First- and Second-Line Therapies. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 631501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hojo, M.; Asaoka, D.; Takeda, T.; Shimada, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Yatagai, N.; Akazawa, Y.; Ueda, K.; Ueyama, H.; et al. Randomized controlled study on the effects of triple therapy including vonoprazan or rabeprazole for the second-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820966247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sue, S.; Shibata, W.; Sasaki, T.; Kaneko, H.; Irie, K.; Kondo, M.; Maeda, S. Randomized trial of vonoprazan-based versus proton-pump inhibitor-based third-line triple therapy with sitafloxacin for Helicobacter pylori. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.C.; Lee, Y.J.; An, B.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, Y.C.; Moon, B.S. Rifabutin-based high-dose proton-pump inhibitor and amoxicillin triple regimen as the rescue treatment for Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mori, H.; Suzuki, H.; Matsuzaki, J.; Tsugawa, H.; Fukuhara, S.; Miyoshi, S.; Hirata, K.; Seino, T.; Matsushita, M.; Nishizawa, T.; et al. Rifabutin-based 10-day and 14-day triple therapy as a third-line and fourth-line regimen for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A pilot study. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2016, 4, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Hubscher, E.; Pelletier, C.; Jacob, R.; Vinals, L.; Yadlapati, R. Helicobacter pylori infection treatment in the United States: Clinical consequences and costs of eradication treatment failure. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 16, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, P.; Nelson, A.D.; Bi, Y.; Stancampiano, F.F.; Murray, L.P.; Pujalte, G.G.; Gomez, V.; Harris, D.M. Treatment Approach of Refractory Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Comprehensive Review. J. Prim. Care Community Health 2021, 12, 21501327211014087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Dunbar, K.B.; Mitui, M.; Arnold, C.A.; Lam-Himlin, D.M.; Valasek, M.A.; Thung, I.; Okwara, C.; Coss, E.; Cryer, B.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Clarithromycin Resistance and Treatment Failure Are Common in the USA. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumpan, N.; Issariyakulkarn, N.; Mahachai, V.; Graham, D.; Yamaoka, Y.; Vilaichone, R.-K. Management of Helicobacter pylori treatment failures: A large population-based study (HP treatment failures trial). PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.-Y.; Zhao, J.-T.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, J.-R.; Lan, C.-H. High dose PPI-amoxicillin dual therapy for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820937115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirley, M. Vonoprazan: A Review in Helicobacter pylori Infection. Drugs 2024, 84, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Calvet, X. Review article: Rifabutin in the treatment of refractory Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 35, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, S.; Dickinson, J.A.; Somayaji, R. Update on the adverse effects of antimicrobial therapies in community practice. Can. Fam. Physician 2020, 66, 651–659. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, M.C.; Wald-Dickler, N.; Loomis, K.; Luna, B.M.; Spellberg, B. Pharmacology, Dosing, and Side Effects of Rifabutin as a Possible Therapy for Antibiotic-Resistant Acinetobacter Infections. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, J.M.; Ferrer-Barceló, L.; Suárez, P.; Barcelo-Cerda, S.; Sempere, J.; Saracino, I.M.; Fiorini, G.; Vaira, D.; Pérez-Aísa, Á.; Jonaitis, L.; et al. Role of compliance in Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment: Results of the European Registry on H. pylori management. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2024, 12, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, O.P.; Perez-Aisa, A.; Tepes, B.; Castro-Fernandez, M.; Kupcinskas, J.; Jonaitis, L.; Bujanda, L.; Lucendo, A.; Jurecic, N.B.; Perez-Lasala, J.; et al. Adverse Event Profile During the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori: A Real-World Experience of 22,000 Patients from the European Registry on H. pylori Management (Hp-EuReg). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, J.; Li, Y.; Qu, J.; Yang, X.; Han, Z.; Zuo, X. Effects of enhanced education for patients with the Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: From biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Peng, X.-J.; Liu, X.-L.; Hu, X.-K.; Xing, D.-M. Current and future perspectives for Helicobacter pylori treatment and management: From antibiotics to probiotics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1042070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Lu, H. Meta-analysis: High-dose vs. low-dose metronidazole-containing therapies for Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Meng, W.; Dai, Y.; Wang, W. Empirical versus tailored therapy based on genotypic resistance detection for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16, 17562848231196357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Shi, Y.; Suo, B.; Tian, X.; Zhou, L.; Song, Z. PPI-amoxicillin dual therapy four times daily is superior to guidelines recommended regimens in the Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy within Asia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.-M.; Duan, M.; Han, Z.-X.; Song, X.-H.; Zhang, F.-L.; Wang, Z.; Ning, Z.; Zeng, S.-Y.; Kong, Q.-Z.; Zhang, W.-L.; et al. Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Randomized Clinical Trial of 10 and 14 Days. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2024, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of probiotic-supplemented therapy on the eradication of H. pylori and incidence of therapy-associated side effects. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.; Lee, Y.; Wu, M. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection and its long-term impacts on gut microbiota. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.-M.; Chen, P.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-T.; Wu, M.-S. Toward population specific and personalized treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P. Empirical or susceptibility-guided treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection? A comprehensive review. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820968736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Shao, Y.; Yan, J.; Ye, G. Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: From potential biomolecular mechanisms to clinical practice. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2023, 37, e24885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).