Pharmacokinetics and Nephrotoxicity of Polymyxin MRX-8 in Rats: A Novel Agent against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LC-MS/MS Method Development for MRX-8 and Metabolite MRX-8039
2.2. LC-MS/MS Method Validation
2.3. Pharmacokinetics of MRX-8 and PMB in Rats
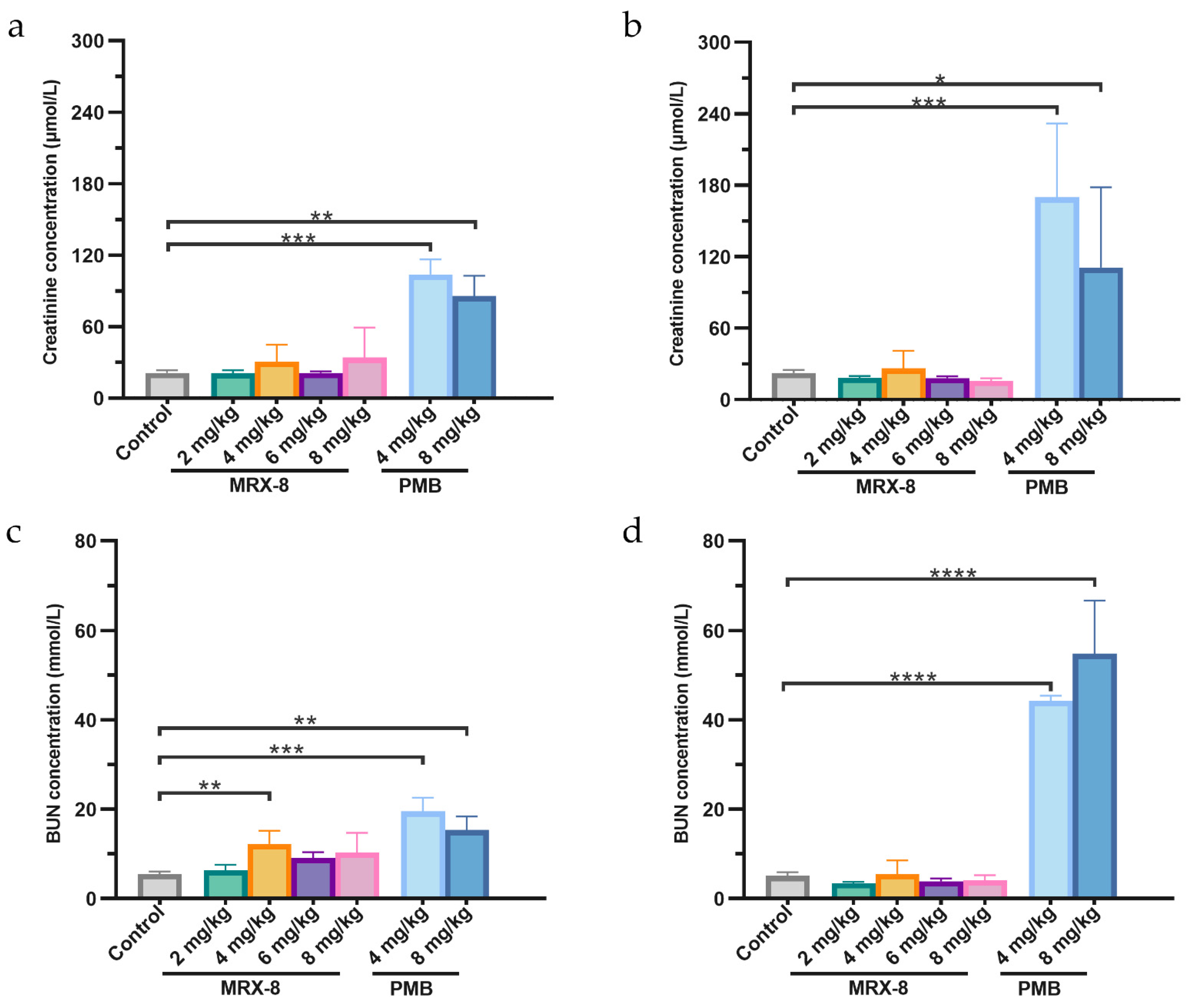
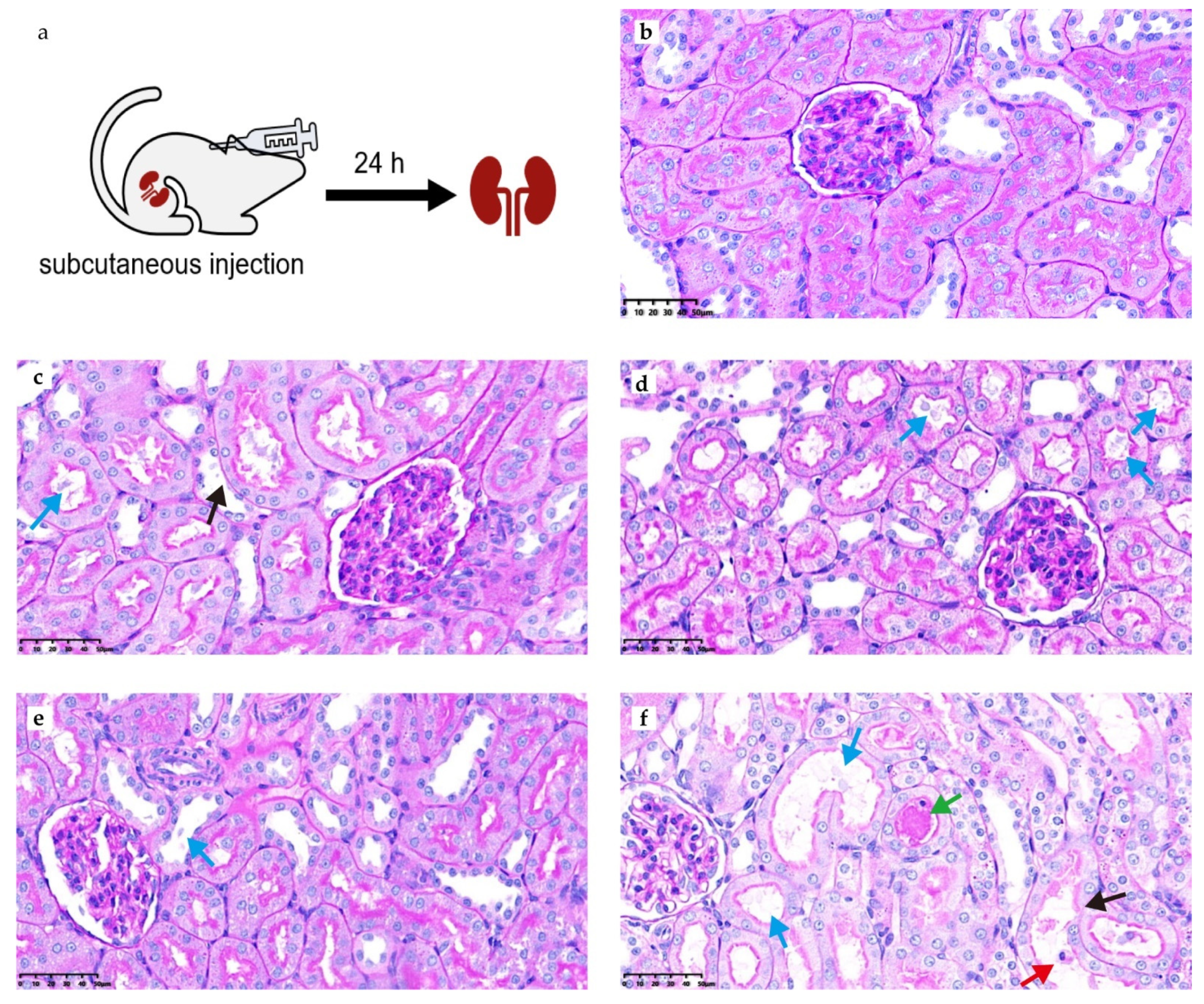
2.4. Comparative Safety and Nephrotoxicity Evaluations of MRX-8 and PMB in Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. LC-MS/MS Determination Method and Validation
4.2.1. LC-MS/MS Conditions
4.2.2. Plasma Sample Preparation for LC-MS/MS
4.2.3. Method Validation
4.3. Pharmacokinetics Experimental Design
4.4. Pharmacokinetics Analysis
4.5. Measurement of Kidney Injury Indicators
4.6. PAS Staining and SQS
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nang, S.C.; Azad, M.A.K.; Velkov, T.; Zhou, Q.T.; Li, J. Rescuing the Last-Line Polymyxins: Achievements and Challenges. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 679–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, S.S.; Gould, I.M.; Lee, W.S.; Hsueh, P.R. New Drugs for Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Organisms: Time for Stewardship. Drugs 2019, 79, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardakas, K.Z.; Falagas, M.E. Colistin versus polymyxin B for the treatment of patients with multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.; Qu, X.; Zhang, J.; Nang, S.C.; Bergen, P.J.; Zhou, Q.T.; Chan, H.K.; Feng, M.; Li, J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of peptide antibiotics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 183, 114171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenlehner, F.; Lucenteforte, E.; Pea, F.; Soriano, A.; Tavoschi, L.; Steele, V.R.; Henriksen, A.S.; Longshaw, C.; Manissero, D.; Pecini, R.; et al. Systematic review on estimated rates of nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity in patients treated with polymyxins. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodise, T.P.; Yucel, E.; Obi, E.N.; Watanabe, A.H.; Nathanson, B.H. Incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) and its impact on patient outcomes among adult hospitalized patients with carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative infections who received targeted treatment with a newer β-lactam or β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor-, polymyxin- or aminoglycoside-containing regimen. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 79, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea-Henry, T.N.; Carland, J.E.; Stocker, S.L.; Sevastos, J.; Roberts, D.M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics in Kidney Disease: Fundamental Principles. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepak, A.J.; Wang, W.; Andes, D.R. Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of MRX-8, a Novel Polymyxin, in the Neutropenic Mouse Thigh and Lung Infection Models against Gram-Negative Pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01517-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, L.R.; Wang, W.; Sader, H.S. In Vitro Potency and Spectrum of the Novel Polymyxin MRX-8 Tested against Clinical Isolates of Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0013922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.T.; Akova, M.; Paterson, D.L. Next-Generation Polymyxin Class of Antibiotics: A Ray of Hope Illuminating a Dark Road. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yin, D.; Zhi, P.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Hu, F. In Vitro Activity of MRX-8 and Comparators Against Clinical Isolated Gram-Negative Bacilli in China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 829592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Gao, S.; Hu, M.; Chow, D.S.; Tam, V.H. A validated ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of polymyxin B in mouse serum and epithelial lining fluid: Application to pharmacokinetic studies. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voitenko, V.G.; Bayramashvili, D.I.; Zebrev, A.I.; Zinchenko, A.A. Relationship between structure and histamine releasing action of polymyxin B and its analogues. Agents Actions 1990, 30, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Ma, N.; Liu, R.; Wang, N.; Zhang, T.; He, L. Polymyxin B and polymyxin E induce anaphylactoid response through mediation of Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor X2. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 308, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheah, S.E.; Bulitta, J.B.; Li, J.; Nation, R.L. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry assay for polymyxin B in bacterial growth media. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 92, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakeev, A.P.; Yanovskaya, E.A.; Yanovsky, V.A.; Andropov, M.O.; Frelikh, G.A.; Yu Chukicheva, I.; Kutchin, A.V. LC-MS/MS method for the determination of a semi-synthetic phenolic antioxidant 2,6-diisobornyl-4-methylphenol in rats after different administration routes. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2022, 1213, 123537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, W.F.; Jacobsen, B. Subcutaneous absorption of biotherapeutics: Knowns and unknowns. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraouf, K.; He, J.; Ledesma, K.R.; Hu, M.; Tam, V.H. Pharmacokinetics and renal disposition of polymyxin B in an animal model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 5724–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Abdelraouf, K.; Ledesma, K.R.; Chow, D.S.; Tam, V.H. Pharmacokinetics and efficacy of liposomal polymyxin B in a murine pneumonia model. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrezenmeier, E.V.; Barasch, J.; Budde, K.; Westhoff, T.; Schmidt-Ott, K.M. Biomarkers in acute kidney injury—Pathophysiological basis and clinical performance. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 554–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lin, Q.; Dai, X.; Chen, J.; Bai, Z.; Li, X.; Fang, F.; Li, Y. Derivation and validation of urinary TIMP-1 for the prediction of acute kidney injury and mortality in critically ill children. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Ott, K.M. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of acute kidney injury—Where do we stand today? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvidberg, V.; Jacobsen, C.; Strong, R.K.; Cowland, J.B.; Moestrup, S.K.; Borregaard, N. The endocytic receptor megalin binds the iron transporting neutrophil-gelatinase-associated lipocalin with high affinity and mediates its cellular uptake. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballı, F.N.; Ekinci, P.B.; Kurtaran, M.; Kara, E.; Dizman, G.T.; Sönmezer, M.; Hayran, M.; Demirkan, K.; Metan, G. Battle of Polymyxin Induced Nephrotoxicity: Polymyxin B versus Colistin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 63, 107035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavascki, A.P.; Nation, R.L. Nephrotoxicity of Polymyxins: Is There Any Difference between Colistimethate and Polymyxin B? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02319-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.D.; Luo, J.; Jia, L.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Xun, Z.K.; Liu, M. Cytochrome C suppresses renal accumulation and nephrotoxicity of polymyxin B. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Wu, S.; Jiang, G.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y. Baicalein ameliorates polymyxin B-induced acute renal injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via regulation of SIRT1/p53 acetylation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 382, 110607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Hu, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Lin, G. Effect of Different Dosage Frequency of Polymyxin B on Rat Nephrotoxicity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariano, F.; Malvasio, V.; Risso, D.; Depetris, N.; Pensa, A.; Fucale, G.; Gennari, F.; Biancone, L.; Stella, M. Colistin Therapy, Survival and Renal Replacement Therapy in Burn Patients: A 10-Year Single-Center Cohort Study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 5211–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Q2(R2) Validation of Analytical Procedures. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/q2r2-validation-analytical-procedures (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- National Medical Products Administration. The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (the 2020 Edition); National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2020.
- ICH Guideline M10 on Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-guideline-m10-bioanalytical-method-validation-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, B. Development and validation of ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric methods for simultaneous and rapid determination of contezolid and its major metabolite M2 in plasma and urine samples and its application to a study in subjects with moderate liver impairment. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2022, 1191, 123129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, S.L. Ways to fit a PK model with some data below the quantification limit. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2001, 28, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, J.M.; Chen, G.; Hill, P.A.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Melatonin attenuates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4044–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| MRX-8 | MRX-8039 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Measured Conc (mg/L) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | Mean Measured Conc (mg/L) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | |||
| Intra-day (n = 5) | LLOQ | 0.0100 | 0.00974 | 97.4 | 7.1 | 0.0109 | 109.0 | 8.0 |
| QCL | 0.0300 | 0.0287 | 95.6 | 4.3 | 0.0302 | 100.6 | 5.8 | |
| QCM | 0.500 | 0.501 | 100.2 | 7.4 | 0.515 | 102.9 | 6.7 | |
| QCH | 8.00 | 7.60 | 95.0 | 7.9 | 7.79 | 97.3 | 4.2 | |
| Inter-day (n = 15) | LLOQ | 0.0100 | 0.0101 | 101.1 | 7.2 | 0.0103 | 103.0 | 14.2 |
| QCL | 0.0300 | 0.0286 | 95.2 | 7.8 | 0.0293 | 97.8 | 7.3 | |
| QCM | 0.500 | 0.524 | 104.9 | 9.4 | 0.505 | 100.9 | 8.6 | |
| QCH | 8.00 | 8.12 | 100.5 | 8.2 | 7.88 | 98.5 | 8.3 | |
| Dose (mg/kg) | Cmax (mg/L) | Tmax (h) | T1/2 (h) | AUC0–8 h (mg·h/L) | AUC0–24 h (mg·h/L) | CLz (L/h/kg) | V (L/kg) | MRT (h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRX-8 | 2 | 2.01 ± 0.18 | 0.38 ± 0.14 | 1.21 ± 0.10 | 6.16 ± 0.78 | / | 0.32 ± 0.05 | 0.56 ± 0.06 | 2.27 ± 0.37 |
| 4 | 3.33 ± 0.64 | 1.60 ± 0.55 | 2.86 ± 0.54 | 15.00 ± 2.15 | 18.70 ± 3.85 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 0.91 ± 0.22 | 4.04 ± 0.41 | |
| 6 | 3.73 ± 0.54 | 2.20 ± 1.10 | 2.97 ± 0.31 | 19.64 ± 3.13 | 24.54 ± 5.97 | 0.20 ± 0.12 | 0.90 ± 0.54 | 4.12 ± 0.55 | |
| 8 | 5.09 ± 0.77 | 3.25 ± 1.50 | 2.66 ± 0.45 | 27.81 ± 4.83 | 41.59 ± 10.44 | 0.20 ± 0.06 | 0.75 ± 0.12 | 4.95 ± 0.65 | |
| MRX-8039 | 2 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 1.75 ± 0.50 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 4 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 3.33 ± 1.15 | 8.38 ± 1.49 | 0.39 ± 0.09 | 0.72 ± 0.23 | / | / | 11.98 ± 2.46 | |
| 6 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 4.00 ± 0.00 | 7.67 ± 2.81 | 0.49 ± 0.11 | 0.99 ± 0.42 | / | / | 10.53 ± 2.57 | |
| 8 | 0.13 ± 0.05 | 4.50 ± 1.00 | 6.85 ± 0.37 | 0.66 ± 0.28 | 1.63 ± 0.54 | / | / | 10.13 ± 0.84 | |
| PMB | 4 | 1.77 ± 0.51 | 4.80 ± 1.10 | 4.55 ± 0.56 | 9.55 ± 2.54 | 17.09 ± 3.90 | 0.24 ± 0.06 | 1.52 ± 0.27 | 8.66 ± 0.70 |
| 8 | 3.15 ± 0.44 | 6.00 ± 0.00 | 4.09 ± 0.44 | 17.92 ± 3.05 | 31.25 ± 3.14 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 1.49 ± 0.31 | 8.23 ± 0.71 |
| Abnormality Grade | Percentage of the Kidney Slice Affected in Individual Rats of Each Group (n = 5) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saline Control | MRX-8 4 mg/kg | MRX-8 8 mg/kg | PMB 4 mg/kg | PMB 8 mg/kg | |
| 1 | 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 | 0, 10, 0, 10, 0 | 0, 10, 0, 0, 0 | 0, 5, 0, 0, 25 | 0, 0, 0, 45, 8 |
| 2 | 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 | 25, 0, 35, 0, 0 | 0, 0, 15, 8, 15 | 15, 0, 35, 25, 0 | 20, 3, 35, 0, 0 |
| 3 | 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 | 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 | 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 | 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 | 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
| SQS for individual rats | 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 | +2, +1, +2, +1, 0 | 0, +1, +1, +1, +1 | +1, +1, +2, +1, +1 | +2, +1, +2, +1, +1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, X.; Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Xi, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Pharmacokinetics and Nephrotoxicity of Polymyxin MRX-8 in Rats: A Novel Agent against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040354
Qu X, Guo C, Liu S, Li X, Xi L, Liu X, Zhang J. Pharmacokinetics and Nephrotoxicity of Polymyxin MRX-8 in Rats: A Novel Agent against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(4):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040354
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Xingyi, Chenxue Guo, Shaojun Liu, Xin Li, Lin Xi, Xiaofen Liu, and Jing Zhang. 2024. "Pharmacokinetics and Nephrotoxicity of Polymyxin MRX-8 in Rats: A Novel Agent against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria" Antibiotics 13, no. 4: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040354
APA StyleQu, X., Guo, C., Liu, S., Li, X., Xi, L., Liu, X., & Zhang, J. (2024). Pharmacokinetics and Nephrotoxicity of Polymyxin MRX-8 in Rats: A Novel Agent against Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics, 13(4), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13040354






