Detecting Class 1 Integrons and Their Variable Regions in Escherichia coli Whole-Genome Sequences Reported from Andean Community Countries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bacterial Isolate Dataset
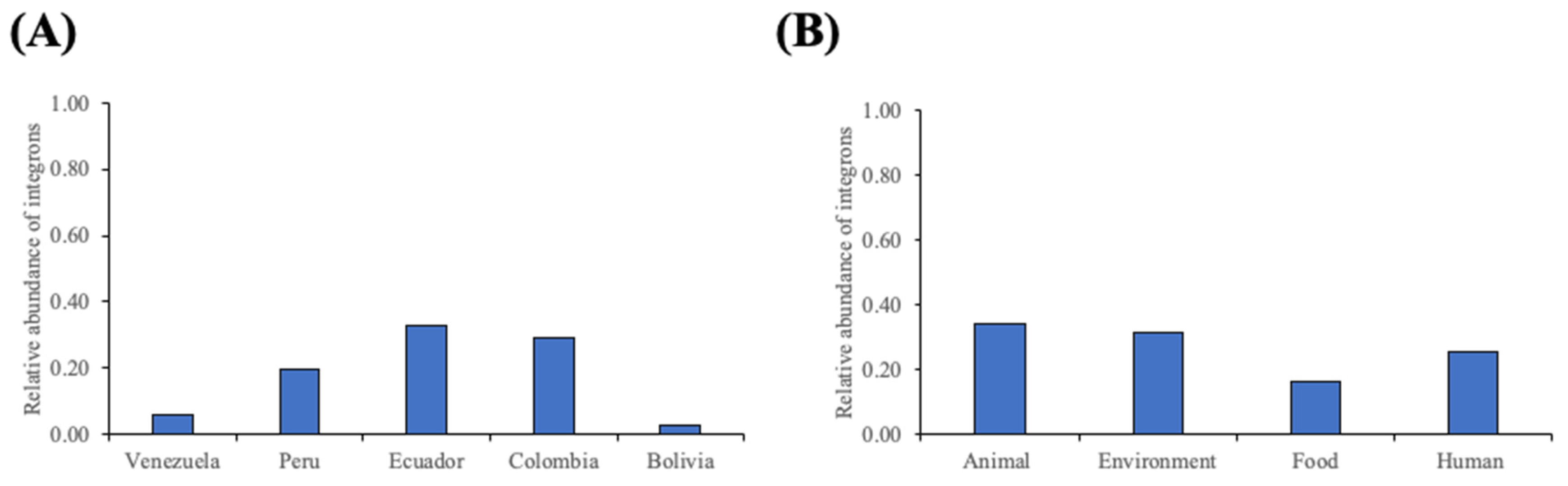
2.2. Integron Characterization by Country and Source
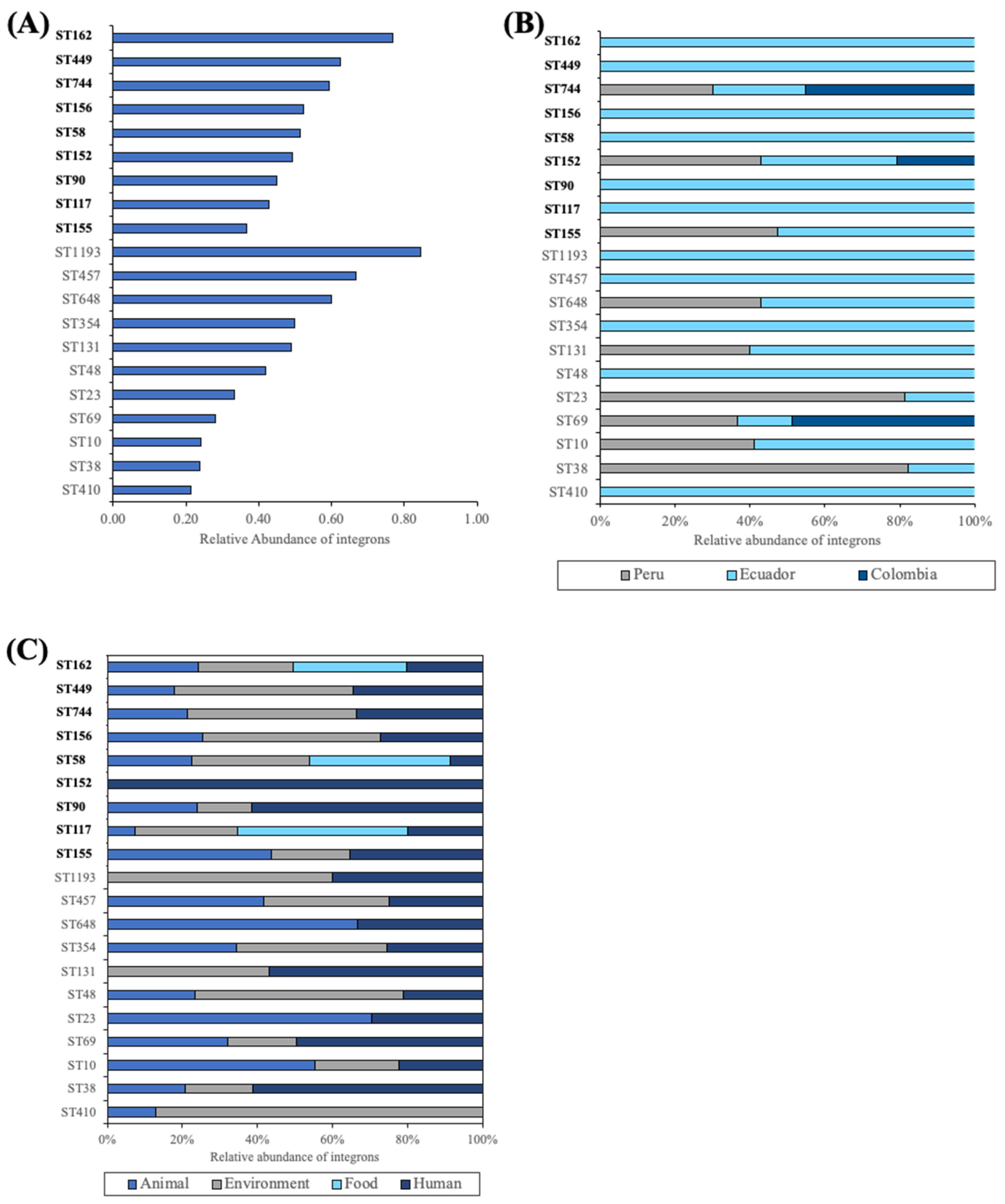
2.3. Integron Characterization by ST
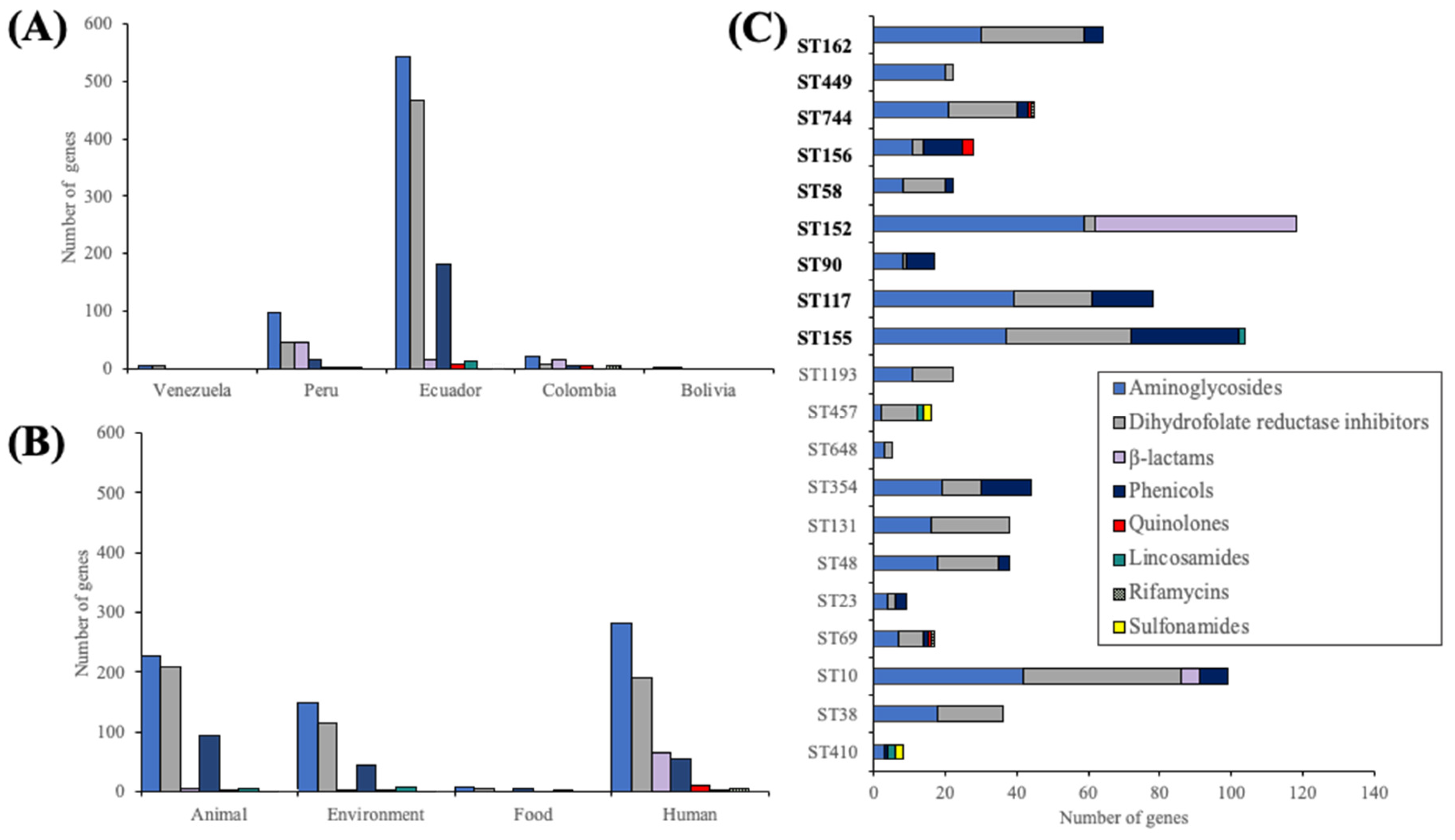
2.4. Integrons and Antibiotic Resistance Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Selection of Dataset
4.2. Multilocus Sequence Type Identification
4.3. IntFinder v1.0
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leimbach, A.; Hacker, J.; Dobrindt, U. E. coli as an All-rounder: The Thin Line between Commensalism and Pathogenicity. In Between Pathogenicity and Commensalism: Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Dobrindt, U., Hacker, J., Svanborg, C., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 358, pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, T.; Cohen, P.S. Commensal and pathogenic Escherichia coli metabolism in the gut. Metab. Bact. Pathog. 2015, 3, 343–362. [Google Scholar]
- Szmolka, A.; Nagy, B. Multidrug resistant commensal Escherichia coli in animals and its impact for public health. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, B.D.; Thuras, P.; Porter, S.B.; Anacker, M.; VonBank, B.; Vagnone, P.S.; Witwer, M.; Castanheira, M.; Johnson, J.R. Global molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli (2002–2017). Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021; ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Erb, A.; Stürmer, T.; Marre, R.; Brenner, H. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli: Overview of geographical, temporal, and methodological variations. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 26, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, R.R.; Moreira, B.M.; Picão, R.C. Antimicrobial resistance among Enterobacteriaceae in South America: History, current dissemination status, and associated socioeconomic factors. Drug Resist. Updates 2014, 17, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Blas, J.F.; Ovejero, C.M.; Abadia-Patiño, L.; Gonzalez-Zorn, B. Coexistence of mcr-1 and blaNDM-1 in Escherichia coli from Venezuela. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6356–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Garzón, D.; Mattar, S. CTX-M-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from community-acquired urinary tract infections in Valledupar, Colombia. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffré, E.; Iñiguez Rojas, V. Molecular epidemiology of Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (EAEC) isolates of hospitalized children from Bolivia reveals high heterogeneity and multidrug-resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, L.L.; Carhuaricra Huamán, D.; Rodríguez Cueva, C.; Durán Gonzales, C.; León, Y.I.; Silvestre Espejo, T.; Marcelo Monge, G.; Rosadio Alcántara, R.; Maturrano Hernández, L. Genomic analysis of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli strains carrying the mcr-1 gene recovered from pigs in Lima, Peru. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 99, 102019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.R. Horizontal gene transfer in the human gastrointestinal tract: Potential spread of antibiotic resistance genes. Infect. Drug Resist. 2014, 7, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, N.; Ellington, M.J. The Emergence of Antibiotic Resistance by Mutation. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile genetic elements associated with antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverstein-van Hall, M.A.; Blok, H.E.M.; Donders, A.R.T.; Paauw, A.; Fluit, A.C.; Verhoef, J. Multidrug resistance among Enterobacteriaceae is strongly associated with the presence of integrons and is independent of species or isolate origin. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Bao, X.; Ji, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Miao, J.; Chen, D.; Bian, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, G. Resistance integrons: Class 1, 2 and 3 integrons. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2015, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, M.; Kumar, S.; Kapoor, R.K.; Virdi, J.S.; Gulati, P. Integrons in Enterobacteriaceae: Diversity, distribution and epidemiology. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canal, N.; Meneghetti, K.L.; de Almeida, C.P.; da Rosa Bastos, M.; Otton, L.M.; Corção, G. Characterization of the variable region in the class 1 integron of antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from surface water. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk-In, S.; Pulsrikarn, C.; Bangtrakulnonth, A.; Chatsuwan, T.; Kulwichit, W. Occurrence of a novel class 1 integron harboring qnrVC4 in Salmonella Rissen. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 88, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimiyan Rizi, K.; Ghazvini, K.; Farsiani, H. Clinical and pathogenesis overview of Enterobacter infections. Rev. Clin. Med. 2020, 6, 146–154. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Abbas, M.; Rehman, M.U.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Gong, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) via integrons in Escherichia coli: A risk to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros, M.; Pons, M.J.; Durand, D.; Ochoa, T.J.; Ruiz, J. Class 1 and 2 integrons in Escherichia coli strains isolated from diarrhea and bacteremia in children less than 2 years of age from Peru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2023, 108, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiluisa-Guacho, C.; Escobar-Perez, J.; Dutra-Asensi, M. First detection of the CTXM-15 producing Escherichia coli O25-ST131 pandemic clone in Ecuador. Pathogens 2018, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Paredes, D.; Barba, P.; Mena-López, S.; Espinel, N.; Crespo, V.; Zurita, J. High quantities of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli are present in the Machángara urban river in Quito, Ecuador. J. Water Health 2020, 18, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Paredes, D.; Barba, P.; Mena-López, S.; Espinel, N.; Zurita, J. Escherichia coli hyperepidemic clone ST410-A harboring blaCTX-M-15 isolated from fresh vegetables in a municipal market in Quito, Ecuador. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 280, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Levy, K.; Trueba, G.; Cevallos, W.; Trostle, J.; Foxman, B.; Marrs, C.F.; Eisenberg, J.N.S. Effects of selection pressure and genetic association on the relationship between antibiotic resistance and virulence in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6733–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, K.A.; Zhang, L.; Spicknall, I.; Braykov, N.P.; Levy, K.; Marrs, C.F.; Foxman, B.; Trueba, G.; Cevallos, W.; Goldstick, J.; et al. The role of mobile genetic elements in the spread of antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli from chickens to humans in small-scale production poultry operations in rural Ecuador. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon Toledo, C.; von Mentzer, A.; Agramont, J.; Thorell, K.; Zhou, Y.; Szabó, M.; Colque, P.; Kuhn, I.; Gutiérrez-Cortez, S.; Joffré, E. Circulation of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) isolates expressing CS23 from the environment to clinical settings. mSystems 2023, 8, e00141-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartono, S.; Savin, M.C.; Gbur, E.E. Transmissible plasmids and integrons shift Escherichia coli population toward larger multiple drug resistance numbers. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.H.K.; Bortolaia, V.; Tansirichaiya, S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Roberts, A.P.; Petersen, T.N. Detection of mobile genetic elements associated with antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica using a newly developed web tool: MobileElementFinder. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Dar, S.A.; Singh, S.; Shekhar, C.; Wani, S.; Akhter, N.; Bashir, N.; Haque, S.; Ahmad, A.; Das, S. Integron mediated antimicrobial resistance in diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in children: In vitro and in silico analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Elizalde, L.; Ortega-Paredes, D.; Loaiza, K.; Fernández-Moreira, E.; Larrea-Álvarez, M. In Silico detection of antimicrobial resistance integrons in Salmonella enterica isolates from countries of the Andean community. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srednik, M.E.; Morningstar-Shaw, B.R.; Hicks, J.A.; Tong, C.; Mackie, T.A.; Schlater, L.K. Whole-genome sequencing and phylogenetic analysis capture the emergence of a multi-drug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis clone from diagnostic animal samples in the United States. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1166908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, L.; Cárdenas, P.; Johnson, T.J.; Vasco, K.; Graham, J.; Trueba, G. Diverse commensal Escherichia coli clones and plasmids disseminate antimicrobial resistance genes in domestic animals and children in a semirural community in Ecuador. mSphere 2019, 4, e00316-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braykov, N.P.; Eisenberg, J.N.S.; Grossman, M.; Zhang, L.; Vasco, K.; Cevallos, W.; Muñoz, D.; Acevedo, A.; Moser, K.A.; Marrs, C.F.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in animal and environmental samples associated with small-scale poultry farming in northwestern Ecuador. mSphere 2016, 1, e00021-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, A.M.; Correa, A.; Restrepo, E.; Capataz, C. Escherichia coli ST471 producing VIM-4 Metallo-β-Lactamase in Colombia. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, E.; Caraballo, L.; Takiff, H.; García, D.; Montiel, M. Phenotypic and genotypic study of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from a wastewater treatment plant in Zulia state, Venezuela. Investig. Clínica 2023, 64, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginn, O.; Nichols, D.; Rocha-Melogno, L.; Bivins, A.; Berendes, D.; Soria, F.; Andrade, M.; Deshusses, M.A.; Bergin, M.; Brown, J. Antimicrobial resistance genes are enriched in aerosols near impacted urban surface waters in La Paz, Bolivia. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, W.; Ohsaki, Y.; Taniguchi, Y.; Koide, S.; Kawamura, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kimura, K.; Wachino, J.-I.; Nagano, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; et al. High prevalence of blaCTX-M-14 among genetically diverse Escherichia coli recovered from retail raw chicken meat portions in Japan. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 284, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman-Otazo, J.; Gonzales-Siles, L.; Poma, V.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Thorell, K.; Flach, C.-F.; Iniguez, V.; Sjöling, Å. Diarrheal bacterial pathogens and multi-resistant enterobacteria in the Choqueyapu River in La Paz, Bolivia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita, J.; Yánez, F.; Sevillano, G.; Ortega-Paredes, D.; Paz y Miño, A. Ready-to-eat street food: A potential source for dissemination of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli epidemic clones in Quito, Ecuador. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, L.R.; Donado-Godoy, P.; León, M.; Clavijo, V.; Arevalo, A.; Bernal, J.F.; Timmerman, A.J.; Mevius, D.J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Hordijk, J. High heterogeneity of Escherichia coli sequence types harbouring ESBL/AmpC genes on IncI1 plasmids in the Colombian poultry chain. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhao, L.; Guo, C.; Liu, X.; Qin, L.; Hao, Z. High prevalence and diversity characteristics of blaNDM, mcr, and blaESBLs harboring multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli from chicken, pig, and cattle in China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.; Salvatierra, G.; Dávila-Barclay, A.; Ayzanoa, B.; Castillo-Vilcahuaman, C.; Huang, M.; Pajuelo, M.J.; Lescano, A.G.; Cabrera, L.; Calderón, M.; et al. Market chickens as a source of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli in a peri-urban community in Lima, Peru. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 635871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero-Cáceres, W.; Tadesse, D.; Jaramillo, K.; Villavicencio, X.; Mero, E.; Lalaleo, L.; Welsh, C.; Villacís, J.E.; Quentin, E.; Parra, H.; et al. Characterization of the genetic structure of mcr-1 gene among Escherichia coli isolates recovered from surface waters and sediments from Ecuador. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Cadena, E.; Mojica, M.F.; Castillo, N.; Correa, A.; Appel, T.M.; García-Betancur, J.C.; Pallares, C.J.; Villegas, M.V. Genomic analysis of CTX-M-group-1-producing extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEc) from patients with urinary tract infections (UTI) from Colombia. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, C.J.; Cummins, M.L.; Börjesson, S.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Hasman, H.; Hammerum, A.M.; Roer, L.; Hess, S.; Berendonk, T.; Nešporová, K.; et al. A role for ColV plasmids in the evolution of pathogenic Escherichia coli ST58. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingali, T.; Chapman, T.A.; Webster, J.; Roy Chowdhury, P.; Djordjevic, S.P. Genomic characterisation of a multiple drug resistant IncHI2 ST4 plasmid in Escherichia coli ST744 in Australia. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, R.D.S.; Tacão, M.; Ramalheira, E.; Ferreira, S.; Henriques, I. Report and comparative genomics of an NDM-5-producing Escherichia coli in a Portuguese hospital: Complex class 1 integrons as important players in bla NDM spread. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, L.; Sellera, F.P.; Fuga, B.; Sano, E.; Monte, D.F.M.; Cardoso, B.; Côrtes, L.D.A.; Lincopan, N. Phylogenomic analysis of CTX-M-15-positive Escherichia coli from companion animal reveals intercontinental dissemination of ST90 within a One Health framework. Microb. Drug Resist. 2023, 29, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavides, J.A.; Godreuil, S.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Mahamat, O.O.; Falcon, N.; Oravcova, K.; Streicker, D.G.; Shiva, C. Long-term maintenance of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli carried by vampire bats and shared with livestock in Peru. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurita, J.; Sevillano, G.; Paz y Miño, A.; Haro, N.; Larrea-Álvarez, M.; Alcocer, I.; Ortega-Paredes, D. Dominance of ST131, B2, blaCTX-M-15, and papA-papC-kpsMII-uitA among ESBL Escherichia coli isolated from bloodstream infections in Quito, Ecuador: A 10-year surveillance study (2009–2019). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; An, J.-U.; Woo, J.; Song, H.; Yi, S.; Kim, W.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Ryu, S.; Cho, S. Prevalence, characteristics, and clonal distribution of Escherichia coli carrying mobilized colistin resistance gene mcr-1.1 in swine farms and their differences according to swine production stages. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 873856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio, R.; Boerlin, P.; Beyrouthy, R.; Madec, J.-Y.; Schwarz, S.; Mulvey, M.R.; Zhanel, G.G.; Cormier, A.; Chalmers, G.; Bonnet, R.; et al. Dynamics of extended-spectrum cephalosporin resistance genes in Escherichia coli from Europe and North America. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izdebski, R.; Baraniak, A.; Fiett, J.; Adler, A.; Kazma, M.; Salomon, J.; Lawrence, C.; Rossini, A.; Salvia, A.; Samso, J.V.; et al. Clonal structure, extended-spectrum β-lactamases, and acquired AmpC-type cephalosporinases of Escherichia coli populations colonizing patients in rehabilitation centers in four countries. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platell, J.L.; Johnson, J.R.; Cobbold, R.N.; Trott, D.J. Multidrug-resistant extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli of sequence type ST131 in animals and foods. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocsis, B.; Gulyás, D.; Szabó, D. Emergence and dissemination of extraintestinal pathogenic high-risk international clones of Escherichia coli. Life 2022, 12, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Q.; Shi, X.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Lv, D.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, M.; Ma, H.; et al. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of clinical Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates from Shenzhen, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roer, L.; Overballe-Petersen, S.; Hansen, F.; Schønning, K.; Wang, M.; Røder, B.L.; Hansen, D.S.; Justesen, U.S.; Andersen, L.D.; Fulgsang-Damgaard, D.; et al. Escherichia coli sequence type 410 is causing new international high-risk clones. mSphere 2018, 3, e00337-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manges, A.R. Escherichia coli causing bloodstream and other extraintestinal infections: Tracking the next pandemic. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1269–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitout, J.D.D.; Peirano, G.; Chen, L.; DeVinney, R.; Matsumura, Y. Escherichia coli ST1193: Following in the footsteps of E. coli ST131. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e00511-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amézquita-Montes, Z.; Tamborski, M.; Kopsombut, U.G.; Zhang, C.; Arzuza, O.S.; Gómez-Duarte, O.G. Genetic relatedness among Escherichia coli pathotypes isolated from food products for human consumption in Cartagena, Colombia. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuicapuza, D.; Loyola, S.; Velásquez, J.; Fernández, N.; Llanos, C.; Ruiz, J.; Tsukayama, P.; Tamariz, J. Molecular characterization of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales in a tertiary hospital in Lima, Peru. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e02503-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, H.K.; Loayza, F.; Salinas, L.; Paredes, D.; Garcia, D.; Sarzosa, S.; Saraiva-Garcia, C.; Johnson, T.J.; Pickering, A.J.; Riley, L.W.; et al. Risk factors for extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli carriage among children in a food animal-producing region of Ecuador: A repeated measures observational study. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaufler, K.; Semmler, T.; Wieler, L.H.; Trott, D.J.; Pitout, J.; Peirano, G.; Bonnedahl, J.; Dolejska, M.; Literak, I.; Fuchs, S.; et al. Genomic and functional analysis of emerging virulent and multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli lineage sequence type 648. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Wakeham, D.; Brouwers, H.J.M.; Cobbold, R.N.; Abraham, S.; Mollinger, J.L.; Johnson, J.R.; Chapman, T.A.; Gordon, D.M.; Barrs, V.R.; et al. Human-associated fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli clonal lineages, including ST354, isolated from canine feces and extraintestinal infections in Australia. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacotte, Y.; Ploy, M.C.; Raherison, S. Class 1 integrons are low-cost structures in Escherichia coli. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakopoulou, A.; Psichogiou, M.; Tzouvelekis, L.; Tassios, P.T.; Kosmidis, C.; Petrikkos, G.; Charvalos, E.; Passiotou, M.; Avlami, A.; Daikos, G.L. Prevalence and characterization of class 1 integrons in Escherichia coli of poultry and human origin. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheiri, R.; Akhtari, L. Antimicrobial resistance and integron gene cassette arrays in commensal Escherichia coli from human and animal sources in IRI. Gut Pathog. 2016, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojdana, D.; Sieńko, A.; Sacha, P.; Majewski, P.; Wieczorek, P.; Wieczorek, A.; Tryniszewska, E. Genetic basis of enzymatic resistance of E. coli to aminoglycosides. Adv. Med. Sci. 2018, 63, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.N.; Vannoy, D.; Frederick, A.; Chang, S.; Lawler, E. First-line antimicrobial resistance patterns of Escherichia coli in children with urinary tract infection in emergency department and primary care clinics. Clin. Pediatr. 2016, 55, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, K.M.; White, D.G.; McDermott, P.F.; Zhao, S.; Gaines, S.; Maurer, J.J.; Nisbet, D.J. Characterization of chloramphenicol resistance in beta-hemolytic Escherichia coli associated with diarrhea in neonatal swine. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boe, N.M.; Dellinger, E.P.; Minshew, B.H. Effect of clindamycin on growth and haemolysin production by Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1983, 12, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, Z.B.; Zaman, M.H. Evolution of rifampin resistance in Escherichia coli and Mycobacterium smegmatis due to substandard drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaly, T.M.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Tetu, S.G.; Gillings, M.R. The peril and promise of integrons: Beyond antibiotic resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausen, P.T.L.C.; Zankari, E.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Benchmarking of methods for identification of antimicrobial resistance genes in bacterial whole genome data. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2484–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausen, P.T.L.C.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Rapid and precise alignment of raw reads against redundant databases with KMA. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, A.; Soares, M.; Pereira, C.; Leitão, N.; Henriques, I.; Correia, A. Integrall: A database and search engine for integrons, integrases and gene cassettes. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1096–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiza, K. IntFinder Development and Validation. Available online: https://github.com/kalilamali/Integrons (accessed on 25 September 2021).
- Koczura, R.; Mokracka, J.; Jabłońska, L.; Gozdecka, E.; Kubek, M.; Kaznowski, A. Antimicrobial resistance of integron-harboring Escherichia coli isolates from clinical samples, wastewater treatment plant and river water. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Integron | Gene Cassettes in the Variable Region | Antimicrobial Resistance Pattern | Frequency (%) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In1741 | aadA1, cmlA1, aadA2, dfrA12, aadA17, lnu(F) | AG, CHL, FA, LIN | 0.4 | CP042600 |
| In37 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, blaOXA-1, catB3, arr-3 | AG, CIP, PEN-CP, CHL, RIF | 0.1 | AY259086 |
| In1021 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, arr-3, dfrA27, aadA16 | AG, CIP, RIF, FA | 0.1 | KF921558 |
| In1001 | aac(6′)-Ib3, aac(6′)-Ib-cr, catB3, dfrA1 | AG, CIP, CHL, FA | 0.5 | KF921553 |
| In1598 | aadA16, dfrA27, arr-3, aac(6′)-Ib-cr | AG, FA, RIF, CIP | 0.4 | MG196293 |
| In1558 | dfrA12, aadA2, cmlA1, aadA1 | FA, AG, CHL | 8.5 | CP031549 |
| In640 | dfrA12, aadA2, cmlA1, aadA1 | FA, AG, CHL | 1.4 | FM244708 |
| In1632 | aadA1, cmlA1, aadA2b | AG, CHL | 2.2 | CP034788 |
| In1671 | aadA1, cmlA1, aadA2b | AG, CHL | 0.3 | CP036168 |
| In1405 | aadA22, lnu(F), sul3 | AG, LIN, SUL | 0.9 | CP021843 |
| In1004 | aadA2b, cmlA1, aadA1 | AG, CHL | 10.0 | KF921558 |
| In1153 | aadA2b, cmlA1, aadA1 | AG, CHL | 1.7 | CP010575 |
| In1179 | aadA2b, cmlA1, aadA1 | AG, CHL | 0.3 | CP011644 |
| In1621 | blaDHA-1, qnrB4, dfrA17 | PEN-CP, CIP, FA | 0.4 | MK048477 |
| In1058 | blaOXA-4, aadA2, cmlA1 | PEN-CP, AG, CHL | 0.4 | KJ463833 |
| In1262 | aadA2, dfrA12 | AG, FA | 0.3 | KX710093 |
| In322 | aadA1, blaOXA-1 | AG, PEN-CP | 8.6 | AM991977 |
| In1265 | aadA1, dfrA1 | AG, FA | 7.4 | CP011540 |
| In1077 | aadA1, aac(3)-VIa | AG | 2.3 | CP009409 |
| In1637 | aadA2, dfrA12 | AG, FA | 0.1 | LN830952 |
| In1756 | aadA2, dfrA12 | AG, FA | 0.1 | CP042894 |
| In1438 | aadA2, dfrA12 | AG, FA | 14.3 | CP022692 |
| In406 | aadA2, dfrA12 | AG, FA | 0.1 | AP012055 |
| In1546 | aadA5, dfrA17 | AG, FA | 17.2 | CP031110 |
| In294 | ant(2″)-Ia, aadA2b | AG | 0.1 | AJ971341 |
| In1412 | dfrA12, aadA2 | AG, FA | 0.4 | CP019647 |
| In1181 | dfrA17, aadA5 | AG, FA | 0.1 | CP006642 |
| In1449 | dfrA17, aadA5 | AG, FA | 0.3 | CP023145 |
| In1450 | dfrA17, aadA5 | AG, FA | 2.7 | CM008265 |
| In1363 | lnu(F), aadA17 | LIN, AG | 0.5 | CP019443 |
| In1612 | dfrA5 | FA | 3.3 | CP034201 |
| In862 | aadA1 | AG | 0.8 | CP011540 |
| In530 | aadA1 | AG | 3.9 | AM055748 |
| In18 | dfrA1 | FA | 0.1 | X17478 |
| In191 | dfrA14 | FA | 8.1 | HF545433 |
| In1210 | dfrA16 | FA | 0.3 | KT884517 |
| In1205 | dfrA17 | FA | 1.2 | CP012626 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solis, M.N.; Loaiza, K.; Torres-Elizalde, L.; Mina, I.; Šefcová, M.A.; Larrea-Álvarez, M. Detecting Class 1 Integrons and Their Variable Regions in Escherichia coli Whole-Genome Sequences Reported from Andean Community Countries. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050394
Solis MN, Loaiza K, Torres-Elizalde L, Mina I, Šefcová MA, Larrea-Álvarez M. Detecting Class 1 Integrons and Their Variable Regions in Escherichia coli Whole-Genome Sequences Reported from Andean Community Countries. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(5):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050394
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolis, María Nicole, Karen Loaiza, Lilibeth Torres-Elizalde, Ivan Mina, Miroslava Anna Šefcová, and Marco Larrea-Álvarez. 2024. "Detecting Class 1 Integrons and Their Variable Regions in Escherichia coli Whole-Genome Sequences Reported from Andean Community Countries" Antibiotics 13, no. 5: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050394
APA StyleSolis, M. N., Loaiza, K., Torres-Elizalde, L., Mina, I., Šefcová, M. A., & Larrea-Álvarez, M. (2024). Detecting Class 1 Integrons and Their Variable Regions in Escherichia coli Whole-Genome Sequences Reported from Andean Community Countries. Antibiotics, 13(5), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13050394








