The Roles of a Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae High-Risk Clone and Its Resistance Plasmids on the Gastrointestinal Colonization and Host-Defense Effectors in the Gut
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
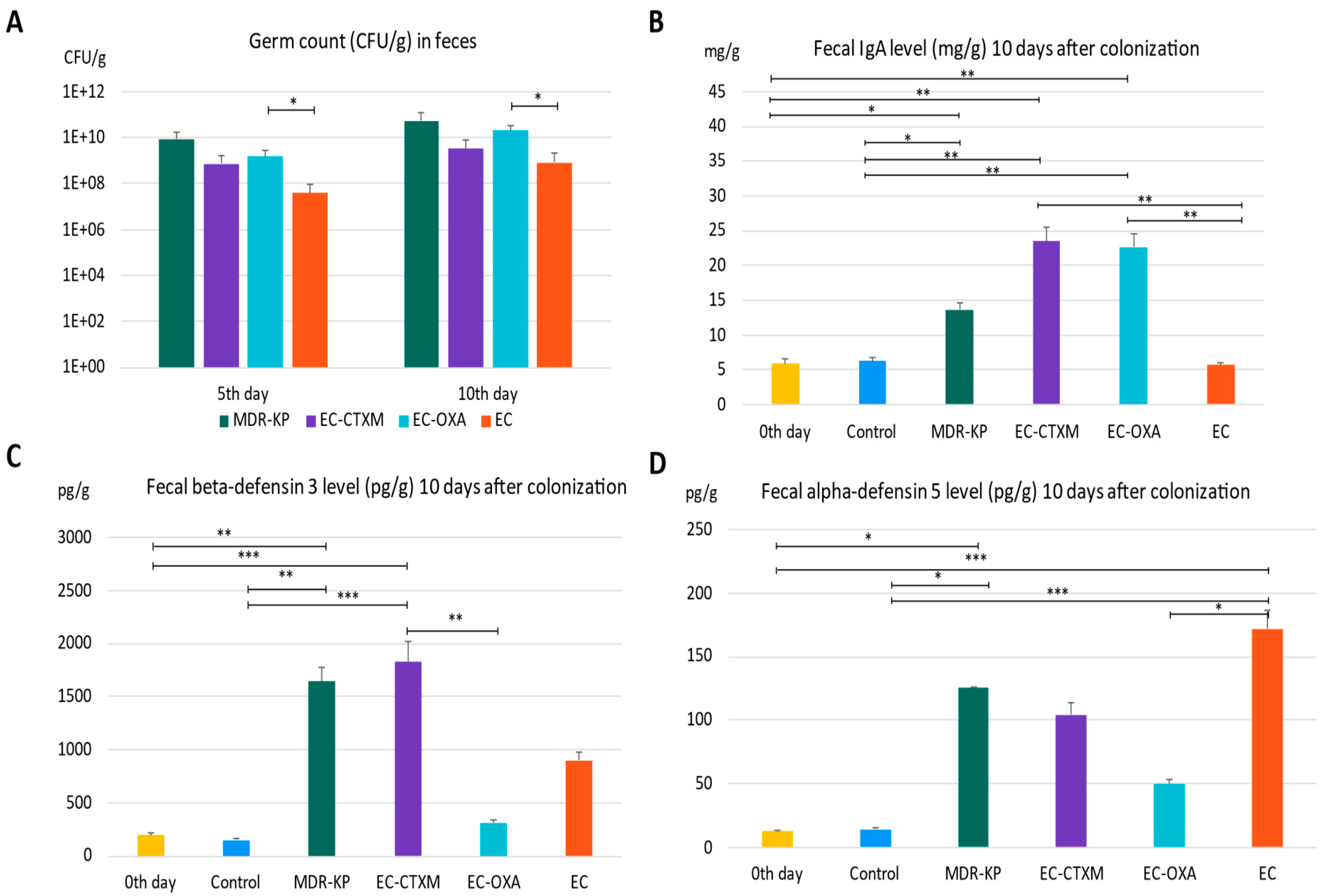
2.1. Bacterial Loads in Feces During Gastrointestinal Colonization
2.2. Fecal IgA Levels During Gastrointestinal Colonization
2.3. Fecal Beta-Defensin 3 Levels During Gastrointestinal Colonization
2.4. Fecal Alpha-Defensin Levels During Gastrointestinal Colonization
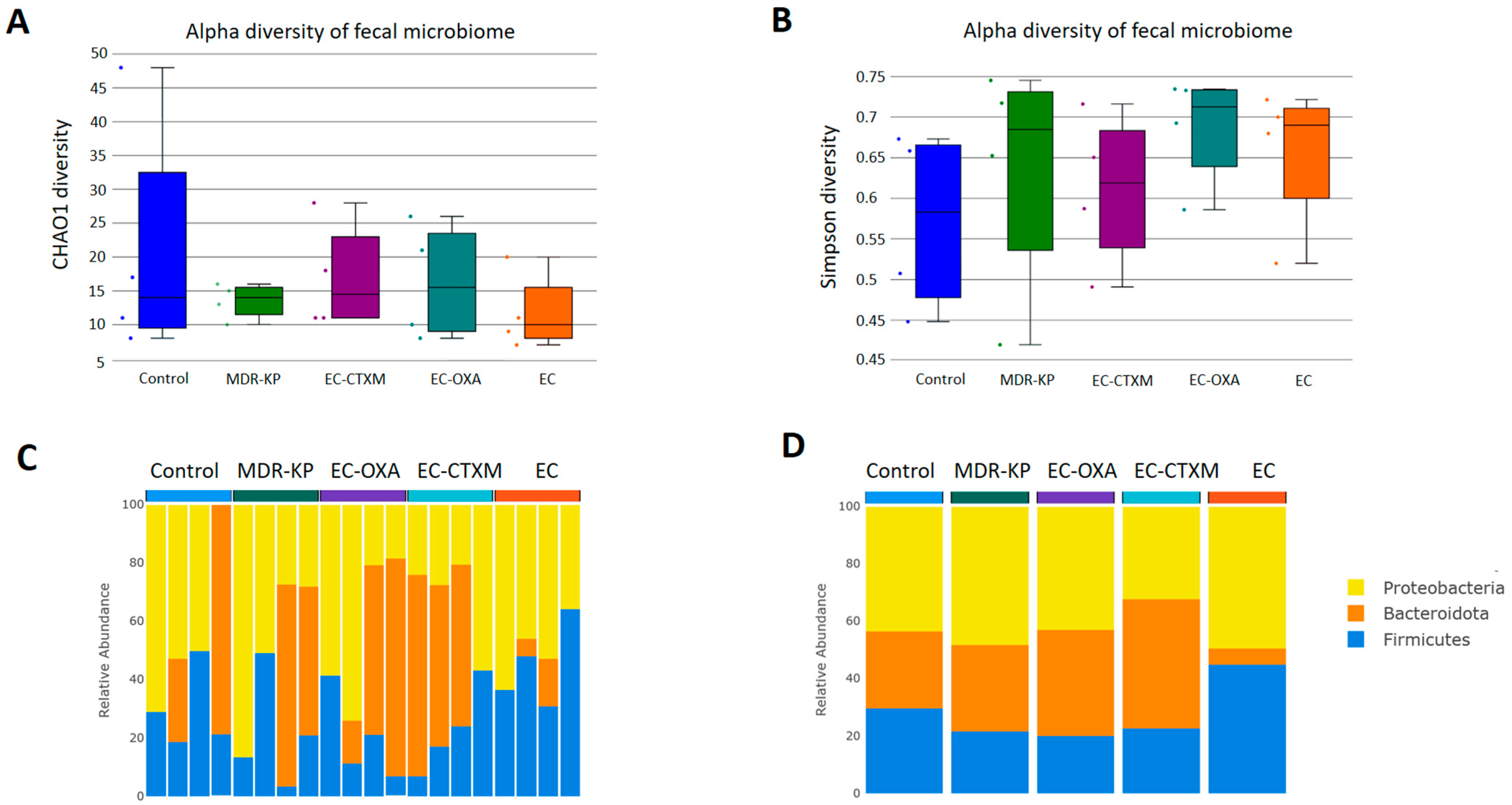
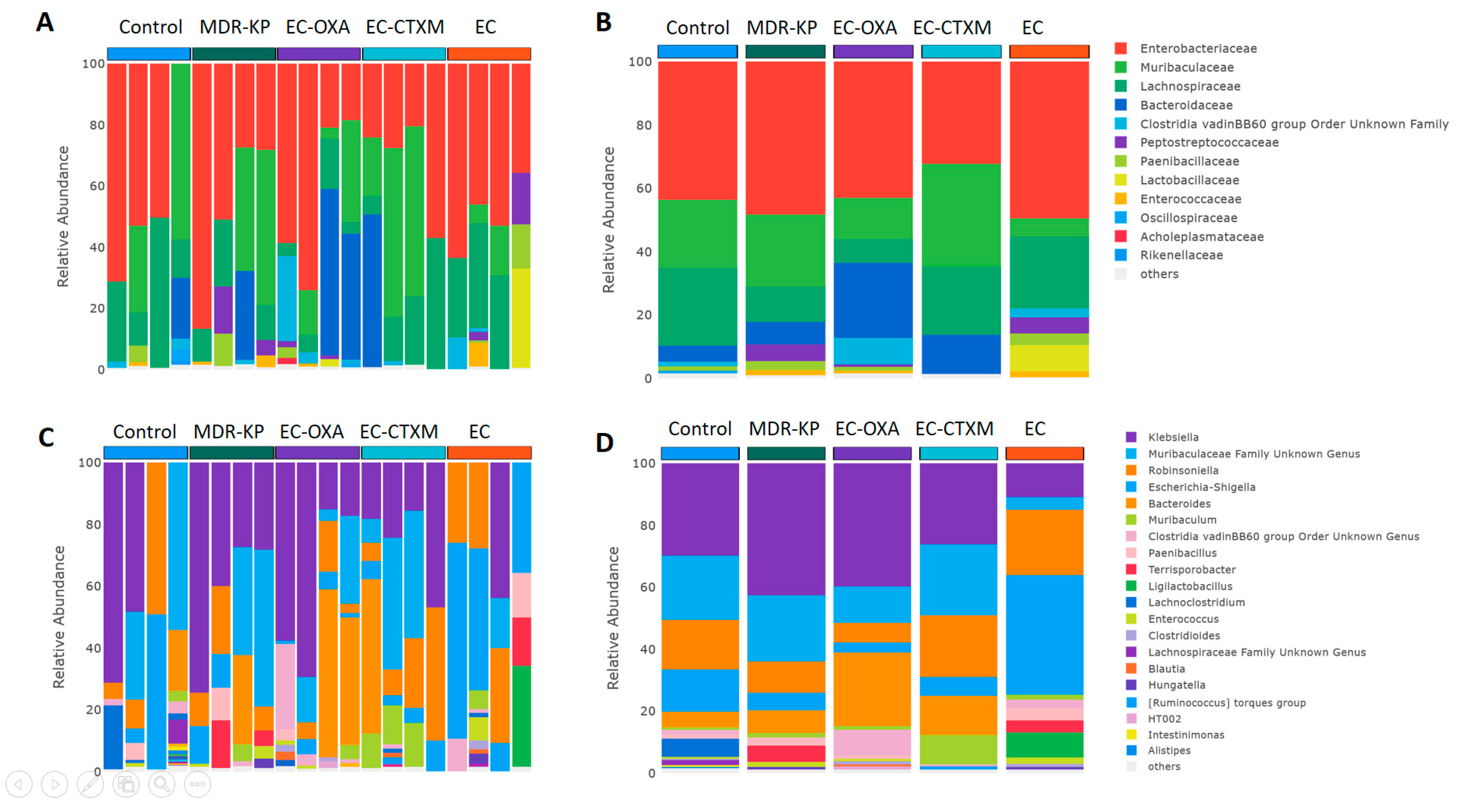
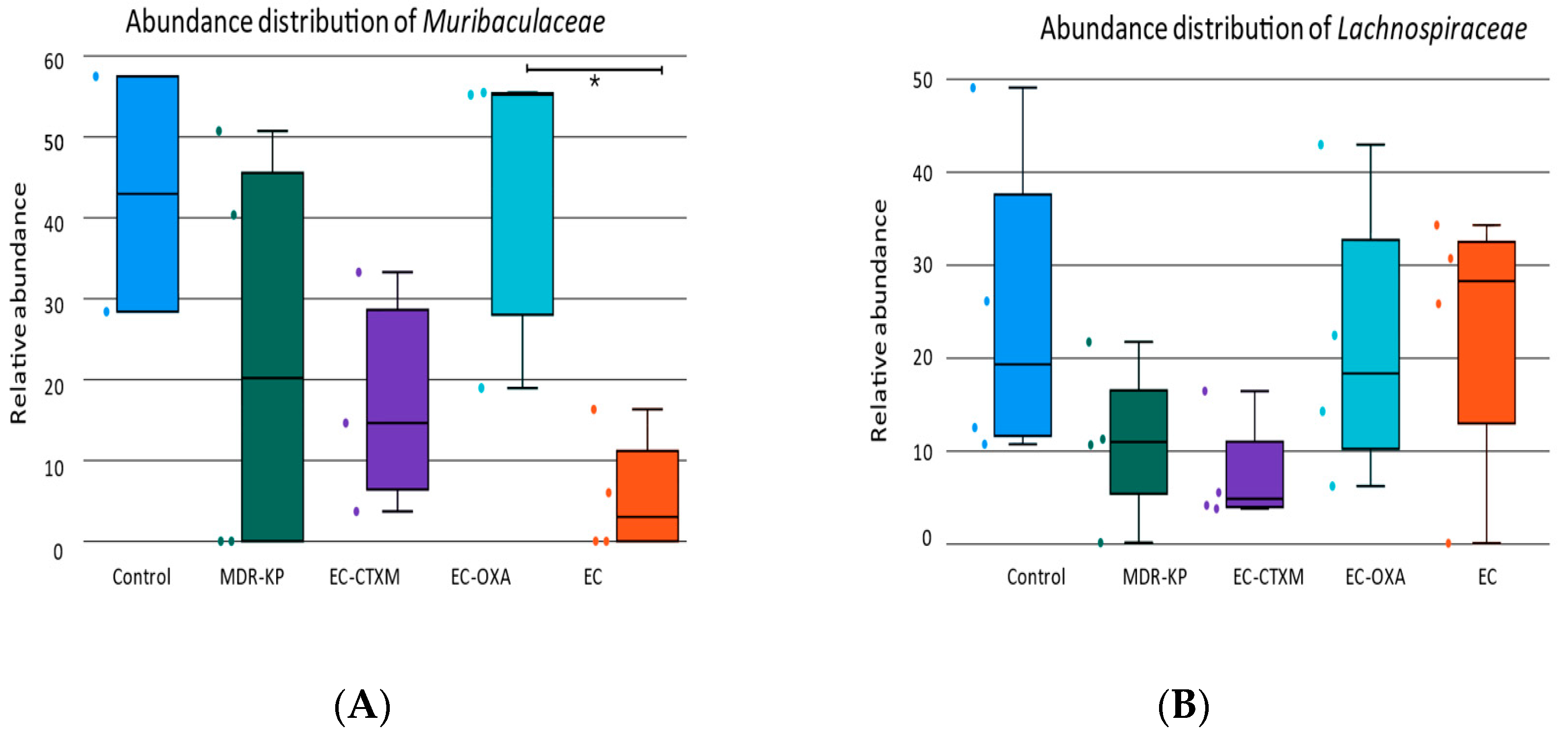
2.5. Fecal Microbiota Composition During Gastrointestinal Colonization
3. Discussion
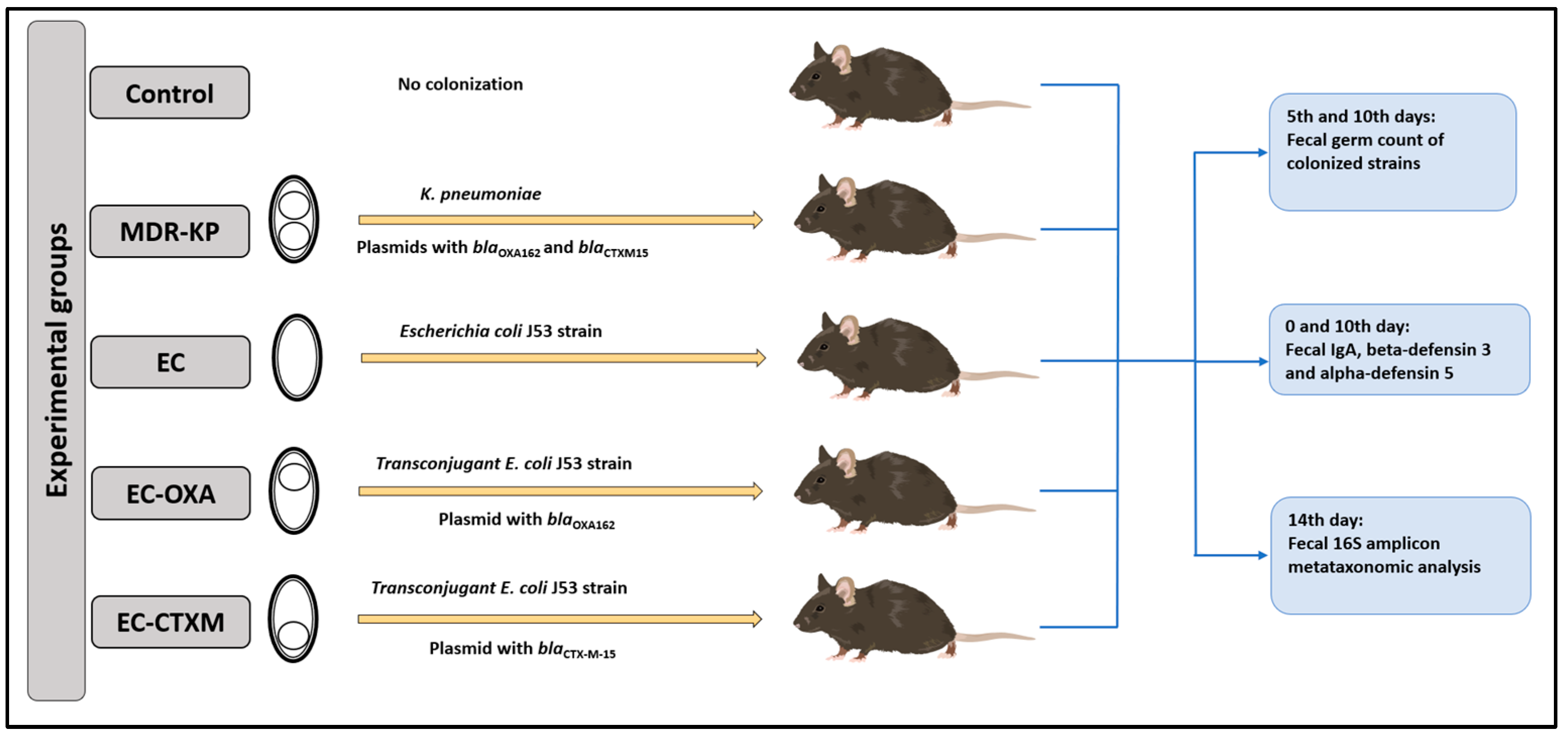
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain and Conjugation Assay
4.2. Animal Study
4.3. Determination of the Fecal Germ Count of Mice
4.4. Determination of Total IgA and Defensin Levels in Stool by ELISA
4.5. Microbiome Composition with 16S Metagenomic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, G.T. Continuous Evolution: Perspective on the Epidemiology of Carbapenemase Resistance Among Enterobacterales and Other Gram-Negative Bacteria. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navon-Venezia, S.; Kondratyeva, K.; Carattoli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Ma, X. Systematic review and meta-analysis of mortality of patients infected with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2017, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindaraj Vaithinathan, A.; Vanitha, A. WHO global priority pathogens list on antibiotic resistance: An urgent need for action to integrate One Health data. Perspect. Public Health 2018, 138, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Ohno, H. IgA in human health and diseases: Potential regulator of commensal microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1024330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuPont, H.L.; Jiang, Z.D.; Alexander, A.S.; DuPont, A.W.; Brown, E.L. Intestinal IgA-Coated Bacteria in Healthy- and Altered-Microbiomes (Dysbiosis) and Predictive Value in Successful Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, K.G.; O’Farrelly, C. beta-Defensins: Farming the Microbiome for Homeostasis and Health. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3072. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakamura, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Yokoi, Y.; Ohira, S.; Hagiwara, M.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Aizawa, T.; Ayabe, T. Decrease of alpha-defensin impairs intestinal metabolite homeostasis via dysbiosis in mouse chronic social defeat stress model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, X.; Fu, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Jin, M. Interplay between gut microbiota and antimicrobial peptides. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.L.; Yang, Y.; Newsome, R.C.; Sun, W.; Sun, X.; Ukhanova, M.; Neu, J.; Issa, J.P.; Mai, V.; Jobin, C. Microbial Colonization Coordinates the Pathogenesis of a Klebsiella pneumoniae Infant Isolate. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budia-Silva, M.; Kostyanev, T.; Ayala-Montaño, S.; Bravo-Ferrer Acosta, J.; Garcia-Castillo, M.; Cantón, R.; Goossens, H.; Rodriguez-Baño, J.; Grundmann, H.; Reuter, S. International and regional spread of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, F.; Díez-Aguilar, M.; Oksuz, L.; Kayacan, C.; Abulaila, A.; Oncul, O.; Morosini, M.I.; Cantón, R.; Aktas, Z. Time kill-assays of antibiotic combinations for multidrug resistant clinical isolates of OXA-48 carbapenemase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2022, 69, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gato, E.; Rodino-Janeiro, B.K.; Gude, M.J.; Fernandez-Cuenca, F.; Pascual, A.; Fernandez, A.; Perez, A.; Bou, G. Diagnostic tool for surveillance, detection and monitoring of the high-risk clone K. pneumoniae ST15. J. Hosp. Infect. 2023, 142, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzidimitriou, M.; Kavvada, A.; Kavvadas, D.; Kyriazidi, M.A.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Varlamis, S.; Papaliagkas, V.; Mitka, S. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Balkans: Clonal distribution and associated resistance determinants. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2024, 71, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajer, H.B.; Salimizand, H.; Gharanizadeh, D.; Hossainpanahi, A.; Ramazanzadeh, R. Investigation of NDM-1 and OXA-48 producing carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST15 in Iran. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2023, 70, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peirano, G.; Pitout, J.D.D. Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae: Update on Molecular Epidemiology and Treatment Options. Drugs 2019, 79, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stercz, B.; Farkas, F.B.; Tóth, A.; Gajdács, M.; Domokos, J.; Horváth, V.; Ostorházi, E.; Makra, N.; Kocsis, B.; Juhász, J.; et al. The influence of antibiotics on transitory resistome during gut colonization with CTX-M-15 and OXA-162 producing K. pneumoniae ST15. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, W.P.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Chang, S.C. Risk for subsequent infection and mortality after hospitalization among patients with multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria colonization or infection. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.B.; Soraas, A.; Sundsfjord, A.; Liestol, K.; Leegaard, T.M.; Jenum, P.A. Fecal carriage of extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae after urinary tract infection—A three year prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Revuelta, M.J.; Lopez-Cerero, L.; Serrano, L.; Luna-Lagares, S.; Pascual, A.; Rodriguez-Bano, J. Incidence and Risk Factors for Acquisition of Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Newborns in Seville, Spain: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Chatenoud, L.; Gona, F.; Sala, I.; Nattino, G.; D’Antonio, A.; Castelli, D.; Itri, T.; Morelli, P.; Bigoni, S.; et al. Characteristics and Clinical Implications of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Colonization and Infection, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkel, L.A.; Maechler, F.; Schwab, F.; Kola, A.; Weber, A.; Gastmeier, P.; Pfafflin, F.; Weber, S.; Werner, G.; Pfeifer, Y.; et al. Infections caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales after rectal colonization with ESBL-producing Escherichia coli or Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Rojas, V.; Villanueva-Garcia, D.; Miranda-Vega, A.L.; Aldana-Vergara, R.; Aguilar-Rodea, P.; Lopez-Marceliano, B.; Reyes-Lopez, A.; Alcantar-Curiel, M.D. Gut colonization and subsequent infection of neonates caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1322874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seekatz, A.M.; Bassis, C.M.; Fogg, L.; Moore, N.M.; Rhee, Y.; Lolans, K.; Weinstein, R.A.; Lin, M.Y.; Young, V.B.; Hayden, M.K.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Clinical Features Distinguish Colonization with Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae at the Time of Admission to a Long-term Acute Care Hospital. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, D.; Hong, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; Cho, N.H.; Kim, M.N.; Lee, Y.J.; Wi, Y.; Lee, E.H.; Han, S.H.; et al. Prevalence of carbapenemase producing Enterobacterales colonization and risk factor of clinical infection. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callejon Fernandez, M.; Madueno Alonso, A.; Abreu Rodriguez, R.; Aguirre-Jaime, A.; Castro Hernandez, M.B.; Ramos-Real, M.J.; Pedroso-Fernandez, Y.; Lecuona Fernandez, M. Risk factors for colonization by carbapenemase-producing bacteria in Spanish long-term care facilities: A multicentre point-prevalence study. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Huang, S. Epidemiology and risk factors of rectal colonization of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae among high-risk patients from ICU and HSCT wards in a university hospital. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errico, G.; Gagliotti, C.; Monaco, M.; Masiero, L.; Gaibani, P.; Ambretti, S.; Landini, M.P.; D’Arezzo, S.; Di Caro, A.; Parisi, S.G.; et al. Colonization and infection due to carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in liver and lung transplant recipients and donor-derived transmission: A prospective cohort study conducted in Italy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannella, M.; Bartoletti, M.; Campoli, C.; Rinaldi, M.; Coladonato, S.; Pascale, R.; Tedeschi, S.; Ambretti, S.; Cristini, F.; Tumietto, F.; et al. The impact of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae colonization on infection risk after liver transplantation: A prospective observational cohort study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madueno, A.; Gonzalez Garcia, J.; Ramos, M.J.; Pedroso, Y.; Diaz, Z.; Oteo, J.; Lecuona, M. Risk factors associated with carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae fecal carriage: A case-control study in a Spanish tertiary care hospital. Am. J. Infect. Control 2017, 45, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Mazzaferri, F.; de Smet, A.M.; Bragantini, D.; Eggimann, P.; Huttner, B.D.; Kuijper, E.J.; Lucet, J.C.; Mutters, N.T.; Sanguinetti, M.; et al. ESCMID-EUCIC clinical guidelines on decolonization of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria carriers. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.; Galazzo, G.; van Hattem, J.M.; Arcilla, M.S.; Melles, D.C.; de Jong, M.D.; Schultsz, C.; Wolffs, P.; McNally, A.; Schaik, W.V.; et al. Enterobacteriaceae and Bacteroidaceae provide resistance to travel-associated intestinal colonization by multi-drug resistant Escherichia coli. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2060676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, A.; El Dani, M.; Ajrouche, R.; Demontant, V.; Cheval, J.; Lacombe, K.; Cosson, G.; Rodriguez, C.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Woerther, P.L.; et al. Gut microbiome diversity and composition in individuals with and without extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales carriage: A matched case-control study in infectious diseases department. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducarmon, Q.R.; Zwittink, R.D.; Hornung, B.V.H.; van Schaik, W.; Young, V.B.; Kuijper, E.J. Gut Microbiota and Colonization Resistance against Bacterial Enteric Infection. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2019, 83, e00007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guern, R.; Grandjean, T.; Stabler, S.; Bauduin, M.; Gosset, P.; Kipnis, E.; Dessein, R. Gut colonisation with multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae worsens Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, W.Y.; Kweon, M.N.; Huh, J.W. Gut microbiota alterations in critically Ill patients with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae colonization: A clinical analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1140402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.L.; Olsen, M.H.; Palleja, A.; Ebdrup, S.R.; Sorensen, N.; Lukjancenko, O.; Marvig, R.L.; Moller, K.; Frimodt-Moller, N.; Hertz, F.B. Microbiome Compositions and Resistome Levels after Antibiotic Treatment of Critically Ill Patients: An Observational Cohort Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormerod, K.L.; Wood, D.L.; Lachner, N.; Gellatly, S.L.; Daly, J.N.; Parsons, J.D.; Dal’Molin, C.G.; Palfreyman, R.W.; Nielsen, L.K.; Cooper, M.A.; et al. Genomic characterization of the uncultured Bacteroidales family S24-7 inhabiting the guts of homeothermic animals. Microbiome 2016, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Lesker, T.R.; Hitch, T.C.A.; Galvez, E.J.C.; Smit, N.; Neuhaus, K.; Wang, J.; Baines, J.F.; Abt, B.; Stecher, B.; et al. Sequence and cultivation study of Muribaculaceae reveals novel species, host preference, and functional potential of this yet undescribed family. Microbiome 2019, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterlin, D.; Fadlallah, J.; Adams, O.; Fieschi, C.; Parizot, C.; Dorgham, K.; Rajkumar, A.; Autaa, G.; El-Kafsi, H.; Charuel, J.L.; et al. Human IgA binds a diverse array of commensal bacteria. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20181635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Ren, C.; Han, X.; Huang, W.; You, Y.; Zhan, J. Role of IgA in the early-life establishment of the gut microbiota and immunity: Implications for constructing a healthy start. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1908101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corebima, B.; Rohsiswatmo, R.; Gayatri, P.; Patole, S. Fecal human beta-defensin-2 (hBD-2) levels and gut microbiota patterns in preterm neonates with different feeding patterns. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2019, 11, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moranta, D.; Regueiro, V.; March, C.; Llobet, E.; Margareto, J.; Larrarte, E.; Garmendia, J.; Bengoechea, J.A. Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule polysaccharide impedes the expression of beta-defensins by airway epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqib, Z.; De Palma, G.; Lu, J.; Surette, M.; Bercik, P.; Collins, S.M. Alterations in fecal beta-defensin-3 secretion as a marker of instability of the gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2233679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, E.R.; Chadee, K. Antimicrobial Human beta-Defensins in the Colon and Their Role in Infectious and Non-Infectious Diseases. Pathogens 2013, 2, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Wi, Y.M.; Thoendel, M.J.; Raval, Y.S.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Abdel, M.P.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Chia, N.; Patel, R. Evaluation of the CosmosID Bioinformatics Platform for Prosthetic Joint-Associated Sonicate Fluid Shotgun Metagenomic Data Analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stercz, B.; Domokos, J.; Dunai, Z.A.; Makra, N.; Juhasz, J.; Ostorhazi, E.; Kocsis, B.; Szabo, D. The Roles of a Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae High-Risk Clone and Its Resistance Plasmids on the Gastrointestinal Colonization and Host-Defense Effectors in the Gut. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080698
Stercz B, Domokos J, Dunai ZA, Makra N, Juhasz J, Ostorhazi E, Kocsis B, Szabo D. The Roles of a Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae High-Risk Clone and Its Resistance Plasmids on the Gastrointestinal Colonization and Host-Defense Effectors in the Gut. Antibiotics. 2024; 13(8):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080698
Chicago/Turabian StyleStercz, Balazs, Judit Domokos, Zsuzsanna A. Dunai, Nora Makra, Janos Juhasz, Eszter Ostorhazi, Bela Kocsis, and Dora Szabo. 2024. "The Roles of a Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae High-Risk Clone and Its Resistance Plasmids on the Gastrointestinal Colonization and Host-Defense Effectors in the Gut" Antibiotics 13, no. 8: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080698
APA StyleStercz, B., Domokos, J., Dunai, Z. A., Makra, N., Juhasz, J., Ostorhazi, E., Kocsis, B., & Szabo, D. (2024). The Roles of a Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae High-Risk Clone and Its Resistance Plasmids on the Gastrointestinal Colonization and Host-Defense Effectors in the Gut. Antibiotics, 13(8), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics13080698




