Evaluating the Link Between Postoperative Timing of Rifampicin Introduction and the Clinical and Microbiological Outcomes of Orthopedic Staphylococcal Implant Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
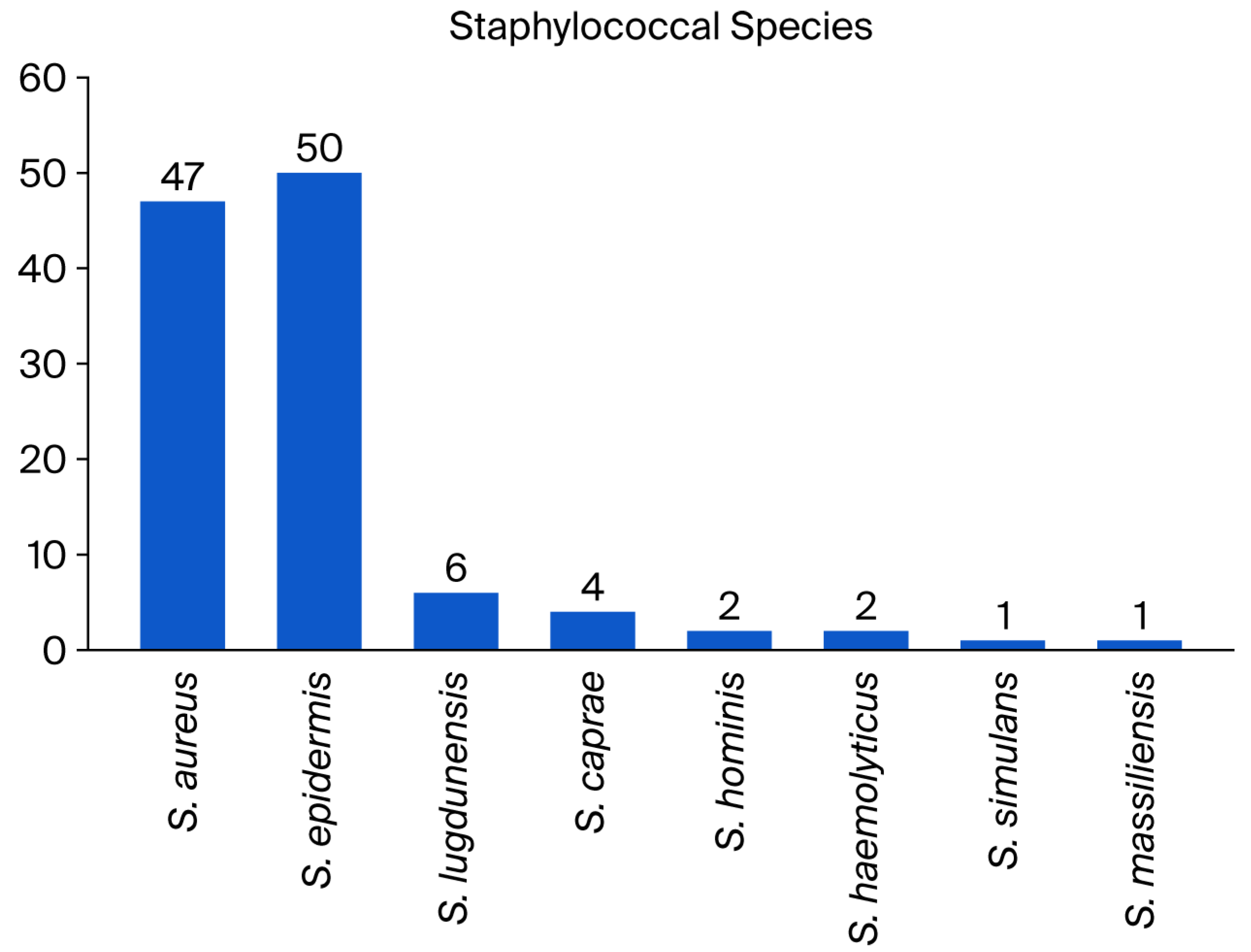
2.1. Patients and Staphylococcal Implant Infections
2.2. Surgical and Medical Therapy with Combined RIFA Use
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Rifampicin Resistance
2.5. Literature Review
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Setting, Study Objective, and Criteria
4.2. Study Definitions and Microbiological Cultures
4.3. Statistical Analysis Plan
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zimmerli, W.; Sendi, P. Role of Rifampin against Staphylococcal Biofilm Infections In Vitro, in Animal Models, and in Orthopedic Device-Related Infections. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2019, 63, e01746-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uçkay, I.; Pittet, D.; Vaudaux, P.; Sax, H.; Lew, D.; Waldvogel, F. Foreign Body Infections Due to Staphylococcus epidermidis. Ann. Med. 2009, 41, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupaibool, J. The Role of Rifampin in Prosthetic Joint Infections: Efficacy, Challenges, and Clinical Evidence. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, G.L.; Johnston, J.L.; Vazquez, G.J.; Haywood, H.B. 3rd. Efficacy of antibiotic combinations including rifampin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis: In vitro and in vivo studies. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1983, 5, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.E.; Khamas, A.B.; Østergaard, L.J.; Jørgensen, N.P.; Meyer, R.L. Combination Therapy Delays Antimicrobial Resistance after Adaptive Laboratory Evolution of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2025, 69, e01483-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünwald, L.; Blersch, B.P.; Fink, B. Early Administration of Rifampicin Does Not Induce Increased Resistance in Septic Two-Stage Revision Knee and Hip Arthroplasty. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, C.L.; Schmidt-Malan, S.M.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Patel, R. Rifampin-Based Combination Therapy Is Active in Foreign-Body Osteomyelitis after Prior Rifampin Monotherapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01822-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnelier, M.; Bouras, A.; Joseph, C.; El Samad, Y.; Brunschweiler, B.; Schmit, J.L.; Mabille, C.; Lanoix, J.P. Impact of Rifampicin Dose in Bone and Joint Prosthetic Device Infections Due to Staphylococcus spp.: A Retrospective Single-Center Study in France. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmer, A.F.; Gaechter, A.; Ochsner, P.E.; Zimmerli, W. Antimicrobial Treatment of Orthopedic Implant-Related Infections with Rifampin Combinations. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 14, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, T.; Uçkay, I.; Vaudaux, P.; François, P.; Schrenzel, J.; Harbarth, S.; Laurent, F.; Bernard, L.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J.; et al. Risk Factors for Treatment Failure in Orthopedic Device-Related Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Eom, Y.; Kim, E.; Chang, E.; Bae, S.; Jung, J.; Kim, M.J.; Chong, Y.P.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; et al. Molecular Characteristics and Prevalence of Rifampin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Patients with Bacteremia in South Korea. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, G.; Albert, J.D.; Arvieux, C.; Guggenbuhl, P. Optimizing Combination Rifampin Therapy for Staphylococcal Osteoarticular Infections. Jt. Bone Spine 2013, 80, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, C.L.; Tyner, H.L.; Schmidt-Malan, S.M.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Patel, R. Causes and Implications of the Disappearance of Rifampin Resistance in a Rat Model of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Foreign Body Osteomyelitis. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2015, 59, 4481–4488. [Google Scholar]
- Bongiorno, D.; Mongelli, G.; Stefani, S.; Campanile, F. Burden of Rifampicin- and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Italy. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwich, A.; Dally, F.J.; Bdeir, M.; Kehr, K.; Miethke, T.; Hetjens, S.; Gravius, S.; Assaf, E.; Mohs, E. Delayed Rifampin Administration in the Antibiotic Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infections Significantly Reduces the Emergence of Rifampin Resistance. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekaj, J.; Dinh, A.; Moldovan, A.; Vaudaux, P.; Gras, G.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Lew, D.; Bernard, L.; Uçkay, I. Efficacy of a Combined Oral Clindamycin–Rifampicin Regimen for Therapy of Staphylococcal Osteoarticular Infections. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 43, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinecke, P.; Morovic, P.; Niemann, M.; Renz, N.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A.; Meller, S. Adverse Events Associated with Prolonged Antibiotic Therapy for Periprosthetic Joint Infections—A Prospective Study with a Special Focus on Rifampin. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W.; Widmer, A.F.; Blatter, M.; Frei, R.; Ochsner, P.E.; Foreign-Body Infection (FBI) Study Group. Role of Rifampin for Treatment of Orthopedic Implant-Related Staphylococcal Infections: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA. 1998, 279, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landersdorfer, C.B.; Kinzig, M.; Höhl, R.; Kempf, P.; Nation, R.L.; Sörgel, F. Physiologically Based Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach for Ciprofloxacin in Bone of Patients Undergoing Orthopedic Surgery. ACS. Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlroth, J.; Kuo, M.; Tan, J.; Bayer, A.S.; Miller, L.G. Adjunctive Use of Rifampin for the Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infections: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora-Tamayo, J.; Murillo, O.; Iribarren, J.A.; Soriano, A.; Sánchez-Somolinos, M.; Baraia-Etxaburu, J.M.; Rico, A.; Palomino, J.; Rodríguez-Pardo, D.; Horcajada, J.P.; et al. A Large Multicenter Study of Methicillin-Susceptible and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Prosthetic Joint Infections Managed with Implant Retention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Matsushita, K.; Kamono, E.; Matsumoto, H.; Saka, N.; Uchiyama, K.; Suzuki, K.; Akiyama, Y.; Onuma, H.; Yamada, K. Effectiveness of Rifampicin Combination Therapy for Orthopaedic Implant-Related Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 64, 107359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, E.; Bramer, W.; Anas, A.A. Clinical Outcomes of Rifampicin Combination Therapy in Implant-Associated Infections Due to Staphylococci and Streptococci: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.; Kreitmann, L.; Triffaut-Fillit, C.; Valour, F.; Mabrut, E.; Forestier, E.; Lesens, O.; Cazorla, C.; Descamps, S.; Boyer, B.; et al. Duration of Rifampin Therapy Is a Key Determinant of Improved Outcomes in Early-Onset Acute Prosthetic Joint Infection Due to Staphylococcus Treated with a Debridement, Antibiotics and Implant Retention (DAIR): A Retrospective Multicenter Study in France. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2020, 5, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, C.C.; Ekhtiari, S.; Oral, I.; Selznick, A.; Mundi, R.; Chaudhry, H.; Pincus, D.; Wolfstadt, J.; Kandel, C.E. The Use of Rifampin in Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, Ø.E.; Borgen, P.; Bragnes, B.; Figved, W.; Grøgaard, B.; Rydinge, J.; Sandberg, L.; Snorrason, F.; Wangen, H.; Witsøe, E.; et al. Rifampin Combination Therapy in Staphylococcal Prosthetic Joint Infections: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushkin, R.; Iglesias-Ussel, M.D.; Keedy, K.; MacLauchlin, C.; Mould, D.R.; Berkowitz, R.; Kreuzer, S.; Darouiche, R.; Oldach, D.; Fernandes, P. A Randomized Study Evaluating Oral Fusidic Acid (CEM-102) in Combination With Oral Rifampin Compared With Standard-of-Care Antibiotics for Treatment of Prosthetic Joint Infections: A Newly Identified Drug-Drug Interaction. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddour, L.M.; Esquer Garrigos, Z.; Rizwan Sohail, M.; Havers-Borgersen, E.; Krahn, A.D.; Chu, V.H.; Radke, C.S.; Avari-Silva, J.; El-Chami, M.F.; Miro, J.M.; et al. Update on Cardiovascular Implantable Electronic Device Infections and Their Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association: Endorsed by the International Society for Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases. Circulation 2024, 149, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, S.M.; Tennent, D.J.; Wenke, J.C. Topical Rifampin Powder for Orthopedic Trauma Part I: Rifampin Powder Reduces Recalcitrant Infection in a Delayed Treatment Musculoskeletal Trauma Model. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 3136–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Değer, I.; Başaranoğlu, M.; Demir, N.; Aycan, A.; Tuncer, O. Efficiency of Topical Rifampin on Infection in Open Neural Tube Defects: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Neurosci. 2021, 131, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Bliziotis, I.A.; Fragoulis, K.N. Oral Rifampin for Eradication of Staphylococcus aureus Carriage from Healthy and Sick Populations: A Systematic Review of the Evidence from Comparative Trials. Am. J. Infect. Control 2007, 35, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.O.; Robert, J.; Abass, K.M.; Thompson, W.; Sarfo, F.S.; Wilson, T.; Sarpong, G.; Gateau, T.; Chauty, A.; Omollo, R.; et al. Rifampicin and Clarithromycin (Extended Release) versus Rifampicin and Streptomycin for Limited Buruli Ulcer Lesions: A Randomised, Open-Label, Non-Inferiority Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuarin, L.; Abbas, M.; Harbarth, S.; Waibel, F.; Holy, D.; Burkhard, J.; Uçkay, I. Changing perioperative prophylaxis during antibiotic therapy and iterative debridement for orthopedic infections? PLoS ONE 2019, 14, 0226674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, Y.K.S.; Ledergerber, B.; Eberhard, N.; Mestres, C.A.; Rancic, Z.; Zimmermann, A.; Zbinden, R.; Brugger, S.D.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Hasse, B.; et al. Open wounds and rifampicin therapy are associated with rifampicin resistance among staphylococcal vascular graft/endograft infections. JAC Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 3, 041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzoni, C.; Uçkay, I.; Belaieff, W.; Breilh, D.; Suvà, D.; Huggler, E.; Lew, D.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Bernard, L. In Vivo Interactions of Continuous Flucloxacillin Infusion and High-Dose Oral Rifampicin in the Serum of 15 Patients with Bone and Soft Tissue Infections Due to Staphylococcus aureus—A Methodological and Pilot Study. Springerplus 2014, 3, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, M.; Bernard, L.; Belaieff, W.; Gamulin, A.; Racloz, G.; Emonet, S.; Lew, D.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Uçkay, I. Epidemiology of Adverse Events and Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea During Long-Term Antibiotic Therapy for Osteoarticular Infections. J. Infect. 2013, 67, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugelman, D.N.; Leal, J.; Shah, S.; Wrenn, R.; Mackowiak, A.; Ryan, S.P.; Jiranek, W.A.; Seyler, T.M.; Seidelman, J. How Often Is Rifampin Therapy Initiated and Completed in Patients With Periprosthetic Joint Infections? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2025, 483, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, H.; David, I.G.; Jinga, M.L.; Popa, D.E.; Buleandra, M.; Iorgulescu, E.E.; Ciobanu, A.M. State of the Art on Developments of (Bio)Sensors and Analytical Methods for Rifamycin Antibiotics Determination. Sensors 2023, 23, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfensberger, A.; Sax, H.; Weber, R.; Zbinden, R.; Kuster, S.P.; Hombach, M. Change of antibiotic susceptibility testing guidelines from CLSI to EUCAST: Influence on cumulative hospital antibiograms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 79130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiuma, M.; Colaneri, M.; Cattaneo, D.; Fusi, M.; Civati, A.; Galimberti, M.; Cossu, M.V.; Gervasoni, C.; Dolci, A.; Riva, A.; et al. Rifampicin Drug Monitoring in TB Patients: New Evidence for Increased Dosage? Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2025, 29, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittinghoff, E.; McCulloch, C.E. Relaxing the Rule of Ten Events per Variable in Logistic and Cox Regression. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 165, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgärtner, T.; Bdeir, M.; Dally, F.J.; Gravius, S.; Hai, A.A.E.; Assaf, E.; Hetjens, S.; Miethke, T.; Darwich, A. Rifampin-resistant periprosthetic joint infections are associated with worse functional outcome in both acute and chronic infection types. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 110, 116447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydın, Ö.; Ergen, P.; Özturan, B.; Özkan, K.; Arslan, F.; Vahaboğlu, H. Rifampin-Accompanied Antibiotic Regimens in the Treatment of Prosthetic Joint Infections: A Frequentist and Bayesian Meta-Analysis of Current Evidence. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| n = 103 | Univariate Results | Multivariate Results |
|---|---|---|
| Infection due to Staphylococcus aureus (vs. coagulase negatives) | 0.9 (0.4–2.0) | 1.0 (0.4–2.4) |
| Methicillin-resistant staphylococci | 1.8 (0.8–4.2) | - |
| Delay in rifampicin introduction (continuous variable) | 1.2 (0.8–1.1) | 1.2 (0.9–1.7) |
| - Delay rifampicin by ≤ 3 days | 1 (default) | 1 (default) |
| - Delay rifampicin by 4–7 days | 1.4 (0.5–3.9) | 1.4 (0.5–4.2) |
| - Delay rifampicin by ≥ 8 days | 1.7 (0.6–5.1) | 2.0 (0.6–6.1) |
| Total duration of rifampicin prescription (continuous variable) | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) |
| Daily rifampicin dose (continuous variable) | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) |
| Arthroplasty infections | 1.0 (0.4–2.2) | 0.9 (0.4–2.2) |
| Number of past revisions | 9.5 (2.2–40.1) | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dessert, V.; Maurer, S.M.; Maurer, M.S.; Albrecht, D.; Farshad, M.; Uçkay, İ. Evaluating the Link Between Postoperative Timing of Rifampicin Introduction and the Clinical and Microbiological Outcomes of Orthopedic Staphylococcal Implant Infections. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101043
Dessert V, Maurer SM, Maurer MS, Albrecht D, Farshad M, Uçkay İ. Evaluating the Link Between Postoperative Timing of Rifampicin Introduction and the Clinical and Microbiological Outcomes of Orthopedic Staphylococcal Implant Infections. Antibiotics. 2025; 14(10):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101043
Chicago/Turabian StyleDessert, Valeria, Steven M. Maurer, Marc S. Maurer, David Albrecht, Mazda Farshad, and İlker Uçkay. 2025. "Evaluating the Link Between Postoperative Timing of Rifampicin Introduction and the Clinical and Microbiological Outcomes of Orthopedic Staphylococcal Implant Infections" Antibiotics 14, no. 10: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101043
APA StyleDessert, V., Maurer, S. M., Maurer, M. S., Albrecht, D., Farshad, M., & Uçkay, İ. (2025). Evaluating the Link Between Postoperative Timing of Rifampicin Introduction and the Clinical and Microbiological Outcomes of Orthopedic Staphylococcal Implant Infections. Antibiotics, 14(10), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14101043







