Effective Dosage of Oral Vancomycin in Treatment for Initial Episode of Clostridioides difficile Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
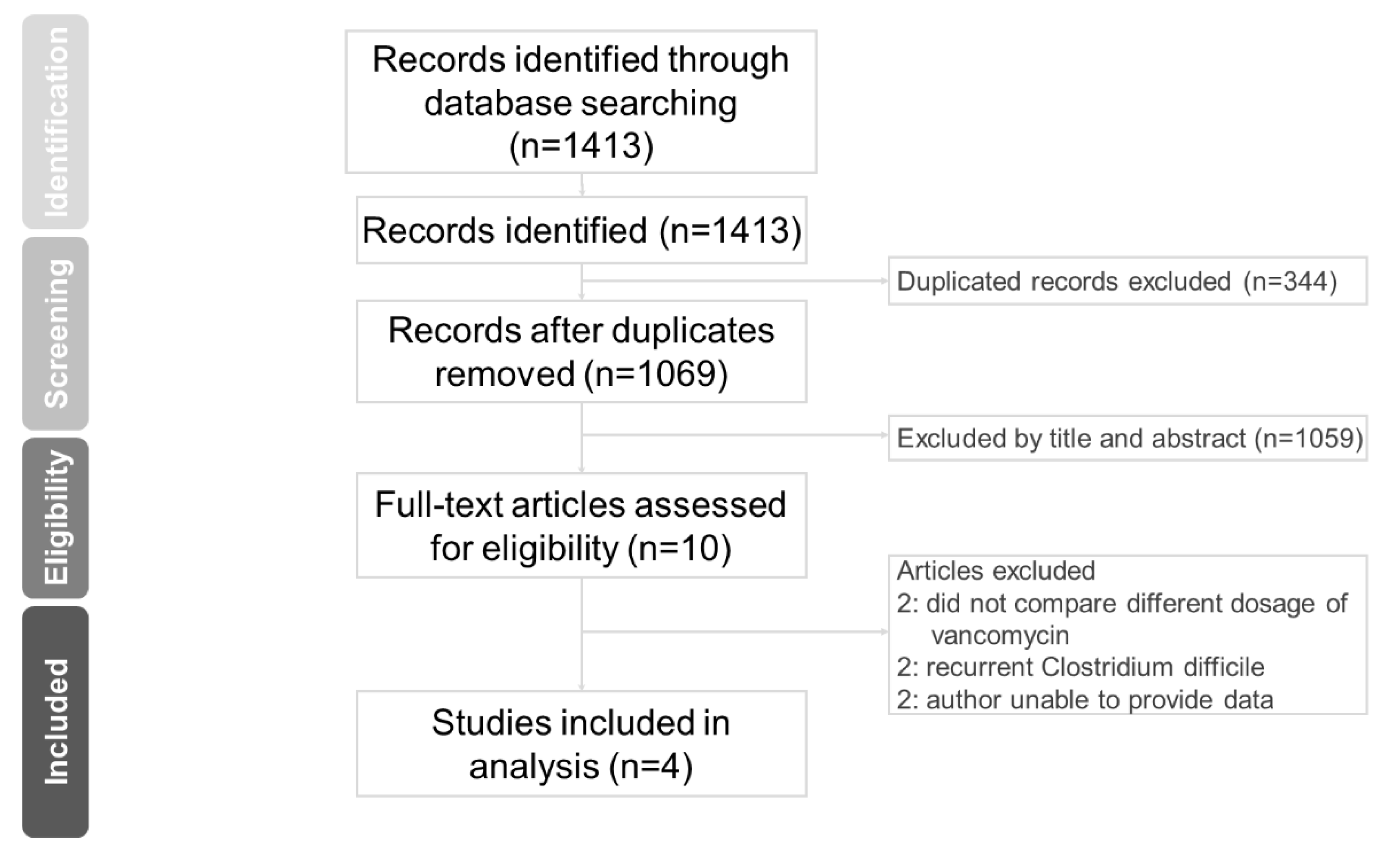
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction and Bias Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
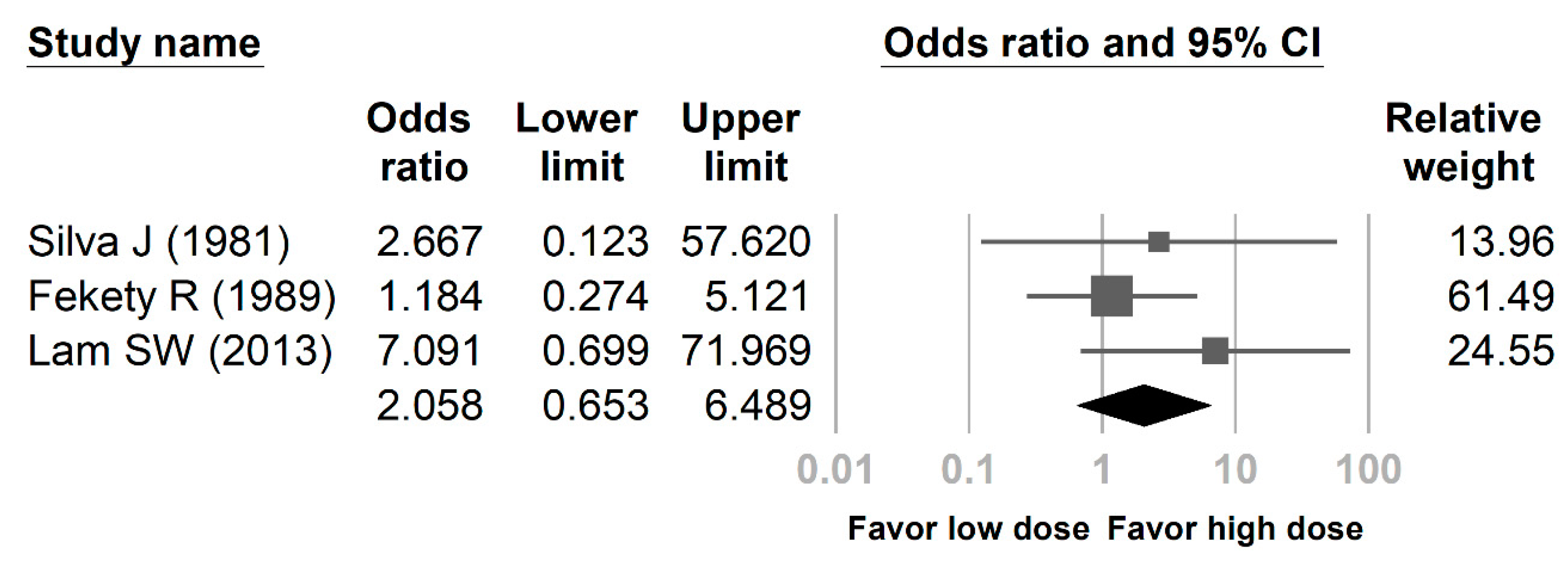
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Reference
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Study Name | Low Dose | High Dose | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Number | Mean | SD | Number | |
| Silva J (1981) | 5 | 6 | 4 | 4.22 | 2.95 | 9 |
| Fekety R (1989) | 3.8 | 6.859 | 24 | 4.3 | 8.442 | 22 |
| Lam SW (2013) | 6.766 | 2.064 | 16 | 7.105 | 2.212 | 32 |
| Cunha BA (2018) | 5.08 | 2.088 | 113 | 5.4 | 3.204 | 14 |
| Sum | 157 | 77 | ||||
| Study Name | Low Dose | High Dose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recurrent Case | Total Case Number | Recurrent Case | Total Case Number | |
| Silva J (1981) | 1 | 4 | 1 | 9 |
| Fekety R (1989) | 5 | 24 | 4 | 22 |
| Lam SW (2013) | 3 | 25 | 1 | 53 |
| Cunha BA (2018) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Sum | 9 | 53 | 6 | 84 |
References
- Barbut, F.; Petit, J.C. Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile-associated infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2001, 7, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, L.C.; Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Bakken, J.S.; Carroll, K.C.; Coffin, S.E.; Dubberke, E.R.; Garey, K.W.; Gould, C.V.; Kelly, C.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults and Children: 2017 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, e1–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, J.G. Historical perspectives on studies of Clostridium difficile and C. difficile infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46 (Suppl. 1), S4–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Y.; Hall, W.H. Staphylococcal Enterocolitis—Treatment with Oral Vancomycin. Ann. Intern. Med. 1966, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.W.; Bartlett, J.G.; Gorbach, S.L.; Onderdonk, A.B. Clindamycin-induced enterocolitis in hamsters as a model of pseudomembranous colitis in patients. Infect. Immun. 1978, 20, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Green, R.H. The association of viral activation with penicillin toxicity in guinea pigs and hamsters. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1974, 47, 166–181. [Google Scholar]
- Bunnell, K.L.; Danziger, L.H.; Johnson, S. Economic Barriers in the Treatment of Clostridium difficile Infection With Oral Vancomycin. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, ofx078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerding, D.N. Is there a relationship between vancomycin-resistant enterococcal infection and Clostridium difficile infection? Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 25 (Suppl. 2), S206–S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.H.; Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Kelly, C.P.; Loo, V.G.; McDonald, L.C.; Pepin, J.; Wilcox, M.H. Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults: 2010 update by the society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the infectious diseases society of America (IDSA). Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 431–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keighley, M.R.; Burdon, D.W.; Arabi, Y.; Williams, J.A.; Thompson, H.; Youngs, D.; Johnson, M.; Bentley, S.; George, R.H.; Mogg, G.A. Randomised controlled trial of vancomycin for pseudomembranous colitis and postoperative diarrhoea. Br. Med. J. 1978, 2, 1667–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J., Jr.; Batts, D.H.; Fekety, R.; Plouffe, J.F.; Rifkin, G.D.; Baird, I. Treatment of Clostridium difficile colitis and diarrhea with vancomycin. Am. J. Med. 1981, 71, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekety, R.; Silva, J.; Kauffman, C.; Buggy, B.; Deery, H.G. Treatment of antibiotic-associated Clostridium difficile colitis with oral vancomycin: Comparison of two dosage regimens. Am. J. Med. 1989, 86, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matzke, G.R.; Halstenson, C.E.; Olson, P.L.; Collins, A.J.; Abraham, P.A. Systemic absorption of oral vancomycin in patients with renal insufficiency and antibiotic-associated colitis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1987, 9, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, L.V.; Elmer, G.W.; Surawicz, C.M. Breaking the cycle: Treatment strategies for 163 cases of recurrent Clostridium difficile disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepin, J.; Alary, M.E.; Valiquette, L.; Raiche, E.; Ruel, J.; Fulop, K.; Godin, D.; Bourassa, C. Increasing risk of relapse after treatment of Clostridium difficile colitis in Quebec, Canada. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, V.W.; Nelson, R.E.; Schwab-Daugherty, E.M.; Khader, K.; Jones, M.M.; Brown, K.A.; Greene, T.; Croft, L.D.; Neuhauser, M.; Glassman, P.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Vancomycin and Metronidazole for the Prevention of Recurrence and Death in Patients with Clostridium difficile Infection. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, T.J.; Miller, M.A.; Mullane, K.M.; Weiss, K.; Lentnek, A.; Golan, Y.; Gorbach, S.; Sears, P.; Shue, Y.K. Fidaxomicin versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile infection. N. Engl. J. 2011, 364, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, F.A.; Bakkanagari, S.R.; Moorthi, K.M.; Davis, M.B. A comparison of vancomycin and metronidazole for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, stratified by disease severity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, M.; Pepin, J.; Frost, E.H.; Carrier, J.C.; Sirard, S.; Fortier, L.C.; Valiquette, L. Faecal pharmacokinetics of orally administered vancomycin in patients with suspected Clostridium difficile infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabit, A.K.; Nicolau, D.P. Impact of vancomycin faecal concentrations on clinical and microbiological outcomes in Clostridium difficile infection. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, B.A.; Sessa, J.; Blum, S. Enhanced Efficacy of High Dose Oral Vancomycin Therapy in Clostridium difficile Diarrhea for Hospitalized Adults Not Responsive to Conventional Oral Vancomycin Therapy: Antibiotic Stewardship Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otremba, S.; Pogue, J.; Chopra, T.; Awali, R.; Mynatt, R.; Kaye, K. The effect of oral vancomycin dose on outcomes for severe Clostridium dif-ficile infection (CDI). Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, A240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.W.; Bass, S.N.; Neuner, E.A.; Bauer, S.R. Effect of vancomycin dose on treatment outcomes in severe Clostridium difficile infection. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 42, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhaneni, S.; Almendares, O.; Farley, M.M.; Reno, J.; Smith, Z.T.; Stein, B.; Magill, S.S.; Smith, R.M.; Cleveland, A.A.; Lessa, F.C. Epidemiology and factors associated with candidaemia following Clostridium difficile infection in adults within metropolitan Atlanta, 2009–2013. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Kupfer, Y.; Pagala, M.; Chapnick, E.; Tessler, S. Systemic absorption of oral vancomycin in patients with Clostridium difficile infection. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 43, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, S.; Shimizu, R.; Furukata, S.; Hoshino, K. Oral vancomycin may have significant absorption in patients with Clostridium difficile colitis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 43, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, P.G.; Eliopoulos, G.M. Systemic Absorption of Enteral Vancomycin in a Patient with Pseudomembranous Colitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1984, 100, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, J.; Lattes, A.; Marcus, E.L. Rash induced by enteral vancomycin therapy in an older patient in a long-term care ventilator unit: Case report and review of the literature. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogue, J.M.; DePestel, D.D.; Kaul, D.R.; Khaled, Y.; Frame, D.G. Systemic absorption of oral vancomycin in a peripheral blood stem cell transplant patient with severe graft-versus-host disease of the gastrointestinal tract. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2009, 11, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettit, N.N.; DePestel, D.D.; Fohl, A.L.; Eyler, R.; Carver, P.L. Risk factors for systemic vancomycin exposure following administration of oral vancomycin for the treatment of Clostridium difficile infection. Pharmacotherapy 2015, 35, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoon, J.W.; Hall, M.; Metropulos, D.; Steiner, M.J.; Jhaveri, R.; Lohr, J.A. A Prospective Pilot Study on the Systemic Absorption of Oral Vancomycin in Children With Colitis. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. JPPT 2016, 21, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Author, Year, Country, Reference | Study Design, Period | Sample Size | Mean Age (Years) | Outcomes Examined | Recurrence Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silva et al., 1981, USA, [11] | Retrospective cohort, NA | Low dose (less than 1g per day): 4 High dose (500 mg given 4 times per day): 9 | NA | Decrease fever, abdominal pain, less than 4 formed stool/day | Within 42 days |
| Fekety et al., 1989, USA. [12] | RCT, NA | Low dose (125 mg given 4 times per day): 24 High dose (500 mg given 4 times per day): 22 | Low dose: 56 High dose: 52 | Cessation of diarrhea, duration of therapy, post treatment carriage rate, follow up (2 to 6 weeks) | Within 42 days |
| Lam et al., 2013, USA, [24] | Retrospective cohort, 2006–2011 | Low dose (125 mg given 4 times per day): 16 High dose (500 mg given 4 times per day): 32 | Low dose: 65 High dose: 69 | Clinical cure, recurrence, length of stay, complication, mortality | Within 30 days |
| Cunha et al., 2018, USA, [22] | Retrospective cohort, 2015–2016 | Conventional dose: 113 ‡ High dose (500 mg given 4 times per day): 14 | Conventional dose: 69.6 High dose: 64 | Clinical resolution, treatment duration | NA # |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, C.-Y.; Sarwal, A.; Feinstein, A.; Hennessey, K. Effective Dosage of Oral Vancomycin in Treatment for Initial Episode of Clostridioides difficile Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040173
Chiu C-Y, Sarwal A, Feinstein A, Hennessey K. Effective Dosage of Oral Vancomycin in Treatment for Initial Episode of Clostridioides difficile Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(4):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040173
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Chia-Yu, Amara Sarwal, Addi Feinstein, and Karen Hennessey. 2019. "Effective Dosage of Oral Vancomycin in Treatment for Initial Episode of Clostridioides difficile Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Antibiotics 8, no. 4: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040173
APA StyleChiu, C.-Y., Sarwal, A., Feinstein, A., & Hennessey, K. (2019). Effective Dosage of Oral Vancomycin in Treatment for Initial Episode of Clostridioides difficile Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics, 8(4), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040173





