Synthesis and Identification of Pentathiepin-Based Inhibitors of Sporothrix brasiliensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Initial Investigation
2.2. Synthesis of Pentathiepin Analogs
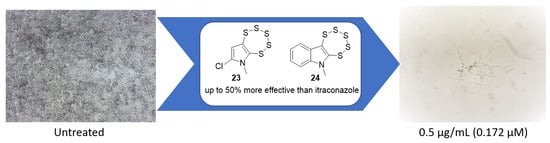
2.3. Evaluation of Pentathiepin Analogs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolate Collection
4.2. General Procedures for Screening
4.3. Chemistry
4.3.1. General Procedure to Afford Compounds 13 and 18
6,8-Bis(diethylamino)thieno(3,4-f)(1,2,3,4,5)pentathiepin (13)
6,8-Bis(dibenzylamino)thieno(3,4-f)(1,2,3,4,5)pentathiepin (18)
4.3.2. General Procedure to Afford Compounds 16 and 19–22
4.3.3. 7-Chloro-6-methyl-6H-(1,2,3,4,5)pentathiepino(6,7-b)pyrrole (23)
4.3.4. 6-Methyl-6H-(1,2,3,4,5)pentathiepino(6,7-b)indole (24)
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dias, N.M.; Oliveira, M.M.; Santos, C.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.M.; Lima, N. Sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix Mexicana, Portugal. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1975–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schenck, B.R. On refractory subcutaneous abscesses casued by a fungus possibly related to the sporotricha. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1898, 93, 286. [Google Scholar]
- Gremião, I.D.; Miranda, L.H.; Reis, E.G.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Pereira, S.A. Zoonotic epidemic of sporotrichosis: Cat to human transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.B.; Schubach Ade, O.; do Valle, A.C.; Gutierrez Galhardo, M.C.; Conceição-Silva, F.; Schubach, T.M.; Reis, R.S.; Wanke, B.; Marzochi, K.B.; Conceição, M. Cat-transmitted sporotrichosis epidemic in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Description of a series of cases. J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida-Paes, R.; de Oliveira, M.M.; Freitas, D.F.; do Valle, A.C.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C. Sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Sporothrix brasiliensis is associated with atypical clinical presentations. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros, M.B.; de Almeida Paes, R.; Schubach, A.O. Sporothrix schenckii and Sporotrichosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 633–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Burik, J.A.; Magee, P.T. Aspects of fungal pathogenesis in humans. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 743–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Bonifaz, A.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Mochizuki, T.; Li, S. Global epidemiology of sporotrichosis. Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; de Hoog, G.S.; de Camargo, Z.P. Sporothrix species causing outbreaks in animals and humans driven by animal-animal transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremião, I.D.F.; Menezes, R.C.; Schubach, T.M.P.; Figueiredo, A.B.F.; Cavalcanti, M.C.; Pereira, S.A. Feline sporotrichosis: Epidemiological and clinical aspects. Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, E.M.M.; Pires, M.C.S.; Andrade, H.B.; Gonçalves, M.L.C.; Almeida-Paes, R.; do Valle, A.C.F.; Bastos, F.I.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Freitas, D.F.S. Zoonotic sporotrichosis with greater severity in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: 118 hospitalizations and 11 deaths in the last 2 decades in a reference institution. Med. Mycol. 2019, myz024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, L.H.M.; Silva, J.N.; Gremião, I.D.F.; Menezes, R.C.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Dos Reis, É.G.; de Oliveira, R.V.C.; de Araujo, D.S.D.A.; Ferreiro, L.; Pereira, S.A. Monitoring fungal burden and viability of Sporothrix spp. in skin lesions of cats for predicting antifungal treatment response. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazum, T.K.; Bricker, B.A.; Flores-Rozas, H.; Ablordeppey, S.Y. The mechanistic targets of antifungal agents: An overview. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, S.N.; Castelli, M.V.; Zacchino, S.A.; Domínguez, J.N.; Lobo, G.; Charris-Charris, J.; Cortés, J.C.; Ribas, J.C.; Devia, C.; Rodríguez, A.M.; et al. In vitro antifungal evaluation and structure-activity relationships of a new series of chalcone derivatives and synthetic analogues, with inhibitory properties against polymers of the fungal cell wall. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 1999–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, J.M.; Cortés, J.C.; Palma, A.; López, S.N.; Zacchino, S.A.; Enriz, R.D.; Ribas, J.C.; Kouznetzov, V.V. Inhibitors of the fungal cell wall. Synthesis of 4-aryl-4-N-arylamine-1-butenes and related compounds with inhibitory activities on beta(1-3) glucan and chitin synthases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2000, 8, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, M.L.Y.; Castelli, M.V.; Kouznetsov, V.V.; Urbina, G.J.M.; López, S.N.; Sortino, M.; Enriz, R.D.; Ribas, J.C.; Zacchino, S. In vitro antifungal activity of new series of homoallylamines and related compounds with inhibitory properties of the synthesis of fungal cell wall polymers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 1531–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, F.A.; Aimar, M.L.; Sortino, M.; Gomez, R.; Sturniollo, A.; Juarez, A.; Zacchino, S.; de Rossi, R.H.; Enriz, R.D. In vitro-in vivo antifungal evaluation and structure-activity relationships of 3H-1,2-dithiole-3-thione derivatives. Farmaco 2004, 59, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladuchick, S.A. Fungicidal Isothiazoles. U.S. Patent 4094985 A, 13 June 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Moberg, K. Fungicidal Compounds. U.S. Patent 4275073 A, 23 June 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Chenard, B.L. Substituted Benzopentathiepins. U.S. Patent 4571404 A, 18 February 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Chenard, B.L. 8-Substituted Pyrazolopentathiepins and Related Compounds. U.S. Patent EP 0138622 A3, 24 April 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Vladuchick, S.A.; Fukunaga, T.; Simmons, H.E.; Webster, O.W. Thiacyanocarbons. 6. 1, 4-Dithiino [2, 3-c; 6, 5-c′] diisothiazole-3, 7-dicarbonitrile, isothiazole [3, 4-f][1, 2, 3, 4, 5] pentathiepine-8-carbonitrille, and disodium 5-cyanoisothiazoledithiolate. J. Org. Chem. 1980, 45, 5122–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenard, B.L.; Miller, T.J. Benzopentathiepins: Synthesis via thermolysis of benzothiadiazoles with sulfur. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, J.; Van Gerven, F.; Fransen, J.; Schrooten, P.; Janssen, P.A. The in vitro antifungal activity of ketoconazole, zinc pyrithione, and selenium sulfide against Pityrosporum and their efficacy as a shampoo in the treatment of experimental pityrosporosis in guinea pigs. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1990, 22, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.R.; Anderson, C.A. Topical selenium sulfide for the treatment of Hyperkeratosis. Dermatol. Ther. 2018, 8, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pekonen, P.; Hiltunen, Y.; Laitinen, R.S.; Pakkanen, T.A. Selenium-77 NMR spectroscopic and X-ray crystallographic characterization of bis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium selenide sulfide mixtures [Ti(C5H5)2SexS5x]. Inorg. Chem. 1991, 30, 3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, C.J.; Segel, I.H. Mechanism of the antimicrobial action of pyrithione: Effects on membrane transport, ATP levels, and protein synthesis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1978, 14, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, M.; Tang, B.; Liang, S.H.; Jiang, X. Sulfur containing scaffolds in drugs: Synthesis and application in medicinal chemistry. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1200–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Meli, M.L.; Konstantinova, L.S.; Laitinen, T.; Peräkylä, M.; Poso, A.; Rakitin, O.A.; Allenspach, K.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hilton, S.T. Evaluation of the antiviral efficacy of bis[1,2]dithiolo[1,4]thiazines and bis[1,2]dithiolopyrrole derivatives against the nucelocapsid protein of the Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) as a model for HIV infection. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Meli, M.L.; Konstantinova, L.S.; Laitinen, T.; Poso, A.; Rakitin, O.A.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Allenspach, K.; Hilton, S.T. Novel fused tetrathiocines as antivirals that target the nucleocapsid zinc finger containing protein of the feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) as a model of HIV infection. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Konstantinova, L.S.; Meli, M.L.; Laitinen, T.; Poso, A.; Rakitin, O.A.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hilton, S.T. Evaluation of substituted 1,2,3-Dithiazoles as inhibitors of the feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) nucleocapsid protein via a proposed Zinc ejection mechanism. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Laitinen, T.; Konstantinova, L.S.; Poso, A.; Rakitin, O.A.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hilton, S.T. Investigation of the pentathiepin functionality as an inhibitor of feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) via a potential zinc ejection mechanism, as a model for HIV infection. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Meili, T.; Laitinen, T.; Baranovsky, I.V.; Konstantinova, L.S.; Poso, A.; Rakitin, O.A.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R. Synthesis and comparison of substituted 1,2,3-dithiazole and 1,2,3-thiaselenazole as inhibitors of the feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) nucleocapsid protein as a model for HIV infection. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, J.A.; Holler, T.P.; Sanchez, J.; Gogliotti, R.; Maloney, L.; Reily, M.D. Biophysical characterization of zinc ejection from HIV nucleocapsid protein by anti-HIV 2,2′-dithiobis[benzamides] and benzisothiazolones. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 4313–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Jeng, K.S.; Lai, M.M.C. Zinc finger-containing cellular transcription corepressor ZBTB25 promotes influenza virus RNA transcription and is a target for zinc ejector drugs. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00842-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekirnik, R.; Rose, N.R.; Thalhammer, A.; Seden, P.T.; Mecinović, J.; Schofield, C.J. Inhibition of the histone lysine demethylase JMJD2A by ejection of structural Zn(II). Chem. Commun. 2009, 42, 6376–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.M.; Hilton, S.T.; Mecinović, J.; Motherwell, W.B.; Figg, W.D.; Schofield, C.J. Epidithiodiketopiperazines block the interaction between hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and p300 by a zinc ejection mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26831–26838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subramanian Vignesh, K.; Deepe, G.S., Jr. Metallothioneins: Emerging modulators in immunity and infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, B.S.; Molinski, T.F.; Barrows, L.R.; Ireland, C.M. Varacin: A novel benzopentathiepin from Lissoclinum vareau that is cytotoxic toward a human colon tumor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 4709–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaudon, M.; Trigalo, F.; Martin, M.; Frappier, F.; Guyot, M. Lissoclinotoxins: Antibiotic polysulfur derivatives from the tunicate Lissoclinum perforatum. Revised structure of lissoclinotoxin A. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Chan, A.S.; Li, T. Acid-accelerated DNA-cleaving activities of antitumor antibiotic varacin. Chem. Commun. 2002, 18, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnone, R.S.; Faulkner, D.J.; Carté, B.K.; Chan, G.; Freyer, A.; Hemling, M.E.; Hofmann, G.A.; Mattern, M.R. Pentathiepins and trithianes from two Lissoclinum species and a Eudistoma sp.: Inhibitors of protein kinase C. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Ohyama, T.; Ogawa, S. Efficient synthesis and biological properties of new benzopentathiepins. Heterocycles 1995, 41, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterji, T.; Gates, K.S. DNA cleavage by 7-methylbenzopentathiepin: A simple analog of the antitumor antibiotic varacin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterji, T.; Gates, K.S. Reaction of thiols with 7-methylbenzopentathiepin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fujiwara, T.; Nishikawa, T.; Mishima, Y.; Nagai, H.; Shida, T.; Tachibana, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Namikoshi, M. Lissoclibadins 1–3, three new polysulfur alkaloids, from the ascidian Lissoclinum cf. badium. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 8611–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, T.D.; Nairn, A.C.; Lombroso, P.J.; Ellman, J.A. Synthesis of benzopentathiepin analogs and their evaluation as inhibitors of the phosphatase STEP. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Chatterjee, M.; Baguley, T.D.; Brouillette, J.; Kurup, P.; Ghosh, D.; Kanyo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Seyb, K.; Ononenyi, C.; et al. Inhibitor of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP reverses cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zakharenko, A.; Khomenko, T.; Zhukova, S.; Koval, O.; Zakharova, O.; Anarbaev, R.; Lebedeva, N.; Korchagina, D.; Komarova, N.; Vasiliev, V.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 inhibitors with a benzopentathiepine moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khomenko, T.M.; Korchagina, D.V.; Baev, D.S.; Vassiliev, P.M.; Volcho, K.P.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Antimicrobial activity of substituted benzopentathiepin-6-amines. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi, 2nd ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, MI, USA, 2008; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida-Paes, R.; Brito-Santos, F.; Figueiredo-Carvalho, M.H.G.; Machado, A.C.S.; Oliveira, M.M.E.; Pereira, S.A.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M. Minimal inhibitory concentration distributions and epidemiological cutoff values of five antifungal agents against Sporothrix brasiliensis. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 2017, 112, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, F.; Degen, B. New Sulfur-containing Cyclic Compounds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1967, 6, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, F.; Langer, M. Contribution to the chemistry of sulfur, no. 104 Synthesis of pentathiepin and benzopentathiepin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1971, 12, 2125–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehér, F.; Langer, M.; Volkert, R.Z. Contributions to the chemistry of sulfur, 112. Naturforsch. B 1972, 27, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinova, L.S.; Rakitin, O.A.; Rees, C.W. Pentathiepins. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 2617–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinova, L.S.; Amelichev, S.A.; Rakitin, O.A. 1,2,3,4,5-Pentathiepines and 1,2,3,4,5-pentathiepanes. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2007, 76, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinova, L.S.; Rakitin, O.A. Design of sulfur heterocycles with sulfur monochloride: Synthetic possibilities and prospects. Mendeleev Commun. 2009, 19, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakitin, O.A.; Konstantinova, L.S. Chapter 4 Sulfur Monochloride in the Synthesis of Heterocyclic Compounds. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 2008, 96, 175–229. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinova, L.S.; Rakitin, O.A.; Rees, C.W.; Souvorova, L.I.; Golovanov, D.G.; Lyssenko, K.A. Unprecedented conversion of triethylamine and disulfur dichloride into a thienopentathiepin and a heptathiocane. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 1939–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelichev, S.A.; Aysin, R.R.; Konstantinova, L.S.; Obruchnikova, N.V.; Rakitin, O.A.; Rees, C.W. Abnormally mild synthesis of bis(dithiolo)pyrroles from 2,5-dimethylpyrroles. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 5725–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinova, L.S.; Amelichev, S.A.; Rakitin, O.A. Regioselective synthesis of pentathiepines fused with pyrrole, thiophene, or indole rings. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2006, 55, 2081–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinova, L.S.; Rakitin, O.A.; Rees, C.W.; Amelichev, S.A. Regioselective synthesis of pentathiepino-fused pyrroles and indoles. Mendeleev Commun. 2004, 14, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelichev, S.A.; Konstantinova, L.S.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Rakitin, O.A.; Rees, C.W. Direct synthesis of fused 1,2,3,4,5-pentathiepins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 3496–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinova, L.S.; Rakitin, O.A.; Rees, C.W. A one-step synthesis of fused pentathiepins. Chem. Comm. 2002, 11, 1204–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boechat, J.S.; Oliveira, M.M.E.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Gremião, I.D.F.; Machado, A.C.S.; Oliveira, R.V.C.; Figueiredo, A.B.F.; Rabello, V.B.S.; Silva, K.B.L.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M.; et al. Feline sporotrichosis: Associations between clinical-epidemiological profiles and phenotypic-genotypic characteristics of the etiological agents in the Rio de Janeiro epizootic area. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 2018, 113, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Compound | Growth Inhibition Percent | Isolates of S. brasiliensis/MIC (µg/mL) a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8547 | 8584 | 8607 | 8612 | 8775 | 8729 | ||
| 13 | 100% | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 50% | > 8 | > 8 | 4 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | |
| 8 | 100% | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Cmpd | R | X | Isolates of S. brasiliensis/MIC (µg/mL) a | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8547 | 8726 | 8440 | 8607 | 8639 | 8775 | 8729 | 8902 | |||
| 13 | N-(Et)2 | S | 8 | nt | nt | 4 | nt | 8 | 8 | nt |
| 18 | N-(Bn)2 | S | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 |
| 16 | CH3 | N–CH3 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 |
| 19 | CH3 | N–CH2CH3 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 |
| 20 | Ph | N–CH3 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 |
| 21 | Cl | N–CH3 | 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 |
| 22 | Cl | N–C(CH3)2 | 8 | > 8 | > 8 | > 8 | 8 | > 8 | > 8 | 8 |
| Name | R | X | Isolates of S. brasiliensis/MIC (µg/mL) a | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8547 | 8726 | 8440 | 8607 | 8639 | 8775 | 8729 | 8902 | |||
| 23 | Cl | N–CH3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 |
| 24 |  | N–CH3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Itraconazole (8) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asquith, C.R.M.; Machado, A.C.S.; de Miranda, L.H.M.; Konstantinova, L.S.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Rakitin, O.A.; Pereira, S.A. Synthesis and Identification of Pentathiepin-Based Inhibitors of Sporothrix brasiliensis. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040249
Asquith CRM, Machado ACS, de Miranda LHM, Konstantinova LS, Almeida-Paes R, Rakitin OA, Pereira SA. Synthesis and Identification of Pentathiepin-Based Inhibitors of Sporothrix brasiliensis. Antibiotics. 2019; 8(4):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040249
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsquith, Christopher R. M., Ana C. S. Machado, Luisa H. M. de Miranda, Lidia S. Konstantinova, Rodrigo Almeida-Paes, Oleg A. Rakitin, and Sandro A. Pereira. 2019. "Synthesis and Identification of Pentathiepin-Based Inhibitors of Sporothrix brasiliensis" Antibiotics 8, no. 4: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040249
APA StyleAsquith, C. R. M., Machado, A. C. S., de Miranda, L. H. M., Konstantinova, L. S., Almeida-Paes, R., Rakitin, O. A., & Pereira, S. A. (2019). Synthesis and Identification of Pentathiepin-Based Inhibitors of Sporothrix brasiliensis. Antibiotics, 8(4), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040249