Abstract
Background: Timely appropriate empirical antibiotic plays an important role in critically ill patients with gram-negative bacteremia. However, the relevant data and significant impacts have not been well studied in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). Methods: An 8-year (1 January 2007–31 December 2014) cohort study of all NICU patients with gram-negative bacteremia (GNB) in a tertiary-care medical center was performed. Inadequate empirical antibiotic therapy was defined when a patient did not receive any antimicrobial agent to which the causative microorganisms were susceptible within 24 h of blood culture sampling. Neonates with GNB treated with inadequate antibiotics were compared with those who received initial adequate antibiotics. Results: Among 376 episodes of Gram-negative bacteremia, 75 (19.9%) received inadequate empirical antibiotic therapy. The cause of inadequate treatment was mostly due to the pathogen resistance to prescribed antibiotics (88.0%). Bacteremia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Odds ratio [OR]: 20.8, P < 0.001) and extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing bacteria (OR: 18.4, P < 0.001) had the highest risk of inadequate treatment. Previous exposure with third generation cephalosporin was identified as the only independent risk factor (OR: 2.52, 95% CI: 1.18–5.37, P = 0.018). Empirically inadequately treated bacteremias were significantly more likely to have worse outcomes than those with adequate therapy, including a higher risk of major organ damage (20.0% versus 6.6%, P < 0.001) and infectious complications (25.3% versus 9.3%, P < 0.001), and overall mortality (22.7% versus 11.0%, P = 0.013). Conclusions: Inadequate empirical antibiotic therapy occurs in one-fifth of Gram-negative bacteremias in the NICU, and is associated with worse outcomes. Additional prospective studies are needed to elucidate the optimal timing and aggressive antibiotic regimen for neonates who are at risk of antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteremia.
1. Background
Bloodstream infection is the major cause of mortality in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), after more advanced perinatal care and improved delivery room resuscitation have been achieved in the recent years [1,2]. Although coagulase-negative staphylococci remains the most common pathogen of neonatal bacteremia, there is an increasing trend of Gram-negative bacteremia (GNB) in the NICU [3,4], especially after long duration of hospitalization, gram-negative bacteria colonization, or underlying gastrointestinal pathology [5,6,7]. The emergence of antibiotic resistance among GNB is a great concern, because the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics for antibiotic resistant GNB may cause a vicious cycle [8,9,10]. The condition may become especially critical when severe GNB, defined as a fulminant and rapidly devastating sepsis, is encountered.
Appropriate initial antibiotic therapy has been demonstrated as the key independent factor of treatment outcomes in patients with Gram-negative bacteremia in previous studies from the adult ICUs or wards [11,12,13,14]. However, this issue has not been fully studied in the NICU, except for a small sample size, case-control study found in the literature [15]. GNB in the NICU are well known to potentially cause life-threatening septic shock, especially by multidrug resistant (MDR) pathogens or in neonates with underlying comorbidities [4,16]. MDR GNB accounts for nearly one-fifth of all neonatal GNBs, or 7%–10% of all neonatal late-onset sepsis [4,17,18]. Neonates with MDR GNB are well known to have a significantly higher risk of mortality than those with antibiotic-susceptible GNB [4,18]. Besides this, it is worthwhile to examine clinical parameters that can be used as prognostic markers in critically ill neonates, which can facilitate the assessment of the GNB course and guide treatment strategies. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the impact of initial inadequate antibiotic therapy on outcomes of neonates with GNB and examine clinical parameters that can be predictors of final adverse outcomes.
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Setting and Study Design
This study was conducted in the NICUs of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CGMH), and all neonates hospitalized in the NICUs of Linkou CGMH were enrolled. These NICUs contains a total of three units and has a total capacity of 47 beds equipped with mechanical ventilator, and 48 beds with special care nurseries. Since 2003, all neonates admitted to our NICUs were included in a database and followed up until death or hospital discharge. This database contained basic demographics, comorbidities of prematurity, all nosocomial infections, and discharge diagnosis. We conducted a retrospective cohort study using this prospectively collected database. Written consent for this study was not required by the Ethics Committee of CGMH, which approved this research.
All patients between January 2007 and December 2014 with microbiologically documented GNB were enrolled for analysis. Polymicrobial infections were also included if one of the pathogens was a Gram-negative organism. Subsequent episodes of bacteremia in study patients within one month from the first episode of Gram-negative bacteremia were excluded due to better outcome analysis. We reviewed the medical records of the neonates with initial inadequate antibiotics and compared them with those who received appropriate initial antimicrobial therapy. The main outcome measures included the infectious complications, early mortality (death within 7 days of bacteremia onset), and overall mortality (death due to any reason within 30 days of bacteremia onset).
2.2. Data Collection
In addition to all basic demographics and complications of prematurity retrieved from our neonatal database, chart and electronic medical records of patients who met the inclusion criteria were reviewed for the presence of the following features: details of clinical features, laboratory data and treatment courses of bacteremias, initial antimicrobial therapy regimen, use of central venous catheter (CVC), total parenteral nutrition (TPN) and/or intrafat, mechanical ventilators, underlying comorbidities, surgical interventions, and receipt of corticosteroid or antibiotics within 30 days prior to bacteremia. Severity of illness was calculated by two investigators (Dr. S.-M.C. and Dr. J.-F.H.) based on the Neonatal Therapeutic Intervention Scoring System (NTISS) [19].
2.3. Definitions
Gram-negative bacteremia was defined as the identification of gram-negative bacilli in a blood culture specimen. Only clinically significant bacteremias were enrolled, which was defined as at least one positive blood culture, together with clinical features compatible with systemic inflammatory response syndrome [4,7,12]. The bacteremia onset was defined as the time point of blood culture sampling through peripheral vein or artery, as we never obtained the blood culture from CVC. Inadequate antimicrobial therapy referred to the administration of antimicrobial agents to which the causative microorganisms were resistant in vitro within the first 24 h of bacteremia onset, or lack of administration of an antimicrobial therapy.
In our institution, blood cultures were incubated in the Bactec 9240 system, and antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed by using the disk diffusion method according to the recommendations of the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute [20]. Multidrug resistance was defined using previously published criteria [21]. In our NICU, empirical antibiotics were prescribed for the coverage of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms, usually oxacillin or vancomycin plus cefotaxime or gentamicin, once late-onset sepsis was suspected. For early-onset sepsis, ampicillin plus gentamicin or cefotaxime were usually prescribed, depending on the physician’s decision. The microbiology laboratory would notify the clinician when a blood culture was positive, and the clinician was responsible to modify the antimicrobial regimens according to subsequent bacterial identification and antimicrobial susceptibility results.
Early-onset sepsis and late-onset sepsis were defined as clinical sepsis combined with bacterial growth on a blood culture obtained within the first 72 h of life and > 72 h of life, respectively [5,8]. A bacteremia was classified as community-acquired in this study if the neonate had been discharged from NICU or baby room for at least two days, and the first positive blood culture occurred ≤ 48 h after hospital admission. Antimicrobial exposure was defined as systemic administration of an antibiotic class for at least 3 days in the preceding 30 days before the onset of bacteremia. All comorbidities of prematurity, including respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), and periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) were based on the latest updated diagnostic criteria in the standard textbook of neonatology [22]. Shock was defined as a mean blood pressure < lower limit according to gestational age that was unresponsive to fluid treatment or required vasoactive agents [23]. Persistent bacteremia was defined as two or more consecutive positive blood cultures for more than 48 h on appropriate antibiotic therapy. Infectious complications were defined as any newly infectious focus or persistent organ damage that occurred within one week after the onset of bacteremia, but not concurrently.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The student’s t test or Mann–Whitney U–test were used to compare continuous variables depending on values distribution, and χ2 or Fisher’s exact test was used to compare categorical variables. A two-sided P value of < 0.05 was considered significant. In identifying the independent risk factors for mortality, a backward stepwise logistic regression analysis was used to control for the effects of confounding factors. Variables with a P value of < 0.05 in the univariate analysis were candidates for multivariate analysis as well as the main variable of interest (i.e., inappropriate initial antimicrobial therapy). Kaplan–Meier analysis was used to compare the survival situation of neonates with GNB treated with appropriate versus inappropriate antibiotics. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 15.0 (SPSS®, Chicago, IL).
2.5. Availability of Data and Materials
The datasets used/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
2.6. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was approved by the institutional review board of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, (the IRB certificate number: 103-3236B) with a waiver of informed consent because all patient records and information were anonymized and de-identified prior to analysis.
3. Results
3.1. The Epidemiology of Gram-Negative Bacteremia in the NICU
During the study period, a total of 333 neonates with 395 episodes of Gram-negative bacteremia were identified; 19 of them were the recurrent episodes which occurred within one month after the first episode and were excluded, leaving a total of 333 neonates with 376 episodes of Gram-negative bacteremia for analysis (Table 1).

Table 1.
Bacterial isolates in 333 neonates with 376 episodes of Gram-negative bacteremia.
Most of our cases were nosocomial infections (371 episodes, 98.7%), and only 5 episodes (1.3%) were community-acquired. There were 354 episodes of late-onset sepsis and 22 episodes of early-onset sepsis. The predominant organisms for monomicrobial bacteremias were Klebsiella spp. (n = 122; 32.4%), Escherichia coli (n = 92; 24.5%), Enterobactor spp. (43; 11.4%), and Acinetobacter baumannii (43; 11.4%). Thirty-three episodes of bacteremias were polymicrobial (8.8%). There were 70 (18.6%) multidrug-resistant organisms among the isolates, including 47 extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producers.
3.2. The Frequency of Inadequate Antibiotic Treatment of Gram-Negative Bacteremia
The antibiotics with Gram-negative activity that were most frequently prescribed during the first 24 h of bacteremias onset were cefotaxime (228; in 60.6% of episodes), gentamicin (51; 13.6%), meropenem (46; 12.2%), ceftazidime (38; 10.1%), and aztreonam (4; 1.1%). In 9 (2.4%) episodes, only monotherapy with vancomycin was prescribed initially. In 348 cases (92.6%), more than one antibiotic were used during this time period.
Seventy-five (19.9%) episodes of Gram-negative bacteremia were treated with inadequate empirical antibiotics. In 66 (88.0%) of these cases, subsequently identified pathogens resistant to the prescribed antibiotics were responsible for the inadequate treatment, including multidrug resistant strains for 51 (68.0%) isolates. For the other 9 (12.0%) cases, the clinicians failed to administer in-vitro susceptible antibiotics within 24 h after the initial positive blood culture was drawn. The median time from bacteremia onset to receive adequate antibiotic treatment in those without initially adequate treatment was 47 h (range: 29–94 h). Within 24 h after notification of antibiotic susceptibility, all patients received adequate antibiotic treatment.
Klebsiella pneumoniae (n = 15, 20.0%) was the most common pathogen treated with initially inadequate antibiotic, followed by E. coli (14, 18.7%) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (12, 16.0%). However, ESBL-producing bacteria (n = 34, 72.3%, odds ratio [OR]: 18.4, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 9.0–37.7, P < 0.001) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (n = 12, 75.0%, OR: 20.8, 95% CI: 5.8–75.3, P < 0.001) had the highest rate of receiving inadequate antibiotics initially (Table 1).
3.3. Factors Associated with Inadequate Empirical Antibiotic Treatment of Gram-Negative Bacteremia
Between patients receiving initially inadequate and adequate empirical treatment, there were no significant differences in terms of demographics, age at onset of bacteremia, use of CVC, TPN and/or intrafat, mechanical ventilation, and underlying chronic conditions (Table 2). Initially inadequately treated bacteremias were more likely to be the recurrent episode (37.3% vs. 22.9%, P = 0.018), and significantly more likely to have antibiotic exposure with a third generation cephalosporin (P < 0.001) and vancomycin (P = 0.004) within one month before bacteremia onset than adequately treated bacteremias. In terms of clinical manifestations and laboratory data at onset of bacteremia, there were no significant differences between the two groups, except higher serum C-reactive protein concentration in the bacteremias without adequate treatment (median, 78.0 vs. 59.1, P = 0.038). With multivariate logistic regression analysis, only previous antibiotic exposure to a third generation cephalosporin within one month was identified as the independent risk factor (Odds ratio [OR]: 2.52, 95% CI: 1.18–5.37, P = 0.018).

Table 2.
Comparison of 376 episodes of Gram-negative bacteremias treated with inadequate versus adequate empirical antibiotic treatment.
3.4. The Outcome of Inadequate Empirically Treated Gram-Negative Bacteremia
Table 3 shows the comparison of clinical outcomes between the patients with and without initially adequately treated bacteremias. Although the rates of persistent bacteremia were comparable, significantly more patients with inadequately treated bacteremias had prolonged feeding intolerance (> 3 days) and higher severity of illness at the third day of bacteremia (scored by NTISS). Besides this, infants with Gram-negative bacteremias but without initially adequate antibiotic therapy had a significantly higher risk of progression to severe sepsis or septic shock (P = 0.002) and infectious complications (p < 0.001).

Table 3.
Outcome comparisons of Gram-negative bacteremia treated with inadequate antibiotics versus adequate antibiotics.
For bacteremias without initial adequate therapy, a total of nine patients died within 7 days, including 5 patients who died within 48 h after bacteremia onset without receiving any effective antimicrobial therapy. Infants without initially adequate antibiotic therapy did not have a significantly higher early mortality rate than those with adequately therapy, and the risk of recurrent bacteremia within one month was also comparable (Table 3). However, inadequately treated bacteremias had significantly higher overall mortality rate than adequately treated bacteremias (22.7% vs. 11.0%, P = 0.013). This can also be confirmed by log rank test (p = 0.051) [Figure 1].
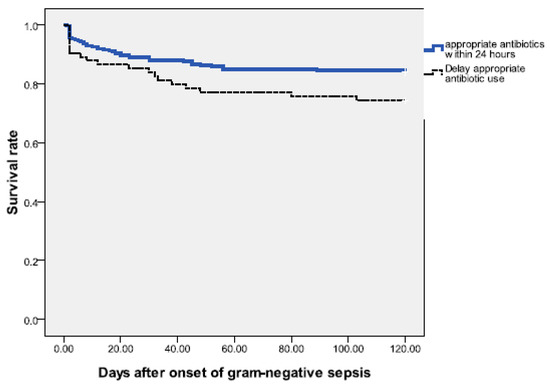
Figure 1.
Survival following onset of gram-negative sepsis from neonates in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). The Kaplan–Meier graph is stratified by the episodes treated with appropriate antibiotics within 24 h and those with delayed initial appropriate antibiotic treatment; [log rank test = 0.051].
4. Discussion
Results from this study indicated that initially inadequate antimicrobial treatment was significantly associated with antibiotic resistant Gram-negative bacteria, mainly P. aeruginosa and ESBL-producing bacteria. Previous antibiotic exposure to a third generation cephalosporin was identified as the independent risk factor for initially inadequately treated bacteremias before blood culture results and antibiotic susceptibilities were available. The possible explanation could be that broad-spectrum cephalosporin exposure caused selection of drug-resistant bacteria, which further resulted in inadequately treated bacteremias, if alternatively more effective antibiotics were not prescribed. The adverse outcomes were in patients with the significantly higher rates of infectious complications and overall mortality (within 30 days) compared with adequately treated patients.
Several factors have been found for inadequate treatment in other settings, e.g., hospital admission in the 90 days prior to the current admission, admission to surgery, nosocomial infection, and polymicrobial infection [16,24,25]. All these factors were not found in the present study. Our finding was consistent with previous reports that previous antibiotic exposure to broad-spectrum cephalosporin is associated with a significantly higher risk of infection caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria [26,27,28,29]. Although some other broad-spectrum antibiotics, such as carbapenem or fluoroquinolones, are also found to cause antibiotic resistant Gram-negative bacteremia [28,30], these antibiotics were much less frequently prescribed in our cohort. Sometimes, bacteremias were inadequately treated because antibiotic-resistant bacteremias are indistinguishable from those that are antibiotic-susceptible. In addition, the initial partial response of these inadequately treated bacteremias would delay clinicians’ decision to modify antibiotics, and sometimes clinicians may have ignored the clinically worsening progression.
The appropriateness of initial antibiotics depends on the empirical antibiotic prescribed and the local antibiotic susceptibility patterns. It seemed reasonable that the lower the rate of drug resistant organisms in the NICU, the lower the rate of initially inadequate antimicrobial therapy. Therefore, the issue of how to reduce antimicrobial resistance in the ICU [31,32] is important but not fully studied in the neonatal settings. For example, in contrast to previous studies indicating that S. marcescens and A. baumannii causing bacteremias were multidrug resistant and associated with high mortality or morbidity in the NICU [33,34], all of the S. marcescens and most of the A. baumannii isolates in our cohort were susceptible to aminoglycoside or cefotaxime, and thus, they were not difficult to treat. The significantly higher mortality of inadequately treated Gram-negative bacteremias may partially be explained by the pathogens themselves, and P. aeruginosa and ESBL-producing bacteria, the major causative organisms of this study, have been found to be more likely to cause fulminant illness or early mortality [35,36].
In this study, the result in neonates with GNB is comparable with that documented in the literature of studies which were conducted in adults [15,24,25]. Gram-negative bacteremias without initially adequate antimicrobial therapy had a significantly higher risk of overall mortality, prolonged illness, progression to severe sepsis, and infectious complications, but not early mortality within seven days of onset. It seemed that in neonates, Gram-negative bacteremias without initially adequate antimicrobial therapy did not cause early mortality within seven days of onset but they caused a prolonged illness, major organs damage, infectious complications, and then led to clinical deterioration, which subsequently resulted in final in-hospital mortality.
This study highlighted the importance of further efforts to elucidate the optimal timing and aggressive antibiotic regimen for neonates who are at risk of antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteremia. Antimicrobial stewardship interventions have been well studied to prompt appropriate antibiotics prescription in the NICU [37,38,39]. In our institute, routine antifungal prophylaxis for extremely preterm neonates has been launched since early 2017, and the influences as well as those of antimicrobial stewardship intervention are currently under investigation. Our previous studies found that MDR GNB accounted for 18.6% of all neonatal GNB [4,7,16].
Because colonization of the newborns with MDR Gram-negative pathogens makes them the potential source of nosocomial outbreaks [8,40], further routine surveillance of colonization is also suggested.
There are some limitations in this study. This study was observational and not randomized; therefore, the choices of initial empirical antibiotic depended on attending physicians, instead of the researchers. We failed to account for some important confounders that might influence the decision of attending physician in modifying antibiotics, such as the clinical progression on the first day of bacteremia. Besides this, the data were derived from a single center; therefore our conclusions are necessarily limited in generalizability to other settings and institutions.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, initial inappropriate antibiotic therapy in neonates with gram-negative bacteremia is associated with a significant higher risk of overall mortality and infectious complications. Early identification of neonatal sepsis caused by antibiotic resistant pathogens, such as ESBL producing gram-negative bacilli or Pseudomonas spp, may reduce the rate of inadequate antibiotic treatment, which can potentially improve the treatment outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: S.-M.C., M.-H.T., and J.-F.H. Data collection and verification: M.-Y.L., M.-H.T., S.-M.C., H.-R.H., M.-C.C., and R.-H.F. Formal analysis: S.-M.C., M.-H.T., and S.-M.C. Funding acquisition: J.-F.H. Investigation: S.-M.C., M.-H.T., and M.-C.C. Methodology: J.-F.H., M.-Y.L., S.-M.C., and H.-R.H. Supervision: M.-H.T. Writing—original draft: S.-M.C. and M.-H.T. Writing—review and editing: M.-H.T. All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Acknowledgments
All authors thank Mrs. Chiao-Ching Chiang for keeping the database of our NICU, and all nursing staff working in our NICUs for keeping extremely detailed patient records, which contributed greatly to the completion of this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| CI | confidence interval; |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid; |
| CVC | central venous catheter; |
| CGMH | Chang Gung Memorial Hospital; |
| EOD | early-onset disease; |
| ESBL | extended-spectrum β-lactamase; |
| GNB | gram-negative bacteremia; |
| GBS | Group B streptococcus; |
| LOD | late-onset disease; |
| NTISS | Neonatal Therapeutic Intervention Scoring System; |
| OR | odds ratio; |
| TPN | total parenteral nutrition. |
References
- Gowda, H.; Norton, R.; White, A.; Kandasamy, Y. Late-onset Neonatal Sepsis—A 10-year Review from North Queensland, Australia. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchenir, L.; Renaud, C.; Khan, S.; Bitnun, A.; Boisvert, A.-A.; McDonald, J.; Bowes, J.; Brophy, J.; Barton, M.; Ting, J.; et al. The Epidemiology, Management, and Outcomes of Bacterial Meningitis in Infants. Pediatrics 2017, 140, 20170476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, L.; Ramy, N.; Saied, D.; Akmal, D.; Salama, N.; Halim, M.M.; Aly, H. Emerging antimicrobial resistance in early and late-onset neonatal sepsis. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2017, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Chu, S.-M.; Hsu, J.-F.; Lien, R.; Huang, H.-R.; Chiang, M.-C.; Fu, R.-H.; Lee, C.-W.; Huang, Y.C. Risk Factors and Outcomes for Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteremia in the NICU. Pediatrics 2014, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgori, L.; Tersigni, C.; Hsia, Y.; Kortsalioudaki, C.; Heath, P.T.; Sharland, M.; Bielicki, J. The relationship between Gram-negative colonization and bloodstream infections in neonates: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.-H.; Tsai, M.-H.; Lai, M.-Y.; Lee, C.-W.; Chiang, M.-C.; Lien, R.; Fu, R.-H.; Huang, H.-R.; Chu, S.-M.; Hsu, J.-F. Incidence, clinical features, and implications on outcomes of neonatal late-onset sepsis with concurrent infectious focus. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.-F.; Chu, S.-M.; Huang, Y.C.; Lien, R.; Huang, H.-R.; Lee, C.-W.; Chiang, M.-C.; Fu, R.-H.; Tsai, M.-H. Predictors of clinical and microbiological treatment failure in neonatal bloodstream infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 482.e9–482.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neemann, K.; Olateju, E.K.; Izevbigie, N.; Akaba, G.; Olanipekun, G.M.; Richard, J.C.; Duru, C.I.; Kocmich, N.J.; Samson, K.K.; Rezac-Elgohary, A.; et al. Neonatal outcomes associated with maternal recto-vaginal colonization with extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae in Nigeria: A prospective, cross-sectional study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauzin, M.; Ouldali, N.; Lévy, C.; Béchet, S.; Cohen, R.; Caeymaex, L. Combination therapy with ciprofloxacin and third-generation cephalosporin versus third-generation cephalosporin monotherapy in Escherichia coli meningitis in infants: A multicentre propensity score–matched observational study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkentzi, D.; Kortsalioudaki, C.; Cailes, B.C.; Zaoutis, T.; Kopsidas, I.; Tsolia, M.; Spyridis, N.; Siahanidou, S.; Sarafidis, K.; Heath, P.T.; et al. Epidemiology of infections and antimicrobial use in Greek Neonatal Units. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018, 104, F293–F297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, M.K.; Stryjewski, M.E.; Wang, W.; Hardin, T.C.; Nogid, B.; Luke, D.R.; Corey, G.R.; Barriere, S.L.; Shorr, A.F. Telavancin Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia Trials: Impact of Gram-Negative Infections and Inadequate Gram-Negative Coverage on Clinical Efficacy and All-Cause Mortality. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Biswas, J.S.; Edgeworth, J.D.; Islam, J.; Jenkins, N.; Judge, R.; Lavery, A.J.; Melzer, M.; Morris-Jones, S.; Nsutebu, E.F.; et al. Gram-negative bacteremia: A multi-center prospective evaluation of empiric antibiotic therapy and outcome in English acute hospitals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoletti, M.; Giannella, M.; Lewis, R.; Caraceni, P.; Tedeschi, S.; Paul, M.; Schramm, C.; Bruns, T.; Merli, M.; Cobos-Trigueros, N.; et al. A prospective multicentre study of the epidemiology and outcomes of bloodstream infection in cirrhotic patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 546.e1–546.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; Xiang, D.; Cao, K.; Qi, L.-W.; Li, P.; Zhu, W.; et al. Predictors of mortality in bloodstream infections caused by multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria: 4 years of collection. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2017, 45, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apisarnthanarak, A.; Holzmann-Pazgal, G.; Hamvas, A.; Olsen, M.A.; Fraser, V. Antimicrobial Use and the Influence of Inadequate Empiric Antimicrobial Therapy on the Outcomes of Nosocomial Bloodstream Infections in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2004, 25, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Hsu, J.-F.; Chu, S.-M.; Lien, R.; Huang, H.-R.; Chiang, M.-C.; Fu, R.-H.; Lee, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-C. Incidence, Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors for Adverse Outcome in Neonates With Late-onset Sepsis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, e7–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litzow, J.M.; Gill, C.; Mantaring, J.B.V.; Fox, M.P.; MacLeod, W.; Mendoza, M.; Mendoza, S.; Scobie, R.; Huskins, C.W.; Goldman, D.A.; et al. High frequency of multidrug-resistant gram-negative rods in 2 neonatal intensive care units in the Philippines. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2009, 30, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Song, X.; Soghier, L.; Floyd, T.T.; Harris, T.R.; Short, B.; DeBiasi, R.L. Reassessing the need for active surveillance of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacteriaceae in the neonatal intensive care population. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2018, 39, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Richardson, D.K.; McCormick, M.C.; Workman-Daniels, K.; A Goldmann, D. Neonatal therapeutic intervention scoring system: A therapy-based severity-of-illness index. Pediatrics 1992, 90, 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twenty-Second Informational Supplement M100-SCLSI; Elsevier: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery’s Diseases of the Newborn, 8th ed.; Taeusch, H.W., Roberta Ballard, A., Christine Gleason, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kermorvant-Duchemin, E.; Laborie, S.; Rabilloud, M.; Lapillonne, A.; Claris, O. Outcome and prognostic factors in neonates with septic shock. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 9, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbarth, S.; Garbino, J.; Pugin, J.; A Romand, J.; Lew, D.; Pittet, D. Inappropriate initial antimicrobial therapy and its effect on survival in a clinical trial of immunomodulating therapy for severe sepsis. Am. J. Med. 2003, 115, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.R.; Friedman, N.D.; Stout, J.E.; Sexton, D.J.; Kaye, K.S. Risk Factors for Ineffective Therapy in Patients With Bloodstream Infection. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, J.; Nguyen, T.; Okamoto, M.; McKamy, S.; Lieberman, J.M. Impact of Empiric Antibiotic Use on Development of Infections caused by Extended-Spectrum ??-Lactamase Bacteria in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkin, D.R.; Fishman, N.O.; Patel, J.B.; Merrill, J.D.; Lautenbach, E. Risk Factors for Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiology 2004, 25, 781–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, D.S.Y.; Jongerden, I.P.; Buiting, A.G.; Hall, M.A.L.-V.; Speelberg, B.; Kesecioglu, J.; Bonten, M.J.M. Antibiotic exposure and resistance development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter species in intensive care units. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 2458–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Li, J.B.; Ye, D.Q.; Jiang, Z.J. Enterobacter Bacteremia: Clinical Features, Risk Factors for Multiresistance and Mortality in a Chinese University Hospital. Infection 2006, 34, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.; Paul, M.; Almanasreh, N.; Tacconelli, E.; Frank, U.; Cauda, R.; Borok, S.; Cohen, M.; Andreassen, S.; Nielsen, A.D.; et al. Benefit of Appropriate Empirical Antibiotic Treatment: Thirty-day Mortality and Duration of Hospital Stay. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.R.; De Almeida, S.M.; Correa, L.; Junior, M.S.; Martino, M.D.V.; Silva, C.V.; Cal, R.G.R.; Edmond, M.B.; Dos Santos, O.F. The effect of limiting antimicrobial therapy duration on antimicrobial resistance in the critical care setting. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2009, 37, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.P.; Catrou, P.G.; Christie, J.D.; Young, P.D.; Polk, R.E. Reduction in broad-spectrum antimicrobial use associated with no improvement in hospital antibiogram. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltezou, H.C.; Tryfinopoulou, K.; Katerelos, P.; Ftika, L.; Pappa, O.; Tseroni, M.; Kostis, E.; Kostalos, C.; Prifti, H.; Tzanetou, K.; et al. Consecutive Serratia marcescens multiclone outbreaks in a neonatal intensive care unit. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2012, 40, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, A.; Muñoz, J.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.; Carbonaro, C.; Montecalvo, M.; Clones, B.; LaGamma, E.F. Outbreak of Acinetobacter Infection in Extremely Low Birth Weight Neonates. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2009, 28, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhoul, I.R.; Sujov, P.; Smolkin, T.; Lusky, A.; Reichman, B. Pathogen-Specific Early Mortality in Very Low Birth Weight Infants with Late-Onset Sepsis: A National Survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hady, H.; Hawas, S.; El-Daker, M.; El-Kady, R. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in neonatal intensive care unit. J. Perinatol. 2008, 28, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantey, J.B.; Wozniak, P.S.; Sánchez, P.J. Prospective Surveillance of Antibiotic Use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzegwu, N.I.; Rychalsky, M.R.; Nallu, L.A.; Song, X.; Deng, Y.; Natusch, A.M.; Baltimore, R.S.; Paci, G.R.; Bizzarro, M.J. Implementation of an Antimicrobial Stewardship Program in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2017, 38, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaan, A.E.; Nour, I.; Eldegla, H.E.; Nasef, N.; Shouman, B.; Abdel-Hady, H. Conventional Versus Prolonged Infusion of Meropenem in Neonates With Gram-negative Late-onset Sepsis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, V.; Jonsson, K.; Giske, C.; Iversen, A.; Aspevall, O.; Jonsson, B.; Camporeale, A.; Norman, M.; Naver, L. Neonatal intestinal colonization with extended-spectrum β-lactamase–producing Enterobacteriaceae—A 5-year follow-up study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).