HNP-1 and HBD-1 as Biomarkers for the Immune Systems of Elite Basketball Athletes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
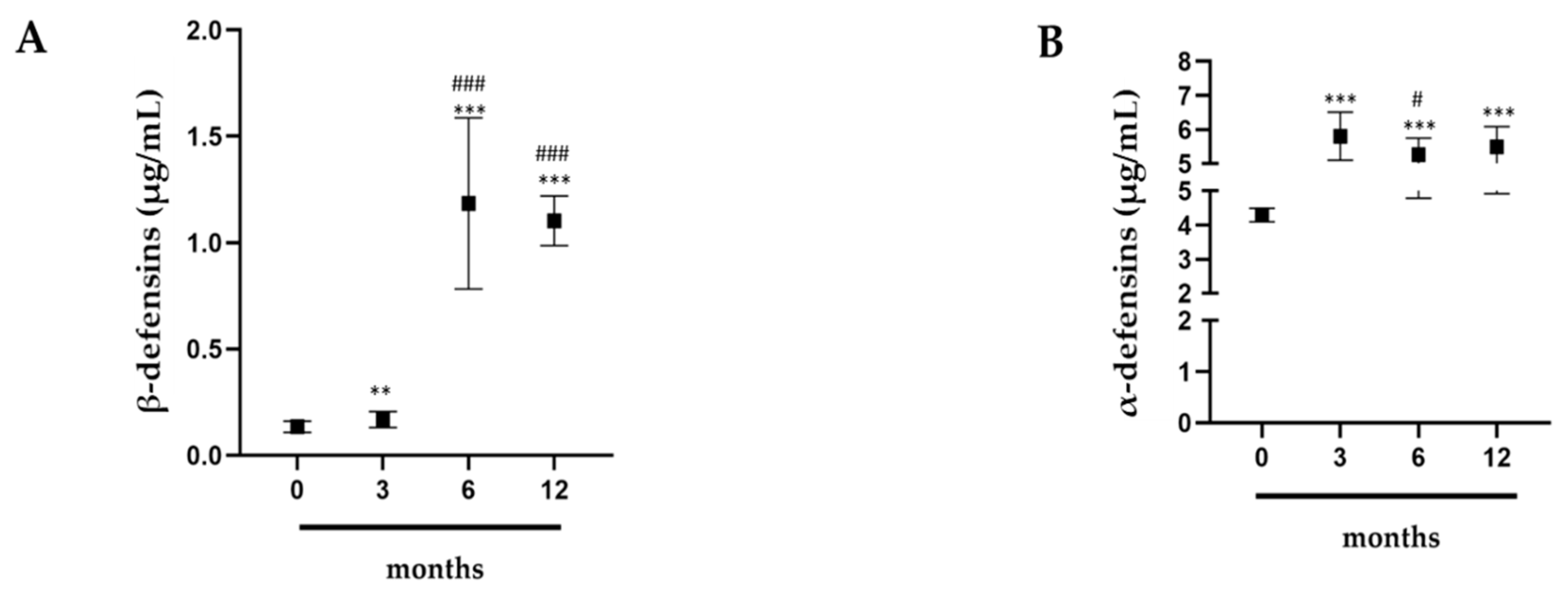
2.1. Evaluation of α- and β-Defensins in Professional Athletes
2.2. Effects of Intense Exercise on White Blood Cells
2.3. Measurements of Cortisol and Testosterone
2.4. Comparison of Inflammatory Indices
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Approach
4.2. Participants
4.3. Blood Sampling
4.4. Biochemical Determinations
4.5. Determination of α- and β-Defensins
4.6. Data Analysis and Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- West, N.P.; Pyne, D.B.; Renshaw, G.; Cripps, A.W. Antimicrobial peptides and proteins, exercise and innate mucosal immunity. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 48, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gleeson, M. Immune function in sport and exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, N.P.; Gleeson, M.; Shephard, R.J.; Gleeson, M.; Woods, J.A.; Bishop, N.C.; Fleshner, M.; Green, C.; Pedersen, B.K.; Hoffman-Goetz, L.; et al. Position statement. Part one: Immune func-tion and exercise. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 17, 6–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.; Delgado, L.; Moreira, P.; Haahtela, T. Does exercise increase the risk of upper respiratory tract infections? Br. Med. Bull. 2009, 90, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Usui, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Orita, K.; Ueda, S.Y.; Katsura, Y.; Fujimoto, S.; Yoshimura, M. Changes in salivary antimicrobial peptides, immunoglobulin A and cortisol after prolonged strenuous exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, G.; Allgrove, J.; Gleeson, M. Salivary antimicrobial peptides (LL-37 and alpha-defensins HNP1-3), antimicrobial and IgA responses to prolonged exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Gallo, R.L. AMPed up immunity: How antimicrobial peptides have multiple roles in immune defense. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hazlett, L.; Wu, M. Defensins in innate immunity. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 343, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selsted, M.E.; Ouellette, A.J. Mammalian defensins in the antimicrobial immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T.; Selsted, M.E.; Szklarek, D.; Harwig, S.S.; Daher, K.; Bainton, D.F.; Lehrer, R.I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 1985, 76, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.E.; Bevins, C.L. Paneth cells of the human small intestine express an antimicrobial peptide gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 23216–23225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.E.; Bevins, C.L. Defensin-6 mRNA in human Paneth cells: Implications for antimicrobial peptides in host defense of the human bowel. FEBS Lett. 1993, 315, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G. Human antimicrobial peptides and proteins. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2014, 7, 545–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suarez-Carmona, M.; Hubert, P.; Delvenne, P.; Herfs, M. Defensins: “Simple” antimicrobial peptides or broad-spectrum molecules? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.J.; Anderson, G.M.; Stolzenberg, E.D.; Kari, U.P.; Zasloff, M.; Wilson, J.M. Human beta-defensin-1 Is a Salt-Sensitive Antibiotic in Lung That Is Inactivated in Cystic Fibrosis. Cell 1997, 88, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesse, R.; Cardinale, F.; Santostasi, T.; Polizzi, A.; Manca, A.; Mappa, L.; Iacoviello, G.; De Robertis, F.; Logrillo, V.P.; Armenio, L. Association of β-defensin-1 gene polymorphisms with Pseudomonas aeruginosa airway colonization in cystic fibrosis. Genes Immun. 2008, 9, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schröder, J.M.; Harder, J. Human beta-defensin-2. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 1999, 31, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, J.; Bartels, J.; Christophers, E.; Schroder, J.M. Isolation and characterization of human beta -defensin-3, a novel human inducible peptide antibiotic. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 5707–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trochimiak, T.; Hübner-Woźniak, E. Effect of exercise on the level of immunoglobulin a in saliva. Biol. Sport 2012, 29, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gleeson, M. Mucosal immune responses and risk of respiratory illness in elite athletes. Exerc. Immunol. 2000, 6, 5–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, M.; McDonald, W.A.; Pyne, D.B.; Cripps, A.W.; Francis, J.L.; Fricker, P.A.; Clancy, R.L. Salivary IgA levels and infection risk in elite swimmers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gleeson, M.; Pyne, D.B. Special feature for the Olympics: Effects of exercise on the immune system: Exercise effects on mucosal immunity. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2000, 78, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C. Exercise immunology: Future directions for research related to athletes, nutrition, and the elderly. Int. J. Sports Med. 2000, 1, S61–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.R. Emergence of antibiotic resistance in upper and lower respiratory tract infections. Am. J. Manag. Care 1999, 11, 651–661. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.M.; Qiao, X.L.; Ai, L.; Zhai, J.J.; Wang, X.X. Isolation of antimicrobial resistant bacteria in upper respiratory tract infections of patients. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scudiero, O.; Brancaccio, M.; Mennitti, C.; Laneri, S.; Lombardo, B.; De Biasi, M.G.; De Gregorio, E.; Pagliuca, C.; Colicchio, R.; Salvatore, P.; et al. Human Defensins: A Novel Approach in the Fight against Skin Colonizing Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olvera, D.P.R.; Cabello Gutiérrez, C. Multifunctional Activity of the β-Defensin-2 during Respiratory Infections. Immune Response Act. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supp, D.M.; Gardner, J.; Klingenberg, J.M.; Neely, A.N. Antibiotic resistance in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus does not impact sensitivity to human beta defensin 4. Burns 2009, 35, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, H.; Chapnik, N.; Froy, O. Albumin and amino acids upregulate the expression of human beta-defensin 1. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałązka-Franta, A.; Jura-Szołtys, E.; Smółka, W.; Gawlikcorresponding, R. Upper Respiratory Tract Diseases in Athletes in Different Sports Disciplines. J. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 53, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyne, D.B. Regulation of neutrophil function during exercise. Sports Med. 1994, 17, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, J.; Suzuki, K. Neutrophil activation, antioxidant supplements and exercise-induced oxidative stress. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 10, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khanfer, R.; Phillips, A.C.; Carroll, D.; Lord, J.M. Altered human neutrophil function in response to acute psychological stress. Psychosom. Med. 2010, 72, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zahorec, R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts--rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2001, 102, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Greenham, G.; Buckley, J.D.; Garrett, J.; Eston, R.; Norton, K. Biomarkers of Physiological Responses to Periods of Intensified, Non-Resistance-Based Exercise Training in Well-Trained Male Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2517–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anane, L.H.; Edwards, K.M.; Burns, V.E.; Drayson, M.T.; Riddell, N.E.; van Zanten, J.J.; Wallace, G.R.; Mills, P.J.; Bosch, J.A. Mobilization of gammadelta T lymphocytes in response to psychological stress, exercise, and beta-agonist infusion. Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, M.; Draganidis, D.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Barbero-Álvarez, J.C.; Castagna, C.; Douroudos, I.; Avloniti, A.; Margeli, A.; Papassotiriou, I.; Flouris, A.D.; et al. Muscle damage, inflammatory, immune and performance responses to three football games in 1 week in competitive male players. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kloet, E.R.; Joëls, M.; Holsboer, F. Stress and the brain: From adaptation to disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos, M.; Gouarne, C.; Bonnemaison, D. Acute and chronic effects of exercise on tissue sensitivity to glucocorticoids. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2003, 94, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenkov, I.J.; Chrousos, G.P. Stress Hormones, Th1/Th2 patterns, Pro/Anti-inflammatory Cytokines and Susceptibility to Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 10, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronsen, O.; Haug, E.; Pedersen, B.K.; Bahr, R. Increased neuroendocrine response to a repeated bout of endurance exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T.; Nagase, T.; Ohga, E.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Yoshizumi, M.; Ouchi, Y. Molecular mechanisms underlying human beta-defensin-2 gene expression in a human airway cell line (LC2/ad). Respirology 2002, 7, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, A.M.; Redfern, R.L.; Zhang, B.; Pei, Y.; Huang, L.; Proske, R.J. Defensin expression by the cornea: Multiple signalling pathways mediate IL-1beta stimulation of hBD-2 expression by human corneal epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starner, T.D.; Agerberth, B.; Gudmundsson, G.H.; McCray, P.B., Jr. Expression and activity of beta-defensins and LL-37 in the developing human lung. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuoppasalmi, K.; Adlercreutz, H. Interaction between catabolic and anabolic steroid hormones in muscular exercise. In Exercise Endocrinology; Fotherby, K., Pal, S.B., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1984; pp. 65–98. [Google Scholar]
- Urhausen, A.; Kindermann, W. The endocrine system in overtraining. In Sports Endocrinology; Warren, M.P., Constantini, N.W., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 347–370. [Google Scholar]
- Budgett, R. Fatigue and underperformance in athletes: The overtraining syndrome. Br. J. Sports Med. 1998, 32, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazar, S.; Hazar, M.; Korkmaz, S.; Bayil, S.; Gürkan, A.C. The effect of graded maximal aerobic exercise on some metabolic hormones, muscle damage and some metabolic end products in sportsmen. Sci. Res. Essays 2011, 6, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Karacabey, K.; Peker, I.; Saygın, O.; Cıloglu, F.; Ozmerdivenli, R.; Bulut, V. University Effect of acute aerobic and anaerobic exercise on humoral immune factors in elite athletes. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014, 19, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.E.; Leyshon, A.; Hughes, M.G.; Davies, B.; Graham, M.; Baker, J.S. The effect of anaerobic exercise on salivary cortisol, testosterone and immunoglobulin (A) in boys aged 15–16 years. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.C.; Seco Calvo, J.; Tur Marí, J.A.; Abecia Inchaurregui, L.C.; Orella, E.E.; Biescas, A.P. Testosterone and cortisol changes in professional basketball players through a season competition. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 4, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, B.; Izzo, V.; Terracciano, D.; Ranieri, A.; Mazzaccara, C.; Fimiani, F.; Cesaro, A.; Gentile, L.; Leggiero, E.; Pero, R.; et al. Laboratory medicine: Health evaluation in elite athletes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 1450–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebisch, A.; Schulz, E.; Grosso, M.; Lombardo, B.; Acierno, G.; Sill, H.; Iolascon, A. Identification of a novel variant of epsilon-gamma-delta-beta thalassemia highlights limitations of next generation sequencing. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, E52–E54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pero, R.; Angrisano, T.; Brancaccio, M.; Falanga, A.; Lombardi, L.; Natale, F.; Laneri, S.; Lombardo, B.; Galdiero, S.; Scudiero, O. Beta-defensins and analogs in Helicobacter pylori infections: mRNA expression levels, DNA methylation, and antibacterialactivity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pero, R.; Brancaccio, M.; Laneri, S.; De Biasi, M.G.; Lombardo, B.; Scudiero, O. A Novel View ofHuman Helicobacter pylori Infections: Interplay between Microbiota and Beta-Defensins. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pero, R.; Coretti, L.; Nigro, E.; Lembo, F.; Laneri, S.; Lombardo, B.; Daniele, A.; Scudiero, O. β-Defensins in the Fight against Helicobacter pylori. Molecules 2017, 22, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colavita, I.; Nigro, E.; Sarnataro, D.; Scudiero, O.; Granata, V.; Daniele, A.; Zagari, A.; Pessi, A.; Salvatore, F. Membrane protein 4F2/CD98 is a cell surface receptor involved in the internalization and trafficking of human β-Defensin 3 in epithelial cells. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girolami, F.; Frisso, G.; Benelli, M.; Crotti, L.; Iascone, M.; Mango, R.; Mazzaccara, C.; Pilichou, K.; Arbustini, E.; Tomberli, B.; et al. Contemporary genetic testing in inherited cardiac disease: Tools, ethical issues, and clinical applications. J. Cardiovasc. Med. (Hagerstown) 2018, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Detta, N.; Frisso, G.; Limongelli, G.; Marzullo, M.; Calabrò, R.; Salvatore, F. Genetic analysis in a family affected by sick sinus syndrome may reduce the sudden death risk in a young aspiring competitive athlete. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 170, e63–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Hymer, W.C.; Nindl, B.C.; Fragala, M.S. Growth Hormone(s), Testosterone, Insulin-Like Growth Factors, and Cortisol: Roles and Integration for Cellular Development and Growth with Exercise. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querques, F.; Cantilena, B.; Cozzolino, C.; Esposito, M.T.; Passaro, F.; Parisi, S.; Lombardo, B.; Russo, T.; Pastore, L. Angiotensin receptor I stimulates osteoprogenitor proliferation through TGFβ-mediated signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragozzino, E.; Brancaccio, M.; Di Costanzo, A.; Scalabrì, F.; Andolfi, G.; Wanderlingh, L.G.; Patriarca, E.J.; Minchiotti, G.; Altamura, S.; Varrone, F.; et al. 6-Bromoindirubin-3’-oxime intercepts GSK3 signaling to promote and enhance skeletal muscle differentiation affecting miR-206 expression in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.T.; Erdman, K.A.; Burke, L.M. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschel, A.; Jack, R.W.; Otto, M.; Collins, L.V.; Staubitz, P.; Nicholson, G.; Kalbacher, H.; Nieuwenhuizen, W.F.; Jung, G.; Tarkowski, A.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus resistance to human defensins and evasion of neutrophil killing via the novel virulence factor MprF is based on modification of membrane lipids with L-lysine. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kristian, S.A.; Durr, M.; van Strijp, J.A.; Neumeister, B.; Peschel, A. MprF-mediated lysinylation of phospholipids in Staphylococcus aureus leads to protection against oxygen-independent neutrophil killing. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, L.; Alder, J.D.; Silverman, J.A. Genetic changes that correlate with reduced susceptibility to daptomycin in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, T.; Yeaman, M.R.; Sakoulas, G.; Yang, S.J.; Proctor, R.A.; Sahl, H.G.; Schrenzel, J.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Bayer, A.S. Failures in clinical treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infection with daptomycin are associated with alterations in surface charge, membrane phospholipid asymmetry, and drug binding. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falanga, A.; Nigro, E.; De Biasi, M.G.; Daniele, A.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, S.; Scudiero, O. Cyclic Peptides as Novel Therapeutic Microbicides: Engineering of Human Defensin Mimetics. Molecules 2017, 20, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scudiero, O.; Nigro, E.; Cantisani, M.; Colavita, I.; Leone, M.; Mercurio, F.A.; Galdiero, M.; Pessi, A.; Daniele, A.; Salvatore, F.; et al. Design and activity of a cyclic mini-β-defensin analog: A novel antimicrobial tool. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6523–6539. [Google Scholar]
- Nigro, E.; Colavita, I.; Sarnataro, D.; Scudiero, O.; Zambrano, G.; Granata, V.; Daniele, A.; Carotenuto, A.; Galdiero, S.; Folliero, V.; et al. An ancestral host defence peptide within human β-defensin 3 recapitulates the antibacterial and antiviral activity of the full-length molecule. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falanga, A.; Valiante, S.; Galdiero, E.; Franci, G.; Scudiero, O.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, S. Dimerization in tailoring uptake efficacy of the HSV-1 derived membranotropic peptide gH625. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sommese, L.; Pagliuca, C.; Avallone, B.; Ippolito, R.; Casamassimi, A.; Costa, V.; Colicchio, R.; Cerciello, R.; D’Armiento, M.; Scarpato, M.; et al. Evidence of Bacteroides fragilis protection from Bartonella henselae-induced damage. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Variables | P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Months | 3 Months | 6 Months | 12 Months | |
| N vs. L | −0.53 | 0.08 | −0.08 | −0.21 |
| T vs. C | 0.28 | 0.04 | −0.32 | 0.39 |
| B vs. C | 0.07 | −0.28 | −0.38 | 0.36 |
| A vs. C | −0.001 | −0.32 | −0.57 | −0.44 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pero, R.; Brancaccio, M.; Mennitti, C.; Gentile, L.; Franco, A.; Laneri, S.; De Biasi, M.G.; Pagliuca, C.; Colicchio, R.; Salvatore, P.; et al. HNP-1 and HBD-1 as Biomarkers for the Immune Systems of Elite Basketball Athletes. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060306
Pero R, Brancaccio M, Mennitti C, Gentile L, Franco A, Laneri S, De Biasi MG, Pagliuca C, Colicchio R, Salvatore P, et al. HNP-1 and HBD-1 as Biomarkers for the Immune Systems of Elite Basketball Athletes. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(6):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060306
Chicago/Turabian StylePero, Raffaela, Mariarita Brancaccio, Cristina Mennitti, Luca Gentile, Adelaide Franco, Sonia Laneri, Margherita G. De Biasi, Chiara Pagliuca, Roberta Colicchio, Paola Salvatore, and et al. 2020. "HNP-1 and HBD-1 as Biomarkers for the Immune Systems of Elite Basketball Athletes" Antibiotics 9, no. 6: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060306
APA StylePero, R., Brancaccio, M., Mennitti, C., Gentile, L., Franco, A., Laneri, S., De Biasi, M. G., Pagliuca, C., Colicchio, R., Salvatore, P., D’Alicandro, G., Terracciano, D., Cennamo, M., La Civita, E., Liotti, A., Mazzaccara, C., Frisso, G., Lombardo, B., & Scudiero, O. (2020). HNP-1 and HBD-1 as Biomarkers for the Immune Systems of Elite Basketball Athletes. Antibiotics, 9(6), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060306












