Analysing the Relationship between Nutrition and the Microbial Composition of the Oral Biofilm—Insights from the Analysis of Individual Variability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Materials and Methods
1.1.1. Inter-Individual Variation and Modelling
1.1.2. Guidance to Interpretation
1.1.3. Heterogeneity in Individual Variation
1.1.4. Sample Size
1.1.5. Software
2. Results
2.1. Traditional Analysis
2.2. Illustrative Applications
2.3. Systematic Application
2.4. Heterogeneity
2.4.1. Heterogeneity in the Standard Deviation of the Initial Values
2.4.2. Heterogeneity in the Standard Deviation of The Increments
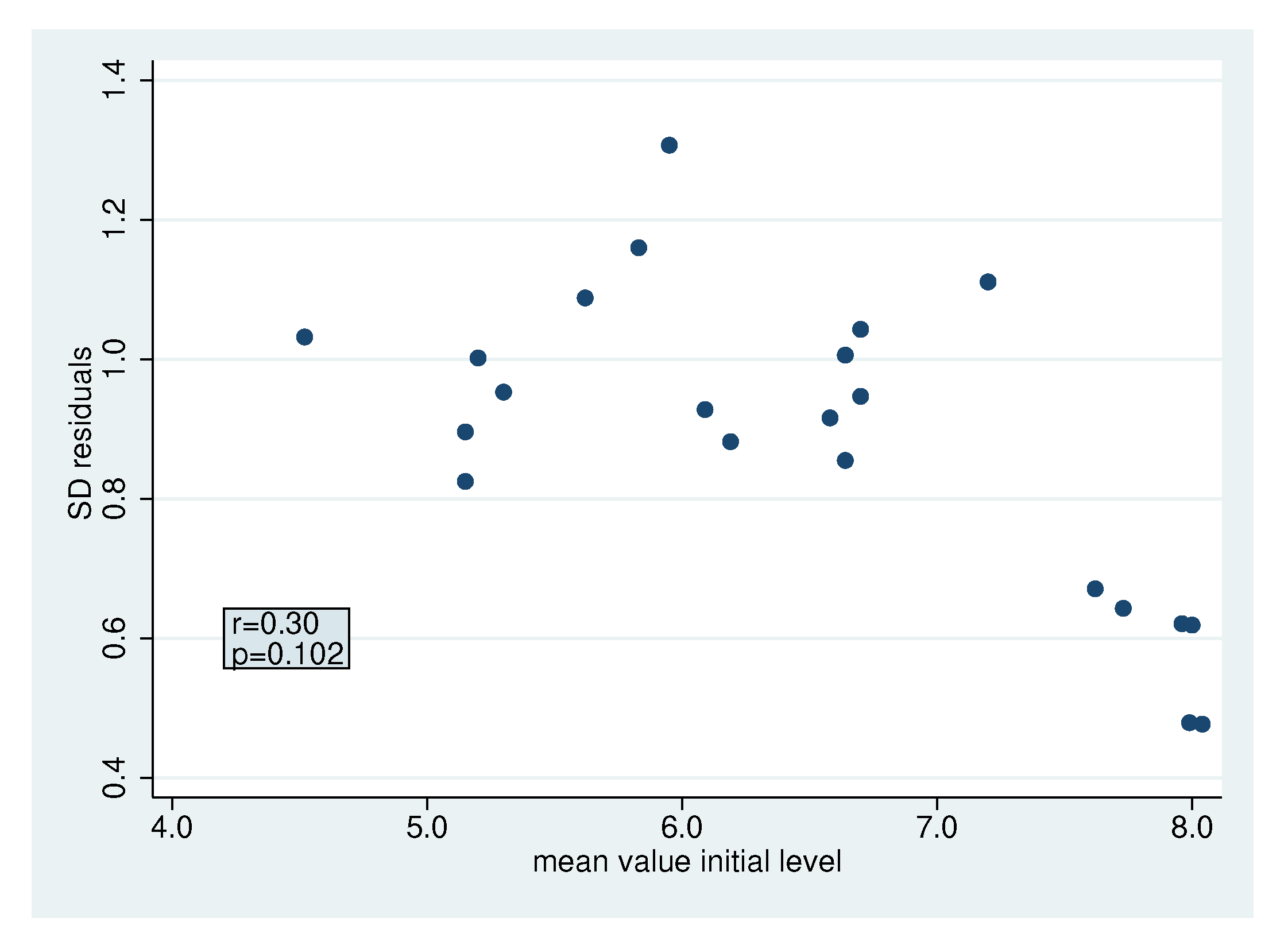
2.4.3. Heterogeneity in the Standard Deviation of The Residuals
2.5. Sample Size Considerations
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Availability of data
Abbreviations
| spp | species pluralis |
| Str | Streptococcus spp. |
| Gem | Gemella spp. |
| Act | Actinomyces spp. |
| Lact vagin | Lactobacillus vaginalis |
| Neiss | Neisseria spp. |
| Capn | Capnocytophaga spp. |
| Haem | Haemophilus spp. |
| Cardiobact | Cardiobacter spp. |
| Citrob | Citrobacter spp. |
| Esch | Escherichia spp. |
| Entero | Enterobacter spp. |
| Kleb | Klebsiella spp. |
| Prev | Prevotella spp. |
| Fuso | Fusobacterium spp. |
| C | Campylobacter spp. |
| Veillo | Veillonella spp. |
| Atop | Atopobium spp. |
| Ols | Olsenella spp. |
| Prop | Propionibacterium spp. |
| Parvi | Parvimonas spp. |
| Bact | Bacteroides spp. |
| Parvi micra | Parvimonas micra |
| aerob fce | aerobic bacteria without faecal contaminants |
| aerob wfc | aerobic bacteria with faecal contaminants |
| all wfc | all bacteria with faecal contaminants |
| all fce | all bacteria without faecal contaminants |
| Gn | Gram-negative |
| Gp | Gram-positive |
Appendix A. Description of the Bacteria Classes
- Aerob fce: Str oralis, Str mitis, Str infantis, Str sanguinis, Str parasanguinis, Str australis, Str peroris, Str gordonii, Str salivarius, Str vestibularis, Str anginosus group, Str mutans, Gem morbillorum, Gem haemolysans, Gem sanguinis, Granulicatella adiacens, Granulicatella elegans, Abiotrophia defectiva, Act oris, Act odontolyticus, Act dentalis, Act georgiae, Act naeslundii, Act spp., Rothia mucilaginosa, Rothia dentocariosa, Rothia aeria, Corynebacterium spp., Lact vagin, Neiss macacae/mucosa, Neiss oralis, Neiss subflava, Neiss bacilliformis, Neiss elongata, Neiss flavescens, Neiss spp., Neiss perflava, Neiss cinerea, Lautrop mirabilis, Capno granulosa, Capno gingivalis, Capno ochracea, Capno sputigena, Capno spp., Haem haemolyticus, Haem parahaemolyticus, Haem parainfluenzae, Haem influenzae, Cardiobact hominis, Eikenella corrodens, Kingella spp., Candida albicans
- Aerob wfc: Str oralis, Str mitis, Str infantis, Str sanguinis, Str parasanguinis, Str australis, Str peroris, Str gordonii, Str salivarius, Str vestibularis, Str anginosus group, Strep mutans, Gem morbillorum, Gem haemolysans, Gem sanguinis, Granulicatella adiacens, Granulicatella elegans, Abiotrophia defectiva, Act oris, Act odontolyticus, Act dentalis, Act georgiae, Act naeslundii, Act sp, Rothia mucilaginosa, Rothia dentocariosa, Rothia aeria, Corynebacterium spp., Lacto vagin, Neiss macacae/mucosa, Neiss oralis, Neiss subflava, Neiss bacilliformis, Neiss elongata, Neiss flavescens, Neiss spp., Neiss perflava, Neiss cinerea, Lautrop mirabilis, Capno granulosa, Capno gingivalis, Capno ochracea, Capno sputigena, Capno spp., HaemHaem haemolyticus, Haem parahaemolyticus, Haem parainfluenzae, Haem influenzae, Cardiobact hominis, Eikenella corrodens, Kingella spp., Candida albicans, Citrob freundii, Citrob koseri, Esch coli, Entero asburiae, Entero cloacae complex, Kleb oxytoca, Kleb variicola, Kleb pneumoniae, Serratia marcescens
- Faecal contaminants: Citrob freundii, Citrob koseri, Esch coli, Entero asburiae, Entero cloacae complex, Kleb oxytoca, Kleb variicola, Kleb pneumoniae, Serratia marcescens
- Anaerobic bacteria: Porphyromonas spp., Prev intermedia, Prev nigrescens, Prev histicola, Prev melaninogenica, Prev loescheii, Prevotella spp., nipig Bact spp., Prev salivae, Fuso nucleatum, Fuso periodontium, C rectus, C concisus, C showae, C spp., Selenomonas spp., Veillo parvula, Veillo dispar, Veillo rogosa, Veillo atypica, Megasphaera micronuciformis, Atop rimae, Atop parvulum, Filifactor alocis, Solobacterium moorei, Lachnoanaerobaculum orale, Lachnoanaerobaculum saburreum, Ols profusa, Catonella morbi clone, Prop acnes, Eubacteium yurii, Parvi micra
- All wfc: aerob wfc + Porphyromonas spp., Prev intermedia, Prev nigrescens, Prev histicola, Prev melaninogenica, Prev loescheii, Prevotella spp., nipig Bact spp., Prev salivae, Fuso nucleatum, Fuso periodontium, C rectus, C concisus, C showae, C spp., Selenomonas spp., Veillo parvula, Veillo dispar, Veillo rogosa, Veillo atypica, Megasphaera micronuciformis, Atop rimae, Atop parvulum, Filifactor alocis, Solobacterium moorei, Lachnoanaerobaculum orale, Lachnoanaerobaculum saburreum, Ols profusa Catonella morbi clone, Prop acnes, Eubacteium yurii, Parvi micra
- All fce: aerob wfc + Porphyromonas spp., Prev intermedia, Prev nigrescens, Prev histicola, Prev melaninogenica, Prev loescheii, Prevotella spp., nipig Bact spp., Prev salivae, Fuso nucleatum, Fuso periodontium, C rectus, C concisus, C showae, C spp., Selenomonas spp., Veillo parvula, Veillo dispar, Veillo rogosa, Veillo atypica, Megasphaera micronuciformis, Atop rimae, Atop parvulum, Filifactor alocis, Solobacterium moorei, Lachnoanaerobaculum orale, Lachnoanaerobaculum saburreum, Ols profusa Catonella morbi clone, Prop acnes, Eubacteium yurii, Parvi micra
- Str oralis 1: Str oralis, Str mitis, Str infantis, Str sanguinis, Str parasanguinis, Str australis, Str peroris, Str gordonii, Str salivarius, Str vestibularis, Str anginosus group
- Str oralis 2: Str oralis, Str mitis, Str infantis, Str australis, Str peroris, Str salivarius, Str vestibularis, Str anginosus group
- Str oralis 3: Str sanguinis, Str parasanguinis, Str gordonii
- Mutans: Str mutans
- Gem Granulicatella Str: Gem morbillorum, Gem haemolysans, Gem sanguinis, Granulicatella adiacens, Granulicatella elegans, Abiotrophia defectiva
- Act spp.: Act oris, Act odontolyticus, Act dentalis, Act georgiae, Act naeslundii, Act spp.
- Rothia spp.: Rothia mucilaginosa, Rothia dentocariosa, Rothia aeria, Corynebacterium spp.
- Lact vagin: Lactobacillus vaginalis
- Neiss spp.: Neiss macacae/mucosa, Neiss oralis, Neiss subflava, Neiss bacilliformis, Neiss elongata, Neiss flavescens, Neiss spp., Neiss perflava, Neiss cinerea, Lautrop mirabilis
- Capn spp.: Capn granulosa, Capn gingivalis, Capn ochracea, Capn sputigena, Capn spp.
- HACEK: Haem haemolyticus, Haem parahaemolyticus, Haem parainfluenzae, Haem influenzae, Cardiobact hominis, Eikenella corrodens, Kingella spp.
- Fungi: Candida albicans
- Faecal contaminants: Citrob freundii, Citrob koseri, Esch coli, Entero asburiae, Entero cloacae complex, Kleb oxytoca, Kleb variicola, Kleb pneumoniae, Serratia marcescens
- Black-pigmented bacteria: Porphyromonas spp., Prev intermedia, Prev nigrescens, Prev histicola, Prev melaninogenica, Prev loescheii, Prevotella spp.
- Not pigmented Bact group: nipig Bact sp, Prev salivae
- Fuso spp.: Fuso nucleatum, Fuso periodontium
- C spp.: C rectus, C concisus, C showae, C spp.
- Selenomonas spp.: Selenomonas spp.
- Gram-positive aerobic cocci: Str oralis, Str mitis, Str infantis, Str sanguinis, Str parasanguinis, Str australis, Str peroris, Str gordonii, Str salivarius, Str vestibularis, Str anginosus group, Strep mutans, Gem morbillorum, Gem haemolysans, Gem sanguinis, Granulicatella adiacens, Granulicatella elegans, Abiotrophia defectiva
- Gram-positive aerobic rods: Act oris, Act odontolyticus, Act dentalis, Act georgiae, Act naeslundii, Act spp., Rothia mucilaginosa, Rothia dentocariosa, Rothia aeria, Corynebacterium spp., Lact vagin
- Gram-negative aerobic cocci: Neiss macacae/mucosa, Neiss oralis, Neiss subflava, Neiss bacilliformis, Neiss elongata, Neiss flavescens, Neiss spp., Neiss perflava, Neiss cinerea, Lautrop mirabilis
- Gram-negative aerobic rods: Capn granulosa, Capn gingivalis, Capn ochracea, Capn sputigena, Capn spp., Haem haemolyticus, Haem parahaemolyticus, Haem parainfluenzae, Haem influenzae, Cardiobact hominis, Eikenella corrodens, Kingella spp.
- Gram-positive anaerobic cocci: Parvi micra
- Gram-positive anaerobic rods: Atop rimae, Atop parvulum, Filifactor alocis, Solobacterium moorei, Lachnoanaerobaculum orale Lachnoanaerobaculum saburreum, Ols profusa, Catonella morbi clone, Prop acnes, Eubacteium yurii
- Gram-negative anaerobe cocci: Veillo parvula, Veillo dispar, Veillo rogosa, Veillo atypica, Megasphaera micronuciformis
- Gram-negative anaerobic rods: Porphyromonas spp., Prev intermedia, Prev nigrescens, Prev histicola, Prev melaninogenica, Prev loescheii, Prev spp., nipig Bact spp., Prev salivae, Fuso nucleatum, Fuso periodontium, C rectus, C concisus, C showae, C spp., Selenomonas spp.
Appendix B. Computation to the Expected Absolute Difference of Two Randomly Chosen Observations
References
- Adler, C.J.; Dobney, K.; Weyrich, L.S.; Kaidonis, J.; Walker, A.W.; Haak, W.; Bradshaw, C.J.; Townsend, G.; Sołtysiak, A.; Alt, K.W.; et al. Sequencing ancient calcified dental plaque shows changes in oral microbiota with dietary shifts of the Neolithic and Industrial revolutions. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumgartner, S.; Imfeld, T.; Schicht, O.; Rath, C.; Persson, R.E.; Persson, G.R. The impact of the stone age diet on gingival conditions in the absence of oral hygiene. J. Periodontol. 2009, 5, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filoche, S.K.; Soma, K.J.; Sissons, C.H. Caries-related plaque microcosm biofilms developed in microplates. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 2, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filoche, S.K.; Soma, D.; Van Bekkum, M.; Sissons, C.H. Plaques from different individuals yield different microbiota responses to oral-antiseptic treatment. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 1, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grenby, T.H.; Andrews, A.T.; Mistry, M.; Williams, R.J. Dental caries-protective agents in milk and milk products: Investigations in vitro. J. Dent. 2001, 2, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woelber, J.P.; Gärtner, M.; Breuninger, L.; Anderson, A.; König, D.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Vach, K.; Dötsch, A.; Ratka-Krüger, P.; et al. The influence of an anti-inflammatory diet on gingivitis. A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 4, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, J.A.; Paster, B.J.; Stokes, L.N.; Olsen, I.; Dewhirst, F.E. Defining the Normal Bacterial Flora of the Oral Cavity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5721–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, M.R.; Paster, B.J.; Leys, E.J.; Moeschberger, M.L.; Kenyon, S.G.; Galvin, J.L.; Boches, S.K.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Griffen, A.L. Molecular Analysis of Bacterial Species Associated with Childhood Caries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.S.; Leys, E.J.; Bryk, J.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Moeschberger, M.L.; Griffen, A.L. Changes in Periodontal Health Status Are Associated with Bacterial Community Shifts as Assessed by Quantitative 16S Cloning and Sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 10, 3665–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledder, R.G.; Gilbert, P.; Huws, S.A.; Aarons, L.; Ashley, M.P.; Hull, P.S.; McBain, A.J. Molecular Analysis of the Subgingival Microbiota in Health and Disease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munson, M.A.; Banerjee, A.; Watson, T.F.; Wade, W.G. Molecular Analysis of the Microflora Associated with Dental Caries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 3023–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wennerholm, K.; Birkhed, D.; Emilson, C.G. Effects of sugar restriction on Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus in saliva and dental plaque. Caries Res. 1995, 1, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.C.; Rothballer, M.; Altenburger, M.J.; Woelber, J.P.; Karygianni, L.; Lagkouvardos, I.; Hellwig, E.; Ahmad, A. In-vivo shift of the microbiota in oral biofilm in response to frequent sucrose consumption. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, S.; Karygianni, L.; Filippi, A.; Anderson, A.C.; Zürcher, A.; Hellwig, E.; Vach, K.; Macchiarelli, G.; Al-Ahmad, A. Combining culture and culture-independent methods reveals new microbial composition of halitosis patients’ tongue biofilm. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirrmeister, J.F.; Liebenow, A.L.; Pelz, K.; Wittmer, A.; Serr, A.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A. New bacterial compositions in root-filled teeth with periradicular lesions. J. Endod. 2009, 3, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C.; Sanunu, M.; Schneider, C.; Clad, A.; Karygianni, L.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A. Rapid species-level identification of vaginal and oral lactobacilli using MALDI-TOF MS analysis and 16S rDNA sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, P.J. Variance Components. In Encyclopedia of Biostatistics, 2nd ed.; Armitage, P., Colton, T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; Volume 8, pp. 5685–5697. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, S.C.; Shao, J.; Wang, H. Sample Size Calculations in Clinical Research, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin. Trials. 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Tenuta, L.M.A.; Filho, A.P.R.; Cury, A.A.D.B.; Cury, J.A. Effect of Sucrose on the Selection of Mutans Streptococci and Lactobacilli in Dental Biofilm Formedin situ. Caries Res. 2006, 6, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyvad, B.; Takahashi, N. Integrated hypothesis of dental caries and periodontal diseases. J. Oral Microbiol. 2020, 12, 1710953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hujoel, P. Dietary carbohydrates and dental-systemic diseases. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woelber, J.P.; Tennert, C. Chapter 13: Diet Periodontal Diseases. Monogr. Oral Sci. 2020, 28, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wittpahl, G.; Kölling-Speer, I.; Basche, S.; Herrmann, E.; Hannig, M.; Speer, K.; Hannig, C. Polyphenolic Compos. Cistus Incanus Herb. Tea Its Antibact. Anti-Adher. Act. Streptococcus Mutans. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jockel-Schneider, Y.; Goßner, S.K.; Petersen, N.; Stölzel, P.; Hägele, F.; Schweiggert, R.M.; Haubitz, I.; Eigenthaler, M.; Carle, R.; Schlagenhauf, U. Stimulation of the nitrate-nitrite-NO-metabolism by repeated lettuce juice consumption decreases gingival inflammation in periodontal recall patients: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoffield, J.; Michalek, S.; Harber, G.; Eipers, P.; Morrow, C.; Wu, H. Dietary Nitrite Drives Disease Outcomes in Oral Polymicrobial Infections. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, K.; Petersen, J.H.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E.; Endahl, L. Interpreting Parameters in the Logistic Regression Model with Random Effects. Biometrics 2000, 3, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

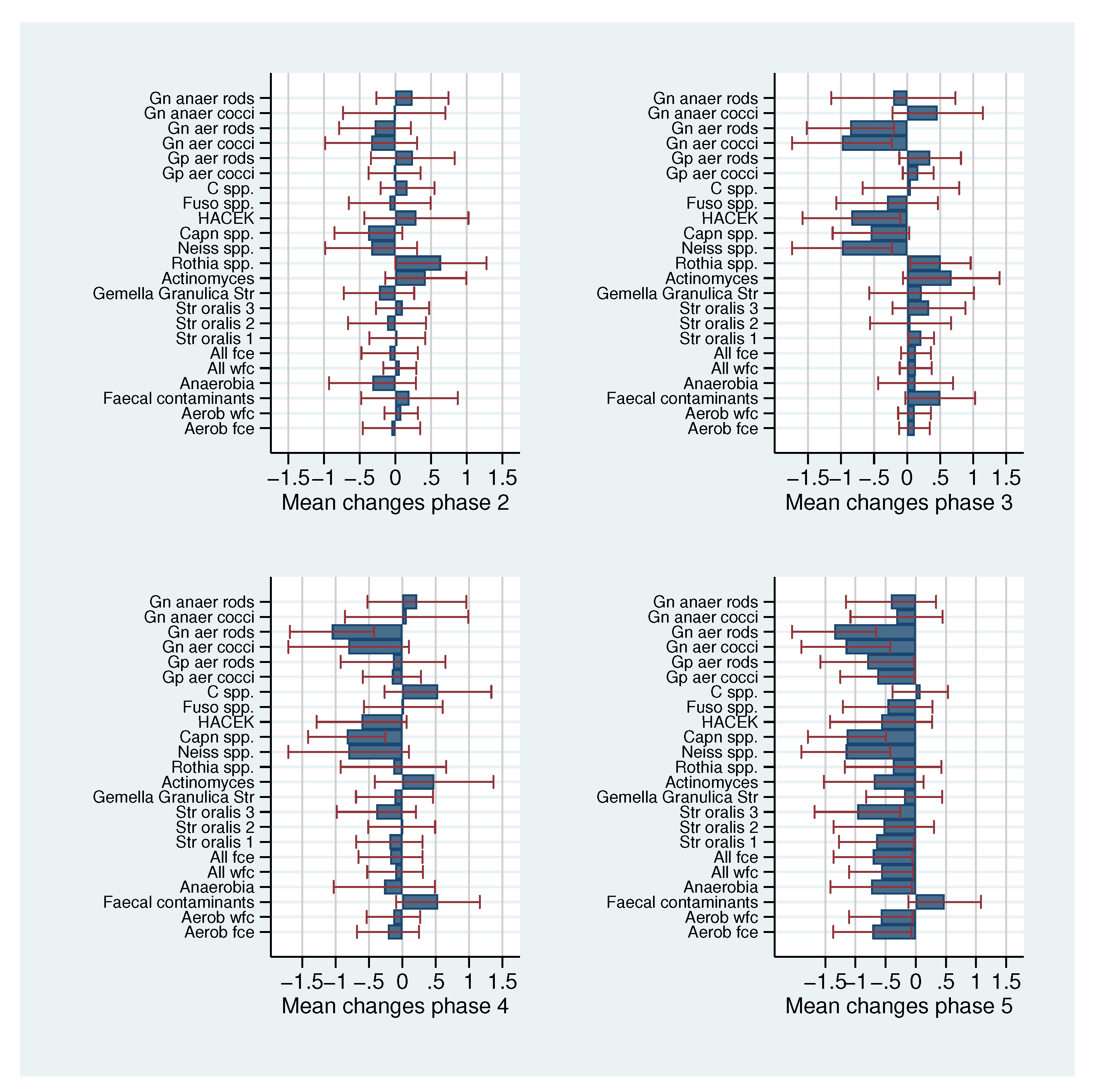





| Estimate | Anaerobic bacteria | Rothia spp. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | 95% CI | Estimate | 95% CI | |
| Initial Values | ||||
| 6.644 | [5.995, 7.294] | 5.833 | [5.355, 6.312] | |
| 1.000 | [ 0.621, 1.611] | 0.435 | [0.212, 0.888] | |
| Increments | ||||
| −0.319 | [−0.840, 0.201] | 0.639 | [0.042, 1.235] | |
| 0.129 | [−0.392, 0.649] | 0.506 | [−0.091, 1.102] | |
| −0.269 | [−0.790, 0.251] | −0.132 | [−0.729, 0.464] | |
| −0.741 | [−1.262, −0.221] | −0.377 | [−0.973, 0.219] | |
| 0.209 | [0.004, 10.142] | 0.000 | [0, ∞ ] | |
| 0.000 | [0.000, 0.404] | 0.000 | [0, ∞ ] | |
| 0.681 | [0.321, 1.448] | 0.605 | [0, ∞ ] | |
| 0.720 | [0.354, 1.463] | 0.556 | [0, ∞ ] | |
| 0.542 | [0.297, 0.990] | 0.290 | [0.041, 2.018] | |
| Coherence | ||||
| 72.3 | 98.6 | |||
| 59.5 | 96.1 | |||
| 69.1 | 67.3 | |||
| 91.5 | 90.5 | |||
| Bacteria | Initial Values | Increments | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nr | Name | |||||||||||
| 1 | Aerob fce | 7.96 | 0.62 | 0.44 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.43 | 0.81 | −0.06 | 0.11 | −0.21 | −0.72 |
| 2 | Aerob wfc | 7.99 | 0.52 | 0.38 | 0 | 0 | 0.38 | 0.68 | 0.08 | 0.11 | −0.13 | −0.58 |
| 3 | Faecal contaminants | 5.15 | 0.45 | 0.25 | 0.58 | 0 | 0.28 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.48 |
| 4 | Anaerobic bacteria | 6.64 | 1.00 | 0.54 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.68 | 0.72 | −0.32 | 0.13 | −0.27 | −0.74 |
| 5 | All wfc | 8.04 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 0 | 0 | 0.41 | 0.70 | 0.06 | 0.13 | −0.11 | −0.57 |
| 6 | All fce | 8.00 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.33 | 0 | 0.45 | 0.82 | −0.08 | 0.13 | −0.18 | −0.71 |
| 7 | Str oralis 1 | 7.62 | 0.59 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 0 | 0.56 | 0.79 | 0.03 | 0.21 | −0.19 | −0.65 |
| 8 | Str oralis 2 | 7.20 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0 | 0.55 | 0.30 | 0.80 | −0.12 | 0.05 | −0.01 | −0.53 |
| 9 | Str oralis 3 | 6.70 | 1.00 | 0.57 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 0.33 | −0.39 | −0.97 |
| 10 | Gem Granulicatella Str | 5.95 | 0.77 | 0.31 | 0 | 0.62 | 0.33 | 0.45 | −0.23 | 0.22 | −0.12 | −0.19 |
| 11 | Act | 5.62 | 1.01 | 0.52 | 0 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.43 | 0.67 | 0.48 | −0.70 |
| 12 | Rothia spp. | 5.83 | 0.44 | 0.29 | 0 | 0 | 0.60 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 0.51 | −0.13 | −0.38 |
| 13 | Neiss spp. | 6.70 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.82 | 0.56 | −0.34 | −0.99 | −0.80 | −1.16 |
| 14 | Capn spp. | 6.19 | 1.12 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.37 | 0.47 | 0.67 | −0.38 | −0.55 | −0.83 | −1.14 |
| 15 | HACEK | 5.20 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.59 | 0 | 0.45 | 0.42 | 0.30 | −0.84 | −0.61 | −0.57 |
| 16 | Fuso spp. | 5.15 | 0.89 | 0.67 | 0 | 0.80 | 0.32 | 0.81 | −0.08 | −0.30 | 0.02 | −0.47 |
| 17 | C spp. | 4.52 | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.54 | 0.08 |
| 18 | Gp aer cocci | 7.73 | 0.61 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0 | 0.40 | 0.77 | −0.01 | 0.17 | −0.15 | −0.64 |
| 19 | Gp aer rods | 6.64 | 0.69 | 0.41 | 0 | 0 | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.24 | 0.35 | −0.14 | −0.81 |
| 20 | Gn aer cocci | 6.70 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.82 | 0.56 | −0.34 | −0.99 | −0.80 | −1.16 |
| 21 | Gn aer rods | 6.58 | 1.04 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.67 | −0.29 | −0.86 | −1.05 | −1.35 |
| 22 | Gn anaer cocci | 6.09 | 0.84 | 0.55 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.81 | 0.55 | −0.02 | 0.46 | 0.06 | −0.32 |
| 23 | Gn anaer rods | 5.30 | 0.94 | 0.81 | 0 | 1.15 | 0.67 | 0.8 0 | 0.24 | −0.21 | 0.22 | −0.41 |
| Bacteria | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerob fce | 55.4 | 59.9 | 68.3 | 94.9 * | 0.62 |
| Aerob wfc | 58.3 | 61.4 | 63.4 | 93.7 * | 0.49 |
| Faecal contaminants | 78.8 | 97.7 * | 98.5 * | 97.3 * | 0.91 |
| Anaerobic bacteria | 72.3 | 59.5 | 69.1 | 91.5 * | 0.85 |
| All wfc | 56.1 | 63.1 | 61.1 | 92.8 * | 0.49 |
| All fce | 57.2 | 61.6 | 65.9 | 94.7 * | 0.64 |
| Str oralis 1 | 52.7 | 68.0 | 66.4 | 92.6 * | 0.69 |
| Str oralis 2 | 59.9 | 54.1 | 50.8 | 86.5 | 1.12 |
| Str oralis 3 | 57.0 | 71.9 | 75.3 | 95.6 * | 0.95 |
| Gem Granulicatella Str | 77.1 | 76.1 | 65.1 | 73.0 | 1.32 |
| Act | 79.6 | 90.1 * | 82.2 | 91.1 * | 1.09 |
| Rothia spp. | 98.6 * | 96.1 | 67.3 | 90.5 | 1.18 |
| Neiss spp. | 71.5 | 95.1 * | 90.9 * | 97.3 * | 1.05 |
| Capn spp. | 76.8 | 85.8 * | 94.5 * | 98.6 * | 0.88 |
| HACEK | 76.8 | 98.0 * | 93.2 * | 91.8 * | 1.00 |
| Fuso spp. | 76.8 | 67.3 | 51.2 | 75.9 | 0.81 |
| C spp. | 61.7 | 54.2 | 82.8 | 55.6 | 1.04 |
| Gp aer cocci | 51.0 | 66.1 | 64.3 | 94.1 * | 0.66 |
| Gp aer rods | 72.1 | 80.3 | 63.4 | 97.6 * | 1.03 |
| Gn aer cocci | 71.5 | 95.1 * | 90.9 * | 97.3 * | 1.05 |
| Gn aer rods | 77.7 | 98.8 * | 99.7 * | 100 * | 0.92 |
| Gn anaer cocci | 51.5 | 79.9 * | 54.3 | 72.0 | 0.93 |
| Gn anaer rods | 61.6 | 60.2 | 60.7 | 69.4 | 0.96 |
| μ | R | Sample Size /Number Observations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9 | 1 | 12/12 | 24/24 |
| 2 | 9/18 | 15/30 | |
| 3 | 7/21 | 11/33 | |
| 4 | 7/28 | 10/40 | |
| 0.7 | 1 | 18/18 | 39/39 |
| 2 | 12/24 | 23/46 | |
| 3 | 10/30 | 17/51 | |
| 4 | 9/36 | 15/60 | |
| 0.5 | 1 | 33/33 | 73/73 |
| 2 | 22/44 | 42/84 | |
| 3 | 18/54 | 31/93 | |
| 4 | 16/64 | 26/104 | |
| 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | |
| 0.3 | 84.1 | 72.6 | 66.6 |
| 0.5 | 95.2 | 84.1 | 76.2 |
| 0.7 | 99.0 | 91.9 | 84.1 |
| 0.9 | 99.9 | 96.4 | 90.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vach, K.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Anderson, A.; Woelber, J.P.; Karygianni, L.; Wittmer, A.; Hellwig, E. Analysing the Relationship between Nutrition and the Microbial Composition of the Oral Biofilm—Insights from the Analysis of Individual Variability. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080479
Vach K, Al-Ahmad A, Anderson A, Woelber JP, Karygianni L, Wittmer A, Hellwig E. Analysing the Relationship between Nutrition and the Microbial Composition of the Oral Biofilm—Insights from the Analysis of Individual Variability. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(8):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080479
Chicago/Turabian StyleVach, Kirstin, Ali Al-Ahmad, Annette Anderson, Johan Peter Woelber, Lamprini Karygianni, Annette Wittmer, and Elmar Hellwig. 2020. "Analysing the Relationship between Nutrition and the Microbial Composition of the Oral Biofilm—Insights from the Analysis of Individual Variability" Antibiotics 9, no. 8: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080479
APA StyleVach, K., Al-Ahmad, A., Anderson, A., Woelber, J. P., Karygianni, L., Wittmer, A., & Hellwig, E. (2020). Analysing the Relationship between Nutrition and the Microbial Composition of the Oral Biofilm—Insights from the Analysis of Individual Variability. Antibiotics, 9(8), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9080479







