Abstract
In this paper, the changes of free chloride ion concentration and bound chloride concentration in cement paste with different total and proportion of mineral admixtures under carbonation were studied. Moreover, the following corrosion resistance of steel bars buried in cement paste under carbonation was researched by testing the electrical resistance and alternating current (AC) impedance spectroscopy of reinforced cement paste. Results indicated that fly ash and granulated blast furnace slag powder with the content less than 20% by mass ratio of total binder hindered the solidification of chloride ions in cement-based materials, and blast furnace slag powder with the content higher than 20% promoted the solidification of chloride ions in cement paste. The carbonation effect was able to decrease the amount of solidified chloride ion and increase the amount of free chloride ions leading to accelerating the corrosion of reinforcement. Meanwhile, the blast furnace slag powder with the content higher than 20% could effectively promote the corrosion resistance of steel bars.
1. Introduction
Reinforced concrete is the main construction building material which has been used for many years due to its economy and practicality [1,2,3]. Nevertheless, reinforced concrete is usually exposed to various environments when in service. Corrosive environments like NaCl freeze-thaw cycles, chloride attacking, carbonation and their coupling effects usually demonstrate corrosive effects on reinforced concrete [4,5,6].
Steel bars in concrete are mainly composed of iron. The electrons were easy to lose when steel bars were exposed to an environment of moist oxygen. The content of free chloride ions in cement-based materials was able to corrode the passivation film and electrical conduction, thus accelerating the corrosion of steel bars. As depicted in Liu’s paper, chloride corrosion is the most serious type of concrete structure deterioration [7]. Some researchers [8,9] reported that the corrosion of chloride salts can reduce the bearing capacity of the building seriously and lead to their destruction.
In recent years, the vigorous development of industrial production leads to large emissions of carbon dioxide in the city. Hence, the concrete constructions were usually exposed to a carbonation environment. In a highly alkaline environment, a dense alkaline passivation film was formed on the surface of steel bars. However, when the concrete is exposed to the environment of carbon dioxide, the calcium hydroxide will react with the carbon dioxide, leading eventually to a reduction of the alkalinity of concrete. Consequently, the alkaline passivation film is corroded. However, little attention was paid to the influence of carbonation effect on the content of free chloride ions in cement-based materials. Ben [10] reported that the effect of carbonation on reinforced concrete could affect porosity of concrete, thus accelerating the corrosion of steel bars.
As described in some journals that alkaline environment is effective to protect the reinforcement in concrete structures against free chloride corrosion, Glass et al. [11] reported that the carbonation effect was able to influence the ingress of chlorides in the concrete. In order to research the corrosion resistance of reinforcement in concrete under a corrosive environment, it is necessary to study the state and distribution of chloride ion of reinforced concrete in the condition of carbonation. It should be noted that electrons of iron element of steel bars in concrete are easy to lose when the concrete is applied in corrosive environments, leading to the corrosion of steel bars and rust [12,13]. Moreover, conductive path of pore solution is blocked by rust and the conductivity is reduced. Therefore, electrical parameters are effective to assess the corrosion resistance of steel bars in cement paste. Nevertheless, few researchers have paid attention to the application of AC electrical resistance and AC impedance spectroscopy in the evaluation of corrosion resistance.
This paper aimed to study the concentrations of free and solidified chloride ions in cement paste with 1% NaCl by mass ratio of binders (cement, fly ash and blast furnace slag) under the condition of carbonation. The additions of 10%–30% fly ash or blast furnace slag and the assembly unit of fly ash (10%–20%) and blast furnace slag (10%–20%) were added to the cement paste. Moreover, the X-ray diffraction was selected to study the crystal structures of cement paste mixed with fly ash and blast furnace slag after carbonation effect. Additionally, the electrical resistance of steel bars reinforced concrete (Plain concrete, specimen with fly ash and specimen with blast furnace slag after) cured in a carbonation environment of different ages, were determined. Furthermore, plain concrete cured in a standard curing environment (with temperature of 20 °C and relative humidity of above 95%) was studied as a reference group.
2. Experimental
2.1. Raw Materials
Ordinary Portland cement (produced by Zhejiang Ningbo conch Co., Ltd.) whose strength grade was 42.5 MPa, was applied in the study. Grade HPB300 plain round steel bars with a diameter of 10 mm were used in experiments. Type I fly ash (FA) was used as a mineral admixture and type S95 fine blast furnace slag (BFS) were used as another mineral admixture. The particle passing percentage and chemical composition of cement are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The water-binder ratio of all groups was 0.4 and the mix proportion of cement paste is shown in Table 3. The specific surface areas of FA, BFS and cement in this study were 387, 421, and 391 m2/kg, respectively.

Table 1.
Particle passing percentage of the cementitious materials.

Table 2.
Chemical composition of the cementitious materials.

Table 3.
Mix proportions of cement paste.
2.2. Samples Preparation and Measurement
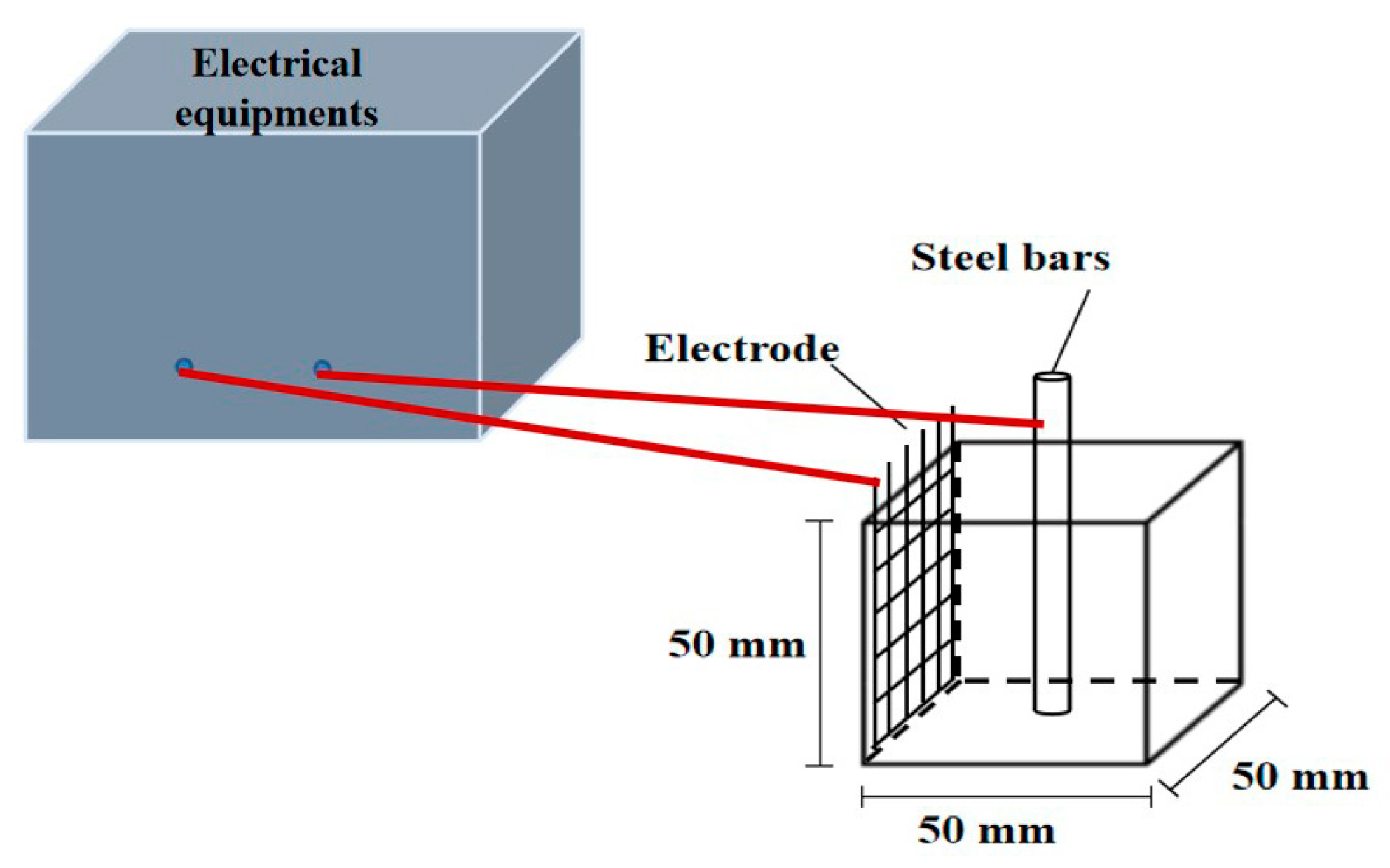
To prepare cement paste samples, the water and binder materials were mixed uniformly in the pot of NJ-160A cement paste mixer (Leiyun Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and agitated at 140 rpm for 2 min. After this mixing, all mixtures were agitated at 285 rpm for another 2 min. When the mixing progress of cement paste was finished, the mixture was poured into the oiled molds to form prism specimens with a size of 40 × 40 × 160 mm3. All specimens were cured in natural curing condition for 1 day, and then the specimens were demolded. After that, the specimens were then cured at a standard fog room (95% RH, 20 ± 2 °C) for another 26 days. After standard curing, some specimens were cured in the carbonation box for 240 days and the remaining specimens were kept in the standard fog room for the same time. After standard curing or carbonation, core samples of the specimens were applied for the measurement of chloride ion concentration and X-ray diffractometer (PANalytical B.V. Co., Ltd., Almelo, The Netherlands). The core samples were crushed and sifted out from square sieve with the diameter of 0.08 mm to form powder. The sieved powder with the particle size less than 0.08 mm was dried in a vacuum drying oven at the temperature of 60 ± 5 °C for 3 days. For the determination of free chloride ions, the experiment process was described as follows: The dried powder was put in the deionized water and stirred uniformity by magnetic mixer in the deionized water for 30 min and then vacuum filtration was provided to test the concentration of free chloride ions by 3000CS chlorine and sulfate analyzer (Thornton Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The solidified chloride ions were calculated by “Concentration of sodium chloride added in cement paste minus the concentration of free chloride”. Moreover, some powder was put into the D8 advance X-ray diffractometer (Thornton Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) produced by Brooke AXS Company to carry out the routine phase analysis and quantitative analysis. Specimens with size of 50 × 50 × 50 mm3 were selected to determine the electrical resistance of steel bar reinforced cement paste. TH2810D LCR digital electric bridge (Changzhou Tonghui Co., Ltd., Changzhou, China) was used to test the electrical resistance with the testing frequency of this electric bridge, ranged from 100 Hz to 10 kHz, and the testing AC voltage varied from 0.1 to 1 V. The schematic diagram of the test device was shown in Figure 1. The measurement of electrical parameters was conducted according to Reference [13]. Each specimen was embedded with a steel bar with length of 6 cm and diameter of 10 mm. A 316L stainless steel mesh and steel bar were served as two electrodes of each specimen, space between steel mesh and axis of steel bar was 2.0 cm. As obtained from prior research [14,15], the signals of AC electrical resistance and AC impedance spectroscopy were relatively stable and accurate, and so therefore they were selected to investigate the corrosion resistance of steel bars in cement paste in this study.
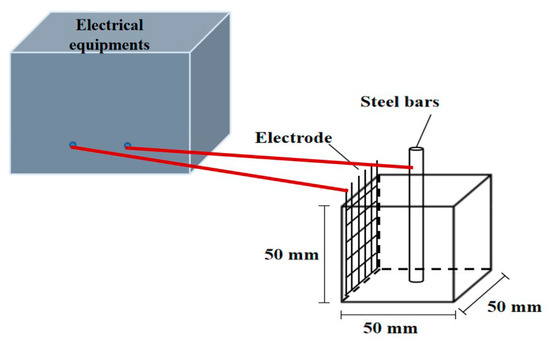
Figure 1.
The measurement of electrical parameters.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The State and Content of Chlorine in Cement Paste
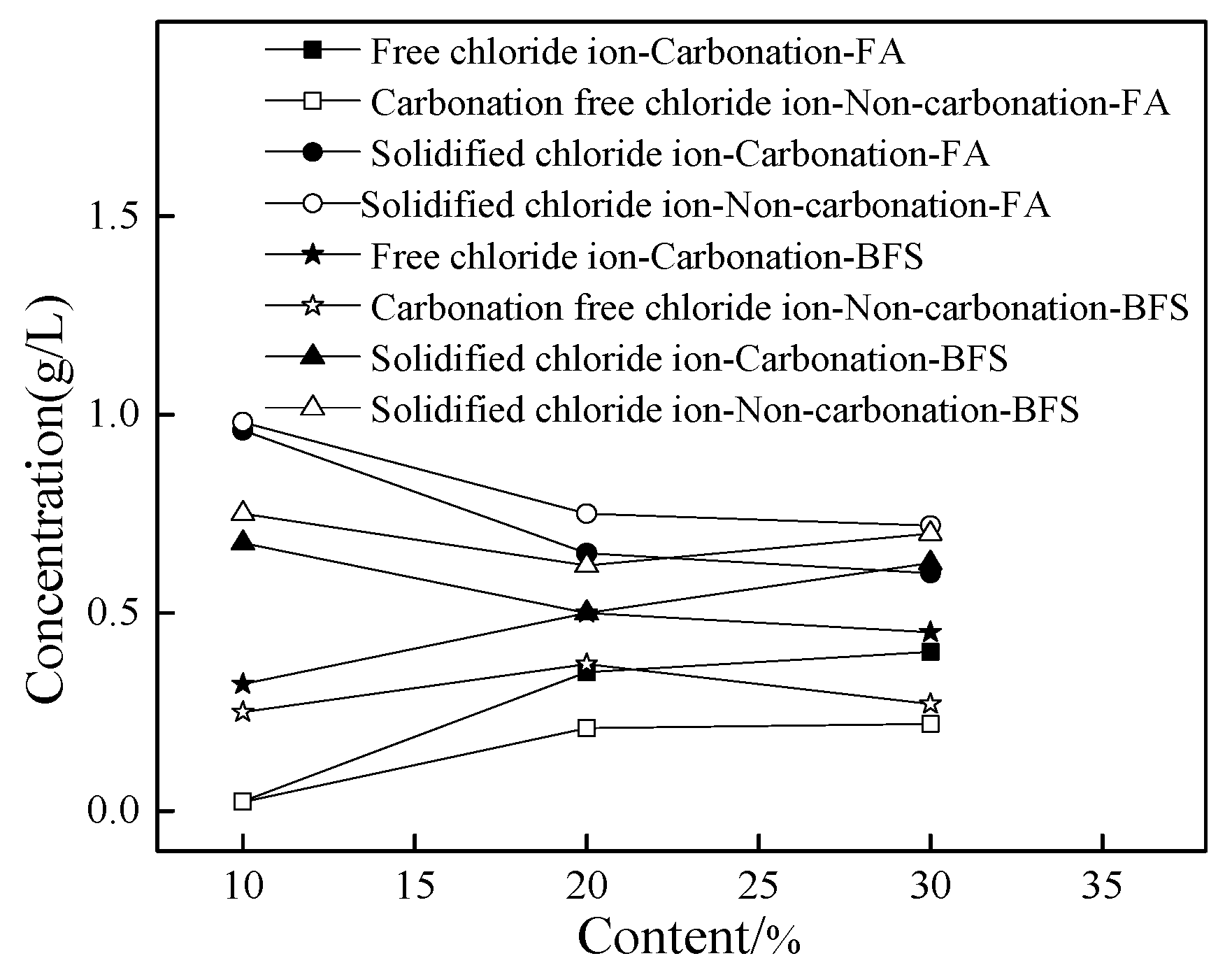
Figure 2 shows the chlorine concentration of cement paste with a different dosage of fly ash and blast furnace slag. As shown in Figure 2, the concentration of free chloride ion increased and the amount of solidified chloride ions decreased with the addition of FA. This might be attributed to the fact that fly ash possessed large specific surface area, thus adsorbing more chloride ions and leading eventually to increasing the amount of free chloride ions and decreasing the amount of solidified chloride ions. However, the content of free chloride ions first increased and then decreased with the increasing dosage of BFS, while the opposite result occurred to the solidified chloride ions. Moreover, it can be observed from Figure 2, the carbonation effect was able to increase the amount of free chlorine content and decrease the concentration of solidified chloride ions. Furthermore, the specimens with FA possessed higher concentration of free chloride ions than that of specimens with BFS. This was attributed to the fact that BFS possessed large specific surface area and could adsorb free chloride ions, leading to decreasing the free chloride ions in cement paste [16,17].
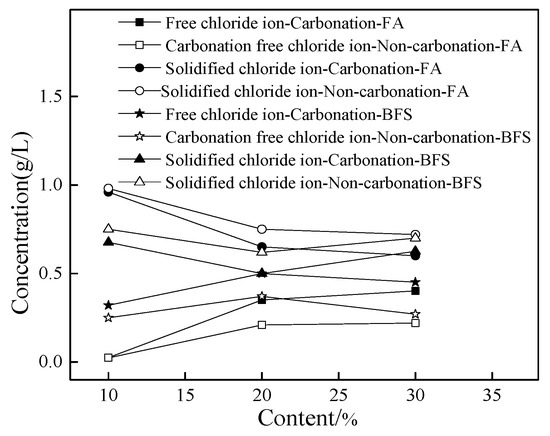
Figure 2.
The chlorine concentration of cement paste.
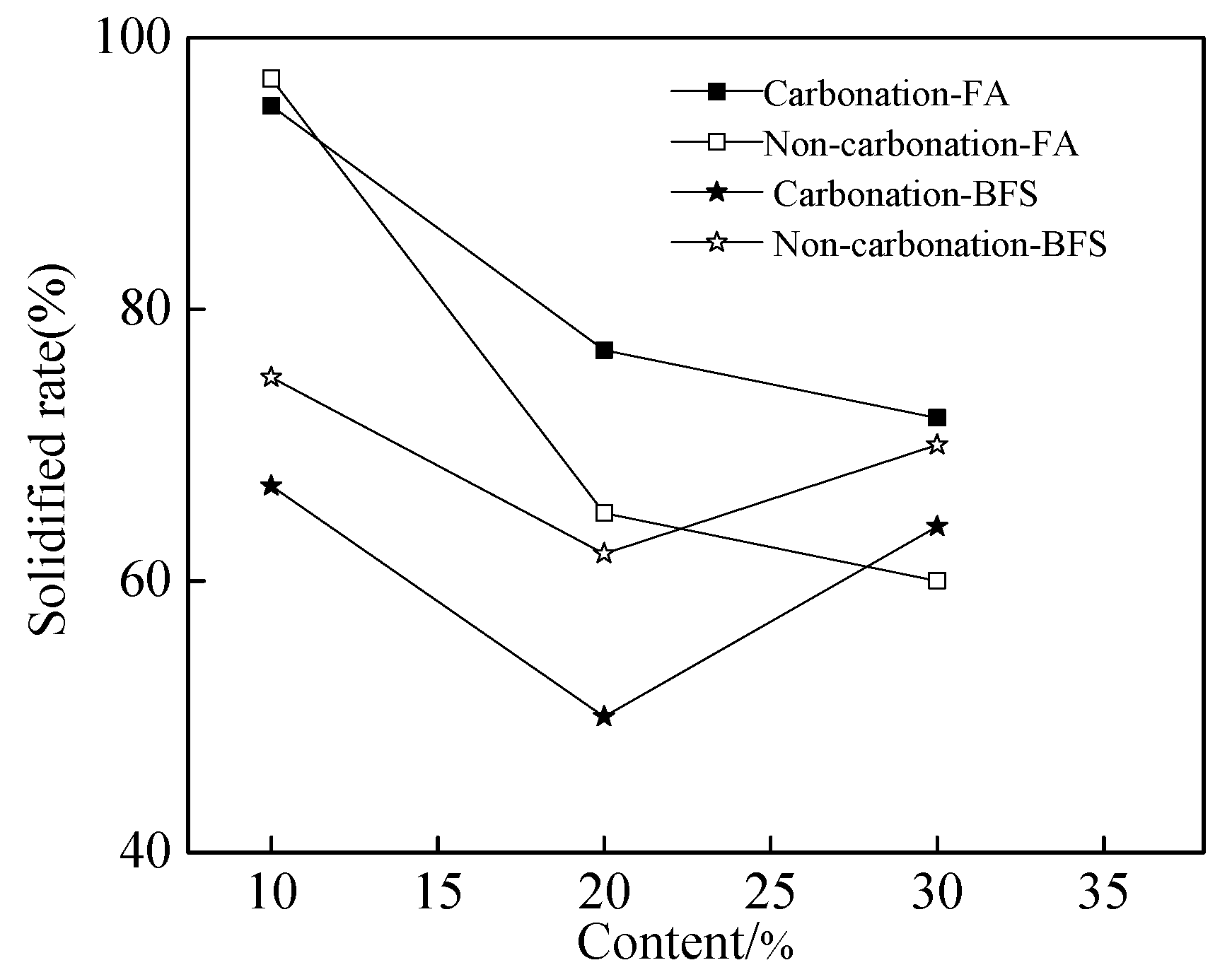
Figure 3 shows the solidified rate of chloride ions of cement paste. As shown in Figure 3, the solidified rate of chloride ions decreased with the increasing dosage of FA. However, the solidified rate first decreased and then increased with the increasing dosage of BFS. It can be observed from Figure 3, when the FA was added into the mixture, the solidified rate was increased by the carbonation effect. However, the solidified rate was decreased by the carbonation effect when the specimens were mixed with BFS. This may be related to some complex reasons which will be studied in the future.
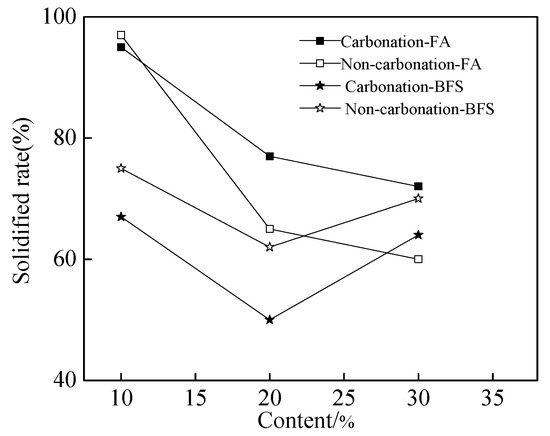
Figure 3.
The solidified rate of chloride ions of cement paste.
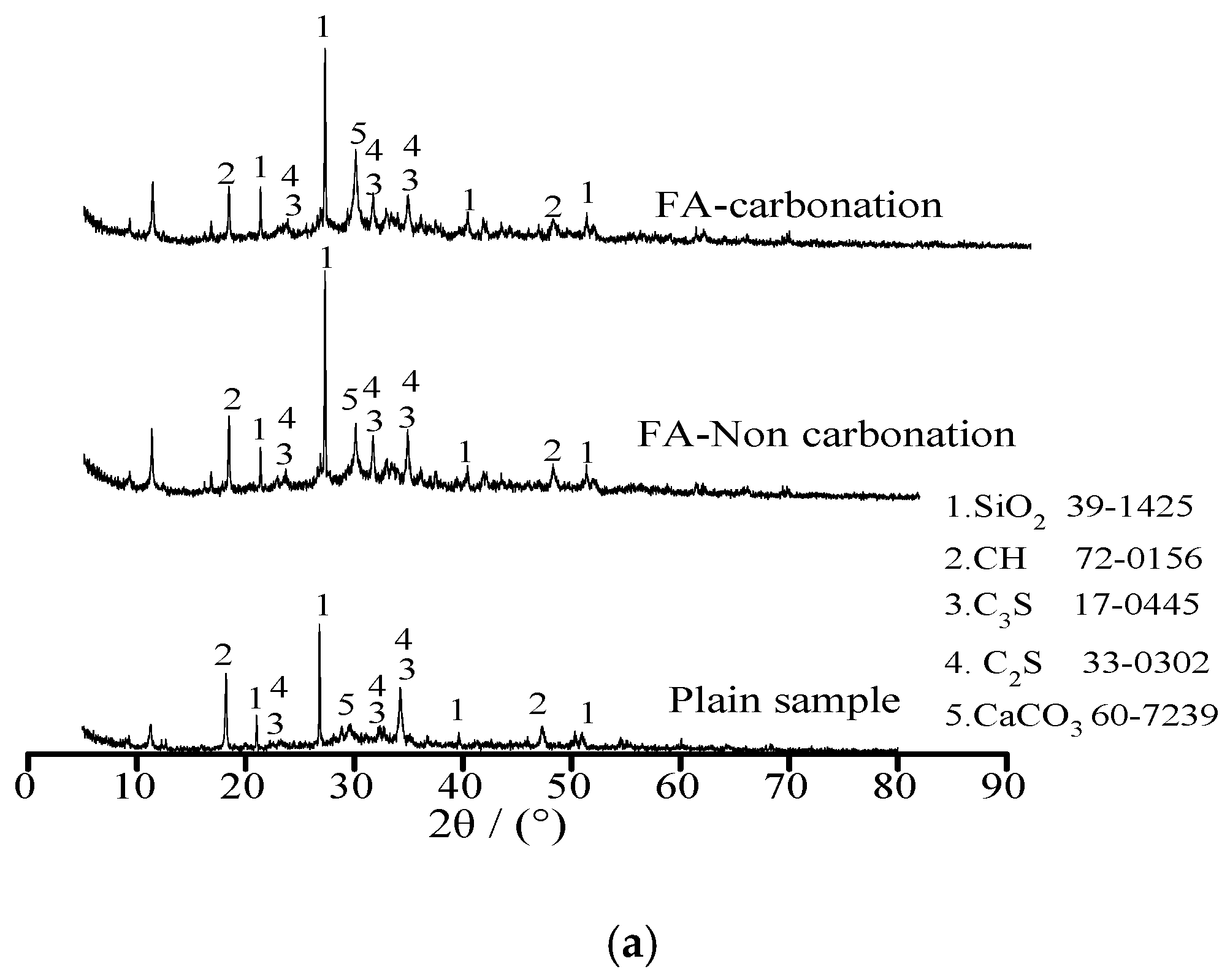
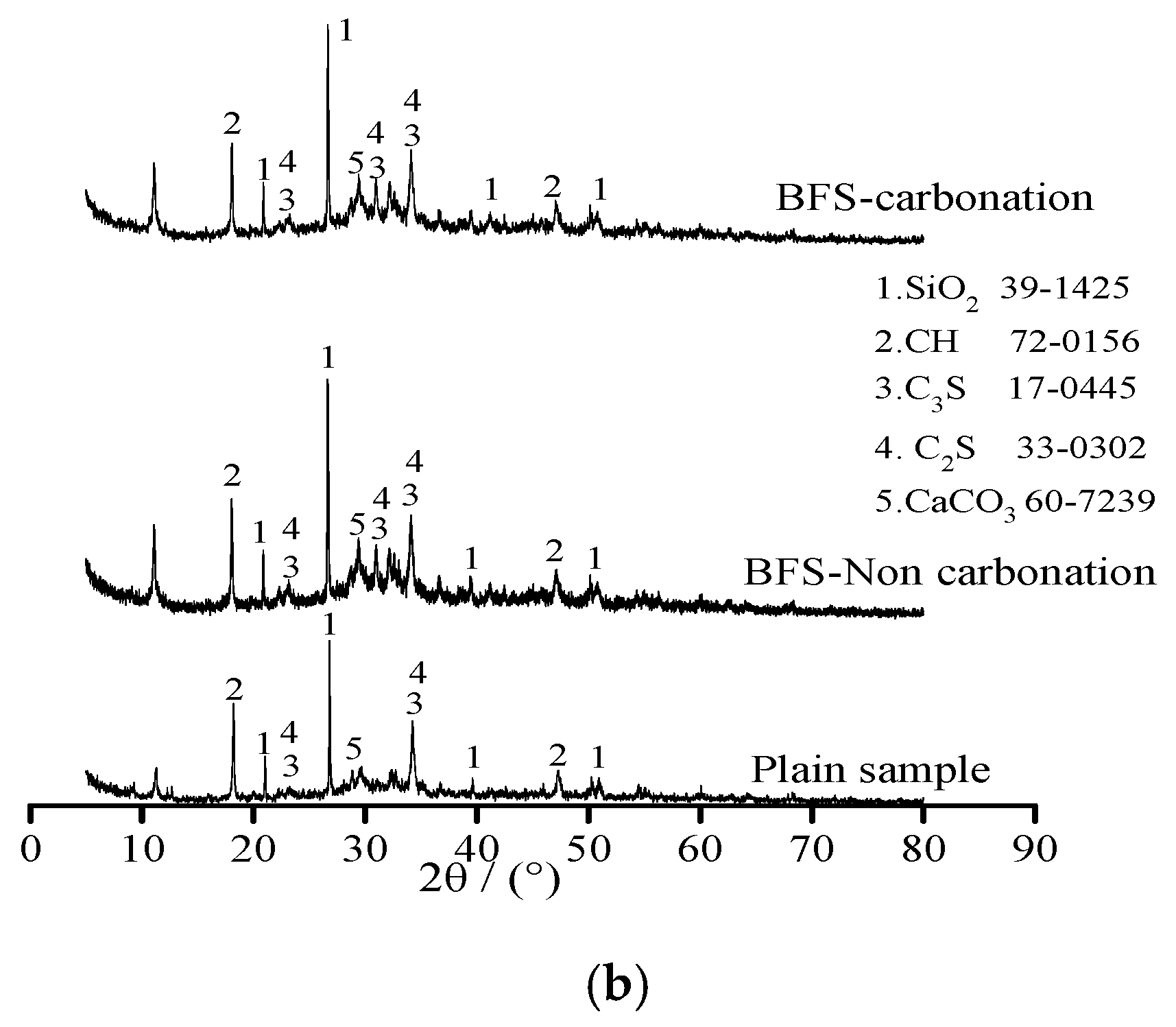
Figure 4 shows the X-ray diffraction of plain sample and specimens with 20% FA and 20% BFS under standard curing environment and carbonation, respectively. As illustrated in Figure 4, the samples were composed by SiO2, Ca(OH)2 (CH), 3CaO·SiO2 (C3S), 2CaO·SiO2 (C2S) and CaCO3. Diffraction peak of calcium hydroxide (CH) decreased with the addition of FA and BFS. This was attributed to the fact that FA and BFS were able to increase the content of SiO2, which was obtained by the diffraction peak of calcium hydroxide SiO2 thus effectively promoting the secondary hydration of cement leading eventually to decreasing the content of CH [18,19]. However, it could be observed from the diffraction peak of CaCO3, the amount of CaCO3 was increased and Ca(OH)2 was decreased by carbonation effect. This was attributed to the fact that Ca(OH)2 reacted with CO2 and CaCO3 was formed after the carbonation effect [20].
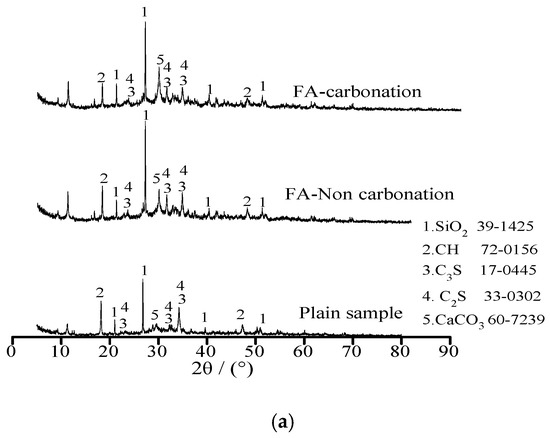
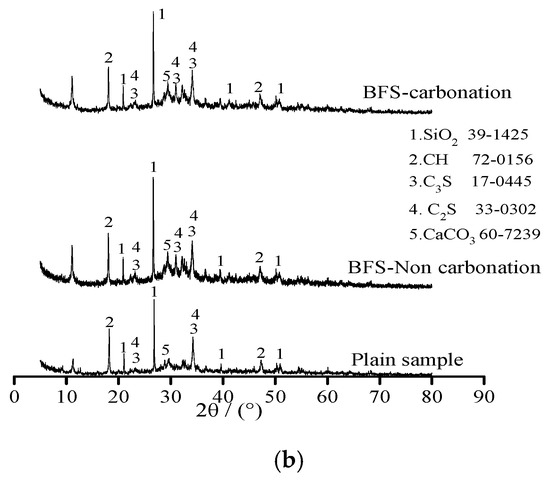
Figure 4.
The X-ray diffraction of specimens. (a) Specimens with FA; (b) Specimens with BFS.
3.2. Corrosion Resistance of Steel Bars
As described in some researches, the electrons loss of iron element on the interface between steel bar and air or water is essential in steel bars’ corrosion. After corrosion, the conductive path of pore solution is blocked by the rust, leading eventually to reducing the conductivity of steel bars reinforced concrete [21,22]. Therefore, specimens with higher electrical resistivity possess better corrosion resistance.
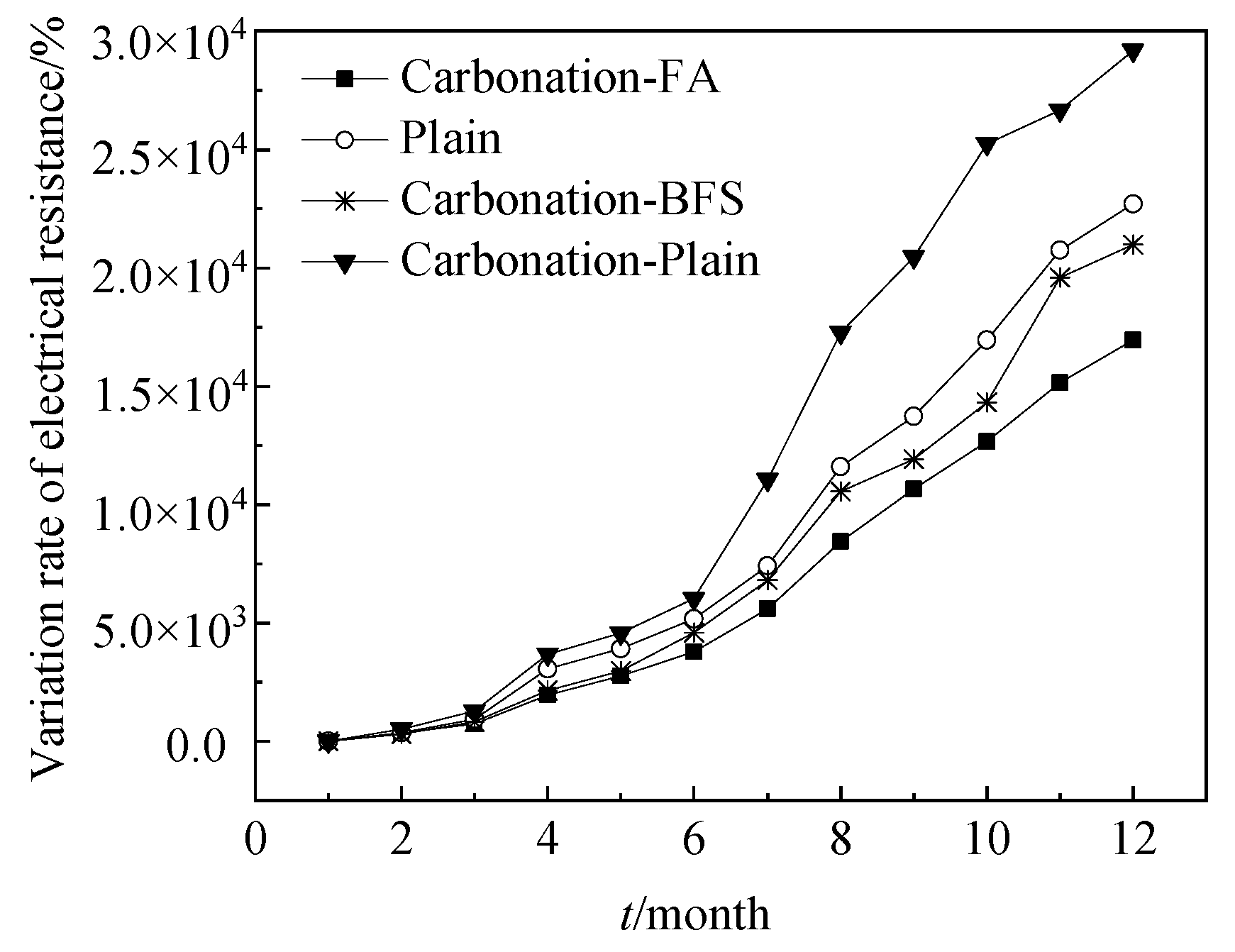
Figure 5 shows the AC electrical resistance-time curves of steel bars reinforced RHA cement paste. The plain samples and specimens with 20% BFS and 20% FA were cured in the environment of carbonation for 12 months. Moreover, the electrical resistance of plain samples cured in standard curing environment (with temperature of 20 °C and relative humidity of above 95%) were studied as a reference group. As shown in Figure 5 that the increasing speed of the variation rate of electrical resistance of specimens decreased in the order of Carbonation-Plain > Plain > Carbonation-BFS > Carbonation-FA confirming the corrosion resistance of specimens decreased in this order of Carbonation-Plain < Plain < Carbonation-BFS < Carbonation-FA. This was attributed to the fact that the free chloride ions increased in the order of Carbonation-Plain < Plain < Carbonation-BFS < Carbonation-FA, which was related with the AC electrical conduction [23,24]
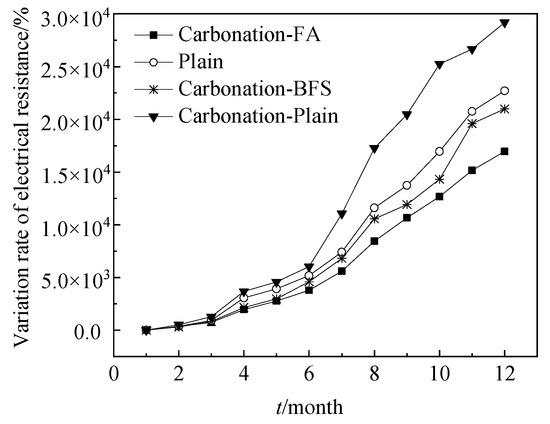
Figure 5.
Electrical resistance-time curves of reinforcement cement paste.
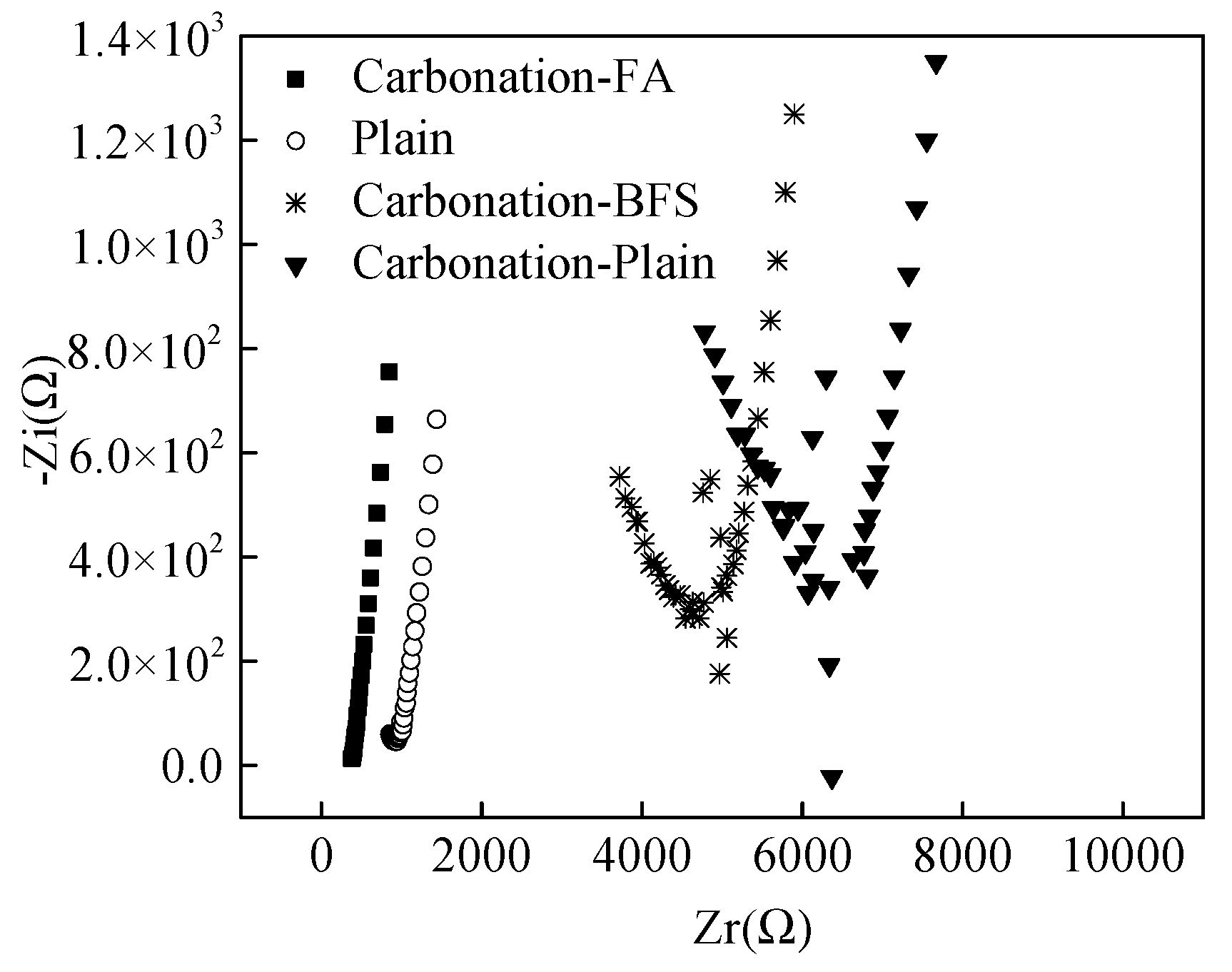
As obtained from some researches [25,26,27], the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) could be determined to reflect the corrosion resistance of steel bars in cement paste. Figure 6 shows the EIS for the specimens after being cured for 12 months. The testing frequency of EIS ranged from 105 to 1 Hz. It was observed from Figure 6, the imaginary part (electrical reactance) of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of specimens with 20% fly ash cured in carbonation and the plain specimens cured in standard curing environment increased linearly with the increasing real part (electrical resistance) as the testing frequency of EIS decreased from 105 to 1 Hz. However, the imaginary part firstly decreased and then increased with the increasing the real part. The minimum value of EIS decreased in this order: Carbonation-Plain > Plain > Carbonation-BFS > Carbonation-FA further confirming corrosion resistance as described in Section 3.2.
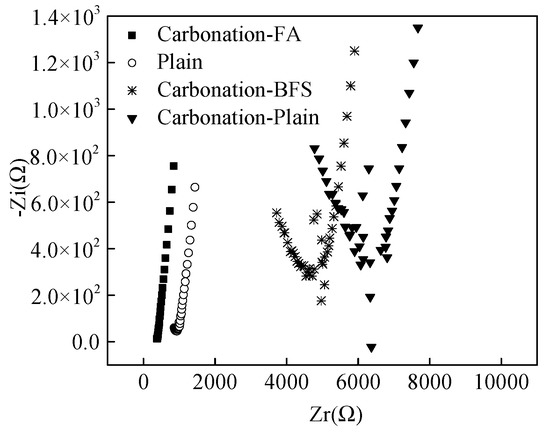
Figure 6.
EIS curves of steel bars reinforce specimens.
4. Conclusions
In this study, influence of carbonation on the content and state of chloride ions and the following corrosion resistance of steel bars in cement paste were investigated. The main findings of this manuscript could be summarized below:
- Compared with the plain cement paste under the carbonation environment, the addition of fly ash and blast furnace slag powder caused larger solidification of chloride ions in cement-based materials due to larger specific surface area and adsorption capacity. Moreover, cement paste with granulated blast furnace slag powder showed the largest solidification capacity of chloride ions.
- The amount of solidified chloride ion was decreased, and the amount of free chloride ions was increased by the carbonation effect leading to accelerating the corrosion of reinforcement.
- According to the results of AC electrical resistance and AC impedance spectroscopy, it can be found that the corrosion resistance of specimens decreased in this order of Carbonation-Plain < Plain < Carbonation-BFS < Carbonation-FA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.W. and J.L.; methodology, A.Z.; software, L.Z. and J.W.; validation, Y.H.; formal analysis, H.W.; investigation, A.Z.; resources, J.L.; data curation, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.W. and J.W.; writing—review & editing, A.Z.; visualization, H.W.; supervision, J.L.; project administration, J.L.; funding acquisition, H.W. and J.L.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China [No. 51808300, No. 51778302, No. 51878360].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- He, B.; Gao, Y.; Qu, L.; Duan, K.; Zhou, W.; Pei, G. Characteristics analysis of self-luminescent cement-based composite materials with self-cleaning effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Lijuan, Z.; Guowen, S.; Caihui, W.; Ying, Z.; Pengshuo, W.; Aoxue, X. Simulation of chloride ion transport in concrete under the coupled effects of a bending load and drying–wetting cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 118045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Li, M.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Preparation for micro-lithium slag via wet grinding and its application as accelerator in portland cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Su, Y.; He, X.; Tan, H.; Yang, W.; Strnadel, B. Eco-friendly treatment of low-calcium coal fly ash for high pozzolanic reactivity: A step towards waste utilization in sustainable building material. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qu, L.; He, B.; Dai, K.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, R. Study on effectiveness of anti-icing and deicing performance of super-hydrophobic asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, T.; Strnadel, B. Feasibility of incorporating autoclaved aerated concrete waste for cement replacement in sustainable building materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, B.; Tan, H.; Gu, B.; Zhang, T.; Chen, P.; Li, H.; Mei, J. Effect of aluminum sulfate on the hydration of Portland cement, tricalcium silicate and tricalcium aluminate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, P.; Palazzo, B.; Mariniello, A. Effects of the axial force eccentricity on the time-variant structural reliability of aging r.c. cross-sections subjected to chloride-induced corrosion. Eng. Struct. 2017, 130, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.M.; Zhao, J.; Chan, B.Y.B. Service life prediction of RC bridge structures exposed to chloride environments. J. Bridg. Eng. 2009, 14, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mansour, H.; Dhouibi, L.; Idrissi, H. Effect of phosphate-based inhibitor on prestressing tendons corrosion in simulated concrete pore solution contaminated by chloride ions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, G.; Buenfeld, N. The influence of chloride binding on the chloride induced corrosion risk in reinforced concrete. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, T.-Z.; Dong, Z.-H.; Guo, X.-P. Application of wire beam electrode technique to investigate the migrating behavior of corrosion inhibitors in mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Shu, H.; Wang, J. Study on the influence of compound rust inhibitor on corrosion of steel bars in chloride concrete by electrical parameters. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.-H.; Gao, X.; Shi, F. Electrical and piezoresistive properties of carbon nanofiber cement mortar under different temperatures and water contents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.; Wang, Z.; Lu, S.; Zhao, D.; Yao, Y. Development of mathematical models for predicting the compressive strength and hydration process using the EIS impedance of cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogirigbo, O.; Ukpata, J. Effect of chlorides and curing duration on the hydration and strength development of plain and slag blended cements. J. Civ. Eng. Res. 2017, 7, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.; Lee, C.-G.; Choi, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-K.; Park, S.-J. Evaluation of the use of sea sand, crushed concrete, and bentonite to stabilize trace metals and to interrupt their release from contaminated marine sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Su, Y.; He, X.; Tan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Strnadel, B. Pore structure evaluation of cementing composites blended with coal by-products: Calcined coal gangue and coal fly ash. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 181, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rêgo, J.; Nepomuceno, A.; Figueiredo, E.; Hasparyk, N. Microstructure of cement pastes with residual rice husk ash of low amorphous silica content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 80, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Gao, X.; Su, A.; Li, Q. Effect of carbonation curing on sulfate resistance of cement-coal gangue paste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 278, 123897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Muhammad, Y.; Su, Z.; Yang, J. Studies on the properties of modified heavy calcium carbonate and SBS composite modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 218, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhozaimy, A.; Hussain, R.R.; Al-Negheimish, A. Electro-chemical investigation for the effect of rebar source and surface condition on the corrosion rate of reinforced concrete structures under varying corrosive environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 244, 118317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.; Bazarchi, E.; Chiniforush, A.; Aghdam, P.P.; Hosseini, M.R.; Akbarnezhad, A.; Martek, I.; Ghodoosi, F. Rebar corrosion detection, protection, and rehabilitation of reinforced concrete structures in coastal environments: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, S.; Wang, N.; Zheng, X. Fabrication of superhydrophobic concrete used in marine environment with anti-corrosion and stable mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Han, X.; Guo, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C. Rebar corrosion investigation in rubber aggregate concrete via the chloride electro-accelerated test. Materials 2019, 12, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehwah, H. Corrosion resistance of self-compacting concrete incorporating quarry dust powder, silica fume and fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Lu, F.; Qiu, P.; Yang, F.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Zhong, H. Formation of a hydrophobic and corrosion resistant coating on manganese surface via stearic acid and oleic acid diethanolamide. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 555, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).