Abstract
A fluoropolyurethane-encapsulated process was designed to rapidly fabricate low-flow resistance surfaces on the zinc substrate. For the further enhancement of the drag-reduction effect, Cu2+-assisted chemical etching was introduced during the fabrication process, and its surface morphology, wettability, and flow-resistance properties in a microchannel were also studied. It is indicated that the zinc substrate with a micro-nanoscale roughness obtained by Cu2+-assisted nitric acid etching was superhydrophilic. However, after the etched zinc substrate is encapsulated with fluoropolyurethane, the superhydrophobic wettability can be obtained with a contact angle of 154.8° ± 2.5° and a rolling angle of less than 10°. As this newly fabricated surface was placed into a non-standard design microchannel, it was found that with the increase of Reynolds number, the drag-reduction rate of the superhydrophobic surface remained basically unchanged at 4.0% compared with the original zinc substrate. Furthermore, the prepared superhydrophobic surfaces exhibited outstanding reliability in most liquids.
1. Introduction
Industrial pipeline drag reduction technology has been in existence for a long time, and the modern superhydrophobic interface undoubtedly provides a new research direction for drag reduction. Therefore, the efficient preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces may generally include (1) constructing suitable micro/nanostructures on low surface energy materials or (2) modifying surfaces with low surface energy materials [1].
Polyurethane has the advantages of wear resistance, tear resistance, flex resistance, etc. over many other coating materials, but it also has disadvantages, because the bubbles are easily trapped in the polyurethane due to its long curing process and high surface energy. The copolymerization of silicone and polyurethane can address these defects; e.g., using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) reacted with isocyanates or prepolymer formed a silicone–polyurethane copolymer through addition polymerization and a chain-extension reaction [2]. Besides, the advanced siloxane-modified polyurethane with polyamino functional groups in the side chain was also used to further enhance its original performance [3,4,5]. The amino siloxane attached as the side chain of the polyurethane could be conducive to the migration of silicon atoms to the surface and effectively improve the surface and mechanical properties of the polyurethane [5,6]. Although the surface energy of polysiloxane is already very small, perfluoroalkane could be even half of the polysiloxane. Therefore, the introduction of perfluoroalkyl groups into the chain of polysiloxane could not only make the surface energy as low as fluorine, but the flexibility and softness could also become similar to that of silicone [7,8,9].
Except for the modification of surface materials, the surface microstructure could also provide an important methodology for the surface modification. The microstructure of lotus leaves and shark-skin surfaces have been analyzed in recent years. Studies also have shown that these microstructure surfaces indicate good superhydrophobic and self-cleaning effects [10]. In 1997, German botanists Barthlott and Neinhuis [11] referred to this characteristic of the lotus leaf as the Lotus Effect. Cottin et al. [12] found that the superhydrophobic surface of this micro/nanostructure can significantly reduce the flow resistance as well. Many researchers have developed superhydrophobic surfaces by analyzing the surfaces of plant leaves, whose slipping phenomenon could significantly reduce the flow resistance. What is more, various experimental approaches are capable of creating such a microstructure interface, which include template methods, plasma texturing, lithography [13,14], and chemical deposition at present. However, the preparation process of the template method, which requires pre-preparation of the template, is so complicated that has not been widely used yet [15,16]. The processing of plasma texturing with thermal oxidation method takes so much time, and it is applicable for limited substrate materials. Although the plasma-induced nanotexture is uniform and indicates outstanding superhydrophobic wettability in the recent work of K. Ellinas et al., the good attachment of plasma fluorocarbon deposition could be obtained in polymer substrate only [17]. It is still easy to be scratched, which needed to be further enhanced with more than one polymeric layer on the commonly used metal substrates. As for the chemical deposition method, which has advantages such as its simple process and equipment, it is merely able to be applied on those metals that are less active than others [18,19,20]. The strong acid and alkali solution are mainly used for the chemical etching for some commercial formations of surface textures. However, the etching stability of the reaction process is poor because of the variation of the concentration, the surface microscopic size, and morphology are difficult to control [21,22].
In previous attempts of fabricating piping materials and preparing marine coatings, it is found that the modification of the surface material and deposition of a coating with a low surface energy at the original surface material can also significantly reduce the flow resistance. The lateral adhesion force between a liquid drop and a solid can also be divided into static and kinetic regimes. With the decrement of the surface energy and increment of the superhydrophobicity, the lateral adhesion force between the liquid and the surface would be reduced, and the drops would start sliding over solid surface easily [23]. Besides, the spatial surface structures formed by chemical etching and the substitution reaction would also enhance the drag-reduction effect. As the roughness increased, the threshold force to initiate the drop motion would decrease [24]. Hence, the combination of a chemical etching method and a proper coating material could not only extend the original mechanical and chemical durability by the protective coating, but its surface structure advantages could also be reserved [25]. Moreover, the drag-reduction performance of the substrate could be further enhanced. The durability of the surface, especially the chemical durability probed by immersion in liquids, is also another factor to consider regarding the fabrication. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) are the typical materials that are being used in the fabrication of low surface energy coating, while the superhydrophobic fluoropolyurethane surface and its drag-reduction behavior have been seldom documented [26,27,28,29].
This paper proposed a fast method to fabricate a drag-reduction fluoropolyurethane surface. The nanostructure of this drag-reduction surface could be further enhanced by a chemical etching process [27]. Through the flow-resistance test in the microchannel, such surface exhibited a drag-reduction rate of 4.0% and an outstanding reliability of surface wettability. The effects of how the surface characteristics have influenced the microchannel flow resistance are also discussed in this paper.
2. Experiment and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
Methyl perfluorooctadecanoate (PC5139M, CF3·(CF2)16·COOCH3) (3B Scientific Corporation, Wuhan, China), aminopropyl polydimethyl siloxane (APS, H2N(CH2)3 (Me2SiO)8·Me2Si(CH2)3NH2) (GE, Tokyo, Japan), polypropylene glycol (PPG, Mn = 2000 ± 100, China National Pharmaceutical Group Chemicals Co., Chengdu, China), 2,4-toluene diisocyanate (TDI) (Shanghai Chemicals Co., Shanghai, China), xylene (Tianjin Chemicals Co., Tianjin, China), 3,3’-dichloro-4, 4’-Diamino-diphenylmethane (MOCA) (Japan Mitsui Chemicals Co., Tokyo, Japan), copper nitrate, anhydrous ethanol, nitric acid (Kelong Chemicals Co., Chengdu, China), and zinc substrate (1.8 mm thickness, purity ≥ 94%) (Guangzhou Yudi Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China).
2.2. Fabrication of Drag-Reduction Substrate
2.2.1. Etching Treatment of Zinc Substrate
Firstly, the 30 mm × 30 mm zinc substrate was rinsed with acetone 5 times and ultrasonically cleaned in deionized water for 15 min. After being dried in the oven at 100 °C for 30 min, the samples were etched by a mixing solution with 5.0 mL of nitric acid, 30.0 mL of distilled water, and 1.0 g of copper nitrate for 60 s at 60.0 °C. Finally, these samples were rinsed thoroughly with deionized water and dried at 100 °C for another 30 min.
2.2.2. Fluoro-Modified Polyurethane Encapsulated Treatment
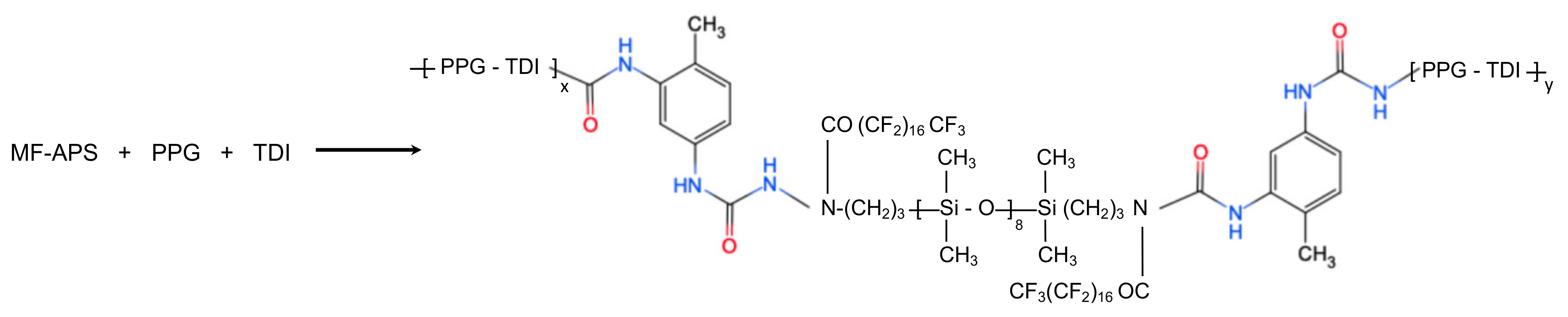
Firstly, Methyl Fluoro-Aminopropyl Polydimethyl Siloxane (MF-APS) was synthesized by Methyl perfluorooctadecanoate (PC5139M) and aminopropyl polydimethyl siloxane (APS) droplets under 50 °C and stirred at 6.7 s−1 for 2.5 h. After the vacuum distillation of the previous substituted process, the PPG were treated together with MF-APS by vacuum dehydration at 25 °C for another 10 min (Figure S1). Then, a proper amount of xylene and excess 2,4-toluene diisocyanate (TDI) were added into the dehydrated mixture, preheated, and reacted for another 2.5 h at 90 °C to synthesize the isocyanate-terminated polyurethane prepolymer (Figure 1) [28]. After the synthesis of polyurethane prepolymer, the melted 3,3’-dichloro-4,4’-Diamino-diphenylmethane (MOCA) was added in and stirred at 13.3 s−1 for 60 s. Finally, the reacted fluropolyurethane was sprayed on the etched/unetched zinc substrate, cured at 60 °C for 7 days, and then dried at room temperature for another day to prepare fluoropolyurethane treated drag-reduction surface material. Furthermore, the etched zinc substrate capped with fluoropolyurethane and unetched zinc substrate capped with and w/o fluoropolyurethane were the test surfaces, while the unetched zinc substrate served as the control group in this experiment.
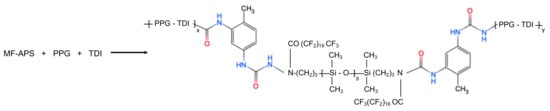
Figure 1.
Synthesis of prepolymer end capped by isocyanate (–NCO) groups.
2.3. Surface Characterization
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR spectra) was obtained at room temperature on a Nicolet-6700 spectrophotometer (Thermo Electron Corporation, Waltham, MA, USA) between 4000 and 600 cm−1 with the resolution of 4 cm−1. The surface morphology of the samples was characterized by S-4700 SEM (Hitachi, CA, USA) and surface roughness data were obtained by an Alpha-Step D-500 stylus profiler (KLA-Tencor Corporation, Milpitas, CA, USA) with a force of 10.0 mg, speed at 0.10 mm/sec, and data points filter at 8 points. The contact angles (CAs) and surface energy (SE) were measured and analyzed by OCA15 plus and attached SCA 20 software (Data physics, Filderstadt, Germany). At the same time, continuous shooting was used to observe the spreading and rolling of water droplets on the sample surface. For the testing of wettability stability, all samples were immersed in deionized water; 8.0 wt % hydrochloric acid (acid), 8.0 wt % sodium hydroxide (alkaline), and 40.0 wt % sodium chloride (saline) solution respectively were measured for continuous 10 days [26,29,30,31,32,33,34].
2.4. Microchannel Drag Reduction Test
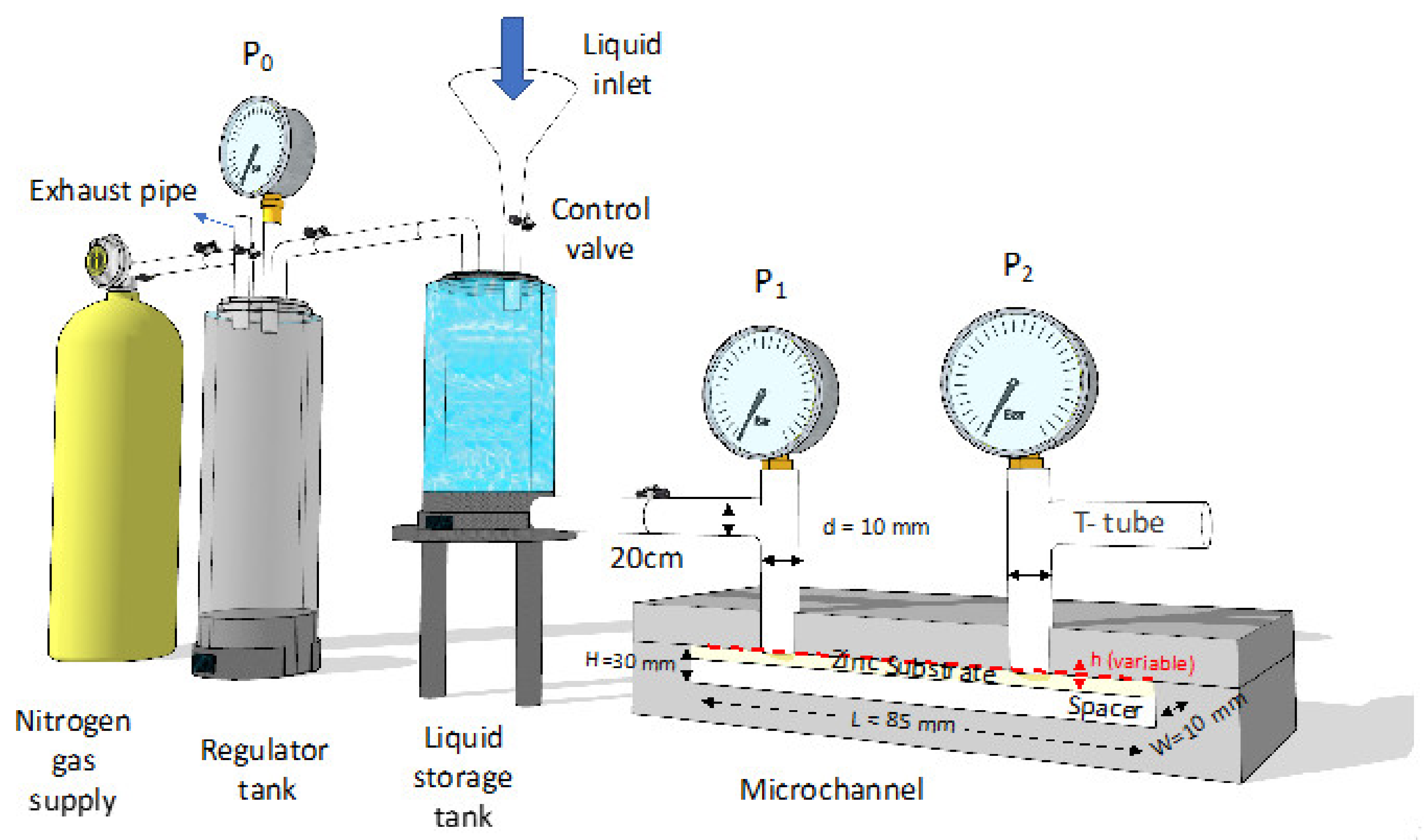
As the reference and unified standard for the microchannel drag reduction test was seldom documented, the microchannel test of superhydrophilic/hydrophobic surfaces was finally carried out using a non-standard design microchannel flow resistance test device. The parameters of its microchannel are shown in Figure 2. After stabilization by a regulator tank, the deionized water was pressurized with nitrogen gas and driven into the microchannel. The height of the microchannel was adjusted by tightening the screw. At each height of the microchannel, the pressure difference (ΔP) over the increment of the Reynold number was obtained. Besides, the flow resistance and drag reduction effect of the superhydrophilic/hydrophobic surface was evaluated by the pressure drop ΔP at the same Reynolds number in comparison with the unetched zinc substrate [35,36,37,38]. As the length (L) of the microchannel was a thousand times its height (h) and the Reynold number regions inside the microchannel could be varied from 50 to 1200 in this experiment, the experimental parameters for the flow-resistance test could still cross the laminar (less than 600) and turbulent phases (above 800) [39,40,41,42,43], and the drag reduction effect inside the microchannel could be well reflected. The uncertainty/error and parameters of the non-standard design microchannel are indicated in Table S1. Only the stable and unchanged reading would be recorded for each variation of microchannel height as well as Reynolds number.
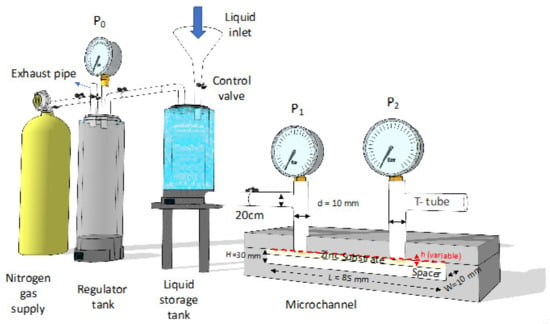
Figure 2.
Non-standard design microchannel flow resistance test device.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Characterization of Fluoropolyurethane Prepolymer
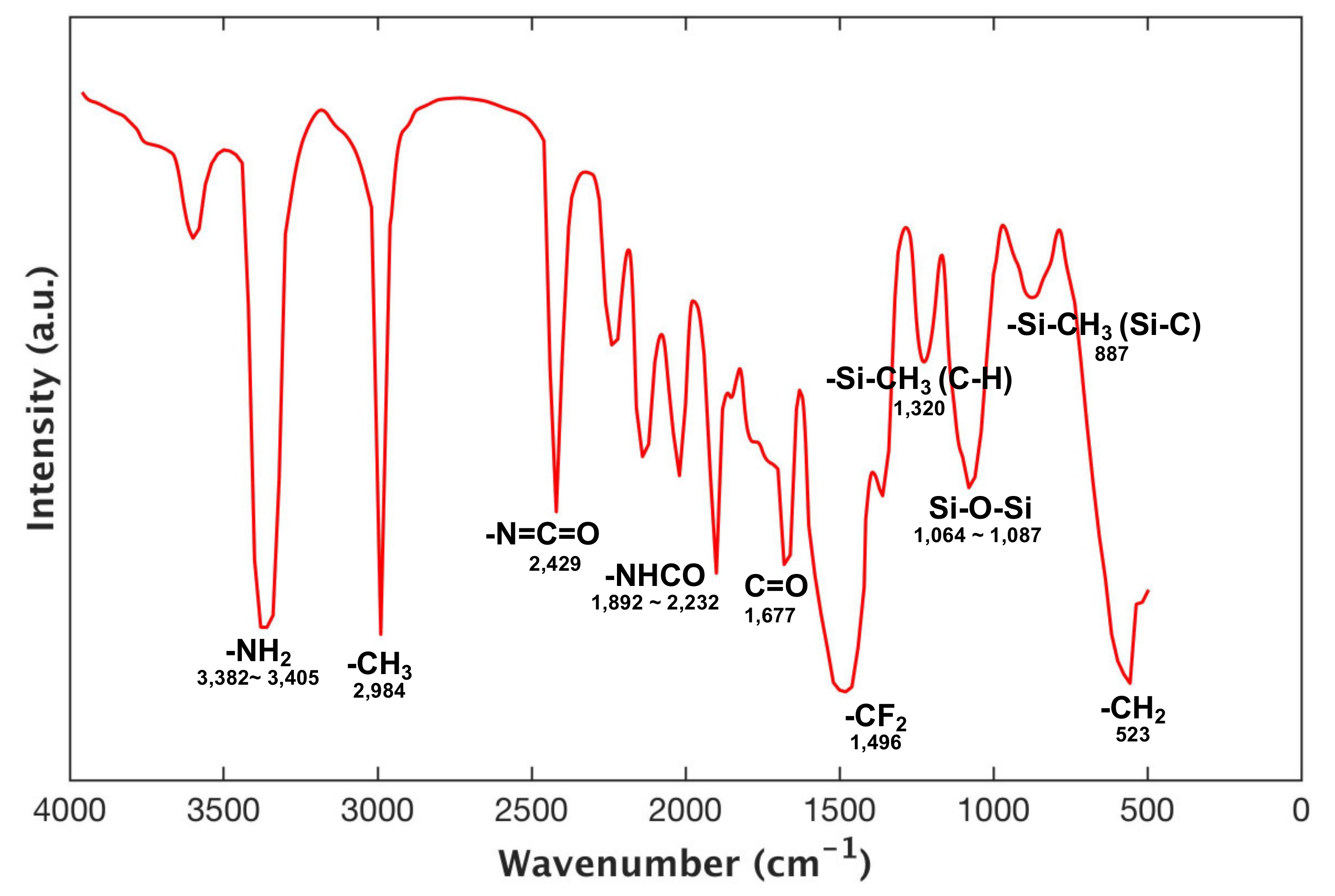
To confirm that the fluoropolyurethane has been successfully fabricated, the FTIR spectra of the polyurethane sprayed on the etched zinc substrate was obtained (Figure 3). The MF-APS and PPG treated with TDI exhibited the absorption peaks of –NHCO between 1892 and 2232 cm−1, indicating the immobilization of PPG and MF-APS in the polyurethane. The FTIR spectra of the fluoropolyurethane displayed that the typical characteristic peaks of –N=C=O, –CF2 (C–F) and Si–O–Si function groups from the original compound appeared at 2429 cm−1, 1496 cm−1 and 1064–1087 cm−1 respectively.
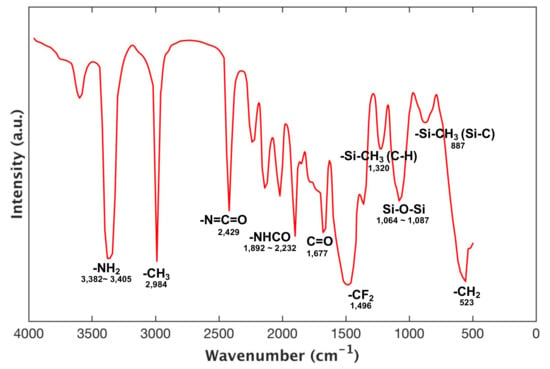
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of fluoropolyurethane.
3.2. Surface Morphology
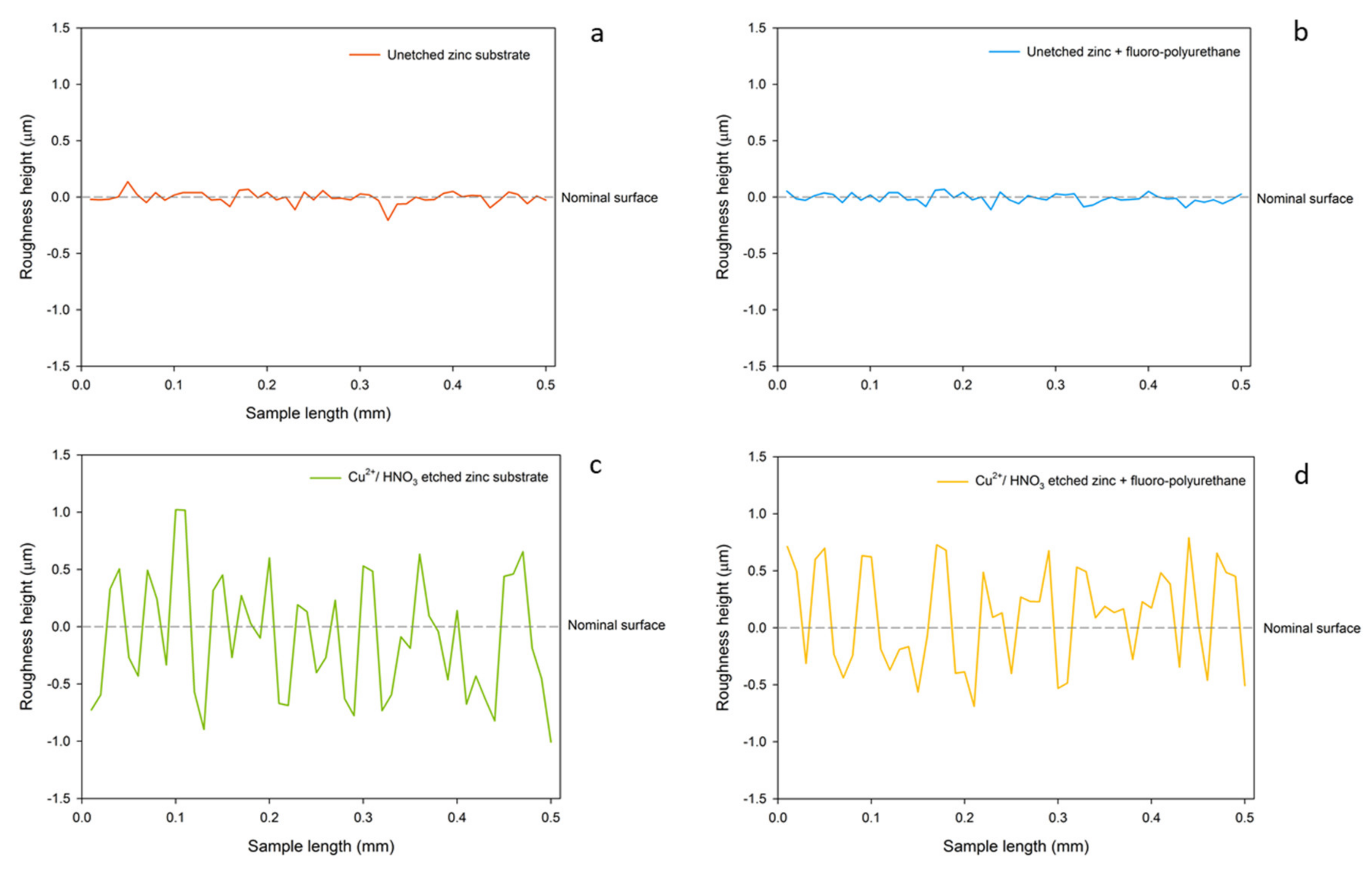
In the case of amplifying 1000 and 50,000 times, the surface profiling of all four groups were indicated in Figure 4, the surface of the zinc substrate etched by Cu2+/ HNO3 was rough and had many convex structures, and the fluoropolyurethane demonstrates well-adhesion to zinc substrates as it could still maintain its original surface textures, as shown in the comparison between Figure 4a,b and Figure 4c,d. The trapped air bubbles in the coating because of its long curing time were addressed through the temperature control, as shown in Figure 4b,d. Moreover, in previous experiments, another group of zinc substrate structure etched by nitric acid with copper ions for 10 and 60 s had also been observed. The surface formed by corrosion for 10 s only indicated shallow texture, but the surface texture for the ones with 60 s corrosion was more prominent and deeper, which was considered as the optimal group in the trial drag-reduction tests.
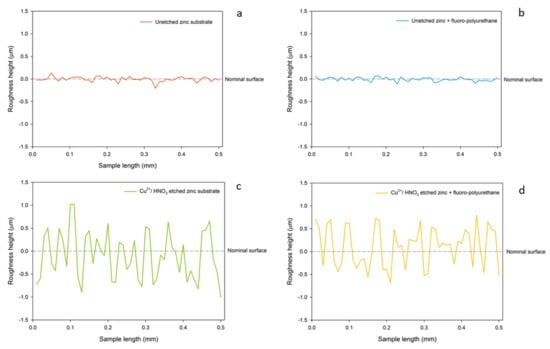
Figure 4.
Surface profiling of (a) unetched zinc substrate, (b) unetched zinc + fluoropolyurethane, (c) Cu2+/ HNO3-etched zinc, and (d) Cu2+/ HNO3-etched zinc + fluoropolyurethane.
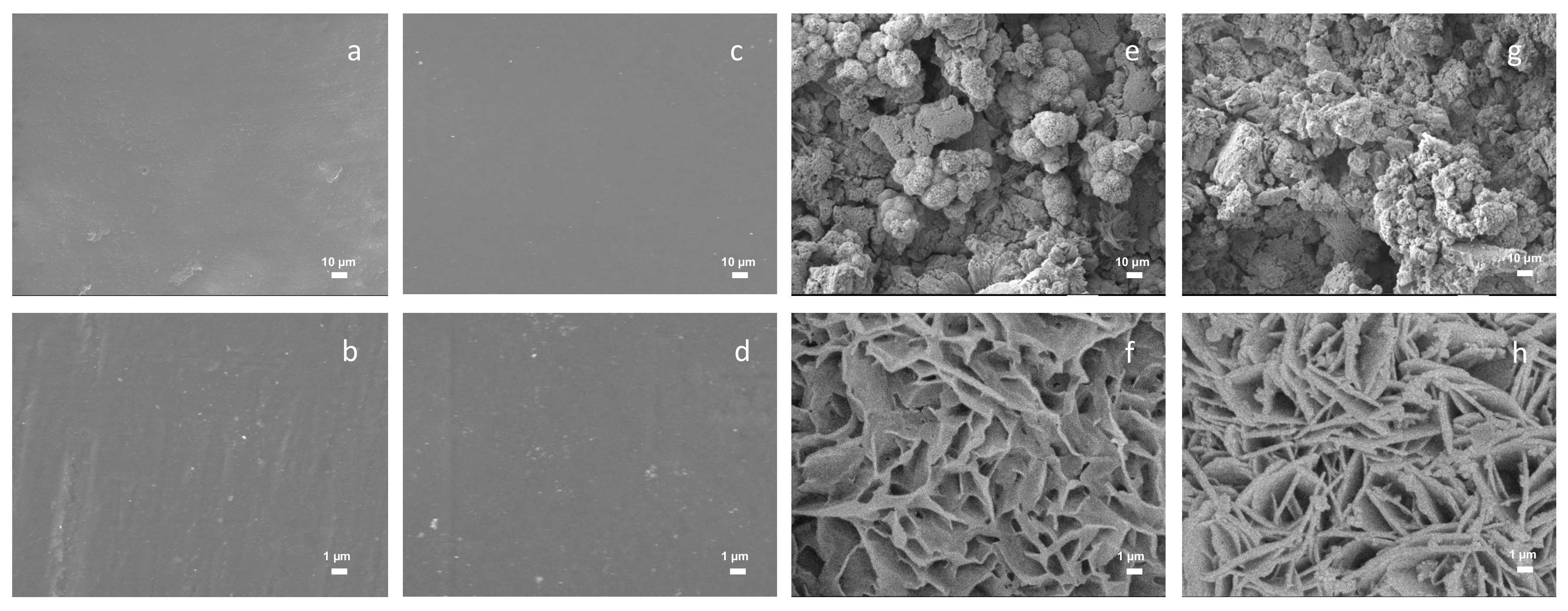
An unetched zinc substrate encapsulated with fluoropolyurethane from the Scanning Electron Micrograph (SEM) of zinc substrate had a smooth surface without too much surface structure. A comparative observation of the zinc substrate structure without the corrosion of copper ionized nitric acid solution and with copper ionized nitric acid solution is indicated in Figure 5a,h. In the case of a magnification of 50,000 times, the surface structures of the different zinc substrates were compared, and it was found that the topography of the etched ones was rough. The additional fluoropolyurethane, as shown in Figure 5c,d and Figure 5g,h, indicated a minor morphology difference compared with the Cu2+/ HNO3-etched only zinc substrate in Figure 5a,b and Figure 5e,f, and outstanding compactness on the etched surface. From the following contact angle (CA) analysis, this surface structure also contributed to the construction of superhydrophobic surfaces [23,24].
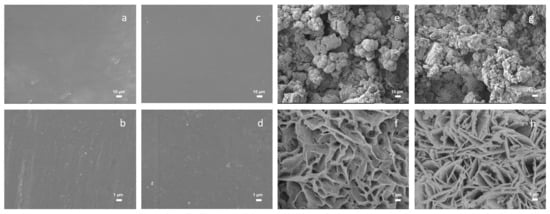
Figure 5.
Scanning Electron Micrograph (SEM) of surface morphology: (a) Unetched zinc (×1000 times), (b) Unetched zinc (×50,000 times), (c) Unetched zinc + fluoropolyurethane (×1000 times), (d) Unetched zinc + fluoropolyurethane (×50,000 times), (e) Cu2+/ HNO3-etched zinc (×1000 times), (f) Cu2+/ HNO3-etched zinc (×50,000 times), (g) Cu2+/ HNO3-etched zinc + fluoropolyurethane (×1000 times), and (h) Cu2+/ HNO3 etched zinc + fluoropolyurethane (×50,000 times).
3.3. Surface Wettability Analysis
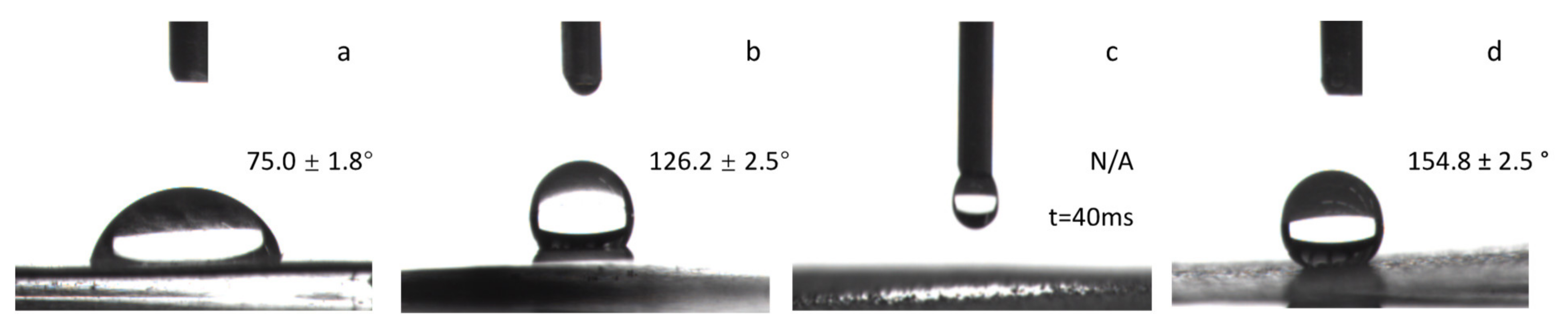
The contact angle of the zinc substrate only without any corrosion was 75.0° ± 1.8°. After being corroded by Cu2+/HNO3, the water droplets were quickly spread out, as shown in Figure 6, showing superhydrophilicity, and the contact angle was less than 3.0°.

Figure 6.
Surface contact angle of zinc substrate (a) Unetched zinc substrate, (b) Unetched zinc + fluoropolyurethane, (c) Cu2+/HNO3-etched zinc, and (d) Cu2+/HNO3-etched zinc + fluoropolyurethane.
As shown in Figure 6, after the fluoropolyurethane was applied, the water contact angle of the zinc substrate etched by the Cu2+/HNO3 solution and encapsulated with fluoropolyurethane could reach as high as 154.8° ± 2.5°, showing superhydrophobic properties, while water drops spread rapidly on the surface of superhydrophilic zinc substrates etched by the Cu2+/HNO3 solution only.
It was shown that a nano/micrometer superhydrophobic surface could be formed on the surface of the zinc substrate through chemical etching. Such a surface could provide good properties of superhydrophobicity and drag reduction [24]. This surface was not stained with water, and the rolling was extremely likely to occur. The zinc substrate was slightly inclined at the angle of 8.0°, and the water droplets could roll freely (Figure S2). The surface energy (SFE) result of an etched zinc substrate by diluted nitric acid with Cu2+ ion encapsulated with fluoropolyurethane also indicated low readings at 22.4 mJ/m2 only, while the one without etching by any diluted nitric acid with fluoropolyurethane was at 30.5 mJ/m2.
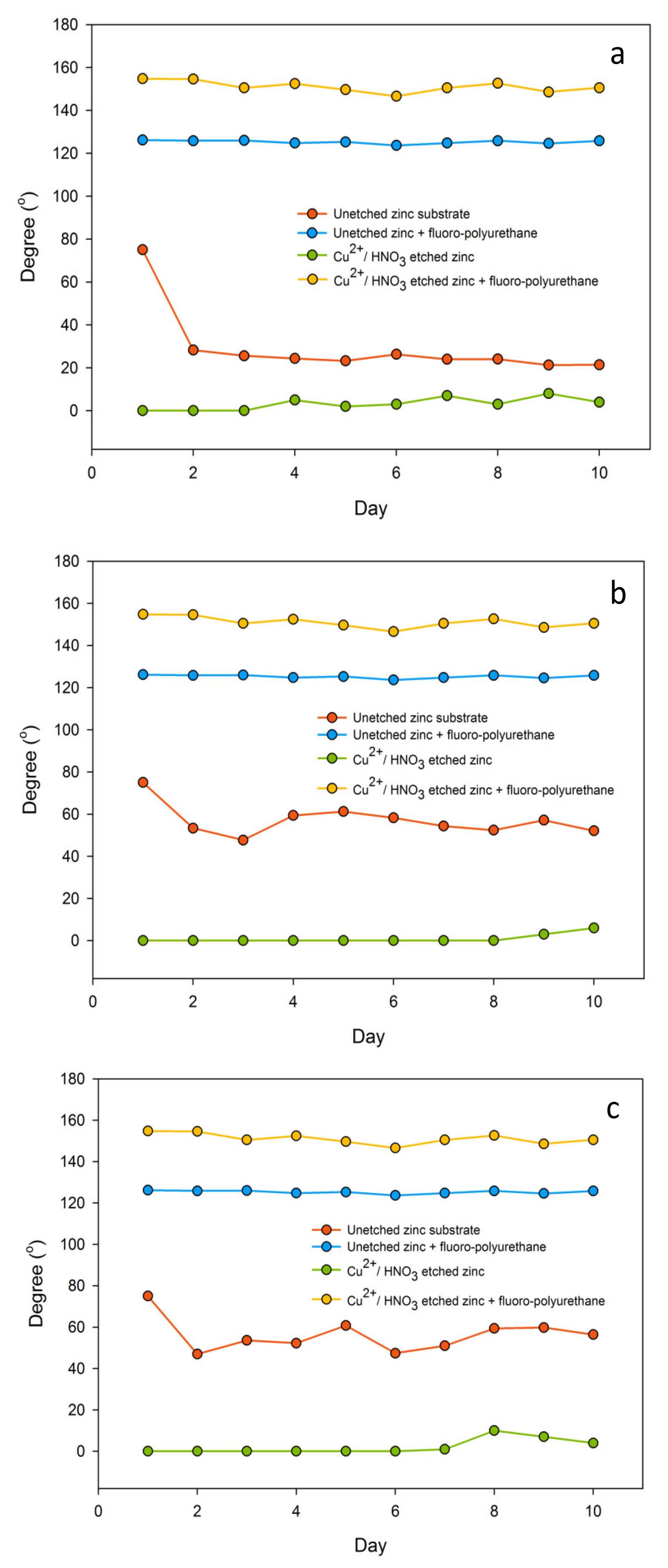
In the experiment of chemical durability probed by immersion in different liquids [26,34], this fluoropolyurethane coating platform was capable of maintaining a relatively long-term stability in different environments as shown in Figure 7, since immersion in liquids usually results in degradation of the surface/coating properties. It exhibited remarkable resistance to water and acid/alkaline/salt chemicals and extreme durability against immersion over 10 continuous days. Static contact angle measurements of water were performed [26,29]. Hydrophilicity is mostly due to the material characteristics and micro-nano roughness of the surface [30,31,32,33]. As long as the surface structure is not changed, it will not affect the superhydrophilicity of surface itself at all. Even comparing with the other superhydrophobic materials, the contact angle of this fluoropolyurethane coating was doing as well as polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), or polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), and it would remain at 154.8° for most of time [26,30,31,32,33,34]. In addition, it also indicated good adhesion on the etched zinc surface without any sign of peeling.
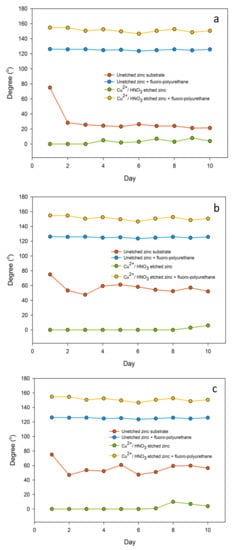
Figure 7.
Surface wettability variability for continuous 10 days in three different chemicals (a) 8.0 wt % hydrochloric acid (acid), (b) 8.0 wt % sodium hydroxide (alkaline), and (c) 40.0 wt % sodium chloride (saline) solution.
3.4. Microchannel Drag-Reduction Analysis
The microchannel drag-reduction experiment was aimed to investigate the drag reduction effect at all the flow rates to stimulate the practical application during commercial usage. In the experiment, since it is not a circular pipe, the equivalent diameter W’ = 2Wh/(W + h) was used, where W = 10 mm and variable h were the width and height of the microchannel. In order to observe the actual flow-resistance effect, the pressure drop must be tested at the same Reynolds number. The Reynolds number (Re) is a dimensionless number that can be used to characterize fluid flow, which is expressed as Re, Re = ρvd/µ, where v, ρ, µ are the flow velocity, density, and viscosity coefficient of the fluid, respectively. As d was supposed to be the feature length of the microchannel, so the W’ was also used as the ‘feature length’ (d) in calculating Re. The use of Reynolds numbers to distinguish fluid flow was laminar or turbulent and can also be used to determine the resistance to flow of an object in a fluid.
Firstly, we measure under the condition of water inlet pressure by taking the readings of the cylinder and pressure meters on the microchannel. The flow rate under inlet pressures was measured, and the pressure–flow linear relationship was demonstrated according to the formula:
i.e., vz was obtained through the flow volume meter, ΔP was the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet water supply, W’ = 10 × 10−3 h / (10 × 10−3 + h) mm, L = 85 mm, and µwater was taken as 1.00 mPa·s. The microchannel height h = 192.53 μm was determined by solving the above equations [35,36,37,38,39,40].
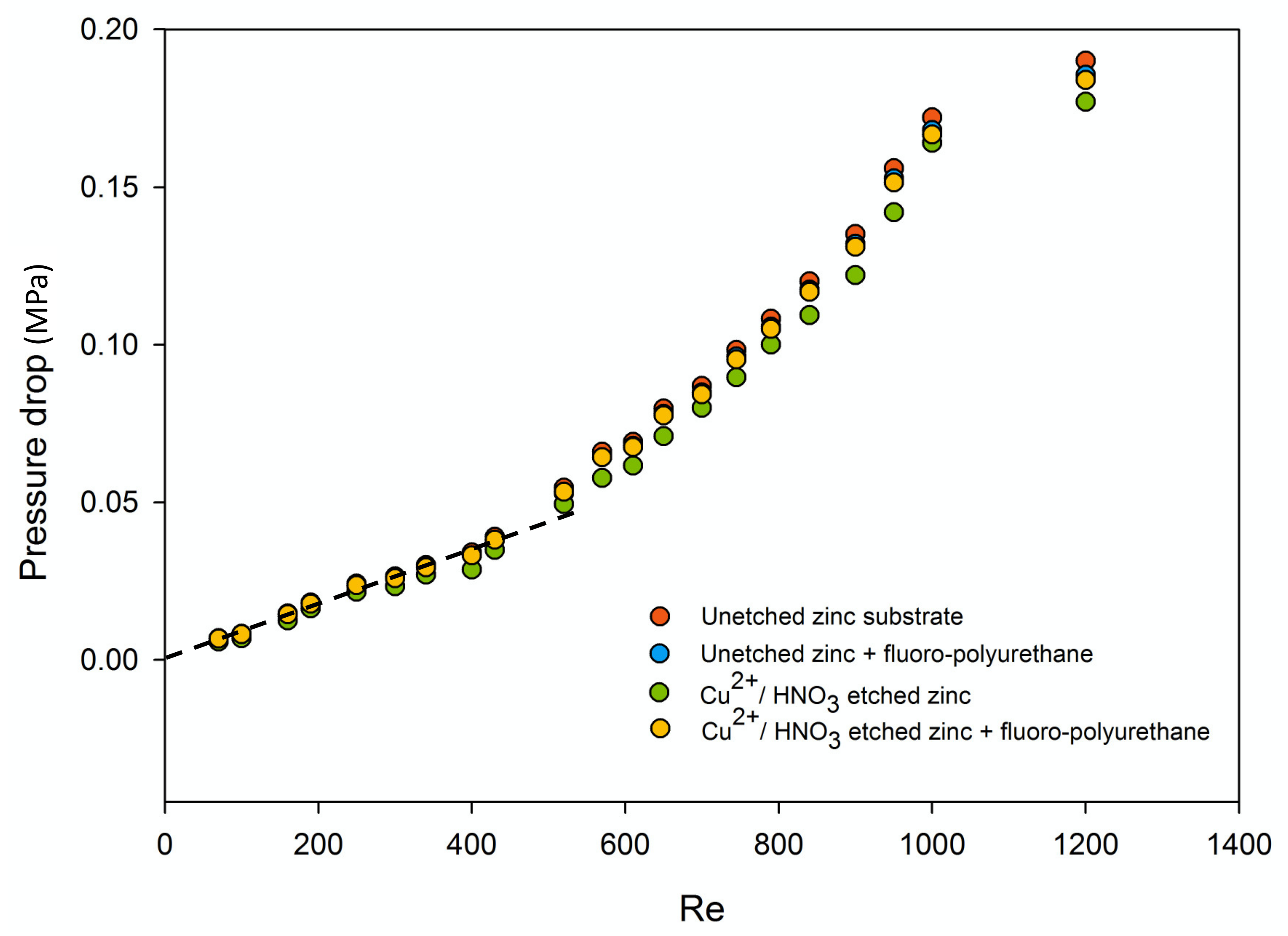
Comparing to the relationship of the pressure drop according the increment of Reynolds number, the diagram as shown in Figure 8 was finally generated. The trendline indicated the laminar flow regions under the height of 192.53 μm, which should be in between Re = 0 and Re = 580. As the Reynolds number at the horizontal ordinate was constant, the less the pressure dropped, the less flow resistance the surface should have. Therefore, it could be observed that the pressure drops of these fluoropolyurethane-capped zinc substrates were smaller than those of the unetched zinc substrate at the same Reynolds number, which indicted a better drag reduction effect. Moreover, as the Reynolds number increased under the same channel height, the drag reduction effect would increase slightly as well.
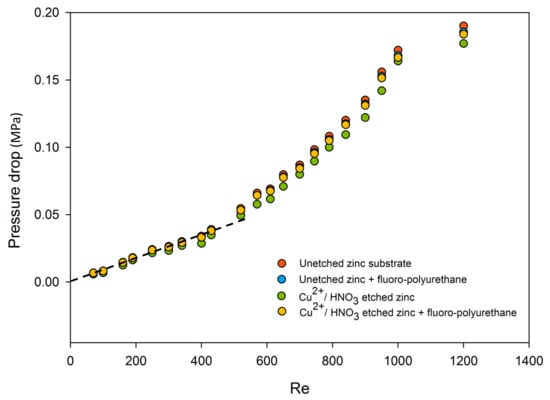
Figure 8.
Pressure drop–Reynolds number diagram at h = 192.53 μm microchannel height.
Then, comparing with the unetched zinc substrate (control group), the drag reduction rate of the superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic zinc substrate were made. The drag reduction rate (%) was calculated using following equation:
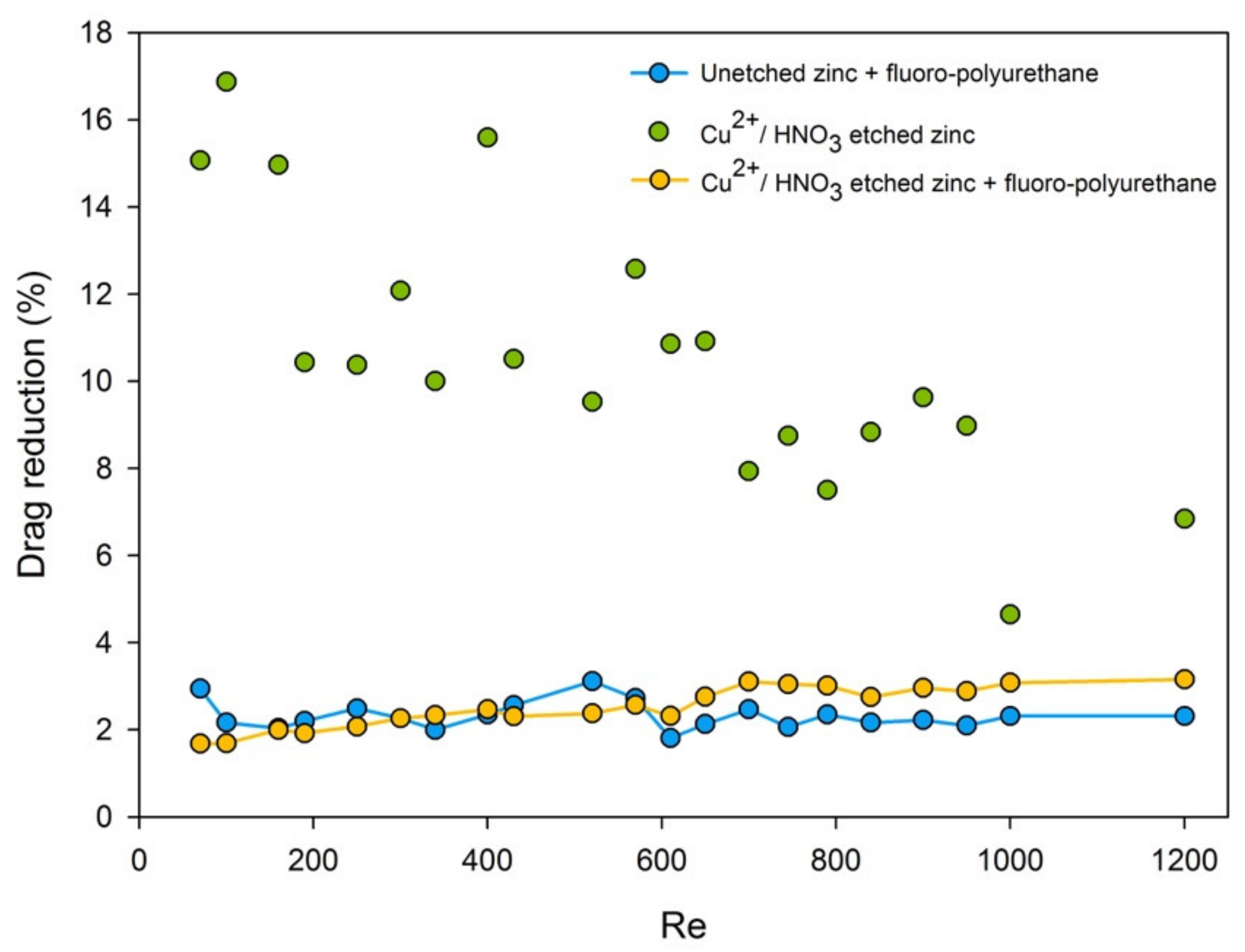
where ΔPb was the pressure drop with no surface modification or corrosion (control group), ΔPa was the pressure drop after corrosion or capped with fluoropolyurethane [41,42,43]. Diagrams of the drag reduction rate (%) over Reynolds number, for a total of 21 points, were plotted for each zinc substrate group. It could be observed that the superhydrophilic drag-reduction rate was decreased with the increment of the Reynolds number. The superhydrophobic drag reduction rate in the all flow zone was basically maintained at about 3.16%, as shown in Figure 9.
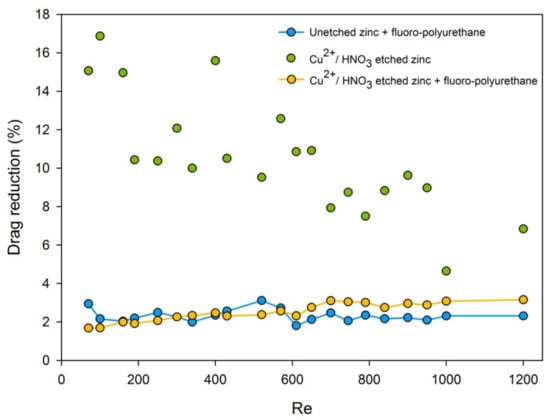
Figure 9.
Drag-reduction rate–Reynolds number diagram of the superhydrophilic/hydrophobic surface compared with an unetched zinc substrate at h = 192.53 μm.
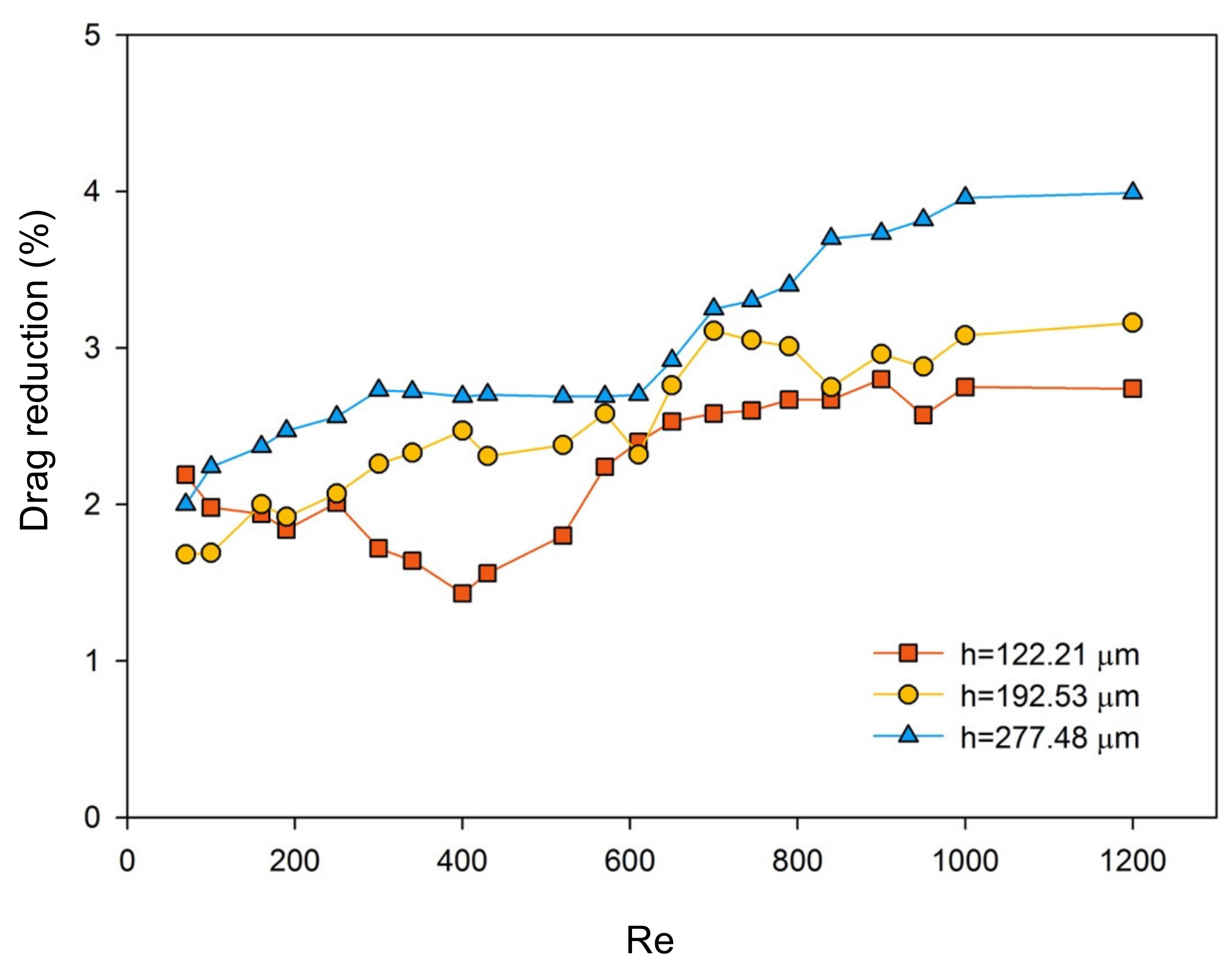
After each Reynolds-number group under h = 192.53 μm drag-reduction test was finished, the height of the channel was adjusted to reduce or increase by tightening the screws at h = 122.21 μm and h = 277.48 μm, respectively. Measurements were taken to obtain the pressure drop and Reynolds number data of different zinc substrates. Comparing the Reynolds number and pressure drop diagrams tested under different channel heights, two sets of pressure drop Reynolds number relationship diagrams were generated also, and all the data were under the same pattern [44].
It is known from Figure 10 that the resistances of all the surfaces were changed by varying the microchannel height. Under all the flow regions, from laminar to turbulent, both the superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic surfaces indicated certain drag-reduction effects. With the decrement of the flow rate or the increment of channel height, the superhydrophilic drag reduction rate became smaller, and the superhydrophobic drag reduction rate remained unchanged at around 4.0%, which was relatively stable. As for the superhydrophobic surface fabricated in this paper, it is generally believed that there is a non-shear air/water interface on the low Van der Waals force, and the fluid can shear freely at the gas–liquid interface with almost no resistance, which results in wall slippage, a lower friction coefficient, and flow resistance [23,41,42,43]. Since air was also able to be dissolved in the water, the non-shear air–water interface was formed by the separated air and the coating surface during the time that water flew over. Hence, for those etched surfaces, water molecules could not directly contact the surface of the fluoropolyurethane, and these surface characteristics could reduce the friction factor. As for continuously increasing the Reynolds number and flow rate, the non-shear air–water interface might become thinner and thinner [45,46].
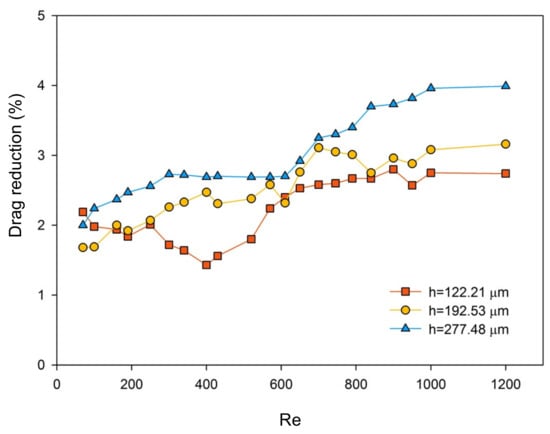
Figure 10.
Cu2+/HNO3-etched zinc + fluoropolyurethane drag reduction rate at different channel heights and Reynolds numbers.
However, the superhydrophilic drag reduction effect was even more obvious than the superhydrophobic. This interesting and repeatable scenario was supposededly caused by the ripple effect regarding the dissolved gas with higher affinity and electrical polarization sticking to the superhydrophilic surface than the superhydrophobic one, an achievement of microbubble drag reduction by the structure change of the boundary layer [45,46,47,48], and surface abrasion that resulted from high fluid velocity and enabled the substituted copper particles rolling near the wall surface. This causality is still under further analysis through experimental and modeling methodology separately in ongoing work [26,43,46,47,48].
To conclude, the main achievement of this research regards the aspects of the novel modification of the polyurethane-coating system, the good combination between an inorganic substrate and organic coating for drag reduction, the new methodology for a flow resistance test in the microchannel, and inclusive discussion about the drag-reduction effect and mechanisms with the latest research findings. As it was known to date, superhydrophobic, hierarchical, nanotextured polymerics were applied to the surface to enhance its superhydrophobicity and drag-reduction effect [17,48]. However, the adhesion force between the organic-coating matrix and the public use metal surface is still low for most polymeric coatings. When the pressure impact to the surface becomes higher, the surface texture would be certainly destroyed, and the coating layer would be even peeled off [30,31,32,33,34]. In this study, the polyurethane-based coating system, which had good adhesion with zinc substrates, was fluoro-modified and then applied in the microchannel for the flow resistance test. The microchannel was designed with variable height and extremely small ratios between the length, width, and height. The experimental result and mechanism analysis indicated that at low Reynolds number flow conditions, the surface texture friction and intermolecular forces between water and fluoropolyurethane would be the main factors that influenced the drag reduction, while at high Reynolds numbers, the low surface energy and the slight non-shear air–water interface would dominate the drag-reduction effect.
4. Conclusions
This paper proposed a fast method to fabricate a superhydrophobic and low flow-resistance fluoropolyurethane surface. Its drag-reduction effect could be further enhanced by the micro-nanoscale structures on the zinc substrate, which was formed by the copper-ion assisted nitric acid etching on the zinc substrate via a simple process. As expected, the micro-nanostructures obtained by chemical etching could contribute to the enhancement of the superhydrophobicity of the surface characters and low flow resistance.
As this newly fabricated surface was applied into a non-standard design microchannel, the drag reduction rate remained basically unchanged at 4.0% with the all variations of Reynolds numbers. Furthermore, the prepared superhydrophobic surface exhibited outstanding surface durability when it was immersed in solutions of acid, alkali, and salt.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6412/10/4/377/s1, Figure S1: Synthesis of prepolymer and fluoro-polyurethane, Figure S2. Waterdrops rolled on Cu2+/HNO3-etched zinc + fluoropolyurethane (rolling angle 8 ± 1.6°), Table S1. Uncertainty/error and parameters of non-standard design microchannel.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L.; Data curation, Y.L.; Formal analysis, Y.L.; Funding acquisition, S.N. and Z.D.; Investigation, Y.L.; Methodology, Q.Z.; Resources, Y.L. and Q.Z.; Supervision, Z.C., S.N. and Z.D.; Writing – original draft, Y.L.; Writing – review & editing, Y.L., Z.C., S.N. and Z.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by MOE Academic Research Fund (AcRF) Tier 1 Project “Nano-structured Titania with tunable hydrophilic/hydrophobic behavior and photocatalytic function for marine structure application”, Grant Call (Call 1/2018) _MSE (EP Code EP5P, Project ID 122018-T1-001-077), Ministry of Education (MOE), Singapore.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ma, M.; Randal, M. Superhydrophobic surfaces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.; Murthe, S.S.; Mohamed, N.; Perumal, V.; Mohamed Saheed, M. Nanoscaled Surface Modification of Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Using Carbon Nanotubes for Enhanced Oil and Organic Solvent Absorption. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 15907–15915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Luo, Y. Synthesis and characterization of siloxane-modified two-component waterborne polyurethane. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, C. Waterborne polyurethane wood coatings based on rapeseed fatty acid methyl esters. Prog. Org. Coat. 2012, 74, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, D.K.; Raju, K.V.S.N. Structural engineering of polyurethane coatings for high performance applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 352–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Kurmvanshi, S.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S. Preparation and characterization of siloxane modified: Epoxy terminated polyurethane-silver nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E2390–E2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhenage, T.; Webster, D.; Moreira, A.; Burgett, R.; Stafslien, S.; Vanderwal, L.; Clare, A. Poly(ethylene) glycol-modified, amphiphilic, siloxane–polyurethane coatings and their performance as fouling-release surfaces. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; Sun, B.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Y. Reports on Materials Science Findings from Wuhan University of Technology Provide New Insights (Evaluation On Self-healing Mechanism and Hydrophobic Performance of Asphalt Modified By Siloxane and Polyurethane).Report. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, A.; Zia, K.; Tabasum, S.; Aftab, W.; Shahid, M.; Zuber, M. Structural elucidation and biological aptitude of modified hydroxyethylcellulose-polydimethyl siloxane based polyurethanes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y. Super-hydrophobic surfaces from natural to artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, B.; Barrat, J.; Bocquet, L. Low-friction flows of liquid at nanopatterned interfaces. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S.; Charlaix, E.; Benyagoub, A. Contact angle hysteresis on nano- structured surfaces. Surf. Sci. 2003, 540, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Hwang, W.; Park, H.C.; Lee, K.H. Super-hydrophobic nano-wire entanglement structures. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Xiao, X. Research Progress of Superhydrophobic Surface Coatings. Mod. Chem. 2013, 23, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Song, Y.; Zhai, J.; Liu, B.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Creation of a super- hydrophobic surface from an amphiphilic polymer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinas, K.; Tserepi, A.; Gogolides, E. Superhydrophobic, passive microvalves with controllable opening threshold: Exploiting plasma nanotextured microfluidics for a programmable flow switchboard. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2014, 17, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadanaga, K.; Morinaga, J.; Matsuda, A.; Minami, T. Super-hydrophobic–super- hydrophilic micropatterning on flowerlike alumina coating film by the sol–gel method. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngblood, J.; McCarthy, T. Ultrahydrophobic polymer surfaces prepared by simultaneous ablation of polypropylene and sputtering of poly(tetrafluoroethylene) using radio frequency plasma. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 6800–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Feng, L.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Reversible wettability of a chemical vapor deposition prepared ZnO film between super-hydrophobicity and super- hydrophilicity. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5659–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Nakade, K.; Li, S.; Kawai, K.; Arima, K. Chemical etching of a semiconductor surface assisted by single sheets of reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 2018, 127, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Shi, F.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Smet, M.; Dehaen, W. Self-assembled monolayers of dendron thiols for electrodeposition of gold nanostructures: Toward fabrication of super-hydrophobic/super-hydrophilic surfaces and pH-responsive surfaces. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1986–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Geyer, F.; Pilat, D.W.; Wooh, S.; Vollmer, D.; Butt, H.J.; Berger, R. How drops start sliding over solid surfaces. Nat. Phys. 2018, 14, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkiris, P.; Ellinas, K.; Gkiolas, D.; Mathioulakis, D.; Gogolides, E. Motion of Drops with Different Viscosities on Micro-Nanotextured Surfaces of Varying Topography and Wetting Properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagubeau, G.; Le Merrer, M.; Clanet, C.; Quere, D. Leidenfrost on a ratchet. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinas, K.; Tserepi, A.; Gogolides, E. Durable superhydrophobic and superamphiphobic polymeric surfaces and their applications: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 250, 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ma, G.; Zhou, P. Research progress on boundary slip of fluid flow. Adv. Mech. 2008, 38, 265–282. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Wang, L.; Ding, Y. Study on drag reduction of superhydrophobic surface. Lubr. Eng. 2009, 34, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Poetes, R.; Holtzmann, K.; Franze, K.U. Steiner, Metastable underwater superhydrophobicity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 166104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Kota, A.; Mabry, J.; Tuteja, A. Superomniphobic surfaces for effective chemical shielding. J Am Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinas, K.; Pujari, S.; Dragatogiannis, D.; Charitidis, C.; Tserepi, A. Zuilhof, Plasma micro-nanotextured, scratch, water and hexadecane resistant, superhydrophobic, and superamphiphobic polymeric surfaces with perfluorinated monolayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6510–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, P. A novel damage-tolerant superhydrophobic and superoleophilic material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, E.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, R.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Y. Facile preparation of superamphiphobic epoxy resin/modified poly(vinylidene fluoride)/fluorinated ethylene propylene composite coating with corrosion/wear-resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Men, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, K.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X.; Xue, Q. Robust superhydrophobic surfaces with mechanical durability and easy repairability. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15793–15797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Kim, C. Large slip of aqueous liquid flow over a nanoengineered super-hydrophobic surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 066001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, B.; Guet, C.; Narasimalu, S.; Dong, L. Preparation and formula analysis of anti-biofouling titania–polyurea spray coating with nano/micro-structure. Coatings 2019, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y. Flow characteristics of water in superhydrophobic microchannels. Chem. J. China 2007, 58, 2721–2726. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, P.; Peters, A.M.; Pirat, C.; Wessling, M.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; Lohse, D. Quan-tifying effective slip length over micropatterned hydrophobic surfaces. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 112002–112008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natrajan, V.; Christensen, K. The impact of surface roughness on flow through a rectangular microchannel from the laminar to turbulent regimes. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2010, 9, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Yamada, T.; Asako, Y.; Faghri, M. Experimental investigations of laminar, transitional and turbulent Gas flow in microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 4397–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjun, K.; Rakesh, K. CFD analysis of thermal performance of microchannel nanofluid flow at different Reynolds numbers. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 41, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Gatapova, E.; Dmitry, S.G. The Drag Reduction of Microchannel Flow by Contrast Wettability. MATEC Web Conf. 2016, 72, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Deng, Y.; Yi, P.; Peng, L. Experimental and numerical investigation on thin sheet metal roll forming process of micro channels with high aspect ratio. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 100, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madavan, N.; Deutsch, S.; Merkle, C. Measurments of local skin friction in a microbubblemodified turbulent boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 1985, 156, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Kim, J.; Han, S.; Hoon, C. Direct measurement of slip flows in superhydrophobic microchannels with transverse grooves. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 113601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, S.; Castano, J. Microbubble skin friction reduction on an axisymmetric body. Phys. Fluids 1986, 29, 3590–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chang, H. Numerical simulation of hydrodynamic and heat transfer characteristics of slug flow in serpentine microchannel with various curvature ratio. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 55, 3343–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, D.P.; Tsougeni, K.; Tserepi, A.; Gogolides, E. Superhydrophobic, hierarchical, plasma-nanotextured polymeric microchannels sustaining high-pressure flows. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2013, 14, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).