Abstract
The present study proposes a novel method, i.e., combined severe shot peening (SP) and reversion annealing treatment, to grain-refine the surface layers of 304L austenitic stainless steel. Steel specimens were shot-peened at 0.7 MPa for 30 min, introducing 40% vol. α′ martensite, and then were annealed at 700 or 800 °C for different durations (30 s). As annealing reversed α′ martensite to austenite, the obtained surface layers consist of fully austenitic ultrafine grains. The smallest grain size obtained is about 500 nm at the top surface. SP elevates the microhardness to more than 500 HV. Although the grain-refined surface layers produced by the combined method are not as hard as that treated by only SP, they are harder (e.g., the specimen annealed at 700 °C for 30 s using a heating rate of 50 °C/s exhibited a peak microhardness of 400 HV) than the untreated surface layer (225 HV) due to grain refinement. Moreover, due to the absence of α′ martensite, they have higher corrosion resistance in H2SO4 solution than that treated by only SP.
1. Introduction
Surface grain refinements based on surface severe plastic deformation (SPD) treatments such as severe shot peening (SP) [1,2], ultrasonic impact/peening treatment (UIT/UPT) [3,4] and surface mechanical attrition treatment (SMAT) [5,6] have been applied widely to austenitic stainless steels (ASSs), in order to harden their surface layers and thus enhance their wear and fatigue resistance. However, significant strain-induced α′ martensite transformation and high density of microstructure defects such as dislocations may accompany with the grain-refinement process in the surface layers, degrading substantially the corrosion/stress-corrosion and hydrogen embrittlement (HE) resistance of the ASSs. For instance, Mordyuk et al. [7] showed that, based on potentiodynamic polarization tests, the 321 ASS specimens after less than 3 min UPT had good passivation capability due to either insignificant content of strain-induced α′ martensite or its homogeneous distribution in surface layers, whereas the 4 min peened specimen exhibited a weak ability to passivation due to the formation of a large volume fraction of α′ martensite. Lu et al. [8] showed that when SP pressure is less than 0.4 MPa the grain-refinement effect plays a main role, thus the stress-corrosion sensitivity of 304 steel decreases with increasing SP pressure. Nevertheless, when SP pressure is higher than 0.4MPa, α′ martensite effect plays a main role, consequently stress-corrosion sensitivity increases with increasing SP pressure. Balusamy et al. [9] found a deleterious effect of SMAT on corrosion resistance of 304 steel in 0.6 M NaCl solution. They indicated that the increase in surface roughness, strain-induced α′ martensite and dislocations nullified the beneficial effect of surface grain refinement. Brass and Chene [10] found that SP made 304 steel more susceptible to HE due to the introduction of α′ martensite, although carbon steel after SP showed a higher resistance to HE due to residual compressive stresses and/or increase of hydrogen trapping sites [11]. In addition, α′ martensite is ferromagnetic, whereas for biomedical applications, nonmagnetic nature is often necessary, for example, in magnetic resonance imaging [12].
On the other hand, bulk SPD treatments such as severe cold-rolling [13] and equal channel angular pressing (EACP) [14] have been used to produce ultrafine-grained ASSs in bulk scale. Moreover, in order to eliminate α′ martensite, annealing is considered as it can not only induce recrystallization but also reverse the α′ martensite to austenite. In fact, it is found that the austenitic grains reverted from deformed and crushed α′ martensite can be very fine in comparison with those reverted from deformed austenite [15,16]. Therefore, bulk SPD and reversion annealing treatment (RAT) have been combined as a means of producing fully austenitic, undeformed and ultrafine-grained bulk ASSs [17,18,19,20,21], which have a remarkable combination of yield strength and ductility due to the reductions of both α′ martensite and microstructure defects. Clearly, there is a need to examine whether or not ASSs can be surface ultrafine-grained by combined surface SPD treatment and RAT, avoiding the residue of α′ martensite and high density of dislocations. In this study, severe SP treatment was used first to impart deformed microstructure and α′ martensite into the surface layer of 304L steel, and then annealing was performed on the shot-peened (SPed) steel. The resulting surface layer grain size, microhardness and electrochemical corrosion behavior via potentiodynamic polarization tests and electrochemical impendence spectroscopy (EIS) tests were investigated to examine the feasibility of using combined severe SP and RAT to refine the surface layer grains of ASSs.
2. Materials and Methods
A commercial hot-rolled 304L sheet in a thickness of 8 mm with a chemical composition of Fe-0.02C-0.37Si-1.15Mn-0.004S-0.031P-18.3Cr-8.1Ni-0.044N-0.014Mo (wt %) was used. Specimens with a dimension of 30 mm × 30 mm × 8 mm were machined. The 30 mm × 30 mm surfaces were shot-peened (SPed) at 0.7 MPa pressure for 30 min using an air blast type machine, to induce a high level of plastic deformation and a large amount of α′ martensite. The shots were ceramic balls (type Z210, 0.21–0.3 mm in diameter and 700 HV in hardness). Annealing treatments were performed in a thermal simulator (Gleeble 3800, DSI, St. Paul, Mn, USA) followed by water quenching. Different annealing temperature, holding duration and heating rate combinations were used, including: annealing at 700 °C for 30 s (denoted as 700 °C-30 s-50 °C/s), 120 s (700 °C-120 s-50 °C/s) and 1200 s (700 °C-1200 s-50 °C/s), respectively, by a heating rate of 50 °C/s, annealing at 800 °C for 30 s (800 °C-30 s-50 °C/s) by 50 °C/s and annealing at 700 °C for 2 s (700 °C-2 s-10 °C/s) and 120 s (700 °C-120 s-10 °C/s), respectively, by a heating rate of 10 °C/s, in order to examine the effect of annealing parameters. 700 and 800 °C were selected because in the scenario of grain refinement in the bulk scale using combined severe cold-rolling and RAT annealing around 700 °C can result in grain size less than 1 μm easily. If a lower temperature is used, a long-time annealing is required to reverse all the martensite, whereas if a temperature higher than 850 °C was used both the reversion of martensite and grain growth is so fast that it is hard to control the grain size. Higher heating rate and lower holding duration are required to avoid significant sensitization.
The cross-sections of surface layers were ground with SiC papers up to 2000 grit grade and polished by 1.5 μm Al2O3 suspensions. They were then observed by an optical microscope (OM) after etching in Beraha’s tint reagent (0.5 g potassium metabisulfite, 20 mL HCl and 100 mL distilled water), which can color α′ martensite in brown and γ austenite in white [17]. They were also observed by a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Quanta TM 250, FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA) after electroetching in a 65% HNO3 solution using a current density of 0.2 mA/cm2 for 30 s, which can reveal grain boundaries readily and thus show grain sizes [17]. Phase identifications were performed on the specimen surfaces using the X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique to examine martensite transformation. The XRD measurements used a diffractometer (D8 ADVANCE, BRUKER, Karlsruhe, Germany) with a Cu-K (λ = 0.154056 nm) radiation operating at 40 kV and 40 mA at a step size of 0.02°. The Vickers hardness measurements were applied using a loading of 100 g. The potentiodynamic polarization tests and EIS tests were performed in a deaerated 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution at room temperature. A saturated calomel electrode (SCE) and a platinum plate were used as a reference electrode and as the counter one, respectively. The specimens were mounted with epoxy with an area of 1 cm2 left open on the surface and polished slightly to remove the contaminations caused by SP.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1a–f show OM images of cross sections. A brown martensitic surface layer in a thickness of 60 μm was revealed in the SPed specimen, Figure 1a. However, little α′ can be found in surface layers of SPed + annealed specimens, Figure 1b–f, indicating the reversion of α′ to austenite due to annealing. Moreover, Figure 1b–f verify the occurrence of grain refinement in surface layers by annealing and recrystallization, as the grain boundaries were partly corroded during etching in Beraha’s reagent, probably because of slight sensitization. With the increase of depth, grain size increased gradually. Figure 2 displays XRD profiles of specimen surfaces, revealing further the phase transformation. Untreated specimen exhibited only γ austenite peaks, but (110), (200) and (211) α′ peaks were detected in the SPed surface layer, in line with the OM observation of Figure 1a and verifying the occurrence of severe α′ transformation induced SP. According to the classic principle that the total integrated intensity of all diffraction peaks for each phase in a mixture is proportional to the volume fraction of that phase, the volume fractions of γ and α′ were quantitatively estimated (for details of the estimation procedure one can refer to [22]), Figure 2. The volume fraction of γ in untreated specimen was more than 90%, whereas the SPed specimen contained 40.8% vol. α′. Figure 2 confirms that annealing could reverse martensite. Except 700 °C-2 s-10 °C/s specimen, which contained a volume fraction of α′ of 15.6% due to a short-time exposure to high temperature and thus uncompleted reversion, the other specimens all exhibited only austenite peaks, indicating completed reversion.

Figure 1.
OM images of surface layers. (a) SPed specimen; (b) 700 °C-30 s-50 °C/s specimen; (c) 700 °C-120 s-50 °C/s specimen; (d) 700 °C-120 s-10 °C/s specimen; (e) 800 °C-30 s-50 °C/s specimen and (f) 700 °C-2 s-10 °C/s specimen.
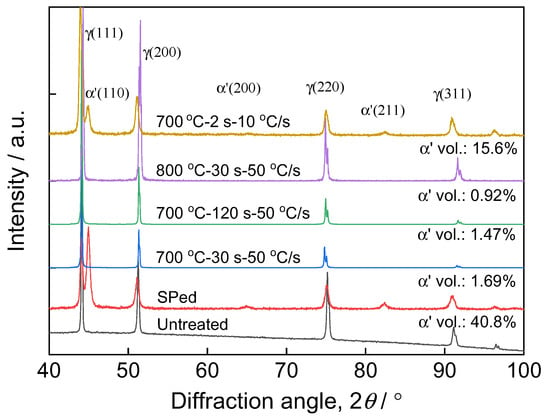
Figure 2.
XRD profiles of surface layers. The volume fractions (vol.) of α′ martensite are also displayed.
To reveal more clearly grain size, Figure 3 shows representative SEM images of specimen cross sections. Based on the standard linear intercept method in ASTM E112 [23], the grains sizes were evaluated roughly, Table 1. Near-equiaxed grains were observed. Grain size decreased with decreasing annealing duration/temperature, and it decreased with increasing heating rate. This trend was similar with that found in the scenario of bulk grain refinement of ASSs based on severe cold-rolling and subsequent RAT [17,18,19,20,21]. At an annealing temperature of 700 °C, extending annealing duration from 30 to 120 s increased the mean grain size from 510 to 850 nm. In fact, annealing at 700 °C for 1200 s by a heating rate of 50 °C/s resulted in a mean grain size bigger than 5 μm and sensitization was even indicated. For the same duration of 30 s, annealing at 800 °C results in a grain size of 1280 nm, which was two times larger than that of 700 °C. 700 °C-120 s-10 °C/s specimen shows a grain size of 2250 nm due to longer exposure to high temperature, whereas the 700 °C-2 s-10 °C/s specimen shows a grain size of 440 nm. In actual industries, the heating rate of heat treatments was often not very high. It is indicated that if a lower heating rate is used, a shorter exposure time is required to obtain ultrafine grains.
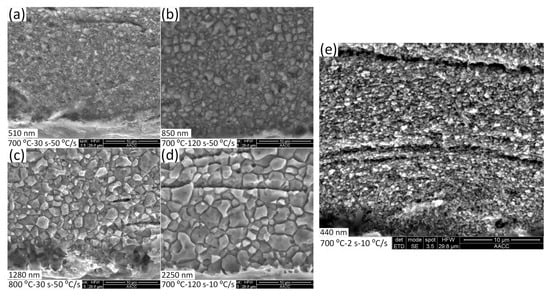
Figure 3.
SEM images of cross sections of surface layers (the grain sizes are shown in the images). (a) 700 °C-30 s-50 °C/s specimen; (b) 700 °C-120 s-50 °C/s specimen; (c) 800 °C-30 s-50 °C/s specimen; (d) 700 °C-120 s-10 °C/s specimen and (e) 700 °C-2 s-10 °C/s specimen.

Table 1.
Grain sizes of specimens.
The specimens with different grain sizes were selected to perform microhardness and corrosion tests. Figure 4 displays microhardness data along depth direction of surface layers. The hardness decreased with increasing depth. SPed specimen exhibited very high microhardness (more than 500 HV), which can be attributed to the combined effects of the formation of harder α′, the introduction of high-density dislocations (work-hardening) and grain refinement as a result of SPD. Annealing after SP reduced the microhardness, Figure 4, due to the reduction of dislocations and the reversion of α′, however the microhardness of SPed + annealed specimens was still higher than that of untreated specimen (225 HV) because of grain refinement [24] induced by annealing recrystallization and α′ reversion. 700 °C-30 s-50 °C/s specimen, which has a grain size of 510 nm, shows a peak microhardness of close to 400 HV at the location close to top surface, which is about twice of that of untreated steel. In addition, Figure 4 indicates that the microhardness increased with decreasing grain size.
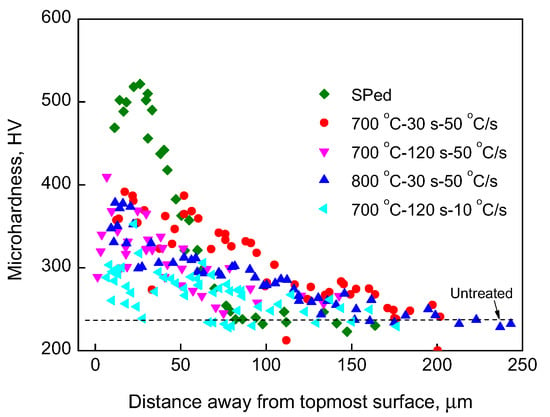
Figure 4.
Vickers microhardness of surface layers along the depth direction.
Figure 5a shows potentiodynamic polarization curves. Corrosion potentials (Ecorr), corrosion current densities (Icorr), critical passive current density (Icpc) and passive current density (Ipass) obtained from the curves are listed in Figure 5a also, revealing general corrosion resistance in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution. The values of Icorr were determined by extrapolating the cathode Tafel lines back to the corresponding values of Ecorr. SP had a slight influence on Ecorr but it increased Icorr, hence SP could impair the corrosion resistance of ASSs. This could be attributed to the introduction of plenty of α′ martensite, which would promote formation of galvanic cells Combined SP and annealing also did not change evidently Ecorr, however it reduced Icorr, for example 700 °C-1200 s-50 °C/s specimen had a very low Icorr of 3980 μA/cm2, suggesting an increase in general corrosion resistance. The Icpc and Ipass of SPed specimen were visibly higher than those of untreated specimen, indicating that severe SP increased the dissolving rate of passive film in the H2SO4 solution, in agreement with [7,9], which can be attributed also to the introduction of α′ and high density of microstructural defects [7,9]. In other words, the passive film on the SPed specimen was less stable, although it was found that surface grain refinement induced by surface SPD may promote the passivation. Balusamy et al. [9] studied the effect ball diameter on corrosion resistance of 304 steel by SMAT. They found the formation of passive film in specimens treated by 2 mm balls, whereas passivation was completely absent for those treated by 5 and 8 mm balls. The introduction of martensite and dislocations and increase of surface roughness nullified the beneficial influence of surface grain refinement. However, the Icpc and Ipass of SPed + annealed specimens were between those of untreated specimen and SPed specimen, suggesting that, although the passive film stability of SPed + annealed specimens was lower than that of untreated specimen, it was higher than that of the SPed specimen. Therefore, it could be concluded that the reduction of microstructural defects and the reversion of α′ by annealing could restore the corrosion resistance of ASSs. Although the SPed + annealed specimens were grain-refined, it was less resistant to corrosion than untreated specimen, probably because the increase in surface roughness increased the active surface area and thereby increased the corrosion current.
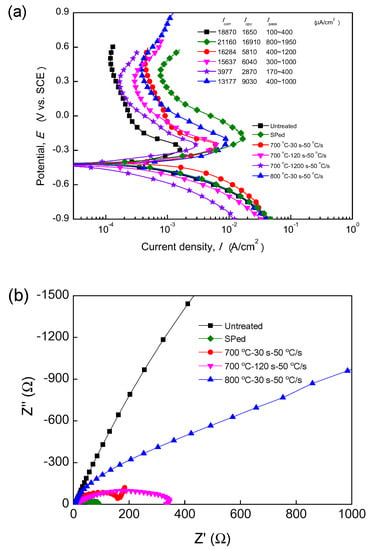
Figure 5.
(a) Potentiodynamic polarization curves and (b) Nyquist plots of impedance spectra of specimens obtained in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution.
Figure 5b shows Nyquist plots of impedance spectra of specimens at open circuit potential obtained from EIS tests. The specimens exhibited depressed capacitive semicircles and the semicircle diameter was in the following order: untreated > 800 °C-30 s-50 °C/s > 700 °C-30 s-50 °C/s > SPed. It was established that these arcs could be related with the metal dissolution in corrosion process at the electrode/electrolyte interface, and the semicircle diameter was associated with the charge-transfer resistance, i.e., corrosion resistance. Simply put, an increase in the semicircle radius suggests an increase in the passive film stability [14]. Thus, the SPed specimen had the lowest film stability, whereas SPed + annealed specimens had better corrosion resistance. The EIS results agreed with the results of potentiodynamic polarization tests, verifying again that the surface layers produced by the combined method was more corrosion-resistant than that treated by only SP due to the absence of martensite.
The present short study focused on the general corrosion in H2SO4 solution. The results also indicate that the general corrosion resistance decreased with decreasing grain size, Figure 5. However, it should be noted that both the beneficial and detrimental effect of grain ultra-refinement on corrosion resistance including general corrosion and localized corrosion have been found in literature (as reviewed by Liu et al. [25]). Different grain refinement processes introduce different microstructures including the degree of grain refinement, phase constitutions and density of microstructural defects. Since different microstructures may result in different passive film characteristics, including the thickness, composition and electronic structure, the effect of grain ultra-refinement on corrosion resistance is controversial. To know more widely about the corrosion behavior including localized corrosion of the surface ultrafine-grained ASSs produced by the present combined method, further studies are required.
4. Conclusions
The present study verified the feasibility of surface grain refinement by combined severe SP and RAT for the 304L stainless steel. The main conclusions are as follows:
- Grain size depended on annealing temperature and duration. It decreased with decreasing RAT temperature and duration. The surface layer of the 304L steel could be refined to 500 nm by the parameters used in this study.
- Air blast SP using 0.7 MPa pressure and 30 min could elevate the microhardness to more than 500 HV. Although the surface layers of SPed+annealed specimens were not as hard as the SPed specimens due to the reversion of α′ martensite during annealing, they still exhibited considerable hardness enhancement because of grain refinement. The specimen annealed at 700 °C for 30 s reached a peak hardness of close to 400 HV in its surface layer.
- SP induced α′ martensite transformation degraded the corrosion resistance of the 304L steel in H2SO4 solution, however SPed+annealed specimens had higher corrosion resistance in comparison with that treated by SP only due to the absence of α′ martensite.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and W.W.; methodology, Y.W. and Z.Z.; validation, Y.W., X.W. and W.W.; investigation, X.W., Z.Q. and H.Z; resources, Y.W.; data curation, X.W.; writing—original draft preparation, X.W., Z.Q. and H.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.W.; visualization, Y.W. and Z.Z.; supervision, Y.W.; project administration, Y.W.; funding acquisition, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province and China University of Mining and Technology (Grant No. KYCX19_2178), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities in China (2019QNA28) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51705516).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- He, Y.; Yoo, K.B.; Ma, H.; Shin, K. Study of the austenitic stainless steel with gradient structured surface fabricated via shot peening. Mater. Let. 2018, 215, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, E.; Unal, O. Shot peening process effects on metallurgical and mechanical properties of 316 L Steel via: Experimental and neural network modeling. Met. Mater. Int. (in press). [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Ling, X.; Wang, D. Enhanced mechanical behaviors of gradient nano-grained austenite stainless steel by means of ultrasonic impact treatment. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ling, X.; Zhou, J. Optimization of the fatigue resistance of AISI 304 stainless steel by ultrasonic impact treatment. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 61, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Hei, Z.K.; Liu, G.; Lu, J.; Lu, K. Formation of nanostructured surface layer on AISI 304 stainless steel by means of surface mechanical attrition treatment. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Brisset, F.; Baudin, T.; Helbert, A.L.; Retraint, D. In-situ EBSD investigation of thermal stability of a 316L stainless steel nanocrystallized by Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment. Mater. Let. 2020, 263, 127249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordyuk, B.N.; Prokopenko, G.I.; Vasylyev, M.A.; Iefimov, M.O. Effect of structure evolution induced by ultrasonic peening on the corrosion behavior of AISI-321 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 458, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Shi, L.; Zhu, S.; Tang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Effect of high energy shot peening pressure on the stress corrosion cracking of the weld joint of 304 austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 637, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balusamy, T.; Narayanan, T.S.N.S.; Ravichandran, K.; Park, I.S.; Lee, M.H. Influence of surface mechanical attrition treatment (SMAT) on the corrosion behaviour of AISI 304 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2013, 74, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brass, A.M.; Chene, J. Role of shot-peening on hydrogen embrittlement of a low-carbon steel and a 304 stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 4517–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, W.; Gong, J. Effect of shot peening coverage on hydrogen embrittlement of a ferrite-pearlite steel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 7169–7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. Recent metallic materials for biomedical applications. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, A.; Najafizadeh, A.; Kermanpur, A.; Forouzan, F. The effect of cold rolling regime on microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 304L stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2010, 210, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.J.; Gao, Y.; Gui, Y.; Zhu, M. Corrosion behaviour of nanocrystalline 304 stainless steel prepared by equal channel angular pressing. Corros. Sci. 2012, 54, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, T.H.; West, D.R.F. Deformation-induced martensite and its reversion to austenite in an Fe–16Cr–12Ni alloy. Metals Tech. 1976, 3, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimura, K.; Takaki, S.; Tanimoto, S.; Tokunaga, Y. Optimal chemical composition in Fe–Cr–Ni alloys for ultra grain refining by reversion from deformation induced martensite. ISIJ Int. 1991, 31, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Microstructural evolutions during reversion annealing of cold-rolled AISI 316 austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 2248–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Song, R.; Wang, T.; Cai, H.; Wen, J.; Guo, K. Grain size refinement and effect on the tensile properties of a novel low-cost stainless steel. Mater. Let. 2020, 260, 126919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzan, F.; Najafizadeh, A.; Kermanpur, A.; Hedayati, A.; Surkialiabad, R. Production of nano/submicron grained AISI 304L stainless steel through the martensite reversion process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7334–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Kang, J.; Zhu, L.; Shu, D.; Peng, P.; She, D.; Meng, D.; Li, Y. Effects of grain size on tensile property and fracture morphology of 316L stainless steel. Mater. Let. 2019, 254, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehsorkhi, R.N.; Sabooni, S.; Karimzadeh, F.; Rezaeian, A.; Enayati, M.H. The effect of grain size and martensitic transformation on the wear behavior of AISI 304L stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, W.; Gong, J. Warm pre-strain: Strengthening the metasTable 304L austenitic stainless steel without compromising its hydrogen embrittlement resistance. Materials 2017, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Society of Testing Materials (ASTM). Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size; ASTM E112: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Guelorget, B.; Sun, Z.; Déturche, R.; Retraint, D. Characterization of gradient properties generated by SMAT for a biomedical grade 316L stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2019, 155, 109788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.H. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of nanocrystalline materials–A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).