Fabrication of a Porous Slippery Icephobic Surface and Effect of Lubricant Viscosity on Anti-Icing Properties and Durability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SLIPSs
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Ice Adhesion Test
2.5. Durability
2.5.1. Icing/De-Icing Cyclic Test
2.5.2. Thermal Durability Test
3. Results and Discussion
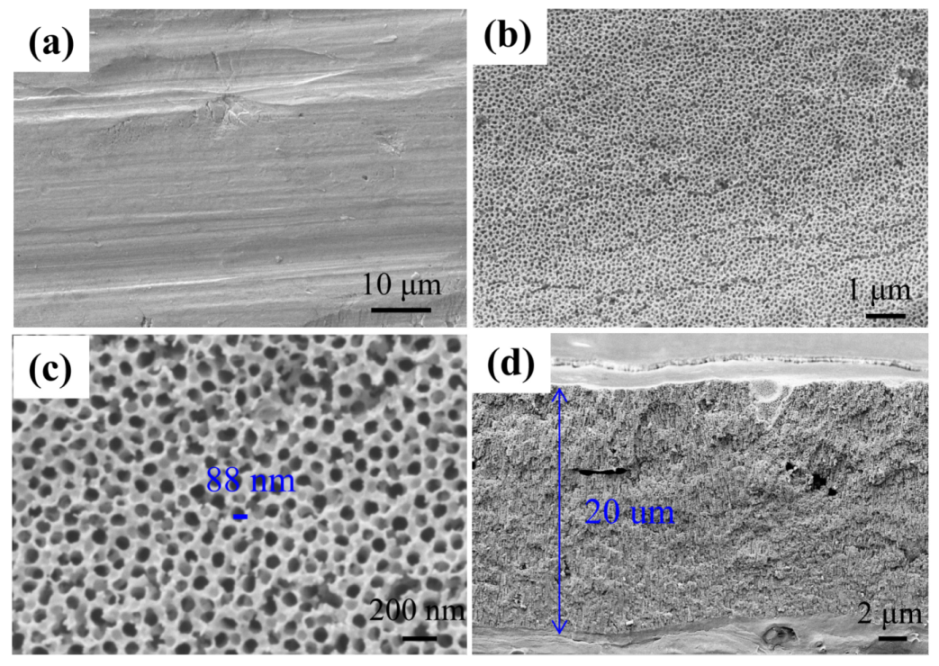
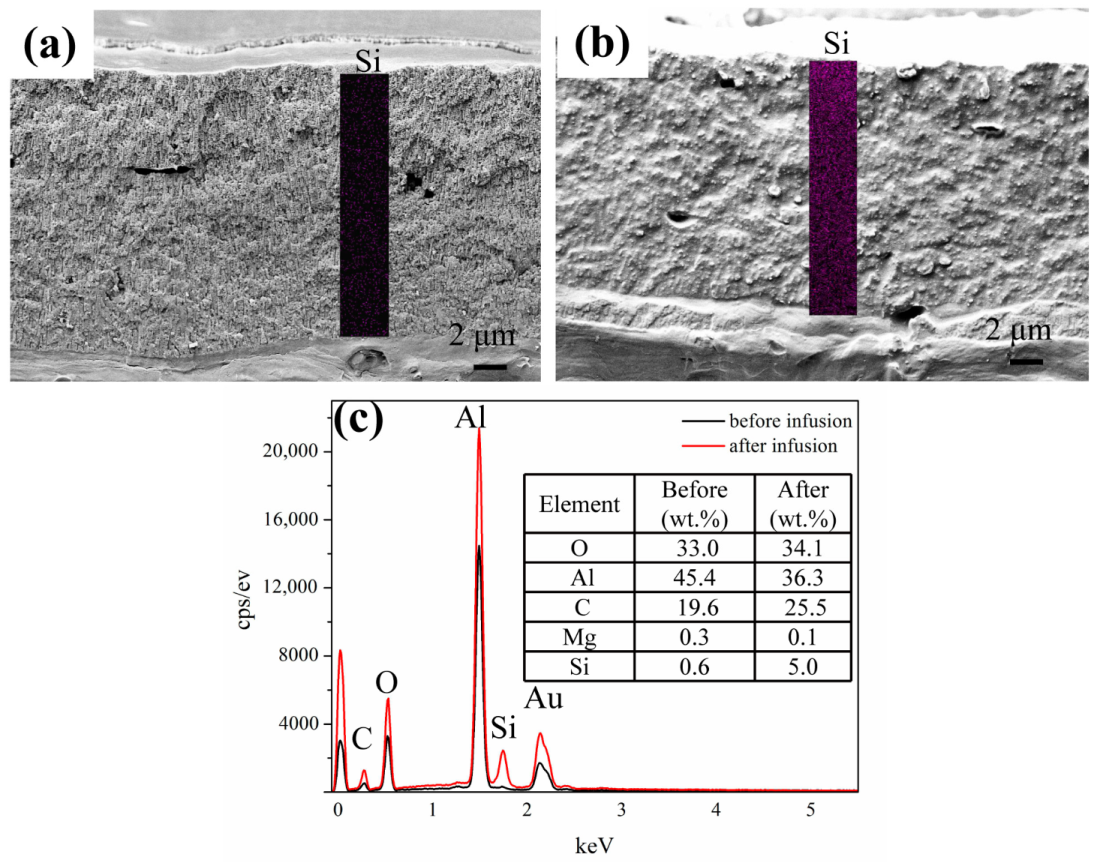
3.1. Morphology and Composition
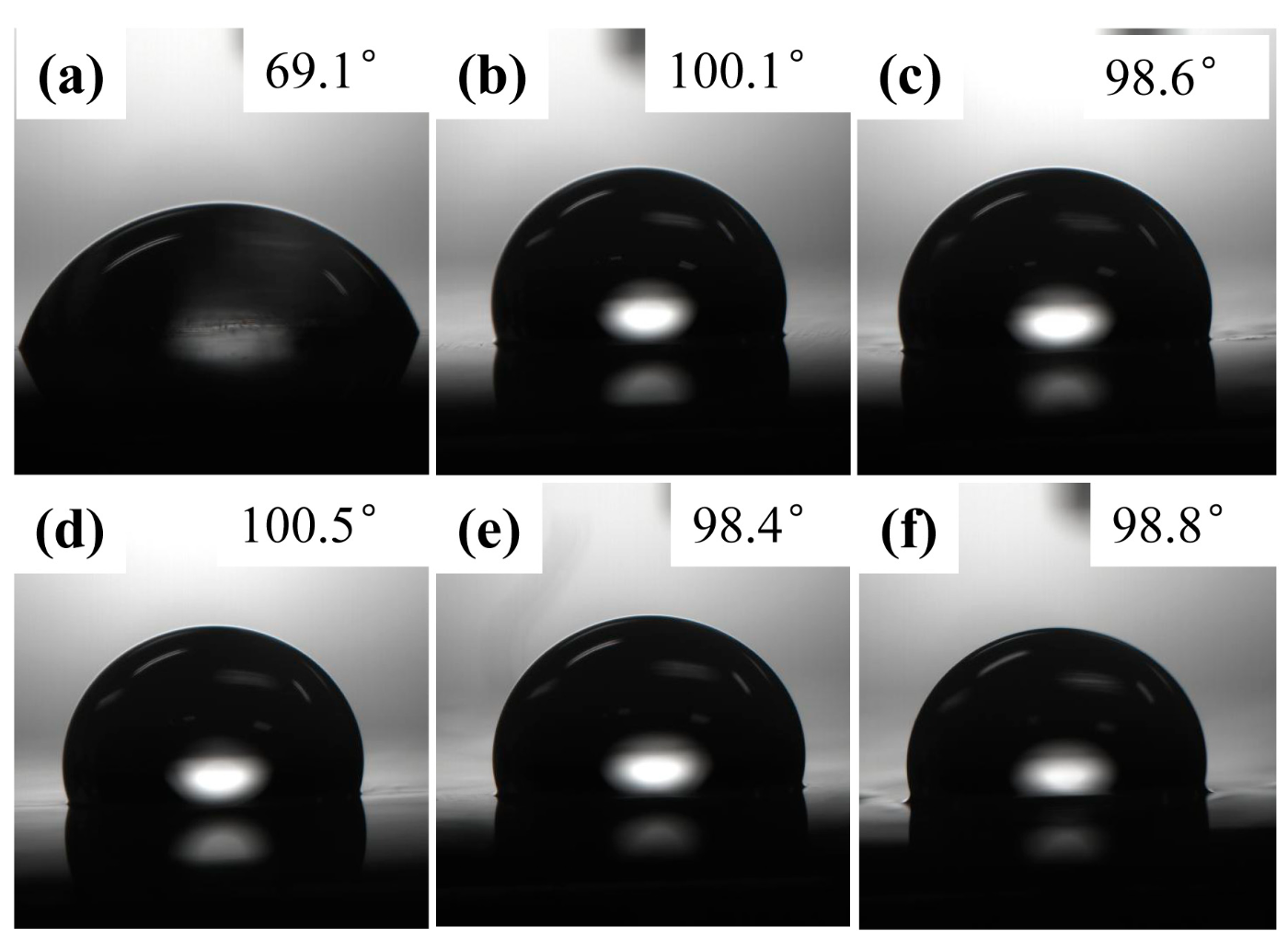
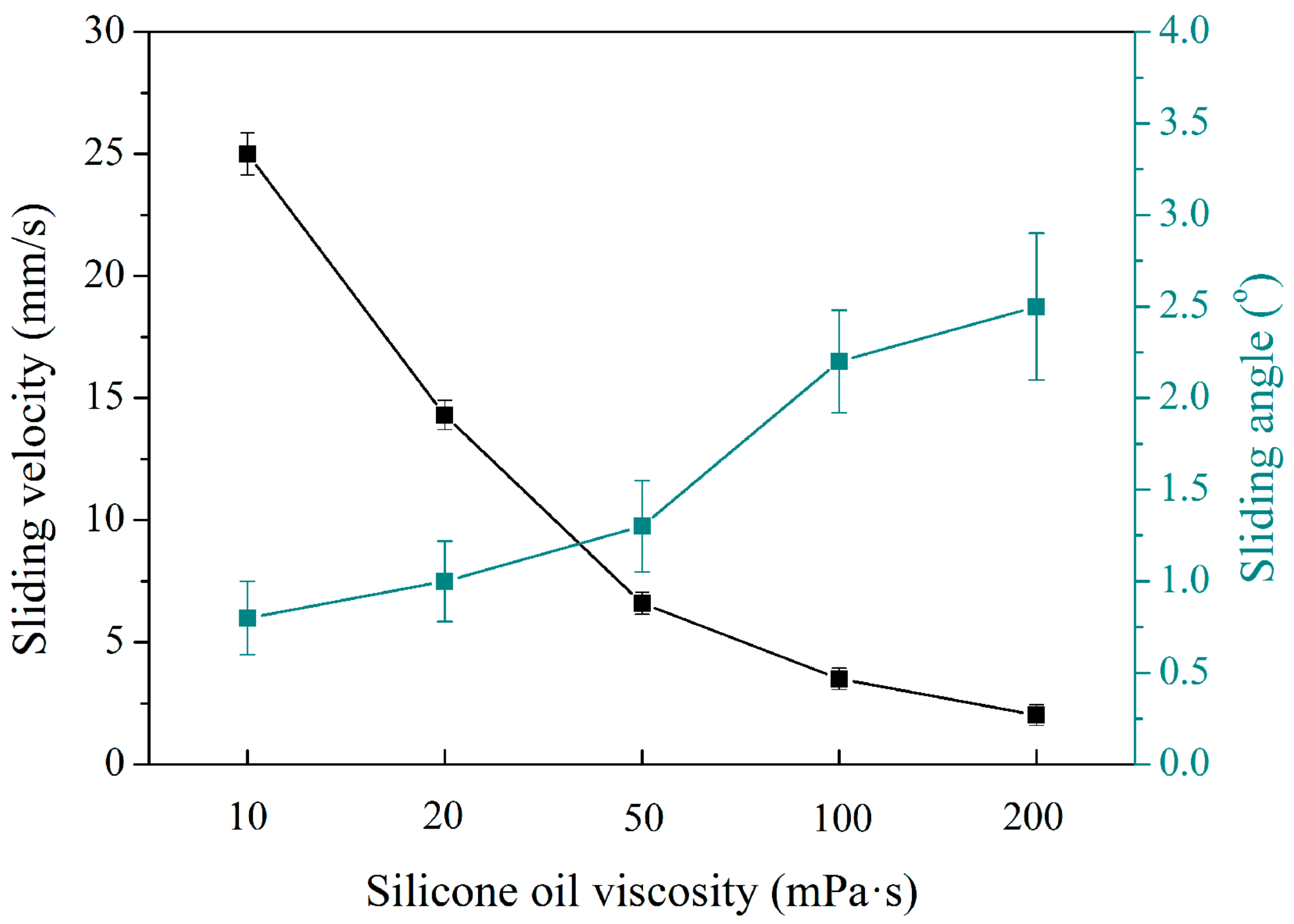
3.2. Slippery Properties
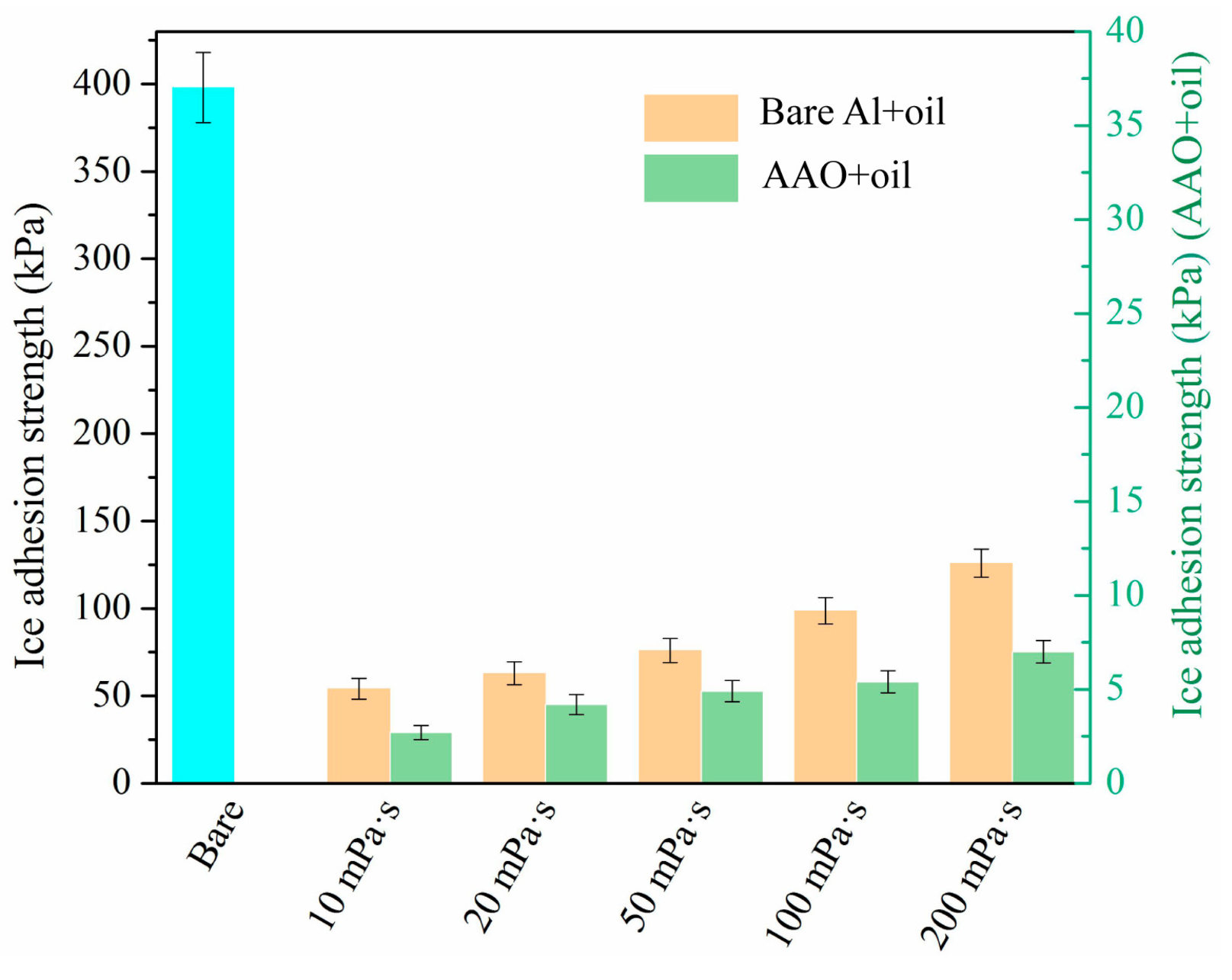
3.3. Ice Adhesion Test
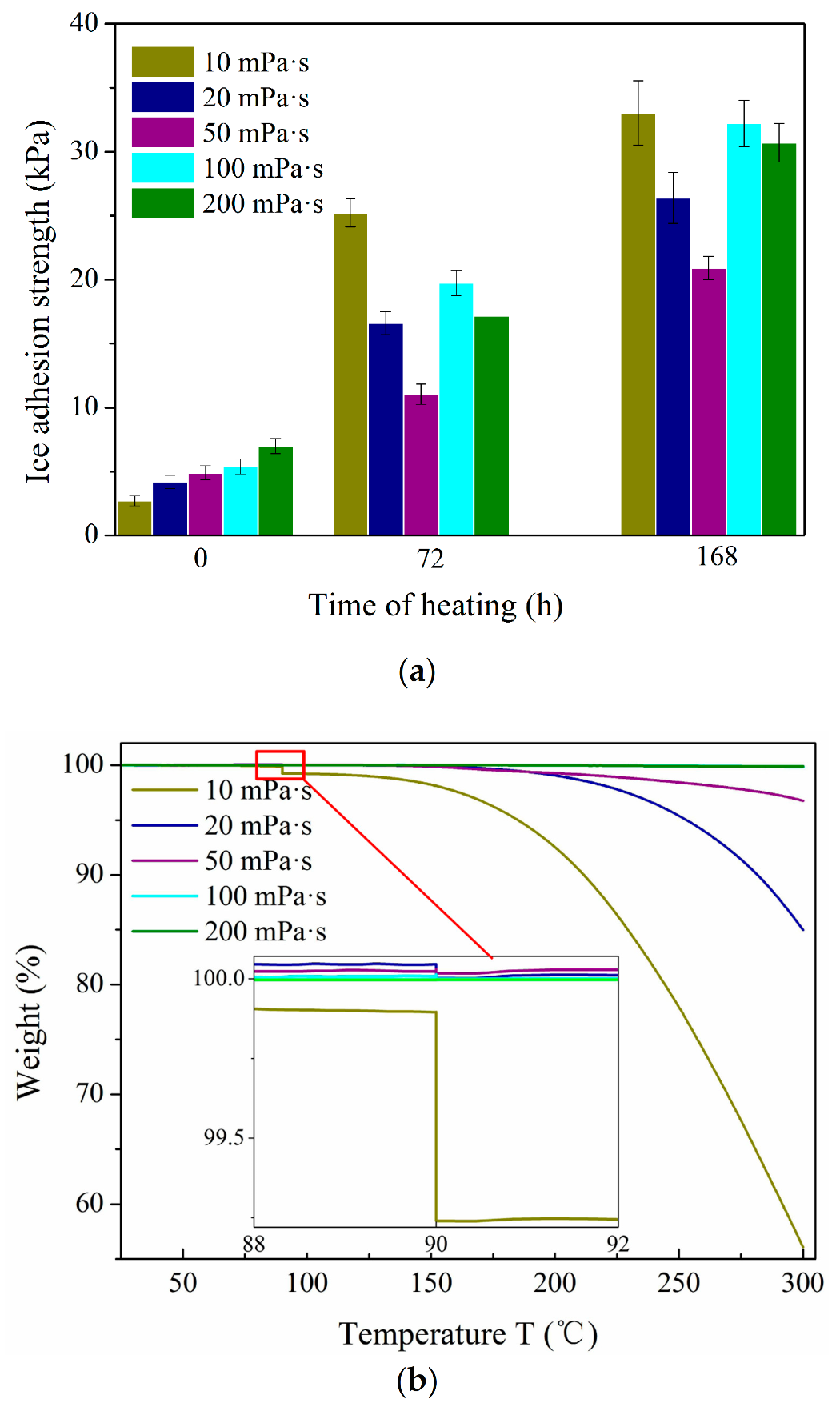
3.4. Durability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huneault, M.; Langheit, C.; St.-Arnaud, R.; Benny, J.; Audet, J.; Richard, J.C. A dynamic programming methodology to develop de-icing strategies during ice storms by channeling load currents in transmission networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2005, 20, 1604–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Fan, C.; Xie, Y. New method of preventing ice disaster in power grid using expanded conductors in heavy icing area. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 12, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chuang, F.; Yiping, C.; Hong, R.; Shukai, X.; Tao, Y.; Licheng, L. Research and Application of DC De–Icing Technology in China Southern Power Grid. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2012, 27, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, S.; Wang, Y. Study on AC Flashover Performance and Discharge Process of Polluted and Iced IEC Standard Suspension Insulator String. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2007, 22, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, Z.; Farzaneh, M.; Kiss, L.I. Assessment of the Current Intensity for Preventing Ice Accretion on Overhead Conductors. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2006, 22, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Song, X.; Liao, R.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, Y. Understanding the anti-icing property of nanostructured superhydrophobic aluminum surface during glaze ice accretion. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 113, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovin, K.; Dhyani, A.; Thouless, M.D.; Tuteja, A. Low-interfacial toughness materials for effective large-scale deicing. Science 2019, 364, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.S.; Kang, S.; Tang, S.K.Y.; Smythe, E.; Hatton, B.; Grinthal, A.; Aizenberg, J. Bioinspired self-repairing slippery surfaces with pressure-stable omniphobicity. Nature 2011, 477, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Youdong, J.; Liang, W. Anti-frosting/anti-icing property of nano-ZnO superhydrophobic surface on Al alloy prepared by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 02640117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Jones, A.K.; Sikka, V.K.; Wu, J.; Gao, D. Anti-Icing Superhydrophobic Coatings. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12444–12448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, K.K.; Deng, T.; Smith, J.D.; Hsu, M.; Bhate, N. Frost formation and ice adhesion on superhydrophobic surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinich, S.A.; Farhadi, S.; Nose, K.; Du, X.W. Superhydrophobic Surfaces: Are They Really Ice-Repellent? Langmuir 2011, 27, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; He, M.; Li, K.; Cui, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, Y. Superhydrophobic surfaces cannot reduce ice adhesion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 41–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovin, K.; Kobaku, S.P.R.; Lee, D.H.; Diloreto, E.T.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Designing durable icephobic surfaces. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rnneberg, S.; Zhuo, Y.; Laforte, C.; He, J.; Zhang, Z. Interlaboratory Study of Ice Adhesion Using Different Techniques. Coatings 2019, 9, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhuo, Y.; Hakonsen, V.; Ronneberg, S.; He, J.; Zhang, Z. Epidermal Gland Inspired Self-Repairing Slippery Lubricant-Infused Porous Coatings with Durable Low Ice Adhesion. Coatings 2019, 9, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, A.; Seeger, S. Nepenthes Pitcher Inspired Anti-Wetting Silicone Nanofilaments Coatings: Preparation, Unique Anti-Wetting and Self-Cleaning Behaviors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, S.; Jiang, Y.; Jeong, C.; Stone, H.A.; Choi, C. Oil-Impregnated Nanoporous Oxide Layer for Corrosion Protection with Self-Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1606040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Song, J.; Huang, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Li, Y. Multi-functional application of oil-infused slippery Al surface: From anti-icing to corrosion resistance. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 16099–16109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Wong, T.S.; Alvarenga, J.; Kreder, M.J.; Adornomartinez, W.E.; Aizenberg, J. Liquid-infused nanostructured surfaces with extreme anti-ice and anti-frost performance. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6569–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykaczewski, K.; Anand, S.; Subramanyam, S.B.; Varanasi, K.K. Mechanism of frost formation on lubricant-impregnated surfaces. Langmuir 2013, 29, 5230–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreder, M.J.; Alvarenga, J.; Kim, P.; Aizenberg, J. Design of anti-icing surfaces: Smooth, textured or slippery? Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Robust Slippery Liquid-Infused Porous Network Surfaces for Enhanced Anti-/De-icing Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 25471–25477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthwal, S.; Lee, B.; Lim, S.H. Fabrication of robust and durable slippery anti-icing coating on textured superhydrophobic aluminum surfaces with infused silicone oil. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 496, 143677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, N.; Belisle, R.A.; Hatton, B.; Wong, T.-S.; Aizenberg, J. Transparency and damage tolerance of patternable omniphobic lubricated surfaces based on inverse colloidal monolayers. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coady, M.J.; Wood, M.; Wallace, G.Q.; Nielsen, K.E.; Kietzig, A.M.; Lagugné-Labarthet, F.; Ragogna, P.J. Icephobic Behavior of UV-Cured Polymer Networks Incorporated into Slippery Lubricant-Infused Porous Surfaces: Improving SLIPS Durability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 10, 2890–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, Y.H.; Wang, C.; Wynne, K.J.; Gupta, M.C. Oil-infused superhydrophobic silicone material for low ice adhesion with long-term infusion stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32050–32059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Heng, L.; Jiang, L. Effect of lubricant viscosity on the self-healing properties and electrically driven sliding of droplets on anisotropic slippery surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, M.; Zhang, Y.; Abu Jarad, N.; Soleymani, L.; Didar, T.F. Liquid-Infused Surfaces: A Review of Theory, Design, and Applications. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8517–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh-Binh, N.; Seungchul, P.; Youngdo, J.; Hyuneui, L. Effects of hydrophobicity and lubricant characteristics on anti-icing performance of slippery lubricant-infused porous surfaces. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 69, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Tonelli, M.; Peppou-Chapman, S.; Ridi, F.; Neto, C. Effect of Pore Size, Lubricant Viscosity, and Distribution on the Slippery Properties of Infused Cement Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 2987–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumli, P.; Teisala, H.; Bauer, H.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D.; Damle, V.; Geyer, F.; D’Acunzi, M.; Kaltbeitzel, A.; Butt, H.R.; Vollmer, D. Flow-Induced Long-Term Stable Slippery Surfaces. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, B.; Yu, S.; Hua, W.; Huang, X. Evaporation of polydisperse perfluoropolyether lubricants in heat-assisted magnetic recording. Appl. Phys. Express 2011, 4, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Liao, R.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. Fabrication of a Porous Slippery Icephobic Surface and Effect of Lubricant Viscosity on Anti-Icing Properties and Durability. Coatings 2020, 10, 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090896
Liu G, Yuan Y, Liao R, Wang L, Gao X. Fabrication of a Porous Slippery Icephobic Surface and Effect of Lubricant Viscosity on Anti-Icing Properties and Durability. Coatings. 2020; 10(9):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090896
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Guoyong, Yuan Yuan, Ruijin Liao, Liang Wang, and Xue Gao. 2020. "Fabrication of a Porous Slippery Icephobic Surface and Effect of Lubricant Viscosity on Anti-Icing Properties and Durability" Coatings 10, no. 9: 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090896
APA StyleLiu, G., Yuan, Y., Liao, R., Wang, L., & Gao, X. (2020). Fabrication of a Porous Slippery Icephobic Surface and Effect of Lubricant Viscosity on Anti-Icing Properties and Durability. Coatings, 10(9), 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10090896




