Arsenic Removal from Contaminated Water Using Natural Adsorbents: A Review
Abstract
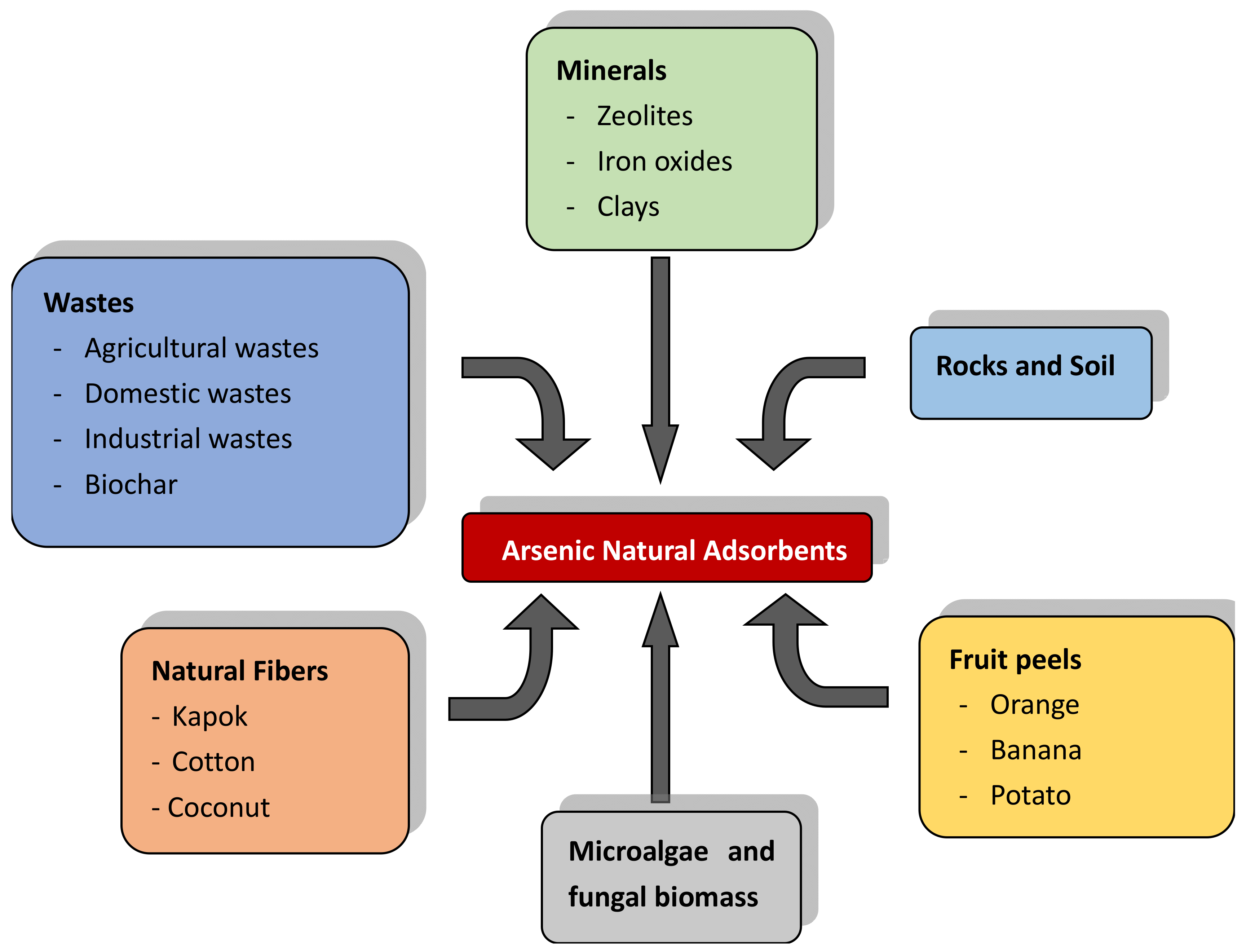
:1. Introduction
2. Harmful Effects of Arsenic
3. Arsenic Removal Technology
3.1. Membrane Filtration
3.2. Coagulation
3.3. Electrochemical Techniques
3.4. Bioremediation
3.5. Ion or Particle Exchange
3.6. Adsorption
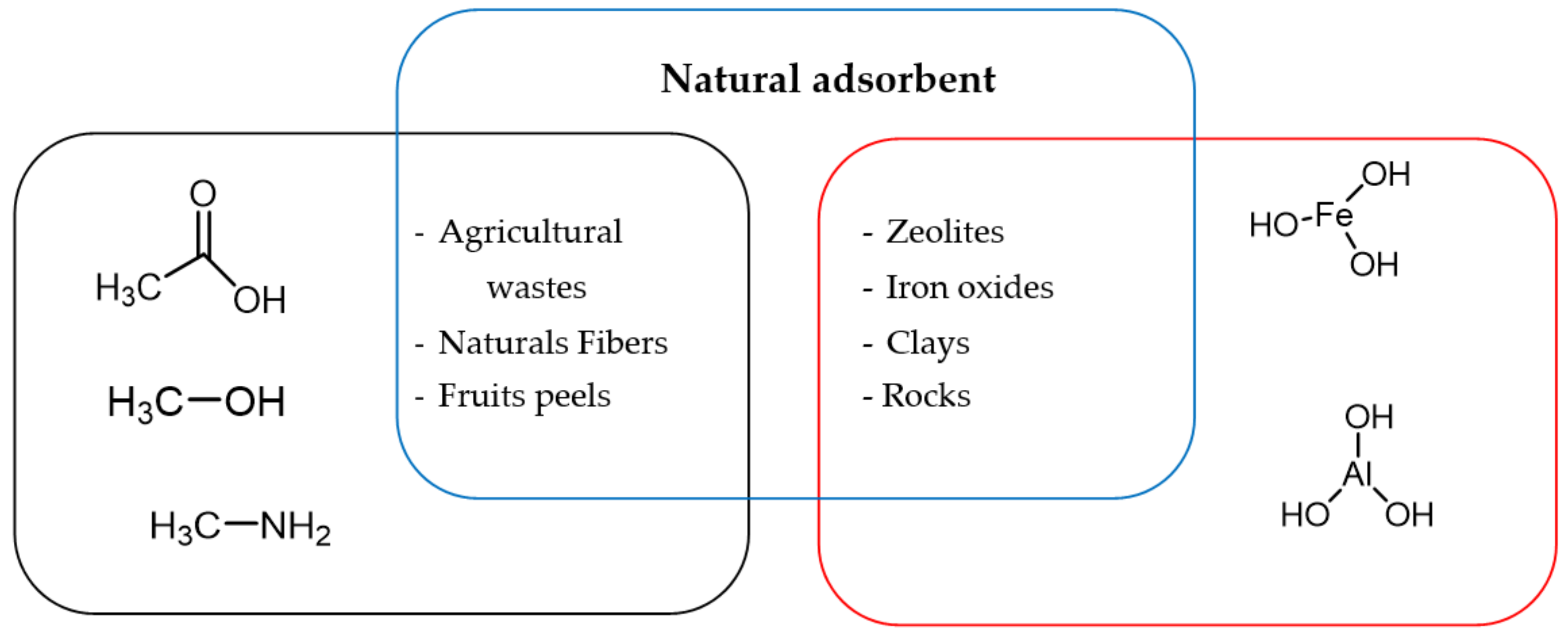
4. Biosorbents
5. Treatment of the Natural Adsorbents
6. As Removal Performance
6.1. Overall Adsorption Performance
6.2. Effects of Contact Time on As Adsorption
6.3. pH
6.4. Reusability
6.5. Thermodynamic
6.6. Influence of Other Ions
6.7. Adsorption Isotherm and Kinetic Model
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, C.; Ali, P.I. Arsenic: Occurrence, Toxicity and Speciation Techniques. Water Res. 2000, 34, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, B.K.; Suzuki, K.T. Arsenic round the world: A review. Talanta 2002, 58, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.; Smith, E.; Owens, G.; Bhattacharya, P.; Nadebaum, P.; Collingwood, V. Managing Arsenic in the Environment from Soil to Human Health; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Rahman, M.M.; Naidu, R.; Dong, Z.; Shahid, M.; Arshad, M. Unraveling Health Risk and Speciation of Arsenic from Groundwater in Rural Areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12371–12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cutter, G. Kinetic controls on metalloid speciation in seawater. Mar. Chem. 1992, 40, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, C.M.; Ahmad, A. Groundwater As Removal by As(III), Fe(II), and Mn(II) Co-Oxidation: Contrasting As Removal Pathways with O2, NaOCl, and KMnO4. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15454–15464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecol, H.; Ergican, E.; Fuchs, A. Molecular level separation of arsenic (V) from water using cationic surfactant micelles and ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 241, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council USA. Arsenic in Drinking Water: 2001 Update; NRC: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Mazumder, D.N.G. Chronic Arsenic Toxicity: Clinical Features, Epidemiology, and Treatment: Experience in West Bengal. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2003, 38, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T. Low-Cost Adsorbents for Heavy Metals Uptake from Contaminated Water: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raul, P.; Devi, R.R.; Umlong, I.M.; Banerjee, S.; Singh, L.; Purkait, M.K. Removal of Fluoride from Water Using Iron Oxide-Hydroxide Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 3922–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daus, B.; Wennrich, R.; Weiss, H. Sorption materials for arsenic removal from water: A comparative study. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2948–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, F.; Feng, X.; Liu, M.; Tan, W.; Qiu, G. Co2+-exchange mechanism of birnessite and its application for the removal of Pb2+ and As(III). J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, X.F.; Ma, J.X. Preparation and Characteristics of a Paper-Based Ultrafiltration Membrane. Bioresources 2012, 7, 545–553. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Vigneswaran, S.; Ngo, H.H.; Shon, H.K.; Kandasamy, J. Arsenic removal by a membrane hybrid filtration system. Desalination 2009, 236, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Z.; Rui, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z. A Review on Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes for Water Purification. Polymers 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pallier, V.; Feuillade-Cathalifaud, G.; Serpaud, B.; Bollinger, J.-C. Effect of organic matter on arsenic removal during coagulation/flocculation treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meharg, A.A.; Whitaker, J. Arsenic uptake and metabolism in arsenic resistant and nonresistant plant species. New Phytol. 2002, 154, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhitomirsky, I. Cathodic electrodeposition of ceramic and organoceramic materials. Fundamental aspects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 97, 279–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.A.; Schennach, R.; Parga, J.R.; Cocke, D.L. Electrocoagulation (EC)—Science and applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 84, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.Y.; Morkovsky, P.; Gomes, J.A.; Kesmez, M.; Parga, J.; Cocke, D.L. Fundamentals, present and future perspectives of electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 114, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y. Water dissociation in ion-exchange membrane electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 203, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casqueira, R.; Torem, M.; Kohler, H. The removal of zinc from liquid streams by electroflotation. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, M.; Moon, I. Indirect Electrochemical Oxidation of Phenol by Ce4+, Controlling Surface Insulation of Au Electrode. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2005, 26, 899–902. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, H. Bio-accumulation of environmental residues of rare earth elements in aquatic flora Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms in Guangdong Province of China. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 214, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maine, M.A.; Duarte, M.V.; Suñé, N.L. Cadmium uptake by floating macrophytes. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2629–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghurye, G.L.; Clifford, D.A.; Tripp, A.R. Combined arsenic and nitrate removal by ion exchange. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1999, 91, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, W.; Liu, X.; Samuelson, L. Influence of arsenic adsorption layers on heterointerfaces in GaInAs/InP quantum well structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 62, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, J.G.; Chen, P.-Y.; Wilkie, J.A.; Elimelech, M.; Liang, S. Arsenic removal by ferric chloride. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1996, 88, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, L.; van Deventer, J.; Landi, W. Factors affecting the mechanism of the adsorption of arsenic species on activated carbon. Miner. Eng. 1995, 8, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghurye, G.; Clifford, D.; Tripp, A. Iron coagulation and direct microfiltration to remove arsenic from groundwater. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2004, 96, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.-T.; Leveque, T.; Austruy, A.; Goix, S.; Schreck, E.; Dappe, V.; Sobanska, S.; Foucault, Y.; Dumat, C. Foliar uptake and metal(loid) bioaccessibility in vegetables exposed to particulate matter. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igwe, J.C.; Abia, A.A.; Okenwa, S.I.; Gbaruko, B.C.; Nwokennaya, E.C. Detoxification of Hg2+, As3+ and Pb2+ metal ions from wastewater by biosorption using modified and unmodified coconut fiber: pH, temperature and particle size effects. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 230, U1878–U1879. [Google Scholar]
- Marín-Rangel, V.M.; Cortés-Martínez, R.; Villanueva, R.A.C.; Garnica-Romo, M.G.; Martínez-Flores, H.E. As (V) Biosorption in an Aqueous Solution Using Chemically Treated Lemon (Citrus aurantifolia Swingle) Residues. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, T10–T14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, A.; DasGupta, S.; Basu, J.K.; De, S. Batch and Column Study: Adsorption of Arsenate Using Untreated Laterite as Adsorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.R.; Tuutijärvi, T.; Bhatnagar, A.; Vahala, R. Adsorptive removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous phase by feldspars: Kinetics, mechanism, and thermodynamic aspects of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, U.; Kaur, M.; Jawa, G.; Sud, D.; Garg, V. Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption on agricultural waste biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.E.; Olin, T.J.; Bricka, R.; Adrian, D. A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.; Abdel-Halim, E.S.; El-Tahlawy, K.F.; Hebeish, A. Enhancement of the Adsorption of Co(II) and Ni(II) Ions onto Peanut Hulls through Esterification Using Citric Acid. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2005, 23, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewail, T.M.; El-Garf, S.A.M. Preparation of agriculture residue based adsorbents for heavy metal removal. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 22, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi, R.; Maleki, A.; Shahmoradi, B.; Daraei, H.; Mahvi, A.H.; Barati, A.H.; Eslami, A. Elimination of arsenic contamination from water using chemically modified wheat straw. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wu, M.; Lin, X.; Huang, P.; Huang, Y. Synthesis of magnetic wheat straw for arsenic adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 193, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, M.; Lorestani, B.; Merrikhpour, H.; Mosaed, H.P. Assessment efficiency of tea wastes in arsenic removal from aqueous solution. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 52, 7235–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamala, C.; Chu, K.; Chary, N.; Pandey, P.K.; Ramesh, S.; Sastry, A.; Sekhar, K. Removal of arsenic(III) from aqueous solutions using fresh and immobilized plant biomass. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2815–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashine, A.; Tembhurkar, A. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for adsorption of As(III) on coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) fiber. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3267–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashine, A.; Tembhurkar, A. Iron oxide impregnated sugarcane bagasse waste material as sorbent for As(III) removal from water: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2016, 65, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urik, M.; Littera, P.; Kolen, M. Removal of arsenic (V) from aqueous solutions using chemically modified sawdust of spruce (Picea abies): Kinetics and isotherm studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaskheli, M.I.; Memon, S.Q.; Siyal, A.N.; Khuhawar, M.Y. Use of Orange Peel Waste for Arsenic Remediation of Drinking Water. Waste Biomass-Valoriz. 2011, 2, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Sharma, P.; Srivastava, S.; Srivastava, M. Biosorption studies on shelled Moringa oleifera Lamarck seed powder: Removal and recovery of arsenic from aqueous system. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 78, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamsonlian, S.; Suresh, S.; Ramanaiah, V.; Majumder, C.B.; Chand, S.; Kumar, A. Biosorptive behaviour of mango leaf powder and rice husk for arsenic(III) from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamsonlian, S.; Suresh, S.; Majumder, C.; Chand, S. Biosorption of Arsenic by Mosambi (Citrus limetta) Peel: Equilibrium, Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Desorption Study. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouédraogo, I.W.K.; Pehlivan, E.; Tran, H.T.; Bonzi-Coulibaly, Y.L.; Zachmann, D.; Bahadir, M. Synthesis of iron oxyhydroxide-coated rice straw (IOC-RS) and its application in arsenic(V) removal from water. J. Water Health 2015, 13, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, E.; Tran, T.; Ouédraogo, W.; Schmidt, C.; Zachmann, D.; Bahadir, M. Removal of As(V) from aqueous solutions by iron coated rice husk. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 106, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.I.Z.; Monteiro, A.S.; Gontijo, E.S.; Bueno, C.C.; de Moraes, M.A.; Rosa, A.H. High efficiency removal of As(III) from waters using a new and friendly adsorbent based on sugarcane bagasse and corncob husk Fe-coated biochars. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anirudhan, T.; Unnithan, M.R. Arsenic(V) removal from aqueous solutions using an anion exchanger derived from coconut coir pith and its recovery. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldhar, D.; Sahoo, S.; Mishra, P. Adsorption of As (III) From Aqueous Solution by Groundnut Shell. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2014, 4, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Chen, F. Removal of Arsenic by Bead Cellulose Loaded with Iron Oxyhydroxide from Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6808–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyono, D.; Valiyayeettil, S. Chemically Modified Sawdust as Renewable Adsorbent for Arsenic Removal from Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, P.; Kakadiya, N.; Timaniya, Z.; Dharaskar, S.; Sillanpaa, M. Removal of arsenic using iron oxide amended with rice husk nanoparticles from aqueous solution. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, S.; Saikia, J.; Phukan, A.; Goswamee, R.L. Adsorption of As(V) from Water over a Hydroxyl-Alumina Modified Paddy Husk Ash Surface and Its Sludge Immobilization. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, S.; Heidari, M. Evaluation and comparison of aluminum-coated pumice and zeolite in arsenic removal from water resources. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2012, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, V.; Saini, V.; Jain, N. Adsorption of As(III) from aqueous solutions by iron oxide-coated sand. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 288, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aredes, S.; Klein, B.; Pawlik, M. The removal of arsenic from water using natural iron oxide minerals. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 29–30, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, C.-S.; Baek, K.; Park, J.-K.; Oh, Y.-K.; Lee, S.-D. Adsorption characteristics of As(V) on iron-coated zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Parette, R.; Zou, J.; Cannon, F.S.; Dempsey, B.A. Arsenic removal by iron-modified activated carbon. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.; Ahmad, S.; Toheed, A.; Ahmed, J. Immobilization of Arsenic on Rice Husk. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 1998, 16, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.A.; Goldberg, S. Modeling Competitive Adsorption of Arsenate with Phosphate and Molybdate on Oxide Minerals. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, M.N.; Kaneco, S.; Kitagawa, C.; Begum, A.; Katsumata, H.; Suzuki, T.; Ohta, K. Removal of arsenic in aqueous solutions by adsorption onto waste rice husk. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 8105–8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doušová, B.; Fuitová, L.; Grygar, T.M.; Machovič, V.; Koloušek, D.; Herzogová, L.; Lhotka, M. Modified aluminosilicates as low-cost sorbents of As(III) from anoxic groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, C.; Puccia, V.; Avena, M. Arsenate adsorption and desorption kinetics on a Fe(III)-modified montmorillonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A. Removal of arsenic from contaminated water sources by sorption onto iron-oxide-coated polymeric materials. Water Res. 2002, 36, 5141–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.R.; Aryal, R.L.; Bhattarai, S.; Koirala, A.R.; Gautam, S.K.; Ghimire, K.N.; Pant, B.; Park, M.; Paudyal, H.; Pokhrel, M.R. Agro-Waste Derived Biomass Impregnated with TiO2 as a Potential Adsorbent for Removal of As(III) from Water. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorg, T.J.; Wang, L.L. Arsenic removal from drunking water by activated alumina and anion exchange treatment. In Proceedings of the Small Drinking Water and Wastewater Systems, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12 January 2000; pp. 282–291. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, A.; Dasgupta, S.; Basu, J.K.; De, S. Adsorption of arsenite using natural laterite as adsorbent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 55, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twidwell, L.G.; Robins, R.G.; Hohn, J.W. The removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by coprecipitation with iron (III). In Proceedings of the Arsenic Metallurgy, Fundamentals and Applications, TMS Annual Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 February 2005; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, L.C.; Hug, S.J.; Ruettimann, T.; Billah, M.; Khan, A.W.; Rahman, M.T. Arsenic Removal with Iron(II) and Iron(III) in Waters with High Silicate and Phosphate Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.; Kao, Y.-H.; Liu, C.-W. Arsenic removal from real arsenic-bearing groundwater by adsorption on iron-oxide-coated natural rock (IOCNR). Desalination 2011, 280, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Chaudhuri, M. Removal of Arsenic from Ground Water by Iron Oxide-Coated Sand. J. Environ. Eng. 1996, 122, 769–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Liu, T.; Peng, J.M. Adsorption Behaviors of Arsenic(V) onto Fe-Based Backwashing Sludge Produced from Fe(II)-Removal Plants. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 295–298, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, Z.; Chen, Z. Removal of arsenic from drinking water using rice husk. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Sankararamakrishnan, N. Column studies on the evaluation of novel spacer granules for the removal of arsenite and arsenate from contaminated water. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2173–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.S.; Pant, K. Experimental and modelling studies on fixed bed adsorption of As(III) ions from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 48, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakat, P.; Gupta, A.; Ayoob, S. Feasibility analysis of As(III) removal in a continuous flow fixed bed system by modified calcined bauxite (MCB). J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliyanni, E.A.; Bakoyannakis, D.N.; Zouboulis, A.; Peleka, E. Removal of Arsenic and Cadmium by Akaganeite Fixed-Beds. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 3967–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, L.; Xue, S.-G.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Hartley, W.; Cui, M.-Q.; Wong, M.H. Arsenic sorption by red mud-modified biochar produced from rice straw. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18168–18178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafique, U.; Ijaz, A.; Salman, M.; Zaman, W.U.; Jamil, N.; Rehman, R.; Javaid, A. Removal of arsenic from water using pine leaves. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2012, 43, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Deng, Y.; Cui, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; He, S.-Y. Performance of a New Magnetic Chitosan Nanoparticle to Remove Arsenic and Its Separation from Water. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Creamer, A.E. Sorption of arsenate onto magnetic iron–manganese (Fe–Mn) biochar composites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 67971–67978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.K.; Choubey, S.; Verma, Y.; Pandey, M.; Chandrashekhar, K. Biosorptive removal of arsenic from drinking water. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Liu, Y.; Feng, B.; Zeng, G.; Yang, C.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, H.; Tan, Z.; Wang, X. Biosorption of cadmium(II), zinc(II) and lead(II) by Penicillium simplicissimum: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, M.; Majumder, C. Predictive approach for simultaneous biosorption and bioaccumulation of arsenic by Corynebacterium glutamicum MTCC 2745 biofilm supported on NL/MnFe2O4 composite. J. Water Process. Eng. 2016, 11, 8–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, M.; Majumder, C. Study of the kinetics of arsenic removal from wastewater using Bacillus arsenicus biofilms supported on a Neem leaves/MnFe2O4 composite. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansone-Bertina, L.; Klavins, M.; Viksna, A. Arsenic removal using natural biomaterial-based sorbents. Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 35, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansone-Bertina, L.; Klavins, M.; Eglite, L. Use of peat-based sorbents for removal of arsenic compounds. Open Chem. 2013, 11, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, L.; Siddique, M.A.; Singh, J.; Bharagava, R.N. As(III) and As(V) removal by using iron impregnated biosorbents derived from waste biomass of Citrus limmeta (peel and pulp) from the aqueous solution and ground water. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.M.; Parra, R.R.; Deng, S. Arsenic removal from groundwater by MnO2-modified natural clinoptilolite zeolite: Effects of pH and initial feed concentration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Harris, W.G.; Migliaccio, K. Removal of arsenic by magnetic biochar prepared from pinewood and natural hematite. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Hu, B.; Dang, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Adsorption of arsenic on modified montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 97–98, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-N.; Chai, L.-Y.; Shu, Y.-D. Study of arsenic(V) adsorption on bone char from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fufa, F.; Alemayehu, E.; Lennartz, B. Sorptive removal of arsenate using termite mound. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 132, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Gupta, A. Analysis and modeling of fixed bed column operations on As(V) removal by adsorption onto iron oxide-coated cement (IOCC). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 290, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.I.; Qazi, I.A.; Zeb, A.; Habib, A.; Awan, M.A.; Khan, Z. Arsenic Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Pure and Metal-Doped Titania Nanoparticles Coated on Glass Beads: Adsorption and Column Studies. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.K.; Pal, A.; Pal, T. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption on laterite soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2007, 42, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, S.K.; Pal, A.; Pal, T.; Adak, A. Sorption kinetics of arsenic on laterite soil in aqueous medium. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2007, 42, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, S.; Kavalakatt, S.S.; Pal, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Mandal, M.; Pal, T. Removal of arsenic using hardened paste of Portland cement: Batch adsorption and column study. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3780–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altundoğan, H.S.; Altundoğan, S.; Tümen, F.; Bildik, M. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption on red mud. Waste Manag. 2000, 20, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Singh, P.; Paling, E.; Delides, S. Arsenic removal from contaminated water by natural iron ores. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Mondal, N.K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Das, B.; Das, K. Removal of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) on chemically modified low-cost adsorbent: Batch and column operations. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korpayev, S.; Kavaklı, C.; Tilki, S.; Kavaklı, P.A. Novel cotton fabric adsorbent for efficient As(V) adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34610–34622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam Khan, T.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Ali, I. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies of As(V) removal from water by zirconium oxide-coated marine sand. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5425–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.K.; Ribeiro, A.; Mateus, E. Biosorption of arsenic(V) with Lessonia nigrescens. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raichur, A.; Panvekar, V. Removal of As(V) by adsorption onto mixed rare earth oxides. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, H.H.; Demarchi, C.A.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Greneche, J.M.; Nedelko, N.; Slawska-Waniewska, A. Adsorption of As(III) on chitosan-Fe-crosslinked complex (Ch-Fe). Chemosphere 2011, 82, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, G.N.; Raji, C.; Anirudhan, T.S. Evaluation of coconut husk carbon for the removal of arsenic from water. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3062–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polowczyk, I.; Bastrzyk, A.; Ulatowska, J.; Szczałba, E.; Koźlecki, T.; Sadowski, Z. Influence of pH on arsenic(III) removal by fly ash. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2612–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, J.; Martinez, M.; De Pablo, J.; Rovira, M.; Duro, L. Arsenic sorption onto natural hematite, magnetite, and goethite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Issa, N.; Rajaković-Ognjanović, V.N.; Marinković, A.; Rajaković, L.V. Separation and determination of arsenic species in water by selective exchange and hybrid resins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.; Fan, M.; Xu, M.; Brown, R.; Sung, S.; Saha, B. Adsorption of arsenic(V) by activated carbon prepared from oat hulls. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedlund, P.J.; Webster, J.G. Adsorption and polymerisation of silicic acid on ferrihydrite, and its effect on arsenic adsorption. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3413–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Burton, E.; Wang, H.; Shaheen, S.; Rinklebe, J.; Lüttge, A. Arsenic removal by perilla leaf biochar in aqueous solutions and groundwater: An integrated spectroscopic and microscopic examination. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, B.; Li, Y. Enhanced arsenic removal by biochar modified with nickel (Ni) and manganese (Mn) oxyhydroxides. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 37, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.; Creamer, A.E.; He, F. Adsorptive removal of arsenate from aqueous solutions by biochar supported zero-valent iron nanocomposite: Batch and continuous flow tests. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Peng, Z.; Lyu, H.; Huang, H.; Nan, Q.; Tang, J. Synthesis and characterization of an iron-impregnated biochar for aqueous arsenic removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-H.; Nakajima, T.; Ohki, A. Adsorption and removal of arsenic(V) from drinking water by aluminum-loaded Shirasu-zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Tong, Q.; Shan, W.; Xing, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wen, S.; Lou, Z. Arsenic transformation and adsorption by iron hydroxide/manganese dioxide doped straw activated carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Xionghui, J.; Ma, L. Efficient arsenate removal by magnetite-modified water hyacinth biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Sari, A.; Mendil, D.; Uluozlu, O.D.; Soylak, M.; Dogan, M. Characterization of biosorption process of As(III) on green algae Ulothrix cylindricum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Cao, X. Sorption of arsenic onto Ni/Fe layered double hydroxide (LDH)-biochar composites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 17792–17799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Farooqi, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Ali, F.; Ali, S.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Arshad, M. Arsenic(V) biosorption by charred orange peel in aqueous environments. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Sharif, F.; Bashir, S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Wang, H.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; et al. Arsenic removal by natural and chemically modified watermelon rind in aqueous solutions and groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Vidyarthi, S.R.; Sankararamakrishnan, N. Concurrent removal of As(III) and As(V) using green low cost functionalized biosorbent—Saccharum officinarum bagasse. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Basu, J.K.; De, S. Removal of arsenic from synthetic and natural groundwater using acid-activated laterite. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2010, 29, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.A.; Zhu, J.; Muhammad, N.; Sheng, T.; Xu, X. Effect of synthesis methods on magnetic Kans grass biochar for enhanced As(III, V) adsorption from aqueous solutions. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 71, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoglu, G.; Altintas, B.; Arica, M.Y. Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamic parameters of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by using a new strong cation-exchange resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Kuang-Wang, M.; Li, Y.-S. Removal of Nickel from Aqueous Solution Using Wine Processing Waste Sludge. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, C.O.; Webster, D.S.; Sabatini, D.A. Arsenate adsorption onto iron oxide amended rice husk char. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.-G.; Liu, S.-B.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zeng, G.-M.; Tan, X.; Yang, C.-P.; Ding, Y.; Yan, Z.-L.; Cai, X. Sorption performance and mechanisms of arsenic(V) removal by magnetic gelatin-modified biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, D.; Viraraghavan, T. Arsenic removal from an aqueous solution by modified A. niger biomass: Batch kinetic and isotherm studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chammui, Y.; Sooksamiti, P.; Naksata, W.; Thiansem, S.; Arqueropanyo, O.-A. Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by adsorption on Leonardite. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.A.; Sheng, T.; Sun, C.; Xue, X.; Tan, L.; Xu, X. Arsenic Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Fe3O4-HBC Composite: Effect of Calcination on Adsorbents Performance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Qiu, W.; Wang, D.; Huang, Q.; Song, Z.; Chau, H.W. Arsenic removal in aqueous solution by a novel Fe-Mn modified biochar composite: Characterization and mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ding, Z.; Zimmerman, A.; Wang, S.; Gao, B. Batch and column sorption of arsenic onto iron-impregnated biochar synthesized through hydrolysis. Water Res. 2015, 68, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Stüben, D.; Berner, Z.A. Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by natural siderite and hematite. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, T. Removal of Dissolved Arsenic by Pyrite Ash Waste. Mine Water Environ. 2017, 36, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsuri, W.; Sadegh-Zadeh, F.; Seh-Bardan, B.J. Adsorption of As(III) and As(V) by Fe coated biochars and biochars produced from empty fruit bunch and rice husk. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedillo, M.J.J.; Olguín, M.; Fall, C.; Colin-Cruz, A. Adsorption capacity of iron- or iron–manganese-modified zeolite-rich tuffs for As(III) and As(V) water pollutants. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 54, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskan, M.B.; Pala, A. Removal of arsenic from drinking water using modified natural zeolite. Desalination 2011, 281, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-S.; Ofomaja, A. Kinetics and thermodynamics of lead ion sorption on palm kernel fibre from aqueous solution. Process. Biochem. 2005, 40, 3455–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-S.; Ofomaja, A. Effects of calcium competition on lead sorption by palm kernel fibre. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 120, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, B.; Varnoosfaderani, S.; Hebard, A.; Yao, Y.; Inyang, M. Preparation and characterization of a novel magnetic biochar for arsenic removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 130, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Olusegun, A.K. Magnetic nanoscale Fe–Mn binary oxides loaded zeolite for arsenic removal from synthetic groundwater. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S. Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometrics 2004, 59, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process. Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Cedillo, M.J.; Olguín, M.T.; Fall, C.; Colin-Cruz, A. As(III) and As(V) sorption on iron-modified non-pyrolyzed and pyrolyzed biomass from Petroselinum crispum (parsley). J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 117, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorraji, M.S.S.; Mirmohseni, A.; Tasselli, F.; Criscuoli, A.; Carraro, M.; Gross, S.; Figoli, A. Preparation, characterization and application of iron (III)-loaded chitosan hollow fiber membranes as a new bio-based As (V) sorbent. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Tan, F.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y. ZnCl2-activated biochar from biogas residue facilitates aqueous As(III) removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 377, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Bricka, M.; Smith, F.; Yancey, B.; Mohammad, J.; Steele, P.H.; Franco, M.A.; Gómez-Serrano, V.; Gong, H. Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Adsorbents | Treatments | Isotherm Model Fit | pH | Adsorption Capacities mg/g | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As(III) | As(V) | |||||
| Wheat Straw [43] | NaHCO3 | Langmuir | 7 | No data | 0.097 | |
| Wheat Straw [44] | FeSO4 and FeCl3 | Langmuir | 6 | No data | 30.24 | |
| Black Tea [45] | No Treatments | Freundlich and Langmuir | 6 | No data | 1.76 | |
| G. cambogia fruits rinds [46] | IICT Technology | Langmuir | 6 | 128.10 | No data | |
| Coconut Fibers [47] | HNO3 and NaOH | Freundlich | 4 | 0.12 | No data | |
| Sugarcane bagasse [48] | (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O) | Langmuir | 6 | 0.6 | No data | |
| Sawdust [49] | Fe(III) | Langmuir | 8 | No data | 5.8 | |
| Orange Peel [50] | No Treatments | Freundlich | 7 | No data | 4.8 | |
| Moringa Lamarck seed [51] | No Treatments | Langmuir | 8 | 1.5 | 2.1 | |
| Rice Husk [52] | No Treatments | Freundlich | 7 | 220.1 | No data | |
| Mango leaf powder [52] | No Treatments | Freundlich | 7 | 250.07 | No data | |
| Mosambi Citrus Peel [53] | No Treatments | Freundlich | 6 | 2.12 | 3.32 | |
| Rice straw [54] | Fe(NO3)3 | Langmuir | 4 | No data | 21.739 | |
| Rice husk [55] | Fe(III) | Langmuir | 4 | No data | 2.47 | |
| Corncob husk [56] | FeCl3 | Langmuir | 6 | 50 | No data | |
| Coconut coir pith (CP) [57] | Epichlorohydrin and dimethylamine | Langmuir | 7 | No data | 13.57 | |
| Groundnut shells [58] | No Treatments | Langmuir | 8 | 0.014 | No data | |
| Bead Cellulose (Cotton) [59] | (FeCl3‚6H2O) | Langmuir | 9 | 4 | 99.6 | 33.2 |
| Sawdust [60] | ZrOCl₂·8H₂O | Langmuir | 9 | 4 | 29 | 12 |
| Rice husk [61] | Iron oxide | Langmuir | 6 | No data | 82 | |
| Paddy Husk Ash [62] | AlCl3·6H2O | Freundlich | 4 | No data | 0.063 | |
| Zeolite stones [63] | Al2(SO4)·16H2O | Freundlich | 6 | No data | 208 | |
| Iron oxide-coated sand [64] | Fe(III) | Langmuir | 7.5 | 28.57 | No data | |
| Goethite [65] | No treatment | No data | 5 | No data | 1 | |
| Iron-coated zeolite [66] | FeCl3 | Langmuir | 4 | No data | 0.68 | |
| Iron-modified activated carbon [67] | Fe(NO3)3·9H2O | Langmuir | 8 | 6 | 43.6 | 51.3 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbent Dosage (g) | Solution Quantity (mL) | Intial Concentration (mg/L) | Removal (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As(V) | As(III) | ||||
| Peat-based sorbents [96] | 0.5 | 40 | 8–904 | No data | 100–43 |
| Red mud-modified biochar (RM-BC) [87] | 0.12 | 30 | 1–50 | 100–32 | 50–4 |
| Novel magnetic chitosan nanoparticle (MCNP) [89] | 0.05 | 100 | 0.2–50 | 100–65 | 100–60 |
| Hematite Pinewood biochar (HPB) [99] | 0.05 | 20 | 1–50 | 25–2 | No data |
| Modified clinoptilolite zeolite (MCZ) [98] | 1 | 200 | 0.005–0.05 | 55–40 | No data |
| Iron-modified peat [96] | 0.5 | 40 | 100–270 | 100–70 | No data |
| Biomass of Citrus limmeta (PPAC-500) [97] | 0.15 | 50 | 0.05–2.5 | 100–62 | 93–55.2 |
| Leaves of P. roxburghii powder [88] | 0.2–2 | 50 | 10 | 4–75 | No data |
| Iron modified montmorillonites [100] | 0.025–0.3 | 25 | 0.005 | 97–100 | 96–100 |
| Corynebacterium glutamicum MTCC 2745 biofilm supported on Neem leaves NL/MnFe2O4 composite [93] | 0.01–0.1 | 100 | 50 | 79–82.5 | 72–77 |
| Bacillus arsenicus biofilms supported on a Neem leaves/MnFe2O4 composite [94] | 0.01–0.1 | 100 | 50 | 86–89 | 79–83 |
| M. charantia plants biomass [91] | 0.05–0.25 | 50 | 0.5 | No data | 66–88 |
| Bone char [101] | 0.05–0.4 | 500 | 0.5 | 30–100 | No data |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbent Dosage (g) | Intial Concentration (mg/L) | Regenetaion | Adsorption Capacity (%) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As(V) | As(III) | ||||||
| The green alga (U. cylindricum) biomass [129] | 0.1 | 10 | 10 | No data | 96–93 | Tuzen M. et al., 2009 | |
| Ni/Mn-layered double hydroxide (LDH) biochar (NMMB) [123] | 0.1 | 40 | 3 | 100–98 | No data | Wang S. S. et al., 2016a | |
| Ni/Fe layered double hydroxide (LDH)-biochar (NFMB) [130] | 0.1 | 50 | 3 | 100–92 | No data | Wang S. S. et al., 2016b | |
| Charred orange peel (COP) [131] | 0.2 | 200 | 3 | 100–90 | No data | Abid M. et al., 2016 | |
| Fe-Mn-straw biochars [127] | 1 | 20 | 3 | No data | 85–78 | Xiong Y. et al., 2017 | |
| Xanthated water melon rind (X-WMR) [132] | 0.2 | As(V) 5 | As(III) 4 | 4 | 100–50 | 100–20 | Shakoor M. B. et al., 2018 |
| Magnetite-modified water hyacinth Biochar (MW2501) [128] | 0.2 | 5 | 4 | 100–50 | No data | Zhang F. et al., 2016 | |
| 20% Iron-impregnated corn straw biochar [125] | 0.2 | 40 | 3 | 87–70 | No data | He R. Z. et al., 2018 | |
| Modified Saccharum officinarum bagasse (SCB-S) [133] | 0.05 | 0.5 | 5 | 100–78 | 100–86 | Gupta A. et al., 2015 | |
| Adsorbents | Thermodynamics | Kenetic | Influence Ions (mg/L) | Removal As (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As(III) | As(V) | |||||
| Acid-activated laterite (AAL) [134] | Endothermic | Pseudo-second-order | PO43− | 0–10 | 89–70 | 95–85 |
| SO42− | 0–40 | 89–68 | 95–83 | |||
| Fe3O4-HBC-1000 °C (Honeycomb Briquette Cinders) [142] | Endothermic | Pseudo-second-order | PO43− | 0–9.5 | 100–15 | 100–60 |
| Fe-Mn modified corn stem biochar (FMBC) [143] | Endothermic | Pseudo-second-order | PO43− | 0–9500 | 100–88 | No data |
| Iron oxide amended rice husk char (950 IOA-RHC) [138] | Endothermic | Pseudo-second-order | PO43− | 0–10 | No data | 100–65 |
| Fe-impregnated hickory chips biochar [144] | No data | No data | PO43− | 0–50 | No data | 100–15 |
| Magnetic Kans Grass (Saccharum spontaneum) Biochars (MKGB4) [135] | No data | Pseudo-second-order | PO43− | 0–95 | 100–20 | 100–80 |
| Leonardite chars [141] | No data | No data | SO42− | 0–5000 | 98–92 | 99–94 |
| Siderite SIO3 [145] | No data | No data | PO43− | 0–10 | No data | 64–28 |
| Hematite HIO1 [145] | No data | First-order | PO43− | 0–10 | No data | 69–36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
YEO, K.F.H.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Dong, Y. Arsenic Removal from Contaminated Water Using Natural Adsorbents: A Review. Coatings 2021, 11, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111407
YEO KFH, Li C, Zhang H, Chen J, Wang W, Dong Y. Arsenic Removal from Contaminated Water Using Natural Adsorbents: A Review. Coatings. 2021; 11(11):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111407
Chicago/Turabian StyleYEO, Kanfolo Franck Herve, Chaokun Li, Hui Zhang, Jin Chen, Wendong Wang, and Yingying Dong. 2021. "Arsenic Removal from Contaminated Water Using Natural Adsorbents: A Review" Coatings 11, no. 11: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111407
APA StyleYEO, K. F. H., Li, C., Zhang, H., Chen, J., Wang, W., & Dong, Y. (2021). Arsenic Removal from Contaminated Water Using Natural Adsorbents: A Review. Coatings, 11(11), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11111407









