Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Light-Wood-Framed Shear Walls Strengthened with Parallel Strand Bamboo Panels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Program
2.1.1. Material Properties
2.1.2. Test Specimens
2.1.3. Test Setup, Instrumentation, and Test Procedure
2.1.4. Load–Displacement Relationships and Lateral Performance Parameters
2.2. Nonlinear Finite-Element Analysis
2.2.1. Nonlinear Finite-Element Analysis Model
2.2.2. Parametric Studies
2.3. Comparison with Design Codes
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Results
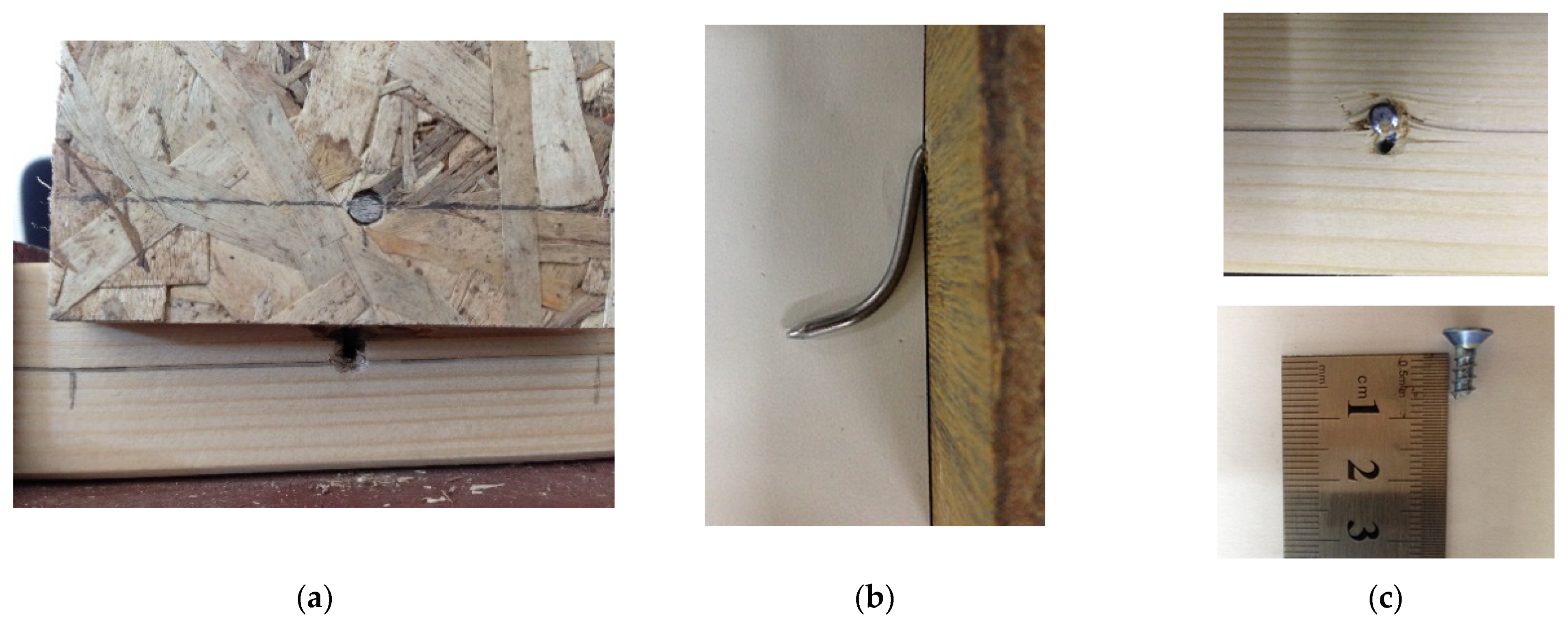
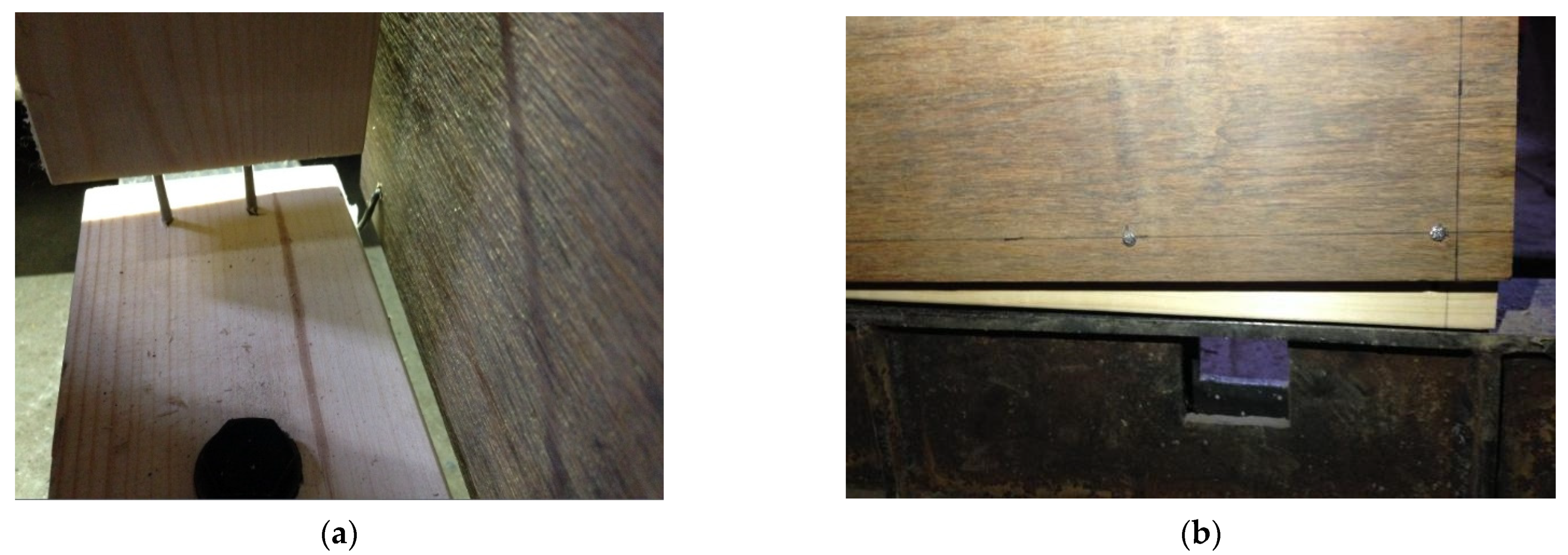
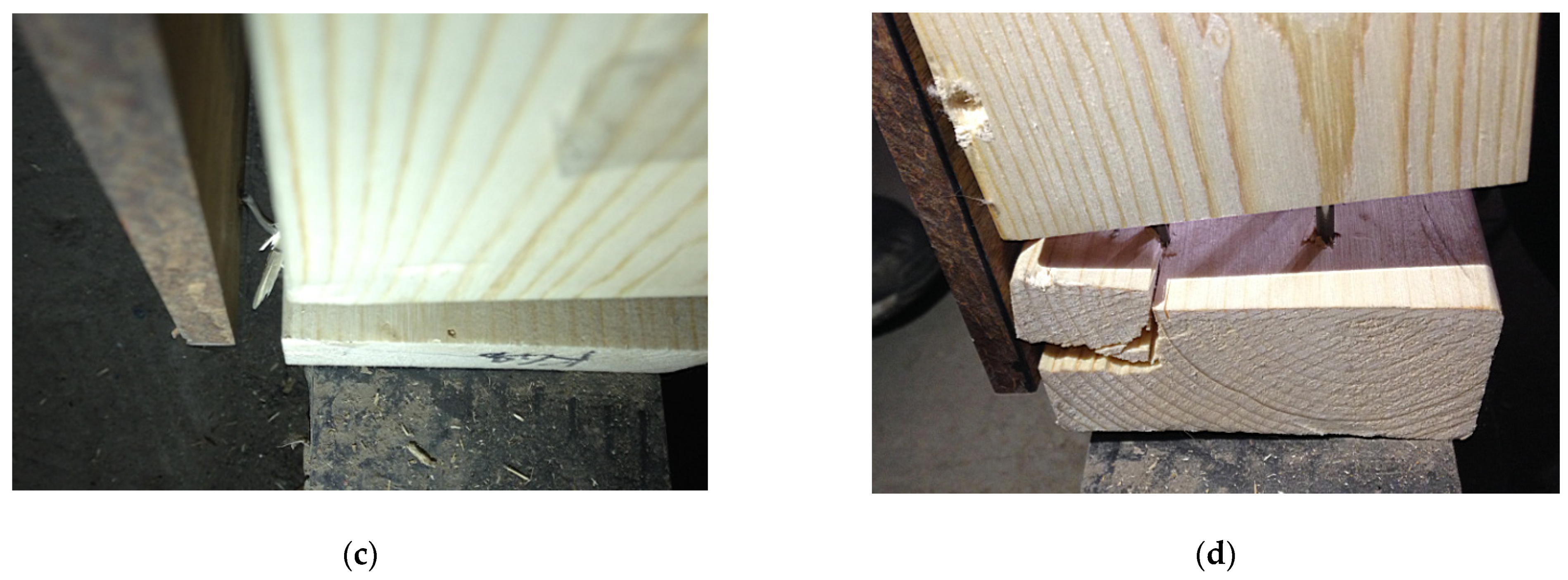
3.1.1. Failure Modes
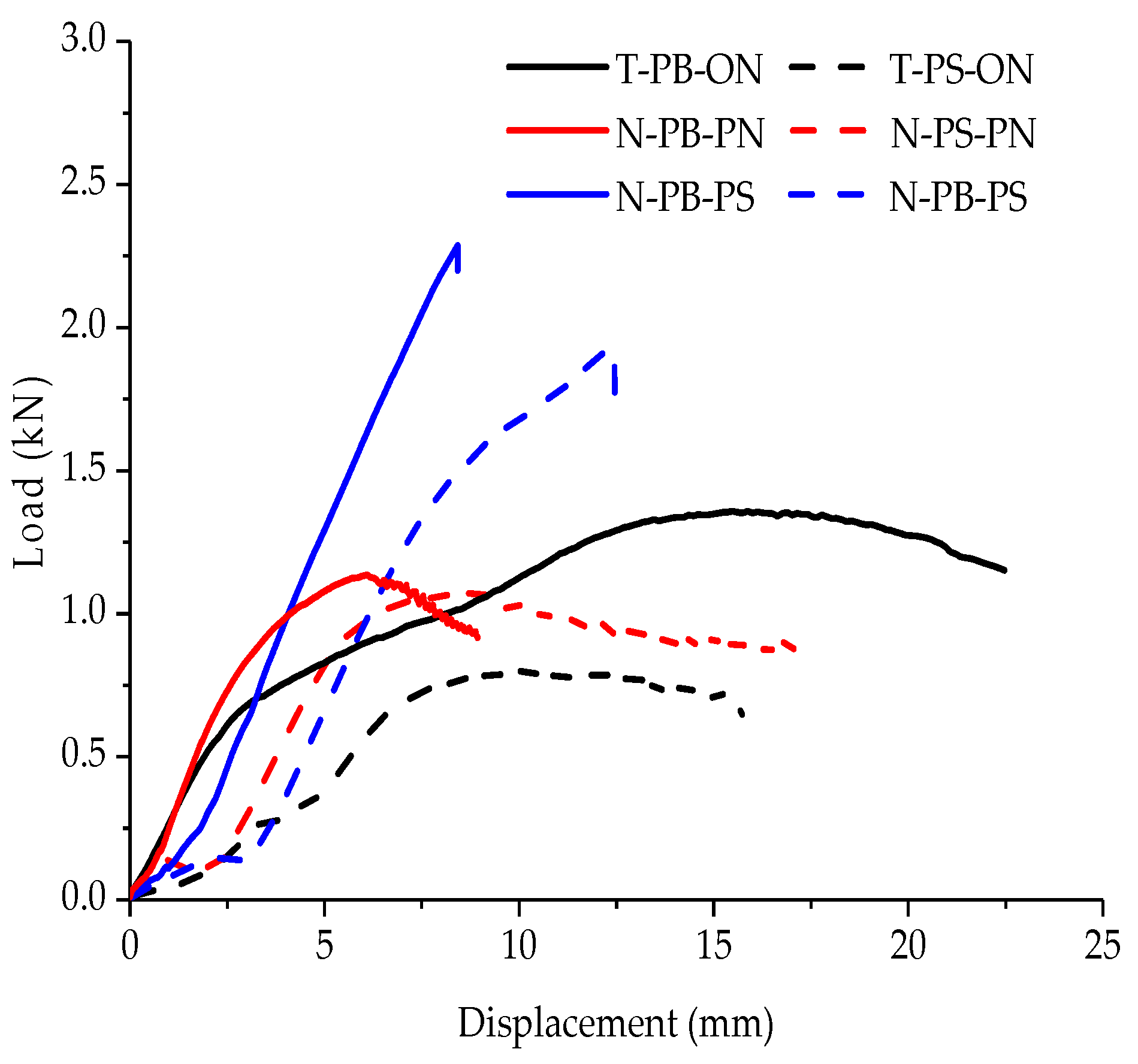
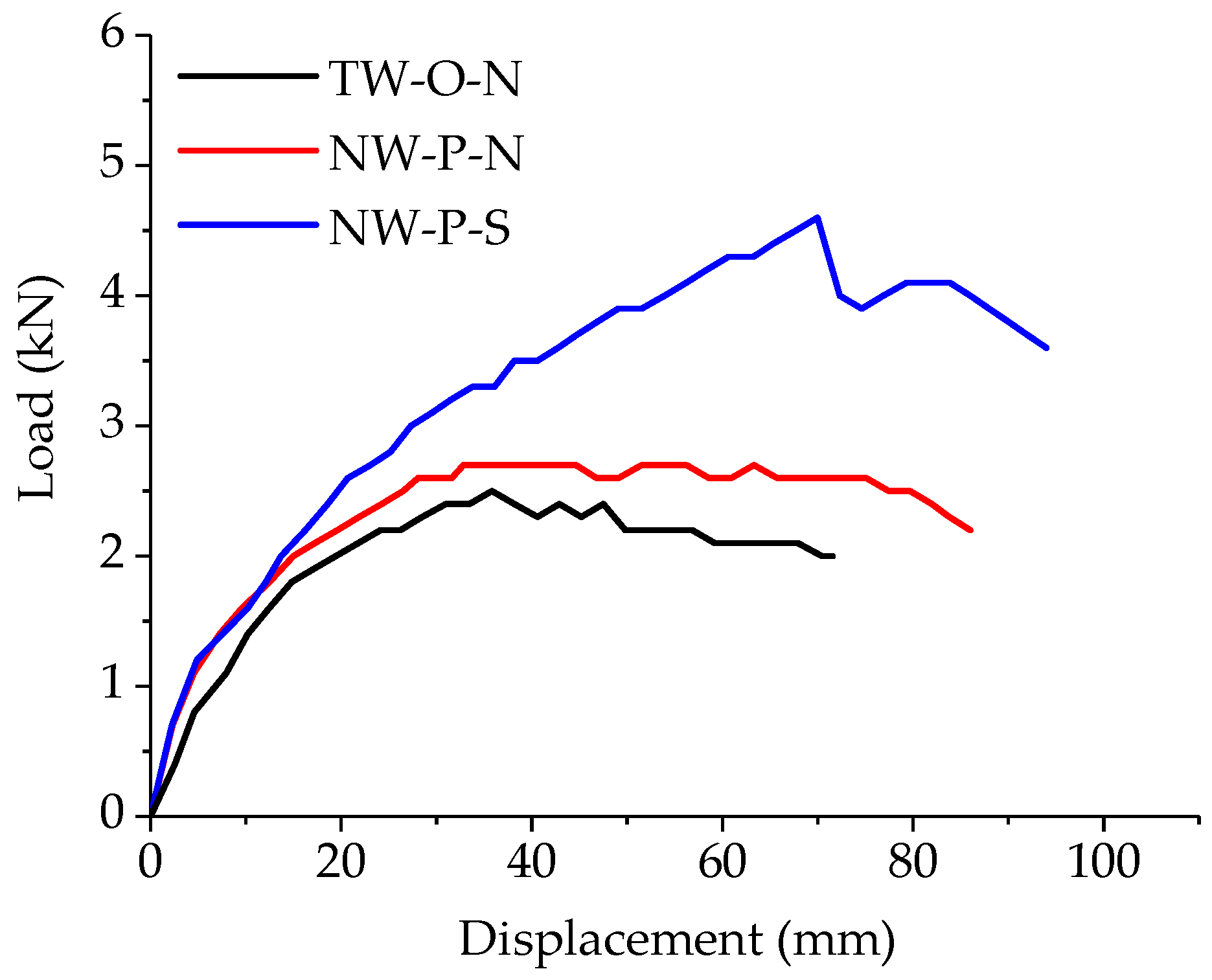
3.1.2. Load–Displacement Relationships and Lateral Performance Parameters
3.2. FEA Results
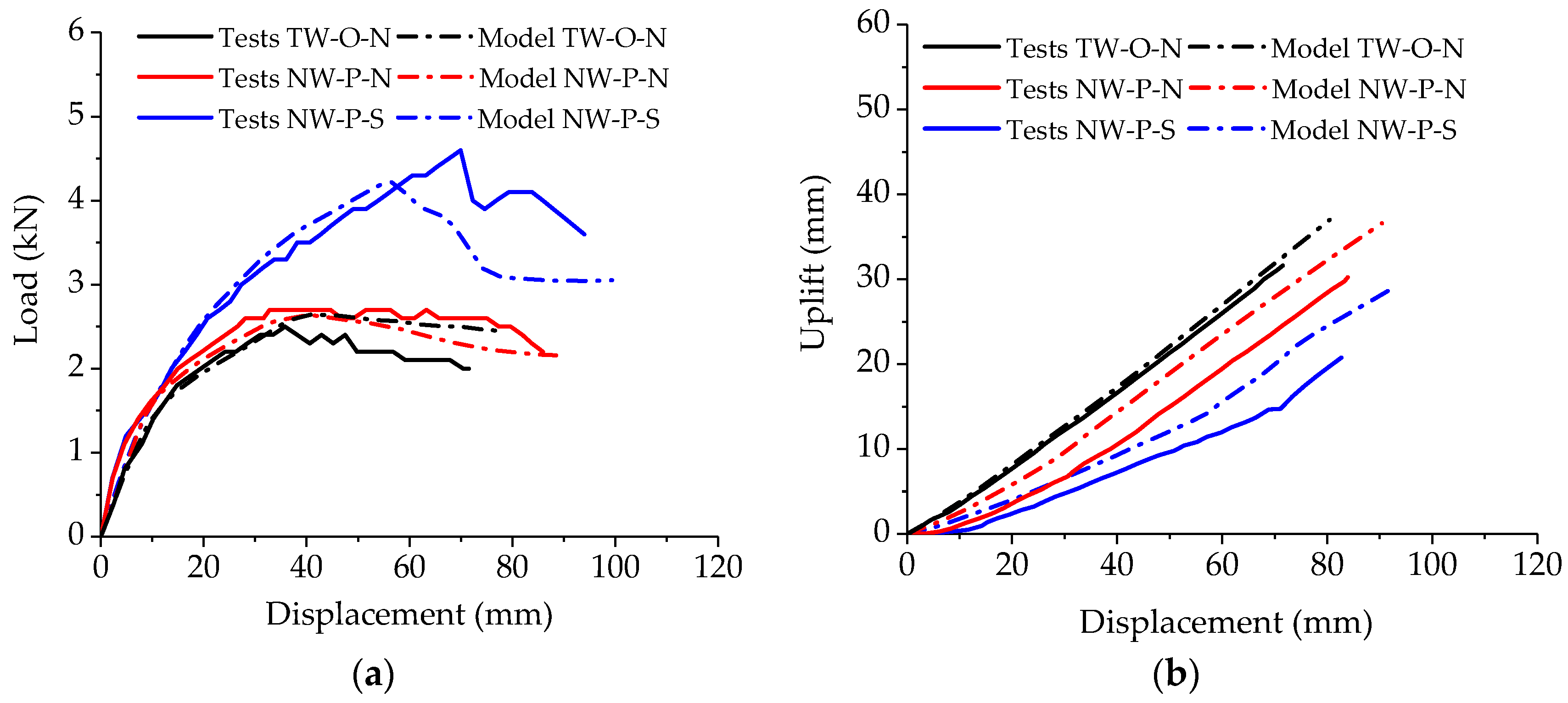
3.2.1. FEA Model Verification
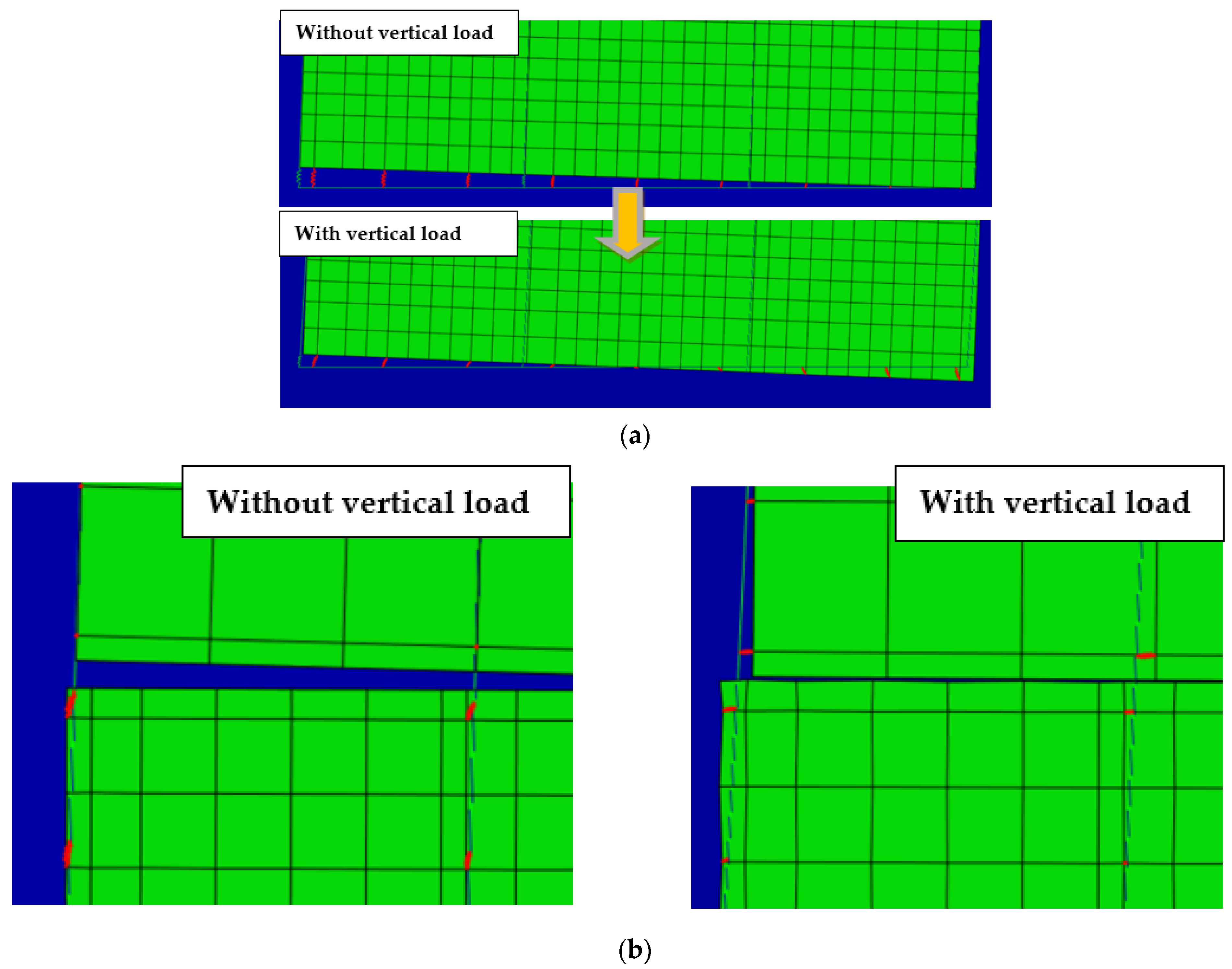
3.2.2. Parametric Studies
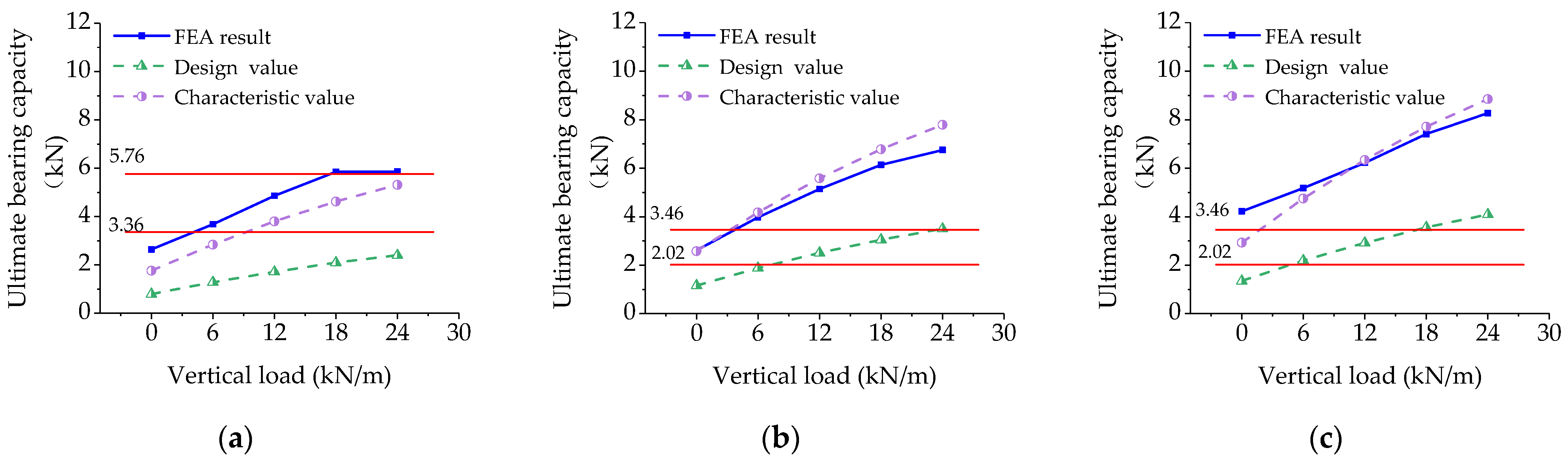
3.3. Comparison with Design Codes
3.3.1. Comparison of Bearing Capacity with Eurocode 5
3.3.2. Comparison of Bearing Capacity with Chinese Code
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ding, M.; Wang, M.; Xu, X. Construction of a phytic acid–silica system in wood for highly efficient flame retardancy and smoke suppression. Materials 2021, 14, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengsri, P.; Ngamkhanong, C.; De Melo, A.L.O.; Kaewunruen, S. Experimental and numerical investigations into dynamic modal parameters of fiber-reinforced foamed urethane composite beams in railway switches and crossings. Vibration 2020, 3, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Landry, V.; Blanchet, P.; Hoang, D.-T.; Dagenais, C. Fire performance of intumescent waterborne coatings with encapsulated APP for wood constructions. Coatings 2021, 11, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létourneau-Gagnon, M.; Dagenais, C.; Blanchet, P. Fire performance of self-tapping screws in tall mass-timber buildings. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasburgh, L.E.; Zelinka, S.L.; Bishell, A.B.; Kirker, G.T. Durability and fire performance of charred wood siding (Shou Sugi Ban). Forests 2021, 12, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, M.; Curling, S.; Dimitriou, A.; Ormondroyd, G. Review of functional treatments for modified wood. Coatings 2021, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, M.A.; Piazza, M. Seismic strengthening and seismic improvement of timber structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 97, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caniato, M.; Bettarello, F.; Ferluga, A.; Marsich, L.; Schmid, C.; Fausti, P. Acoustic of lightweight timber buildings: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.-J.; Li, Y. Seismic collapse risk of light-frame wood construction considering aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties. Struct. Saf. 2010, 32, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB50005-2017. Code for Design of Timber Structures; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Lam, F.; Prion, H.G.L.; He, M. Lateral resistance of wood shear walls with large sheathing panels. J. Struct. Eng. 1997, 123, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gangi, G.; Demartino, C.; Quaranta, G.; Monti, G. Dissipation in sheathing-to-framing connections of light-frame timber shear walls under seismic loads. Eng. Struct. 2020, 208, 110246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasson, S.; Yasumura, M.; Daudeville, L. Sensitivity study of the finite element model for wood-framed shear walls. J. Wood Sci. 2002, 48, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzaleh, A.S.; Steiger, R. Experimental investigation of OSB sheathed timber frame shear walls with strong anchorage subjected to cyclic lateral loading. Eng. Struct. 2020, 226, 111328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdret, Y.; Faye, C.; Elachachi, S.; Le Magorou, L.; Garcia, P. Experimental investigation on stapled and nailed connections in light timber frame walls. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seim, W.; Kramar, M.; Pazlar, T.; Vogt, T. OSB and GFB as sheathing materials for timber-framed shear walls: Comparative study of seismic resistance. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, E4015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, H. Experimental investigation on the behavior of plybamboo sheathing-to-framing screwed connections. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gangi, G.; DeMartino, C.; Quaranta, G. Bamboo lightweight shear walls: Modeling and identification of sheathing-to-framing connections for seismic response analysis. Int. J. Struct. Glas. Adv. Mater. Res. 2020, 4, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, S.; Correal, J.; Yamin, L.; Ramirez, F. Cyclic performance of glued laminated guadua bamboo-sheathed shear walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 139, 2028–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, R.; Shan, B. Production, environmental impact and mechanical properties of glubam. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, R.; Monti, G. Studies of nail connectors used in wood frame shear walls with ply-bamboo sheathing panels. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04014216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ashraf, M.; Li, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Al-Deen, S.; Hazell, P.J. An experimental investigation on parallel bamboo strand lumber specimens under quasi static and impact loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 228, 116724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaowana, K.; Wisadsatorn, S.; Chaowana, P. Bamboo as a sustainable building material—Culm characteristics and properties. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabia, A.; Itani, R. Static and dynamic modeling of light-frame wood buildings. Comput. Struct. 1997, 63, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, A.F.; Datin, P.L.; Prevatt, D.O.; Gupta, R.; Van De Lindt, J.W. Database-assisted design methodology to predict wind-induced structural behavior of a light-framed wood building. Eng. Struct. 2011, 33, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaders, P.; Gupta, R.; Miller, T.H. Monotonic and cyclic load testing of partially and fully anchored wood-frame shear walls. Wood Fiber Sci. J. Soc. Wood Sci. Technol. 2009, 41, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lebeda Daňa, J.; Gupta, R.; Rosowsky David, V.; Dolan, J.D. Effect of hold-down misplacement on strength and stiffness of wood shear walls. Pract. Period. Struct. Des. Constr. 2005, 10, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnston Adrienne, R.; Dean Peter, K.; Shenton Harry, W. Effects of vertical load and hold-down anchors on the cyclic response of wood framed shear walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2006, 132, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, Ö.; Togay, A.; Işleyen, K.; Söğütlü, C.; Döngel, N. Hysteretic behavior of timber framed shear wall with openings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 116, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean Peter, K.; Shenton Harry, W. Experimental investigation of the effect of vertical load on the capacity of wood shear walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2005, 131, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Code for Acceptance of Construction Quality of Timber Structures; GB50206-2012; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Method for Determination of the Moisture Content of Wood; GB/T 1931-2009; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. General Requirements for Physical and Mechanical Tests of Wood; GB/T 1928-2009; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Method of Testing in Compressive Strength Parallel to Grain of Wood; GB/T 1935-2009; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Method of Testing in Tensile Strength Parallel to Grain of Wood; GB/T 1938-2009; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Method of Testing in Compression Perpendicular to Grain of Wood; GB/T 1939-2009; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Method for Determination of the Modulus of Elasticity in Compression Perpendicular to Grain of Wood; GB/T 1943-2009; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Method for Determination of the Modulus of Elasticity in Elasticity in Static Bending; GB/T 1936.2-2009; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Determining bending Yield Moment of Nails; ASTM F1575-03; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Standard Test Methods for Mechanical Fasteners in Wood; ASTM D1761; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Standard Practice for Static Load Test for Shear Resistance of Framed Walls for Buildings; ASTM E564; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. Standard Test Methods for Cyclic (Reversed) Load Test for Shear Resistance of Vertical Elements of the Lateral Force Resisting Systems for Buildings; ASTM E2126-09; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, R. Lateral loading behaviors of lightweight wood-frame shear walls with ply-bamboo sheathing panels. J. Struct. Eng. 2015, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Z. Lateral loading performance of lightweight glubam shear walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Magnusson, H.; Lam, F.; Prion, H.G.L. Cyclic performance of perforated wood shear walls with oversize OSB panels. J. Struct. Eng. 1999, 125, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABAQUS Analysis User’ s Manual, Version 6.12; Dassault Systèmes: Pawtucket, RI, USA, 2012.
- Dolan, J.D.; Foschi, R.O. Structural analysis model for static loads on timber shear walls. J. Struct. Eng. 1991, 117, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, P.; Lindt, J. Experimental and numerical assessment of woodframe sheathing layer combinations for use in strength-based and performance-based design. J. Struct. Eng. 2014, 142, E4014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, J.P.; Fonseca, F.S. Analytical model for sheathing-to-framing connections in wood shear walls and diaphragms. J. Struct. Eng. 2005, 131, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, W.; Shirazi, S.M.H. Corotational model for cyclic analysis of light-frame wood shear walls and diaphragms. J. Struct. Eng. 2013, 139, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Dolan, J. Development of a wood-frame shear wall model in ABAQUS. J. Struct. Eng. 2009, 135, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Standardization CEN. Eurocode 5: Design of Timber Structures—Part 1-1: General—Common Rules and Rules for Buildings; EN 1995-1-1; European Committee for Standardization CEN: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]

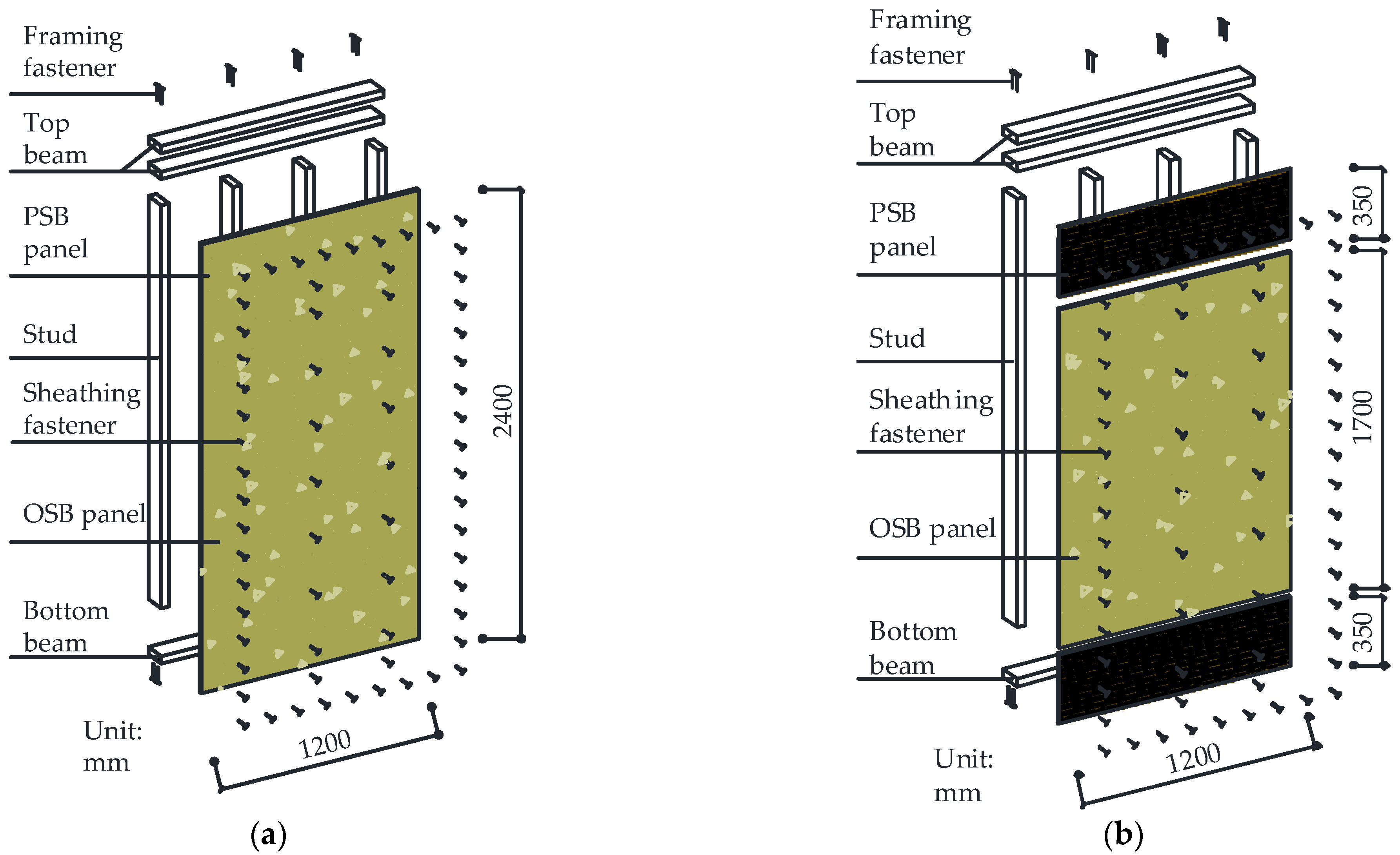

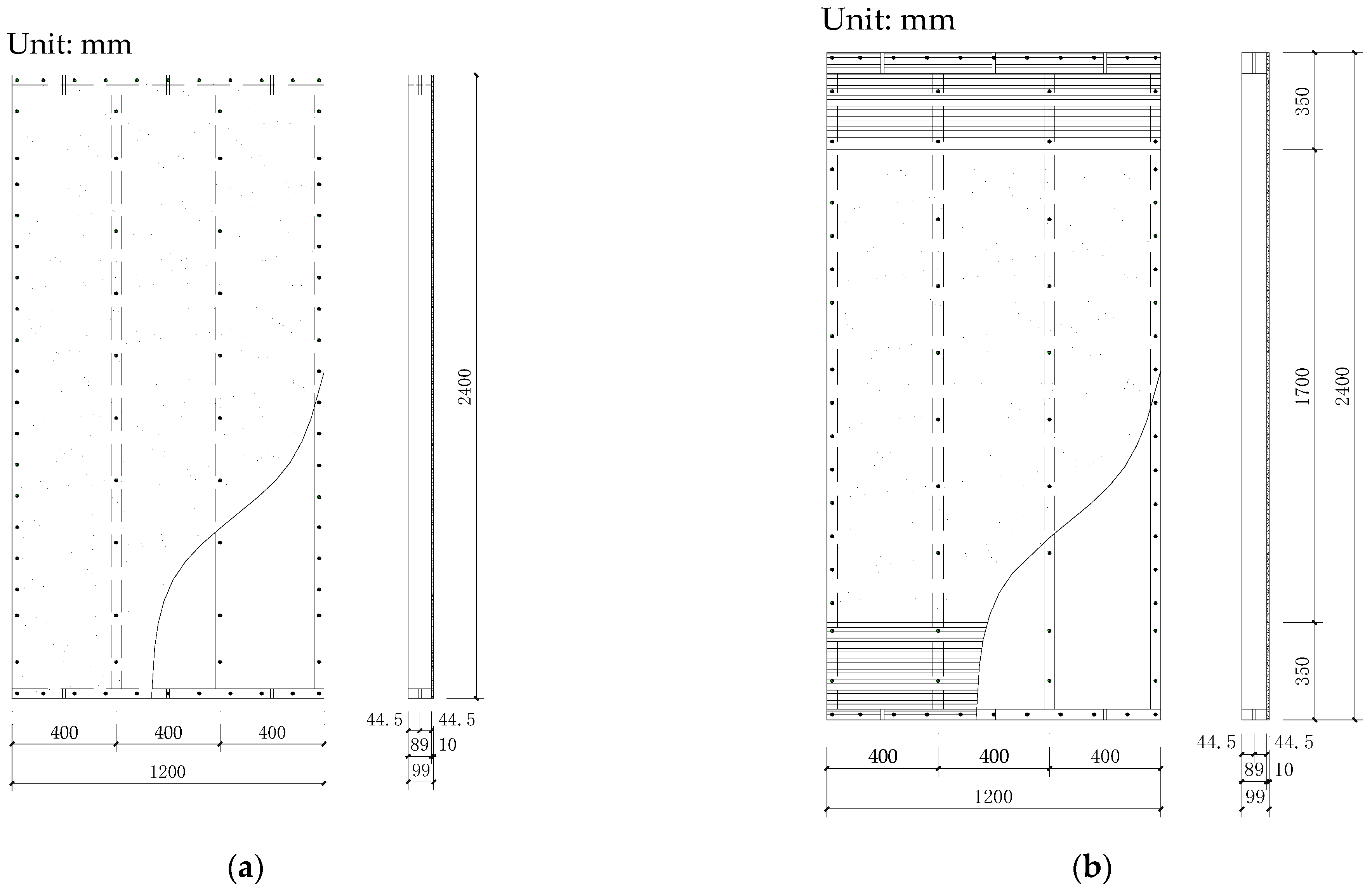

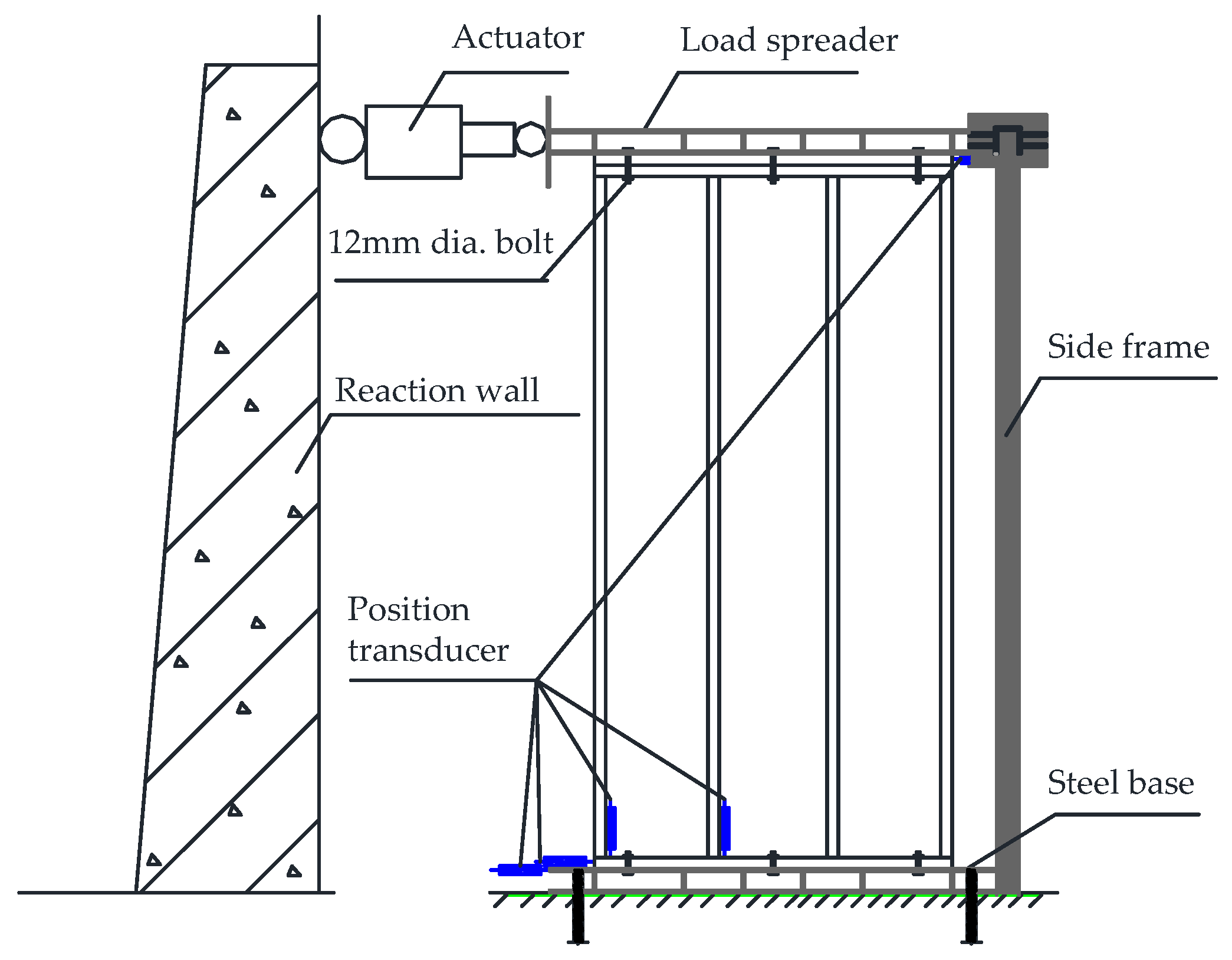
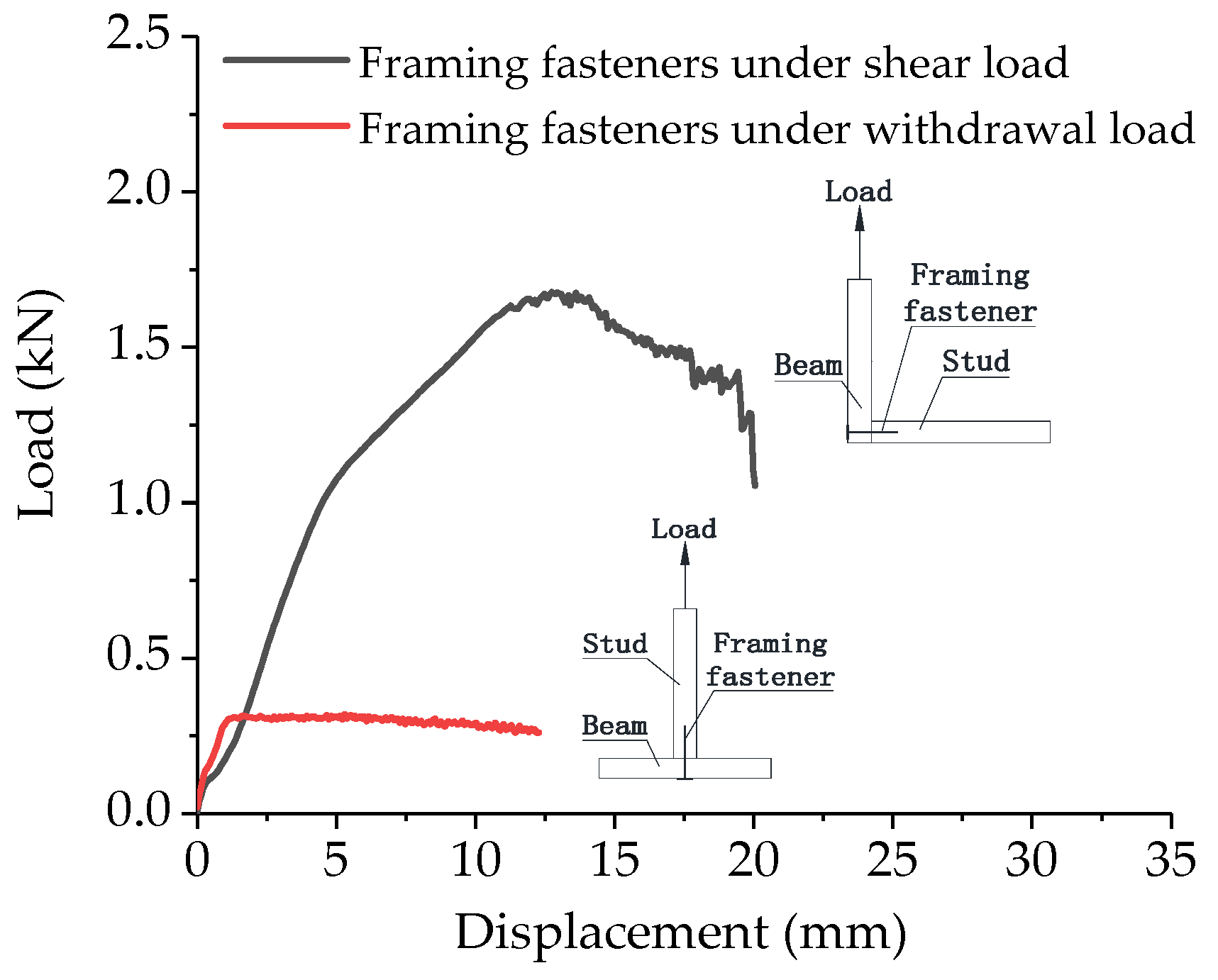
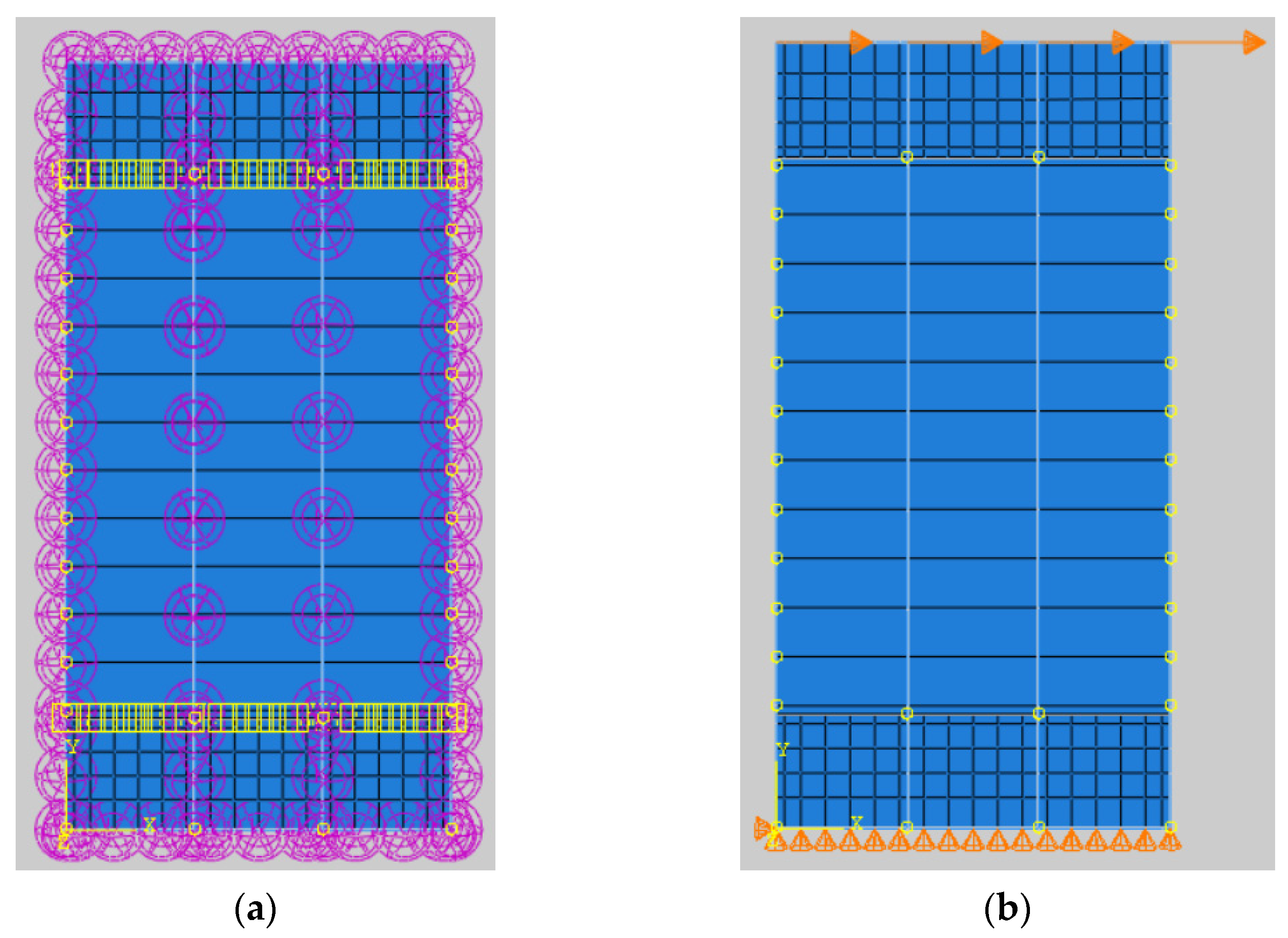








| Element | Material | Specifications | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stud | SPF | Cross-sectional dimensions: 38 mm × 89 mm | |
| Top and bottom beam | |||
| Sheathing panel | OSB | t = 10 mm | |
| PSB | t = 10 mm | ||
| Fastener | Framing nail | Smooth nail | dn = 3.5 mm, l = 85 mm |
| Sheathing fastener | Smooth nail | dn = 2.5 mm, l = 50 mm | |
| Wood screw | de = 2.5 mm, l = 50 mm | ||
| Material Properties | SPF | OSB | PSB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture content | 12% | 9% | 7% |
| Density (kg/m3) | 420 | 560 | 1100 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 71.57 | 13.72 | 115.50 |
| Compression Strength (MPa) | 40.03 | 6.14 | 108.28 |
| Elastic Modulus x direction Ex (Mpa) | 10,000 | 3100 | 12,000 |
| Elastic Modulus y direction Ey (Mpa) | 880 | 1450 | 1400 |
| Elastic Modulus z direction Ez (Mpa) | 470 | 120 | 760 |
| Grouping | Joints | Sheathing Panel | Type of Joints | Type of Sheathing-Fastener |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | T-PB-ON | OSB | Panel-to-beam joint | Smooth nail |
| T-PS-ON | Panel-to-stud joint | Smooth nail | ||
| N | N-PB-PN | PSB | Panel-to-beam joint | Smooth nail |
| N-PB-PS | Screw | |||
| N-PS-PN | Panel-to-stud joint | Smooth nail | ||
| N-PS-PS | Screw |
| Grouping | Walls | Material of the Sheathing Panels | Fastener Used on OSB Panel | Fastener Used on PSB Panel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | TW-O-N | OSB | Smooth nail | Smooth nail |
| II | NW-P-N | OSB + PSB | Smooth nail | Smooth nail |
| III | NW-P-S | Screw |
| Grouping | Models | Panel-to-Frame Joints | Vertical Load (kN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M-TW-ON | M-TW-ON-VL6 | OSB-smooth nail | 6 |
| M-TW-ON-VL12 | 12 | ||
| M-TW-ON-VL18 | 18 | ||
| M-TW-ON-VL24 | 24 | ||
| M-NW-PN | M-NW-PN-VL6 | (PSB-smooth nail) + (OSB-smooth nail) | 6 |
| M-NW-PN-VL12 | 12 | ||
| M-NW-PN-VL18 | 18 | ||
| M-NW-PN-VL24 | 24 | ||
| M-NW-PS | M-NW-PS-VL6 | (PSB-screw) + (OSB-smooth nail) | 6 |
| M-NW-PS-VL12 | 12 | ||
| M-NW-PS-VL18 | 18 | ||
| M-NW-PS-VL24 | 24 |
| Joints | OSB-Nail | PSB-Nail | PSB-Screw |
| Failure modes | Nail yielding followed by withdrawal of nail from the framing member | Nail yielding followed by withdrawal of nail from the framing member | Brittle failure of screw |
| Failure number | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| Light-Wood-Framed Shear Walls | With OSB-Nail Joints | With OSB-Nail and PSB-Nail Joints | With OSB-Nail and PSB-Screw Joints |
| Failure modes | Tear of OSB sheathing panel near the corners at the bottom | Yielding and withdrawal of nail | Bottom beam failure |
| Failure number | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Grouping | Pmax (kN) | Δfailure (mm) | K (kN/mm) | μ | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-PB-ON | 1.36 | 22.48 | 0.25 | 4.80 | 23.56 |
| T-PS-ON | 0.81 | 15.73 | 0.11 | 2.55 | 8.58 |
| N-PB-PN | 1.13 | 9.03 | 0.37 | 3.50 | 7.38 |
| N-PB-PS | 2.26 | 8.42 | 0.32 | 1.88 | 8.87 |
| N-PS-PN | 1.08 | 17.19 | 0.26 | 5.22 | 13.30 |
| N-PS-PS | 1.93 | 12.42 | 0.30 | 3.32 | 11.85 |
| Grouping | Pmax (kN) | Δfailure (mm) | K (kN/mm) | μ | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW-O-N | 2.50 | 71.56 | 0.14 | 4.70 | 140.33 |
| NW-P-N | 2.76 | 85.63 | 0.17 | 8.58 | 200.31 |
| NW-P-S | 4.61 | 92.10 | 0.16 | 3.47 | 238.18 |
| Grouping of Models | Approximate Global Size of Seeds for End Panels in Mesh Control | Number of Elements | Number of Nodes | Total CPU Time of Job (s) | Ultimate Bearing Capacity (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW-O-N | 100 | 532 | 761 | 14.40 | 2.65 |
| 50 | 976 | 1225 | 16.80 | 2.64 | |
| 25 | 1846 | 2121 | 25.40 | 2.64 | |
| NW-P-N | 100 | 620 | 965 | 13.00 | 2.64 |
| 50 | 981 | 1396 | 18.60 | 2.65 | |
| 25 | 1876 | 2407 | 26.20 | 2.66 | |
| NW-P-S | 100 | 620 | 965 | 16.30 | 4.22 |
| 50 | 981 | 1396 | 23.90 | 4.21 | |
| 25 | 1876 | 2407 | 33.10 | 4.24 |
| Lateral Load Capacity | Calculated according to EC5 (kN) | Calculated according to GB50005 (kN) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSB-Nail | PSB-Nail | PSB-Screw | OSB-Nail | PSB-Nail | PSB-Screw | |
| Characteristic value | 0.626 | 0.661 | 0.781 | 0.474 | 0.696 | 0.791 |
| Design value | 0.482 | 0.509 | 0.601 | 0.214 | 0.313 | 0.365 |
| Vertical Load (kN/m) | M-TW-ON | M-NW-ON | M-NW-OS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEA | Design | Characteristic | FEA | Design | Characteristic | FEA | Design | Characteristic | |
| 0 | 2.64 | 1.79 | 2.32 | 2.61 | 1.89 | 2.45 | 4.22 | 2.23 | 2.89 |
| 6 | 3.68 | 2.89 | 3.76 | 3.97 | 3.05 | 3.97 | 5.18 | 3.61 | 4.69 |
| 12 | 4.86 | 3.86 | 5.02 | 5.14 | 4.08 | 5.30 | 6.22 | 4.82 | 6.26 |
| 18 | 5.85 | 4.70 | 6.10 | 6.14 | 4.96 | 6.44 | 7.41 | 5.86 | 7.61 |
| 24 | 5.86 | 5.40 | 7.01 | 6.75 | 5.70 | 7.40 | 8.27 | 6.73 | 8.74 |
| Vertical Load (kN/m) | M-TW-ON | M-NW-ON | M-NW-OS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEA | Design | Characteristic | FEA | Design | Characteristic | FEA | Design | Characteristic | |
| 0 | 2.64 | 0.79 | 1.76 | 2.61 | 1.16 | 2.58 | 4.22 | 1.35 | 2.93 |
| 6 | 3.68 | 1.28 | 2.84 | 3.97 | 1.88 | 4.18 | 5.18 | 2.19 | 4.75 |
| 12 | 4.86 | 1.71 | 3.80 | 5.14 | 2.51 | 5.58 | 6.22 | 2.92 | 6.34 |
| 18 | 5.85 | 2.09 | 4.62 | 6.14 | 3.05 | 6.78 | 7.41 | 3.56 | 7.71 |
| 24 | 5.86 | 2.40 | 5.31 | 6.75 | 3.50 | 7.79 | 8.27 | 4.09 | 8.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di, J.; Zuo, H. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Light-Wood-Framed Shear Walls Strengthened with Parallel Strand Bamboo Panels. Coatings 2021, 11, 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121447
Di J, Zuo H. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Light-Wood-Framed Shear Walls Strengthened with Parallel Strand Bamboo Panels. Coatings. 2021; 11(12):1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121447
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi, Jing, and Hongliang Zuo. 2021. "Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Light-Wood-Framed Shear Walls Strengthened with Parallel Strand Bamboo Panels" Coatings 11, no. 12: 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121447
APA StyleDi, J., & Zuo, H. (2021). Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Light-Wood-Framed Shear Walls Strengthened with Parallel Strand Bamboo Panels. Coatings, 11(12), 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11121447






