Attenuation of Barkhausen Noise Emission due to Variable Coating Thickness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
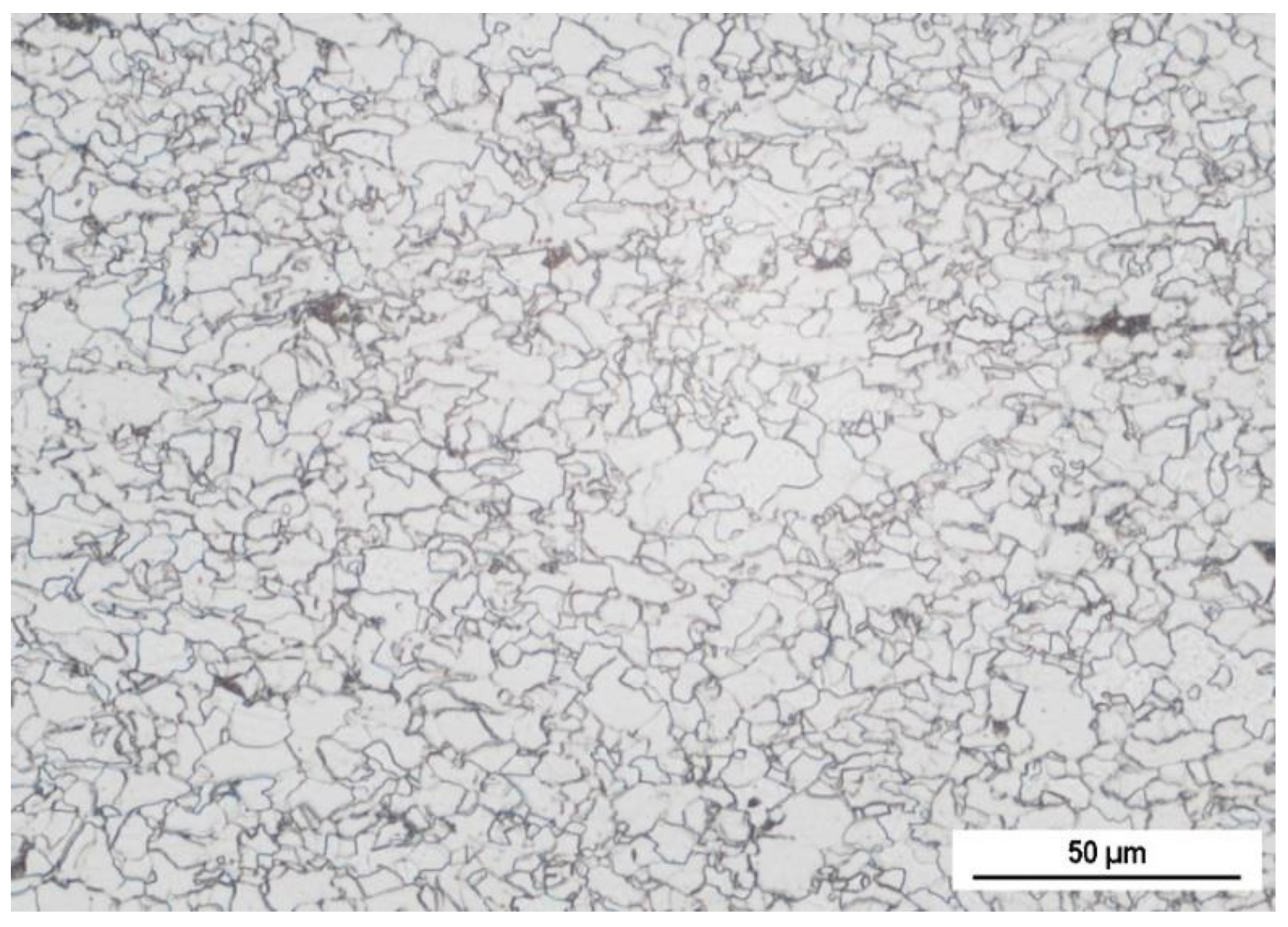
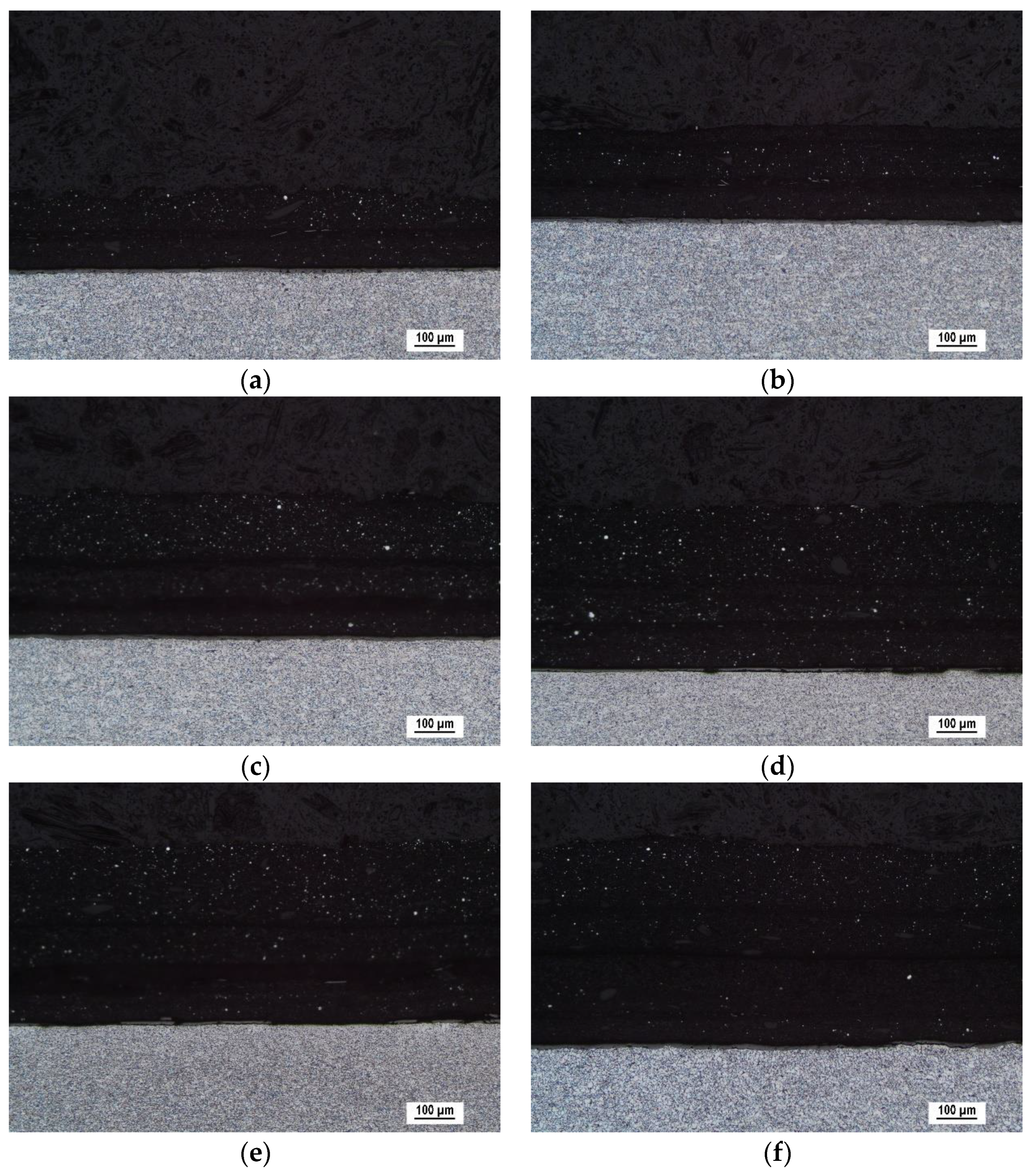
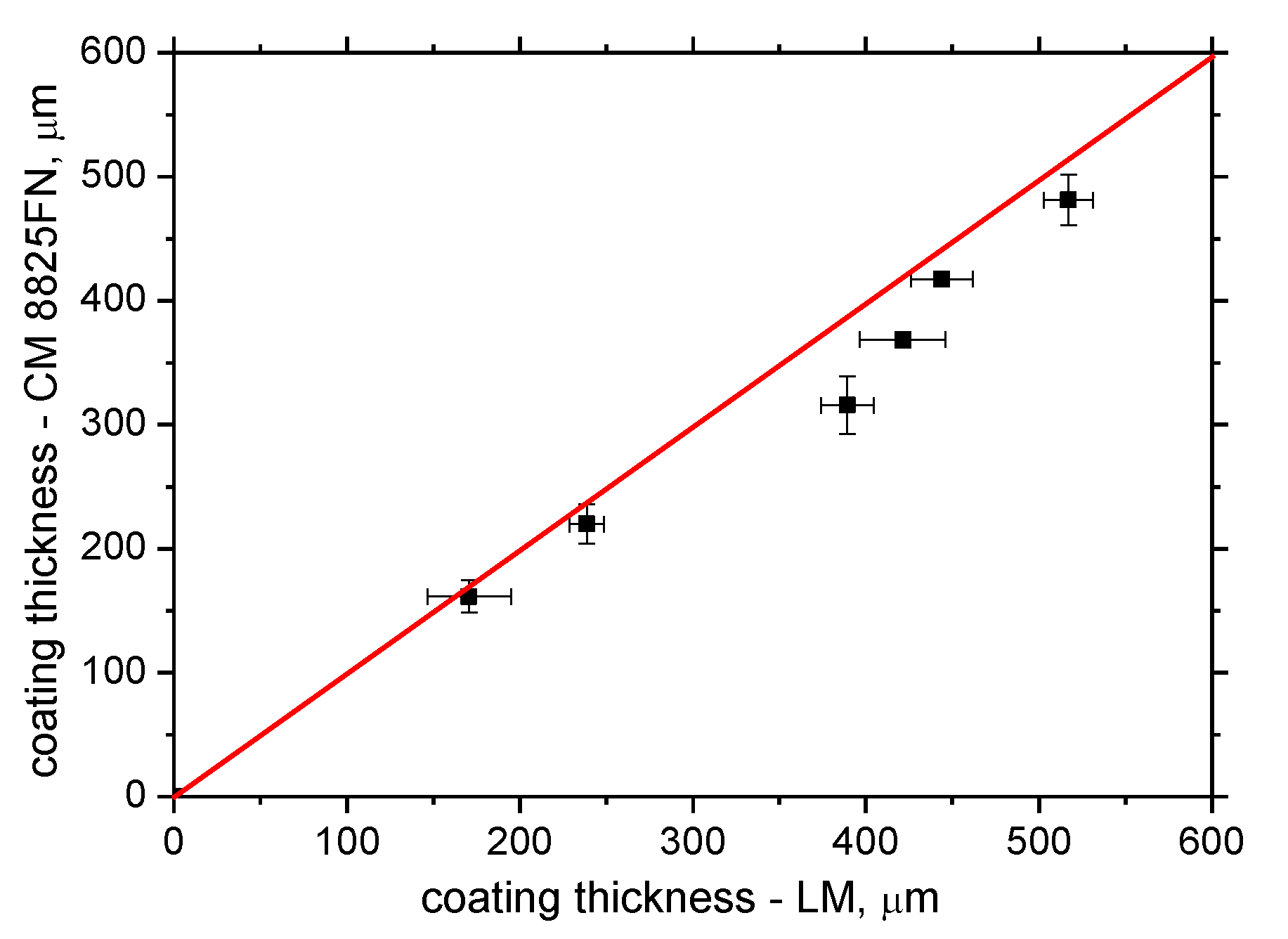
2. Experimental Conditions
3. Results of Experiments and Their Discussion
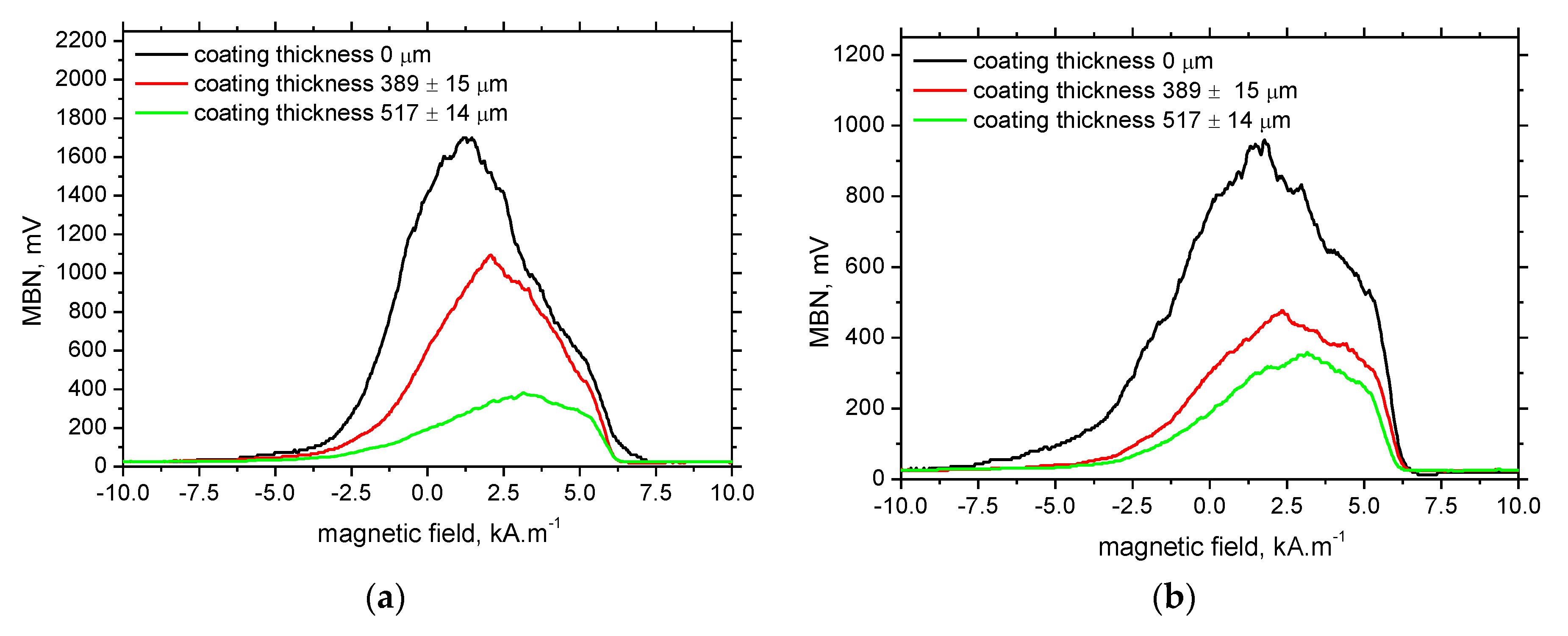
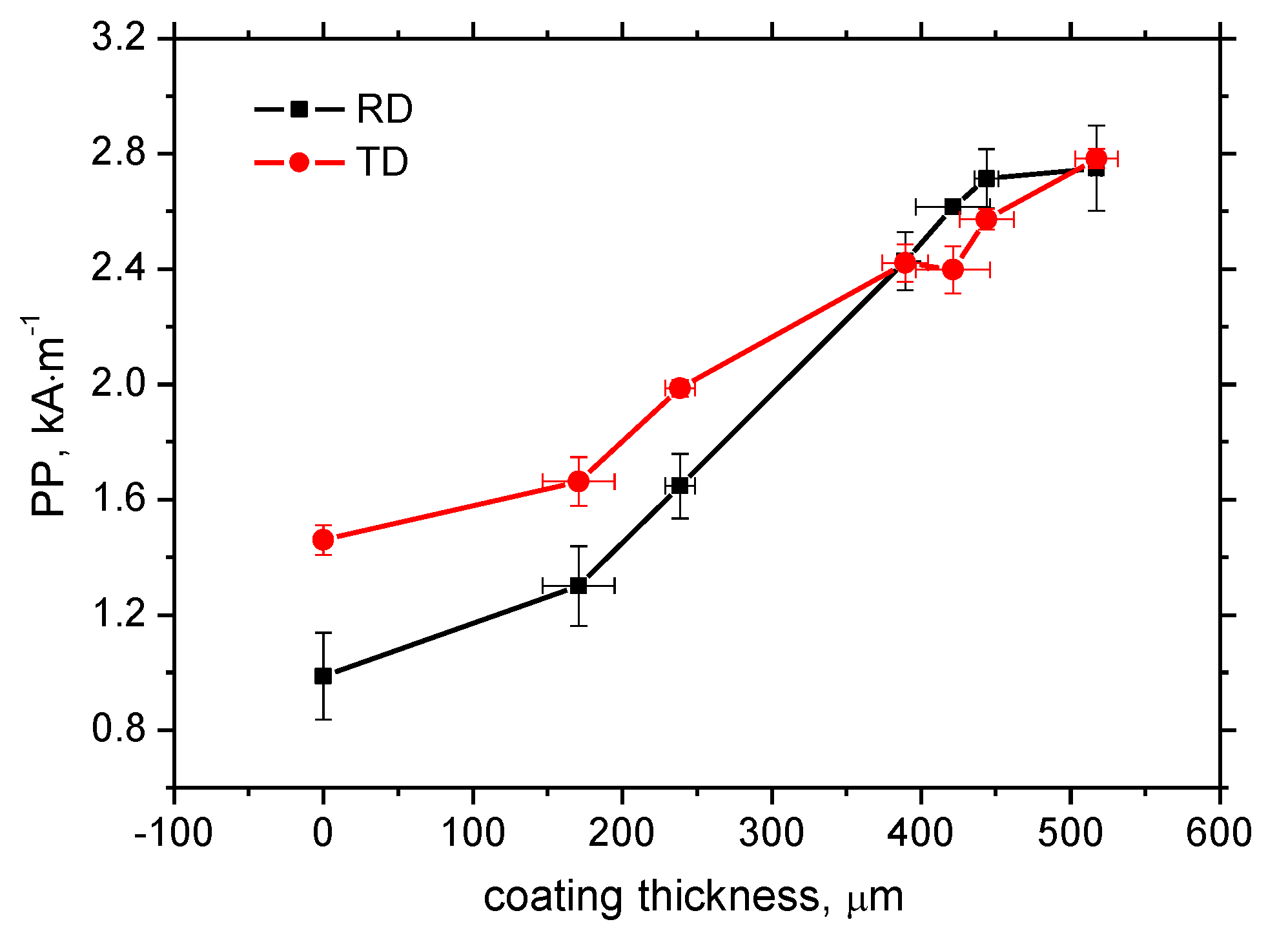
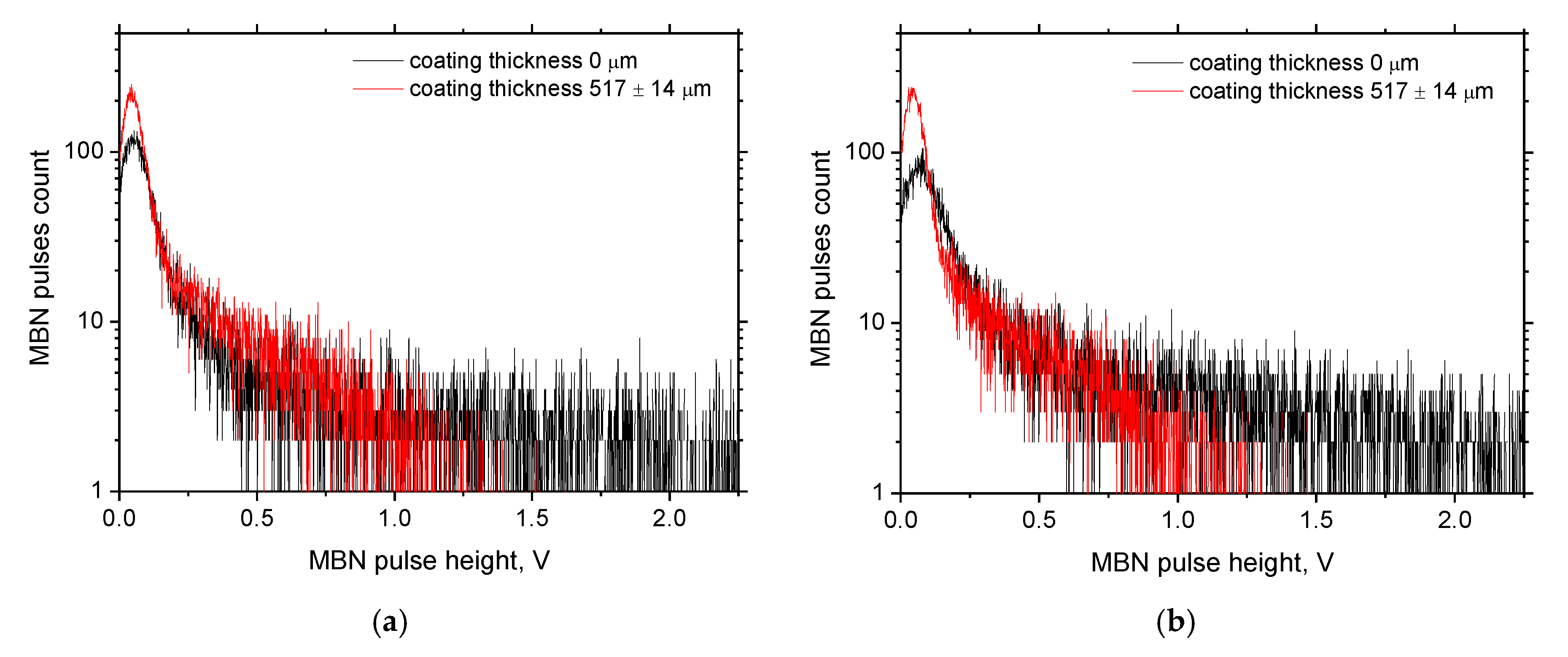
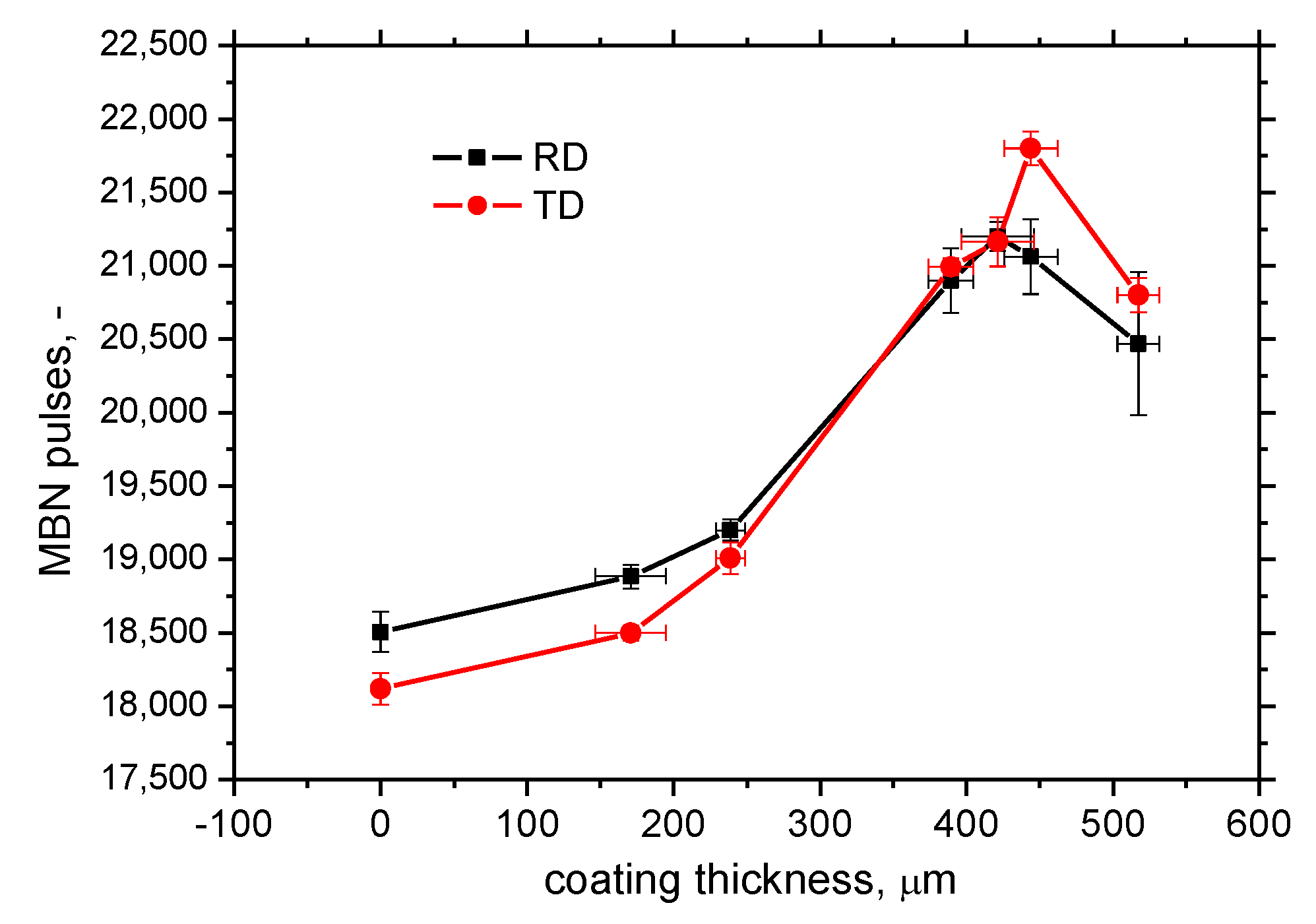
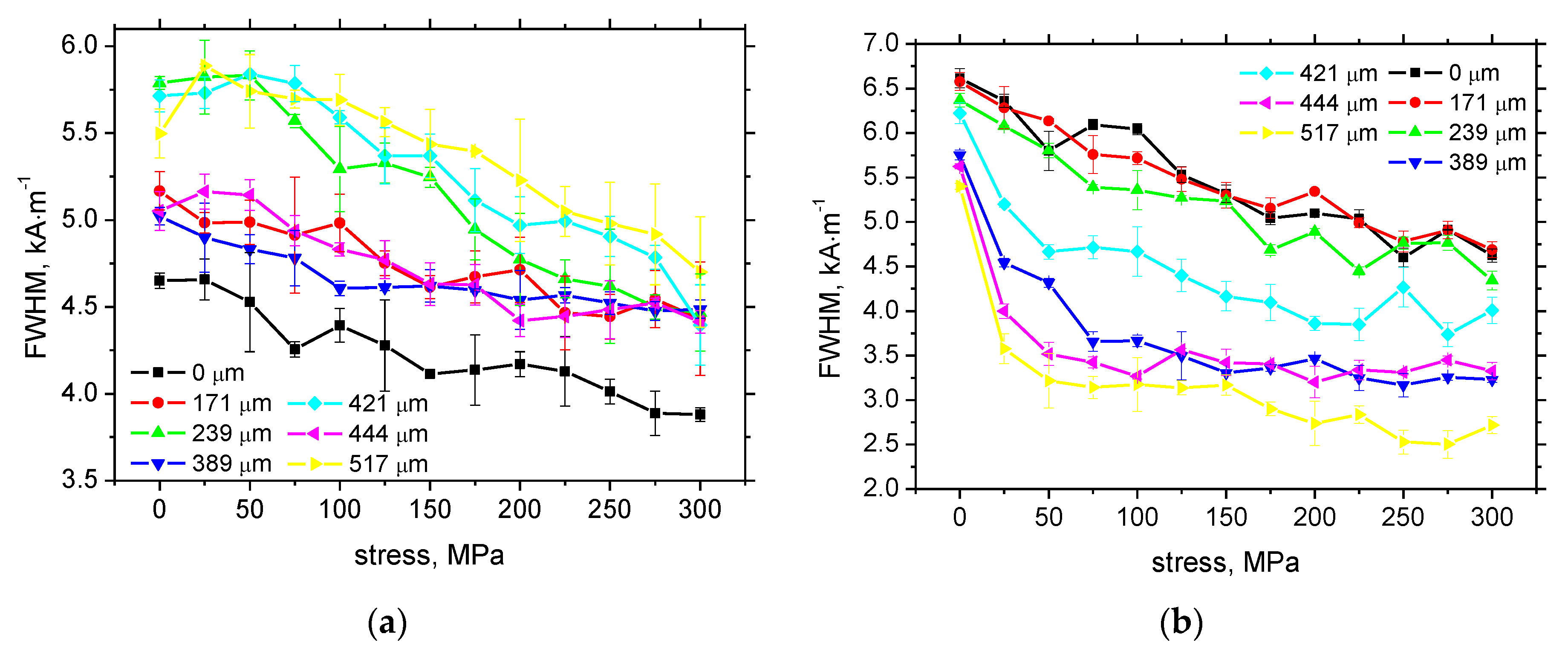
3.1. Unloaded Samples
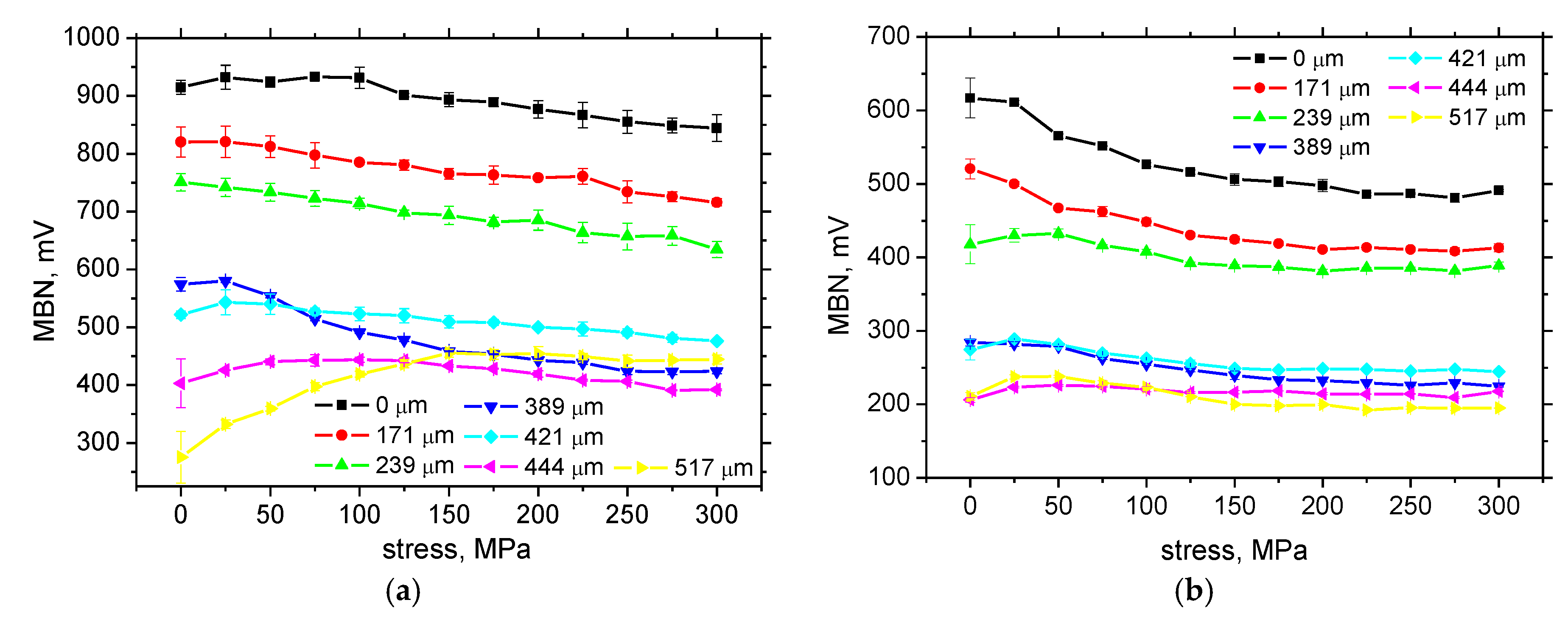
3.2. Tensile Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Tian, G.Y.; Gao, B.; Zeng, K.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J. Micro-macro characteristics between domain wall motion and magnetic Barkhausen noise under tensile stress. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 493, 165719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kypris, O.; Nlebedim, I.C.; Jiles, D.C. Measuring stress variation with depth using Barkhausen signals. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 2016, 407, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpuschewski, B.; Bleicher, O.; Beutner, M. Surface integrity inspection on gears using Barkhausen noise analysis. Proc. Eng. 2011, 19, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chikazumi, S. Physics of Ferromagnetism, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sorsa, A.; Santa-Aho, S.; Wartiainen, J.; Souminen, L.; Vippola, M.; Leviskä, K. Effect of shot peening parameters to residual stress profiles and Barkhausen noise. J. Non-Destruct. Eval. 2018, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gatelier-Rothea, C.; Chicois, J.; Fougeres, R.; Fleischmann, P. Characterization of pure iron and (130 ppm) carbon-iron binary alloy by Barkhausen noise measurements: Study of the influence of stress and microstructure. Acta Metal. 1998, 46, 4873–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neslušan, M.; Bahleda, F.; Trojan, K.; Pitoňák, M.; Zgútová, K. Barkhausen noise in over-stressed wires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 513, 167134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neslušan, M.; Bahleda, F.; Minárik, P.; Zgútová, K.; Jambor, M. Non-destructive monitoring of corrosion extent in steel rope wires via Barkhausen noise emission. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 484, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neslušan, M.; Bahleda, F.; Moravčík, M.; Zgútová, K.; Pastorek, F. Assessment of tendons prestressing after long-term service via the Barkhausen noise technique. Materials 2019, 12, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blisťan, P.; Pacaiova, H. Modelling environmental influence on the pipelines integrity. In Proceedings of the 11th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference, Albena, Bulgaria, 26 June–5 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Anania, L.; Badala, A.; D’Agata, G. Damage and collapse mode of existing post tensioned precast concrete bridge: The case of Petrulla viaduct. Eng. Struct. 2018, 162, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sun, H.; Cai, S. Effect of symmetrical broken wires damage on mechanical characteristics of stay cable. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 461, 114920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krkoška, L.; Moravčík, M.; Zgútová, K.; Neslušan, M.; Uhričík, M.; Bahleda, F.; Pitoňák, M. Investigation of Barkhausen noise emission in steel wires subjected to different surface treatments. Coatings 2020, 10, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, O.; Matre, H.; Dorum, C.; Gagné, M. Experiences with thermal spray zinc duplex coatings on road bridges. Coatings 2019, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zgútová, K.; Neslušan, M.; Kolářik, K.; Šrámek, J. Non-destructive evaluation of stress state of the highway bridge via Barkhausen noise technique. In Proceedings of the Progress in Mechanics and Materials in Design, 7th International conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Albufeira, Portugal, 11–15 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Neslušan, M.; Čížek, J.; Kolařík, K.; Minárik, P.; Čilliková, M.; Melikhová, O. Monitoring of grinding burn via Barkhausen noise emission in case-hardened steel in large-bearing production. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 240, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čížek, J.; Neslušan, M.; Čilliková, M.; Mičietová, A.; Melikhova, O. Modification of steel surfaces induced by turning: Non-destructive characterization using Barkhausen noise and positron annihilation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa-aho, S.; Vippola, M.; Sorsa, A.; Leiviskä, K.; Lindgren, M.; Lepistö, T. Utilization of Barkhausen noise magnetizing sweeps for case-depth detection from hardened steel. NDTE Int. 2012, 52, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupakov, A.; Perevertov, O.; Tomáš, I.; Skrbek, B. Evaluation of surface decarburization depth by magnetic Barkhausen noise technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorsa, A.; Santa-aho, S.; Aylott, C.; Shaw, B.A.; Vipplola, M.; Leviskä, K. Case depth prediction of nitride samples with Barkhausen noise measurement. Metals 2019, 3, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmberg, J.; Lundin, P.; Ovalisson, J.; Sevim, S. Nondestructive testing of surface characteristics after nitro carburizing of three different steel grades. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Barkhausen noise and Micromagnetic Testing, Dresden, Germany, 24–26 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stupakov, A.; Farda, R.; Neslušan, M.; Perevertov, A.; Uchimoto, T. Evaluation of nitride case depth by the magnetic Barkhausen noise. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2017, 36, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čilliková, M.; Uríček, J.; Neslušan, M.; Ballo, V.; Mičietová, A. Monitoring of thermal damage after deposition of coatings via Barkhausen noise technique. Acta Phys. Polonica A 2020, 137, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blažek, D.; Neslušan, M.; Mičica, M.; Pištora, J. Extraction of Barkhausen noise from the measured raw signal in high-frequency regimes. Measurement 2016, 94, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, R. Domain Walls and Their Dynamics, 1st ed.; Pavol Jozef Šafárik University: Košice, Slovakia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Manh, T.L.; Caleyo, F.; Hallen, J.M.; Pérez-Benitez, J.A.; Espina-Hernández, J.H. Novel method for the accurate determination of magnetocrystalline energy from Barkhausen noise in ferromagnetic materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 225, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Gonzalez, A.F.; Martínez-Ortiz, P.; Pérez-Benitez, J.A.; Espina-Hernández, J.H.; Caleyo, F. Comparison of angular dependence of magnetic Barkhausen noise of hysteresis and initial magnetization curve in API5L steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 446, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas-Morgan, M.; Padovese, L.R. Fast detection of the magnetic easy axis on steel sheet using the continuous rotational Barkhausen method. NDTE Int. 2012, 45, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neslušan, M.; Minárik, P.; Grenčík, J.; Trojan, K.; Zgútová, K. Non-destructive evaluation of the railway wheel surface damage after long-term operation via Barkhausen noise technique. Wear 2019, 420–421, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.S.; Thielen, M.; Rabung, M.; Marx, M.; Szielasko, K.; Boller, C. On the role of crystal and stress anisotropy in magnetic Barkhausen noise. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 372, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šrámek, J.; Neslušan, M.; Bahleda, F.; Zgútová, K.; Schenk, P. Influence of sample size and magnetizing voltage on Barkhausen noise during bending and uniaxial tensile test. Acta Phys. Polonica A 2020, 137, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamish, D. Coating thickness measurement. Met. Finish. 2000, 98, 559–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahleda, F.; Bujňáková, P.; Koteš, P.; Hasajová, L.; Nový, F. Mechanical properties of cast-in anchor bolts manufactured of reinforcing tempcore steel. Materials 2019, 12, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, M.; Cao, B.; Ye, B.; Wen, D. Measurement of coating thickness using lift-off point of intersection features from pulsed eddy current signals. NDTE Int. 2020, 116, 102333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, S.; Peter, A.; Wahl, P.; Khinast, J.; Heinrich, S. Measurement of granule layer thickness in a spouted bed coating process via optical coherence tomography. Powder Technol. 2019, 356, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Fe | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Al | Ti | Nb | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| balance | 0.082 | 1.040 | 0.019 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.055 | 0.001 | 0.050 | 0.054 |
| Number of Layers | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured thickness (μm) | 171 ± 24 | 239 ± 10 | 389 ± 15 | 421 ± 25 | 444 ± 18 | 517 ± 14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zgútová, K.; Pitoňák, M. Attenuation of Barkhausen Noise Emission due to Variable Coating Thickness. Coatings 2021, 11, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030263
Zgútová K, Pitoňák M. Attenuation of Barkhausen Noise Emission due to Variable Coating Thickness. Coatings. 2021; 11(3):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030263
Chicago/Turabian StyleZgútová, Katarína, and Martin Pitoňák. 2021. "Attenuation of Barkhausen Noise Emission due to Variable Coating Thickness" Coatings 11, no. 3: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030263
APA StyleZgútová, K., & Pitoňák, M. (2021). Attenuation of Barkhausen Noise Emission due to Variable Coating Thickness. Coatings, 11(3), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030263




